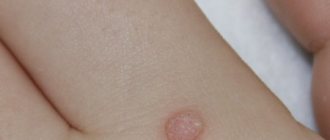
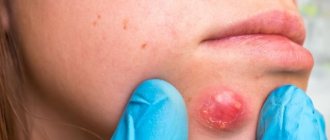
Skin fibroma is a benign neoplasm that has a round shape and consists of connective tissue and fibroblasts. Skin fibroids can develop on the body or face; subcutaneous fibromas form deep in the dermis or in the superficial layer of the epidermis. There are hard, soft fibromas and dermatofibromas (histiocytomas or sclerosing hemangiomas). Dermatofibroma is a benign tumor with a low risk of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm; it looks like a wart or mole.
The Yusupov Hospital diagnoses and treats skin diseases. Tumors can be treated in the hospital's oncology department. The oncology department is equipped with modern equipment, the hospital provides treatment using innovative methods, and uses the latest drugs to treat tumor processes. Modern diagnostics of neoplasms makes it possible to timely distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant process.
The reasons for the development of fibroids have not been fully established. Factors influencing the development of skin fibroids are varied:
- Damage to the skin by ultraviolet rays.
- Age-related changes.
- Pregnancy.
- Diseases of the endocrine organs.
- Menopause.
- Hereditary predisposition to the development of fibroids.
- Various skin injuries.
- Increased sweating.
- Malfunctions of internal organs.
- Exposure to chemicals on the skin.
Features of soft tissue tumors
Malignant soft tissue lesions are rare, accounting for no more than 1% of all cancers.
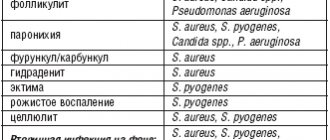
But the aggressiveness of many types of cancer of the skin or underlying tissues is very high. It is somewhat easier to identify them than lesions of internal organs, since they form quite noticeable changes in the color of the skin, its appearance or the density of the tissues under the epidermis. Sarcomas that affect soft tissue and are classified as malignant tumors can appear in the subcutaneous tissue, including stromal and fat cells, in muscle elements, blood vessels or lymphatic capillaries, nerve fibers, and connective tissue of joints. Localization of tumors is possible in any part of the body, but more than 50% of them affect the extremities (legs and arms), the rest are located in the neck and head, torso, less often internal organs or the retroperitoneal space are affected Source: Z.R. Khismatullina Skin neoplasms. Issues of epidemiology, classification, diagnostics // Creative surgery and oncology, 2010, pp. 69-73.
With early detection, radical removal of tumors and a favorable prognosis for recovery are possible.
Prevention of hygroma and its complications
For standard prevention of hygroma of the wrist and other joints, you should:
- avoid injury and hypothermia;
- promptly treat arthritis, arthrosis and other connective tissue diseases;
- minimize the load on the joint, incl. monotonous (from time to time take a break from work or monotonous activities to warm up);
- pay attention to hereditary and metabolic diseases that can negatively affect the health of the musculoskeletal system (gout, diabetes);
- follow safety precautions and exercise rules when playing sports;
- Avoid self-medication for injuries and other lesions in the hands and wrists;
- Monitor your body weight and maintain a low-calorie diet rich in vitamins, minerals and amino acids.
If in your family or for your occupation there is a high predisposition to hygromas and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, you should think about additional measures. Rheumatologists recommend an annual course of prophylaxis with chondroprotective drugs. They help strengthen connective tissue and improve its metabolism, preventing the development of degenerative cells. Artracam is ideal for this purpose.
- due to the high bioavailability of glucosamine sulfate, pleasant taste and convenient sachet form.
Take care of yourself!
Images designed by Freepik
Types of soft tissue cancer
The most common type of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma . This is a thickened area of skin that has a normal color or a pearly-waxy tint. Typically found in the arms, neck or head, up to 20% of lesions are found on the remaining parts of the body.
Another option for skin lesions is squamous cell carcinoma , which looks like a non-healing ulcer, spots with detachment of epithelial scales, and compacted reddened tubercles. The most common localization is the back and chest area, face or arms, neck, ears.
