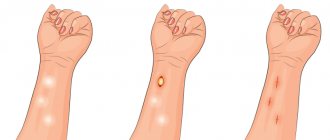
Lipoma or lymph node? This is the question asked by every person who discovers a spherical subcutaneous formation. Since these two structures are similar to each other, it is necessary to know what each of them is, what complications there may be and how to distinguish between them.
What is a wen and its differences from a lymph node
A fatty tissue (medically called lipoma) is a benign neoplasm that develops from adipose tissue cells. The reasons for the appearance are most often violations of the body's metabolic processes, in particular lipolysis, endocrine pathologies, diabetes, etc.
The lymph node, in turn, is a peripheral organ of the lymphatic system. Acts as a so-called “biofilter”. All lymph coming from human organs flows through them. Most often, lymph nodes are located in groups. Such collections of lymph nodes are called regional. By structure, lymph nodes are oval, round or bean-shaped. These structures play an important role in the functioning of the immune system. Lymph, which flows from various organs, carries with it various foreign agents. Immune reactions occur in the lymph nodes, thanks to which human health is maintained.
What is the difference between the symptoms of inflammation of a wen and a lymph node?
It is worth noting that inflammatory processes can occur both in the wen and in the lymph nodes. If the causes of inflammation of the wen are not reliably known, then in the second case they are well studied. Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs for a variety of reasons:
- when an infection enters the body (viruses, bacteria, fungi);
- with parasitic infestation;
- oncological diseases of the immune system;
- with metastasis of various malignant tumors
We recommend reading:
- Wen on the nose
- Atheroma of the scrotum
- Papilloma on the face
There are some features of inflammation of the lymph nodes. These include:
- increased size of lymph nodes;
- the surface may remain smooth or acquire a bumpy structure;
- the consistency of the lymph nodes can be dense or soft;
- in some pathologies, lymph nodes can adhere to surrounding tissues and become immobile;
- the skin that is located directly above the lymph nodes may become hyperemic and swollen.
In turn, the symptoms of lipoma inflammation are:
- significant increase in size;
- redness and aching pain;
- when pressing on the wen, sharp pain may appear and a sensation of the presence of fluid in the capsule of the neoplasm
How to distinguish a lipoma from a lymph node in a child and an adult
How to distinguish a wen from an inflamed lymph node? It should be noted that both children and adults are susceptible to the formation of lipomas. By external signs, both in a child and an adult, benign tumors of adipose tissue and lymph nodes are very similar to each other and it is often difficult to determine which particular formation it is. However, both one and the other have certain characteristics that distinguish them from each other. The wen looks like an inflamed lymph node. All other signs indicate their differences:
- When pressure is applied to the lymph node, painful sensations occur. This will not happen when you press on the wen.
- The occurrence of a lipoma can go unnoticed for a long time due to the fact that it does not manifest itself in any way (there is no pain or other sensations, there is no increase in body temperature).
- Lipoma can be located on any part of the body, wherever fatty tissue is present. Lymph nodes are located regionally and in groups (for example, a group of submandibular lymph nodes, inguinal lymph nodes, etc.).
- Another difference is that the size of a lipoma can reach 10 cm or more, while the size of the lymph nodes is much smaller.
Differences between wen and other formations
Lipoma (popularly known as wen) is a benign tumor consisting of fat cells that are surrounded by a dense capsule and located under the skin. This distinguishes it from a number of other formations. Doctors say the main culprit is heredity. It does not pose a threat to human health and can only be treated surgically (removal). If there is a small lipoma that does not cause discomfort, doctors advise not to perform operations, but to monitor the “behavior” of the growth.
Before you panic, you should understand the difference between pathologies.
Lymph node
The lymph node is a kind of biofilter whose task is to ensure fluid purification.
Lymph nodes are located in groups: on the neck, under the arms, in the groin area, lumbar region, under the knees. Unlike lipomas, the causes of which are still clearly unknown, inflammation can be triggered by the following factors:
- infections (bacteria, viruses);
- fungal infections;
- parasitic infestation;
- metastases.
The differences between a lymph node and a wen lie in the symptoms.
| Lipoma | Inflamed lymph node |
| The growth of the wen stands still or increases at an active pace. | Significantly increases in size. |
| The internal consistency is soft and easy to move. | The internal consistency of the inflamed lymph node can be: lumpy, dense or soft. |
| With the development of inflammation in the fatty tissues, the skin turns red and pain is felt upon palpation. | The skin over the inflamed lymph node remains unchanged. In rare cases, swelling and pigmentation are noted. |
READ ALSO: Herpes in the anus: why it occurs and how to treat it.
Soft tissue fibroma
Fibroma is a benign formation, which, unlike lipoma fatty deposits, consists of fibrous and connective tissue. It grows slowly and does not metastasize.
They can be localized on internal organs (lungs, uterus, ovaries, kidneys, mammary glands) and skin. There are two types:
- hard;
- soft.
When first encountered with fibroma on the skin, it is confused with a wen, although both types are significantly different. Fibroma located in soft tissues differs from lipoma:
| Lipoma | Soft fibroma | Hard fibroma |
| Has different sizes. | Size up to 1 cm. | Size up to 10 cm. |
| It has a soft internal consistency. | Soft, but loose to the touch, mobile. | Hard, smooth, motionless. |
| The skin does not change color. During inflammation, redness of the skin is noticeable. | The formation can be light brown to dark brown in color. | Overgrown tissues merge with the color of the dermis. |
| Appears anywhere under the dermis. | Grows in folds. | Formed on any organs. |
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign tumor that occurs due to the proliferation of vascular tissues. In common parlance it is called a saggy mole. Most often, hemangioma is present on the face, head (hair), less often found on other parts of the body and on internal organs. If the surface of the growth is damaged, bleeding may occur.
Unlike a number of others, the pathology is considered congenital, develops in the first 4 months or is already present in the baby. The tumor actively grows until the child is 1 year old. Afterwards it enters the involution phase. By the age of 9, in 90% of children, the hemangioma disappears completely.
Four types are classified:
- Skin.
- Subcutaneous.
- Internal organs.
- Affects the spine.
It is possible to distinguish whether a hemangioma or a lipoma is a cosmetic defect by external signs.
READ ALSO: How to easily remove belly fat at home | how to effectively remove belly fat | Dr. Bormenthal
| Lipoma | Cutaneous hemangioma | Subcutaneous hemangioma |
| Round in shape, rises above the surface of the body. | A flat spot or formation with smooth contours and a slightly bumpy surface. | Ragged contours without clear edges. A lumpy surface that rises above the skin. |
| Has no tendency to grow and does not create discomfort. | They grow along the perimeter, less often penetrating deep into the dermis. | Growth leads to an increase in the tuberosity. |
| The skin is smooth, even, does not change color. | Pink or burgundy spots. | Reddish-bluish bumps. |
| Large growths are removed surgically. | Regresses completely. | 10% of cases cannot be regressed. |
Papilloma
Papilloma is a benign formation, characterized by a viral etiology.
The human papillomavirus infects epithelial cells, leading to cosmetic defects of the skin. Medicine knows more than 170 strains of the virus, which have not yet been fully studied. Placed on the skin and mucous surfaces. In appearance it may resemble a small papilla “on a stalk” from pale pink to dark brown. HPV is contagious. Infection occurs sexually, through the use of personal hygiene products of the patient.
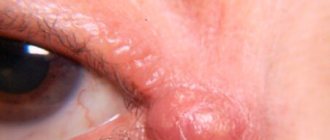
It is difficult to confuse a lipoma with a papilloma, but in cases of growth in the eye area this is possible. You can identify a wen on the eyelid or a papilloma by the characteristic differences:
| Wen in the eye area | Papilloma on the eyelid |
| Small formations look like pimples. Large ones resemble a bag. | Exophytic, with papillary growths on the surface. |
| White or yellowish. | Grayish-yellow color. |
| They do not cause discomfort; when enlarged, a feeling of skin tension may appear. | Large growths located close to the eyeball can cause decreased vision and discomfort when blinking. |
Hernia
Hernia is a protrusion of an organ from its natural cavity under the skin, into the intermuscular space, into internal pockets. A hernia of the white line of the abdomen in its initial development is a preperitoneal lipoma.