Another type - the most aggressive - is melanoma , a tumor that occurs in the area of moles (pigmented areas of the skin). It is characterized by rapid progression and high malignancy. Usually located in the interdigital spaces, in the groin, on the head, torso, and back.
Where can it appear?
In principle, hygroma can appear on any joint or tendon sheath. There are characteristic localizations on the hand:
- Hygroma of the wrist joint can appear on the dorsal (most common) side. In this case, its source is the capsule above the lunate-scaphoid ligament.
- On the palm it comes out near the radial artery (this is where the pulse is felt) from the space between the radioscaphoid and long radiolunate ligaments.
- On the finger, it usually sits at the base on the palmar side in the projection of the skin fold. There it is very small and dense, like a bead. Less commonly, hygroma occurs on the finger in the projection of the proximal interphalangeal joint on the back.
- Mucoid cysts also form on the finger, which are also essentially hygromas, but grow from the distal interphalangeal joint, and not from the tendon sheaths, like the previous two “finger” variants.
I was surprised when I learned that in France hygroma is a disease that we all know in Russia as bursitis of the elbow joint. Well, in fact, they are right, bursitis and hygromas are, in general, the same thing.
Signs
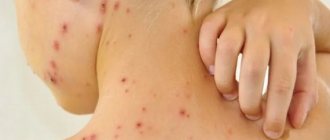
Typical signs of soft tissue cancer - sarcomas are found in the skin or underlying tissues. Initially, this is a painless lump, but as it grows, the nerves become irritated and discomfort occurs. Tumors larger than 40-50 mm with penetration deep into tissues are especially dangerous. The most common types of sarcoma:
- Tumor of adipose tissue - liposarcoma. Typical of the knees, retroperitoneum and thighs.
- Formations from skeletal muscles - rhabdomyosarcomas. They affect the muscles involved in motor acts.
- Fibrosarcomas are neoplasms of connective tissue. Typically appear between muscle fibers in the shoulders, hips or neck.
- Synovial sarcomas affect the membranes of large joints in the arms and legs.
- Leiomyosarcoma occurs in the area of smooth muscle elements of hollow organs - the small intestine, uterus, bladder or stomach.
- Different types of nerve cell sarcomas arise in the area of nerve trunks. These are neuromas, sympathoblastomas or schwannomas.
- A rare type of cancer that is prone to rapid metastasis is hemangiosarcoma , it damages the walls of blood vessels.
- An extremely rare type of lymphangiosarcoma damages the lymphatic ducts and capillaries. Typical for women who, for some reason, had a mastectomy (the mammary gland was removed) Source: L.N. Vashchenko, T.V. Ausheva, E.L. Ibragimova, E.M. Nepomnyashchaya Some clinical issues of soft tissue sarcomas // News of higher educational institutions. North Caucasus region. Natural Sciences, 2013.
Causes of hygroma of the wrist joint
The main causes of hygroma:
- Wrist injury
- Large loads on the hand and wrist joint;
- Consequences of hand surgery.
- Repetitive injuries such as playing tennis or golf.
Hygromas on the hand form when the joint capsule becomes thinner due to injury or degenerative changes. The damaged tissue forms a weak spot in the joint capsule, like a weak spot on a car tire, allowing the inner layer to herniate. The joint fluid begins to squeeze out the weakened layer of the capsule, pushing apart the surrounding tissue. Over time it gets bigger. But if you limit the load on the wrist joint, this will lead to a decrease in the production of intra-articular fluid and stop the growth of hygroma. Cases of spontaneous healing of hygroma after reducing the load have been described.
Why do soft tissue and skin tumors occur?
For various types of skin cancer, UV radiation is considered a key trigger. Prolonged exposure to the open sun, aggressive tanning, and sunburn provoke epithelial and pigment cells to cancerous transformation. This is especially dangerous for fair-skinned people, residents of high mountains and those who have many moles and nevi on their bodies.
For all tumors in general, provocateurs can be:
- Ionizing radiation accounts for up to 5% of cancer. Radiation for the treatment of other types of tumors (lymphoma, breast cancer) is also dangerous. In general, up to 10 years pass between radiotherapy and the formation of sarcomas.
- Unfavorable heredity for melanoma or sarcoma, as well as the presence of certain genetic pathologies, for example, neurofibromatosis - the formation of multiple fibromas on the body, which can develop into cancer.
- Gardner's syndrome is dangerous in terms of the development of soft tissue tumors. It develops polyposis or intestinal cancer, as well as fibrosarcomas or tumors of other localizations.
- Provocateurs of cancerous tumors can be frequent injuries to soft tissues, extensive surgical interventions, and the presence of various structures in the body - knitting needles, plates.
- Possible influence of various chemical carcinogens that damage cells. As a result, DNA suffers and may develop into cancer.
- The presence of precancerous conditions and benign tumors in some situations can lead to their transformation into cancer, for example, with leiomyoma or uterine rhabdomyoma.
When is surgery needed?
Most people with hygroma want a clear answer to this question. However, the doctor cannot answer it. A synovial cyst is not a dangerous disease; it has a chance to go away without any treatment; surgery (like any intervention) has its own possible complications and risks. Whether to operate on a hygroma or not is a patient’s informed decision. When a person understands the situation and is ready to share responsibility for the decision made with the doctor, then one can choose the time and place to perform the intervention.
How is the operation to remove hygroma performed?
I will describe the basic principles using the example of the most common dorsal hygroma on the wrist.
- The operation is outpatient. There is no need to stay in the hospital.
- Local anesthesia. Anesthesia means unnecessary risks, as well as excessive preoperative examination. I use a mixture of lidocaine and epinephrine, this avoids discomfort from the tourniquet, reduces the likelihood of a toxic reaction to the anesthetic and prolongs the effect of pain relief to 4-5 hours.
- Transverse access. Longitudinal access leaves rough, unsightly scars.
- It is imperative to excise the fragment of the joint capsule from which the hand hygroma grows. Only the skin is sutured.
- I don't use immobilization. For the first 2-3 days, a thick soft bandage is applied, which limits movement and makes the early postoperative period as comfortable as possible. Prolonged immobilization after surgery can lead to stiffness, but does not affect the likelihood of relapse.
- The skin heals in about 2 weeks.
Signs of skin tumors and soft tissue oncology
People usually notice the first symptoms of skin cancer in the arms or legs, and less often in the chest and back. Often the appearance of an unusual mole or tumor area is preceded by sunburn, injury or intense exposure (calluses, abrasions). Often tumors appear on scarred tissue, leading to the formation of bumps, ulcers, peeling skin or uneven pigmentation.
A number of signs are typical for melanoma - ABCDE gradation, which distinguish it from all others:
- A (from the English asymmetry) – asymmetrical edges of the mole;
- B (from the English boundary) – uneven, torn edges, teeth;
- C (from the English color) – the coloring of the element is uneven, with areas of light and almost black, bluish inclusions;
- D (from the English diameter) – growth of more than 50-60 mm in diameter;
- E (from the English evolution) - a rapid change in the appearance of a mole within a short time.
Soft tissue sarcomas may not produce pronounced symptoms for a long time until they reach large sizes and begin to compress blood vessels and nerves. There are signs of neuralgia, a crawling sensation, pain, numbness. There may be general malaise, weight loss, loss of strength, a tumor-like uneven compaction without clear edges is found under the skin. It can move relative to the tissues or be motionless, very hard. Non-healing ulcers may develop on the surface of the nodes.
If these are tumors of muscles or joints, ligaments, pain during movement is typical for them, but it can be insignificant and often the cancer is diagnosed at a late stage, when there are already metastases.
Photo of a tumor under the skin on the leg
A hard fibroma is located in a hard capsule, there is no pain when pressed, the capsule practically does not move to the sides, and is most often located on a wide base. A hard fibroma rises above the surface of the skin; when squeezed between the fingers, indentations remain on the fibroma. Two types of fibromas develop in the lower extremity region: dermatofibromas and plantar fibrous formations.
Plantar fibromas affect the soles of the feet, while dermatofibromas affect the entire surface of the lower extremities. The greatest discomfort is caused by hard fibroids that develop on the foot - they interfere with wearing shoes and cause pain when walking. Constant traumatic impact on the plantar fibroma can cause malignancy of the tumor. Doctors recommend removing fibroids on the foot to avoid the development of a malignant disease.
Diagnostic features
The basis for diagnosing soft tissue tumors is the patient’s complaints, changes in the appearance of moles or underlying tissues. In order to clarify the nature of the tumor, its type and degree of malignancy, and draw up a treatment plan, it is necessary:
- Dermatoscopy is the study of the epidermis using a modern dermatoscopy device with illumination and optics.
- A biopsy is taken to determine the cell type.
- Radiography to determine bone and soft tissue damage in different types of sarcomas.
- Ultrasound to detect tumors in soft tissues and organs.
- MRI or CT scan to clarify the size, presence of metastases in lymph nodes or distant organs.
- Angiography, including with contrast to detect vascular tumors.
- These methods are complemented by blood and urine tests, testing for tumor markers, as well as histological, biochemical and cytological analyzes of tissue samples obtained during biopsy Source: A.A. Modestov, E.V. Semenov, R.A. Zukov, E.V. Slepov, E.N. Eremina, E.N. Gaas New approaches to organizing screening for malignant skin tumors. Siberian Journal of Oncology, 2022, No. 16(2), pp. 61-65.
What modern methods of getting rid of hygroma exist?
Removal of this bubble with a gel-like liquid is possible both from the skin and from the joint. There is a thin camera and special instruments that allow you to look inside the wrist joint through small punctures of 2-3 mm. This procedure is called arthroscopy from the words “arthro” joint and “scopy” to look. Through these punctures you can not only look into the joint, but also perform useful manipulations inside, for example, remove a hygroma. The advantages of the arthroscopic method are smaller scars on the skin, faster rehabilitation, and a relatively lower likelihood of relapse.
Treatment of soft tissue cancer
The main method of treating cancer of the skin and underlying tissues is surgical excision of the tumor within healthy tissue. If the formation is large, additional plastic surgery is performed to improve the appearance. In some cases, it is also necessary to remove regional lymph nodes.
If the tumor is inoperable or it is necessary to reduce its size before surgery, chemotherapy is prescribed with modern drugs with minimal side effects and influence on the body. It is possible to use drugs after surgery to destroy remaining cancer cells and prevent relapses.
Targeted therapy protocols have been developed for melanoma, targeting only cancer cells with special monoclonal antibodies. Methods of immunotherapy for skin cancer are used with the introduction of drugs in courses to activate one’s own immune system to fight cancer Source: Paulson KG, Lahman MC, Chapuis AG, Brownell I Immunotherapy for skin cancer // Int Immunol. 2022 Jul 13;31(7):465-475. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxz012.
Treatment of hand hygroma
Treatment of wrist hygroma can be surgical or conservative. The relative risks and benefits of any treatment should be carefully analyzed.
Conservative treatment
Previously, hygromas were treated simply by crushing them. That is, under pressure, the “ball burst” and the contents poured into the surrounding tissue. This is an absolutely harmless procedure. The intra-articular fluid is sterile and cannot in any way inflame the surrounding tissues. But 90% of all those crushed by hygroma recur, because... the edges of this burst capsule grow together very quickly and the liquid begins to accumulate again. This type of treatment is now used only by patients themselves out of ignorance.
50% of hygromas can disappear on their own if you reduce the load on the hand and wrist joint.
Hygroma puncture
A fairly effective method, but it is possible only in the early stages of the disease, when the size of the hygroma does not exceed 1 cm.
Methodology:
Local anesthesia is performed over the area of the hygroma. Next, the hygroma is punctured and its contents are removed with a syringe. Without removing the needle, the syringe is changed and a sclerosing agent is injected. A pressure bandage and orthosis is applied to the wrist joint for 5 weeks to allow the edges of the emptied hygroma to stick together and grow together.
If the patient does not wear an orthosis after the procedure, then movements in the wrist joint will provoke the release of intra-articular fluid and the fragile internal scar will not be able to withstand the pressure. What can cause recurrence of hygroma formation.
Therefore, one of the mandatory conditions and the strictest recommendation is to wear an orthosis.
If the hygroma is more than 1 cm or has a cellular structure (formed by several sacs), then there are indications for surgery, if the hygroma, of course, bothers the patient at all.