READ ALSO: Ulcers on the head: possible causes, symptoms, diagnostic tests, medical supervision and treatment
The linea alba is a narrow plate of tendons located between the rectus abdominis muscles. Weakness or congenital abnormalities of muscles lead to thinning or expansion of connective tissues, forming a gap through which fat cells migrate into the adjacent cavity.
There are 3 distinctive degrees of the disease:
- Preperitoneal lipoma. Preperitoneal fat protrudes through weak connective tissues, forming a hernial sac.
- Initial hernia. The bag is filled with part of the stuffing box.
- Formed hernia. The abdominal organs fill the sac.
Hygroma
A cystic tumor consisting of serous fluid mixed with fibrous or mucous tissue. A “sac” of fluid is localized near the joints and tendons. Hygromas are distinguished by their structure into two types:
- Single-chamber – dense cyst.
- Multi-chamber - an elastic cyst which is characterized by enlargement with germination deep into the tissue.
A hygroma tubercle is often confused with a wen due to its external similarity. Both tumors have the following characteristics:
- being under the skin;
- looks like a lump;
- mobility on palpation;
- smooth surface;
- soft consistency;
- When inflamed, the skin over the tumor turns red, and pain appears when pressure is applied.
If the symptoms are identical, you can identify a lipoma or a cyst by the following differences: place your finger on the surface of the growth. Lightly tap the bump. If it is a cyst, then the fluid inside hits the opposite side, which can be felt under the finger.
Consequences of inflammation of the wen and lymph node
Inflammatory processes occurring in the wen are an unpleasant complication of the disease. It is not recommended to operate on an inflamed lipoma. Not all surgeons will undertake an operation in the presence of inflammation. Before performing surgical procedures, you must first get rid of the inflammation. Treatment of this situation is not difficult. For this purpose, various ointments and preparations from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Vishnevsky ointment and Ichthyol ointment are also used. However, you should not self-medicate. The inflammatory process needs to be diagnosed by a specialist and the selection of an adequate treatment method. The outcome of this complication is most often favorable.
Doctors call this condition as inflammation of the lymph nodes lymphadenitis. As mentioned above, there are a huge number of reasons due to which inflammation of the lymph nodes develops.
There are specific and nonspecific lymphadenitis. The cause of specific inflammation is a severe infectious disease (for example, AIDS, syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.).
Secondary lymphadenitis is caused by pathological processes resulting from pathogens entering the human body. To treat lymphadenitis, it is first necessary to diagnose and identify the primary disease and separate it from cancer. Elimination of lymphadenitis is aimed at curing the primary source of infection.
Conclusion
Inflamed lymph nodes are very similar to fatty tissues.
However, it is still possible to distinguish a lipoma from an inflamed lymph node. Inflammatory processes of both lymph nodes and lipomas are painful conditions that adversely affect the human body. Inflammation of formations has both common symptomatic features and differences. This complication can be treated provided that you contact a specialist in a timely manner, determine the source of the pathology and carry out adequate treatment. The prognosis is often favorable. The article has been verified by the editors
Features of diagnosing formations on the body
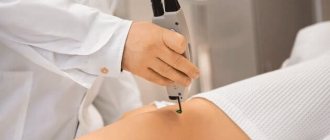
Even knowing the symptoms inherent in subcutaneous formations, self-diagnosis when they appear and differences is unacceptable. Timely contact with a specialist will help avoid consequences and complications. The correct diagnosis must be made by a doctor after appropriate diagnostics, which involves:
- palpation;
- laboratory blood test;
- ultrasonography;
- digital epiluminescent dermatoscopy;
- histological examination.
A tumor detected in time, treated in a timely manner and distinguished from other tumors will help to avoid further complications.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors