Is an allergy to cow's milk treated in a child, what to give to a bottle-fed allergic baby and what should a mother do if her breast milk causes an allergic reaction in the child - these and other popular questions from mothers are answered by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Pediatrics with a course Polyclinic Pediatrics named after. Academician G.N. Speransky Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Further Professional Education RMANPO of the Ministry of Health of Russia Irina Nikolaevna Kholodova.
— Irina Nikolaevna, how can you understand that a newborn or a 1.5-2 year old child has an allergy?
— I would like to draw the attention of parents to the fact that if there are people in the family who suffer from allergies, then, of course, the likelihood of allergies in the child will be quite high. For example, if only the mother suffers from it and all allergy sufferers are on the mother’s side, then the probability of an allergy is 40-50%, and if on both the mother’s and father’s side, then it is already 80%. That is, allergies are inherited
and in a child it can manifest itself from the first days of life. In young children, skin and gastrointestinal forms of allergies are most common.
Skin allergy
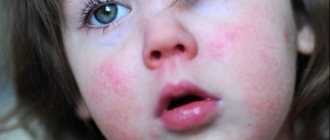
In young children, it is the cutaneous form that predominates (previously it was called exudative-catarrhal diathesis, now it is called atopic dermatitis) - an allergic rash appears on the child’s body. This can be a dry or wet rash, most often with itching.
Gastrointestinal form of allergy
This form is more difficult to diagnose, and it can be very difficult to understand that it is an allergy. Such children may experience severe colic from the first days of life - food is poorly digested, under-oxidized products are formed that irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa and can cause inflammation. In addition, due to impaired fermentation of food, a large amount of gases is formed. Gases stretch the intestines and put pressure on nerves and blood vessels. All this causes spasm and pain.
Subsequently, changes in the character of the stool may appear - there are constipation, but most often diarrhea occurs. Moreover, stool is usually several times a day, and it can be irritating, with a lot of mucus and even streaks of blood. The child begins to eat poorly, there is poor weight gain, and subsequently there may be a slowdown in growth. In such a situation, it is necessary to hospitalize the child to determine the cause - it can be not only an allergy, but also other diseases.
Is milk not for everyone?
The main task of the immune system is to recognize “self” and “foreign” cells. It reacts mainly to substances of protein nature, forming either a “Friend” (so-called immunological tolerance) or “Enemy” (antigen) response. When the response is “Enemy,” specific substances (antibodies) are produced that are aimed at fighting it. But, as with any system, there are failures.
Allergy (atopy) is an example of one such failure, when even friends are blacklisted. The child’s immune system begins to react to BCM inappropriately and excessively, blacklisting it. Beneficial protein turns into an allergen. This reaction is called "hypersensitivity."
The reasons for the occurrence of such “problems” are not reliably known to anyone. Scientists only build hypotheses, accumulate and systematize knowledge. All experts agree that genetic predisposition plays an important role. The only way to break the vicious circle of allergies and help a person is to exclude the causally significant allergen from the diet (environment) of this person.
This is called elimination (and elimination measures).
Milk substitutes in the diet
In recent years, soybean has been considered one of the substitutes for cow's milk, mainly soy milk and soy-based products.
It includes, among others, vitamin E and B, calcium, protein, magnesium, iron, phosphorus and lecithin. However, soy is not always safe. Soy products are not recommended for children under 6 months of age. Moreover, in severe allergies, the intestinal mucosa may be receptive to soy protein, resulting in soy allergy. You can also use coconut, rice or nut milk. Excluding cow's milk, you need to take care of the right amount of calcium in your diet. Its sources: eggs, fish (which contain bones, for example, sardines, sprats), as well as plant products: bread, flour, coarse cereals, dried legume seeds, vegetables (for example, spinach, chard, cabbage), nuts, cocoa, figs and dried apricots. Also allowed: meat, cereals, bread and eggs. Of course, fruits are also highly recommended, but you should be careful with citrus fruits. The menu can be based on these products; you can additionally maintain calcium levels, for example, using tablets.
Forbidden sweets, that is, sweets containing milk, can be replaced with dairy-free analogues, for example, milk chocolate can be replaced with dark chocolate or dried fruit candies, and a purchased cake can be prepared independently by baking it without adding milk.
Atopic diseases. How to suspect them?
Often people don’t even know about the diagnoses listed above because they don’t see a doctor.
The following symptoms should alert you:
- seasonal nasal congestion or runny nose with copious mucus production
- occasional lacrimation
- bouts of coughing and sneezing
- prolonged dry cough
- bouts of difficulty breathing
- wheezing
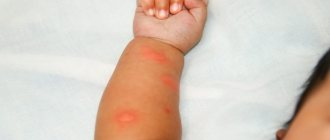
- rashes, redness and itching of the skin
- skin prone to dryness and flaking (periods or after contact with something)
- redness and/or other skin reaction to sun or cold exposure
- skin irritation after contact with something
- reactions to insect bites
- reactions to drugs
If the above symptoms occur, then there is a high probability of atopy. In this case, it is better to seek advice from a specialist. If you have allergies, be sure to tell your pediatrician about it and monitor your child’s diet.
Allowed subject to individual tolerance
- Vegetables and fruits of green and white color (all types of cabbage, zucchini, squash, sweet potato, Jerusalem artichoke, apples, pears, yellow plums, white currants, white raisins, etc.)
- Soups – vegetarian;
- Meat – turkey, rabbit, lean pork (boiled, stewed, steamed);
- Cereals (buckwheat, corn, rice, oatmeal, millet, pearl barley);
- Pasta;
- Wheat, wheat-rye bread;
- Drinks – tea, compotes, fruit drinks from the above mentioned fruits.
The author of the article is professor, doctor of medical sciences. Svetlana Gennadievna Makarova
Is it possible to prevent the development of ABCM?
Yes.
During pregnancy, the process of “friend/foe” recognition begins. The future mother’s nutrition plays a significant role in this. Products containing choline, methionine, zinc, folic acid, vitamins B6 and B12 can regulate gene function and contribute to the formation of tolerance (body resistance) to CMP.
During breastfeeding, you can limit the consumption of dairy products and other obligate allergens. This will reduce the burden on the child’s body and will also contribute to the formation of an adequate response of the immune system to BCM.
Obligate allergens are foods that often cause allergic reactions: eggs, fish, seafood, legumes: peas, beans, soy, peanuts; nuts, honey, strawberries, pomegranate, kiwi, melon, black currant, mushrooms.
Enterosgel and treatment of protein allergies
Enterosgel sorbent is indispensable for the treatment of food allergies in adults and children. The drug effectively absorbs and removes allergens from the body, eliminates unpleasant allergy symptoms and helps restore intestinal microflora.
Doctors advise allergy sufferers to use Enterosgel for preventive purposes. For example, in case of possible dietary violations while visiting, on business trips, or having to eat outside the home.
If supplementary feeding is needed?
In the first three months, all children, regardless of the degree of risk of developing CM, are recommended to use only mixtures with specially prepared protein. Their degree of allergenicity is significantly reduced, which is why they are called hypoallergenic. The NutrilakPremium Hypoallergenic mixture is additionally enriched with probiotics and food substrate for their growth and development (prebiotics). The NutrilakPremium Hypoallergenic fat component in combination with lutein best provides all the needs for the development of the child’s brain, vision and motor skills.
How does an allergy to BCM manifest in a baby?
Symptoms of ABCM can be very different.
With skin lesions:
- the appearance of dry skin, sometimes in the form of plaques
- redness of certain areas of the skin (around the mouth, arms and legs, cheeks, chest and abdomen)
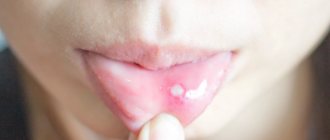
- the appearance of weeping spots and crusts with severe itching
- long lasting diaper rash
Involving the gastrointestinal tract:
- private regurgitation
- colic
- constipation
- diarrhea
- mucus in stool
- blood-streaked stool
- poor appetite and slow weight gain
The mucous membranes of the eyes, nose and respiratory tract may be involved with the following symptoms:
- lacrimation
- prolonged runny nose
- distant wheezes
- paroxysmal cough
All this can also affect the baby’s behavior in the form of:
- irritability
- sleep disorder
- bouts of crying and anxiety
It is important!
If symptoms persist after eliminating the causative allergen from the diet, it may not be a food allergy.
Contact your pediatrician immediately. In this case, a nursing woman needs to return to a balanced diet that includes all foods acceptable in the diet of nursing women (to prevent nutritional deficiencies in both her and the child).
If the baby is on mixed or artificial feeding, then together with the pediatrician it is necessary to decide on the correct selection of nutrition for him.
If the baby is already familiar with complementary feeding products, then together with the doctor, review the menu again. Make changes if necessary. Products containing BCM should be excluded. Keeping a food diary for mother and baby will greatly facilitate the process of finding the allergen and taking measures to eliminate it.
Eating problems due to milk
Milk allergy is becoming more common and is increasingly causing hospitalization. Food allergies are a serious health problem, and their symptoms extend beyond the reactions of the digestive system.
Research in recent years shows that more and more children are being hospitalized due to digestive problems, and more than 40% of them are hospitalized due to cow's milk allergy. The duration and severity of symptoms of this type of allergy increase. On the other hand, restricting an infant's diet can potentially lead to deterioration in the child's growth, development, and overall health.
How to confirm the diagnosis of ABCM?
There are not many tests in a doctor's arsenal for this, and there are no gold standards. There is no analysis that can confirm the diagnosis with 100% certainty.
The immunological tests performed can be divided into:
- nonspecific, confirming the allergic nature of inflammation
- specific, indicating the degree of significance of the influence of a particular allergen
Difficulties in diagnosing ACM It is extremely rare that only one allergen (CAM) is the cause, the trigger that triggers inflammation
- Most often these are several allergens at once (polyvalent allergy)
- There is cross-reaction between different groups of products
- If the child is breastfed, immunological tests are difficult to interpret (due to the presence of maternal antibodies in his blood)
Ways to select nutrition for ABCM
It all depends on the severity of the allergic process, existing symptoms, the age of the child and the type of feeding.
Breastfed
It is enough to organize the mother's nutrition.
With mixed feeding
If supplementary feeding is necessary, experts recommend using a mixture with split protein hydrolyzate. Of these, you can consider the Nutrilak Premium Hypoallergenic mixture.
Compared to whole molecules of cow's milk proteins, the allergenicity of its split protein is reduced by 100,000 times. Nutrilak Premium Hypoallergenic is suitable for the prevention of allergies in children at risk and the treatment of mild skin manifestations.
It is important!
Nutrilak Premium Hypoallergenic contains lactobacilli L.rhamnosus LGG® - this is the most effective and safe probiotic for children from birth, used for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis and eczema.
With artificial feeding
If the baby has pronounced skin manifestations, there are crusts and areas with weeping, or there is persistent heavy regurgitation, streaks of blood in the stool, then only deep hydrolysates (for example, Nutrilak PEPTIDE MCT) or amino acid mixtures can be used from mixtures.
Children over 6 months have a wider choice of food: there is more possibility of using complementary foods and soy mixtures (for example, NutrilakPremium Soya).
Is it possible to outgrow ABCM?
No!
If tolerance has not been formed and hypersensitivity to CMP remains, then the allergic inflammatory process occurs in the background. It may not be as pronounced, but it continues! Gradually, the foundation is laid for the development of chronic pathological diseases, turning into a time bomb.
What else is useful to know?
In the process of forming a reaction to an allergen, not only the response of the immune system is important, but also the background against which it unfolds.
It is known that products such as chocolate, cheese, citrus fruits, vinegar, nuts, marinades, etc. are a source of special substances (histamine liberators). They help maintain allergic inflammation by adding fuel to this fire. Limiting their intake or completely eliminating them will reduce the manifestations of atopy and help alleviate the child’s condition.
The smallest friends are microorganisms. Most of them live in the large intestine. They are our great helpers. Their contribution to curbing allergic reactions and forming the correct response to food is difficult to overestimate. More and more studies are confirming this. And if your own intestinal inhabitants can’t cope with this, then trusted friends – probiotics – can come to the rescue. All over the world, only two microorganisms have the largest evidence base on the antiallergic effect - LGG and BB-12 from Chr. Hansen. One of them even has its own website (https://www.lgg.com/).
Food allergies
Authors : American Academy of Pediatrics
Any food can cause an allergic reaction, but it turns out that 90% of food allergies in children are caused by just 6 foods - milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy and wheat. In adults, the majority of serious allergic reactions are caused by only 4 types of foods: peanuts, tree nuts, fish, shellfish and crustaceans. Allergies to fruits and vegetables are much less common and are usually less severe.
Cow's milk
Allergy to cow's milk is one of the most common allergies in young children. 2-3% of children under 3 years of age are allergic to cow's milk protein. Perhaps the reason is that this is the first foreign protein that young children receive in large quantities, especially if they are bottle-fed. Children with an allergy to cow's milk, even when breastfed, may experience colic or eczema, which disappear when dairy products are eliminated from the nursing mother's diet.
The most common symptom of milk allergy in children is vomiting after feeding. But more severe reactions also occur. Colic, increased gas formation, and anxiety are sometimes the only manifestations of an allergy to cow's milk protein in infants. Other allergy symptoms include dry skin, itching, rash, and atopic dermatitis.
And of course, the most obvious allergy symptoms are hives or breathing problems that appear immediately after eating dairy products.
Most children with an allergy to cow's milk also react to the milk of other animals, so it is not worth replacing cow's milk with goat's or sheep's milk.
It is worth noting that some children with an allergy to cow's milk protein cannot tolerate soy protein. Therefore, soy-based mixtures may also not be suitable for them. In this case, you will have to work with your pediatrician to select a mixture based on deeply hydrolyzed proteins or amino acids.
Many children outgrow their milk allergy as their immune systems mature. However, your pediatrician may suggest that you do an allergy test before your baby tries milk again. If the tests are negative, but the child has had serious allergies in the past, you will most likely be advised to reintroduce it into the child's diet under the supervision of a doctor who can provide medical assistance if necessary.
If a child is lactose intolerant, then allergy tests are usually not needed. You can give milk and dairy products little by little at home and observe the reaction. In addition, you always have the opportunity to choose special low-lactose products or lactose-free formulas for your child.
Milk and dairy products are the most important source of calcium, which is necessary for bones and teeth, as well as for the normal functioning of the nervous, muscular and other body systems. For older children with an allergy to cow's milk protein, calcium sources may include:
- dark green leafy vegetables;
- canned fish with bones, such as sardines, salmon;
- orange juice fortified with calcium;
- dried figs and prunes;
- tofu;
- dried beans.
Eggs
Children with egg allergies react primarily to egg whites. But it is almost impossible to separate the yolk from the white in such a way as to absolutely prevent the latter from getting there. Therefore, it is recommended to exclude them completely from the diet of children with an egg allergy. Although eggs have exceptional nutritional value and are an excellent source of protein, they are fortunately not essential in a healthy diet. You can always replace them with meat, fish, dairy products, grains and legumes - after all, these are the same sources of protein, minerals and vitamins.
If your child is allergic to eggs, carefully study the ingredients of foods and avoid foods such as bread with white glaze, meat or vegetables fried in batter.
Also, do not use egg substitutes, which are recommended when following low-cholesterol diets - they do not contain cholesterol (since there is no yolk, which contains cholesterol), but they still contain egg white.
Egg whites are used in the production of some vaccines. For those with a severe egg allergy, they should be avoided or used with caution. But the measles, rubella and mumps vaccine is considered safe for people with egg allergies. Discuss the choice of flu vaccine and other vaccines that may contain egg whites with your doctor.
Peanuts and nuts
Peanuts are not really nuts! It grows underground and is a member of the legume family (which includes beans, peas, lentils and soybeans). Therefore, children with peanut allergies usually do not have problems with walnuts, pecans, and other tree nuts. However, caution must be exercised as children with peanut allergies are still slightly more likely to develop allergies to other nuts.
Just like eggs, peanuts are tasty, nutritious and healthy, but fortunately not an essential product. Moreover, most people with peanut allergies can tolerate other legumes, such as soy and beans, even if skin or blood tests are positive for allergies to these products.
In general, peanuts are fairly easy to eliminate from the diet, but they can sometimes be found in trace amounts in a wide variety of foods. Ground peanuts and peanut butter are often used in confectionery products (candies, cookies, cakes, etc.). Therefore, it is important not only to read labels carefully, but also, if necessary, to clarify the composition of dishes in restaurants, cafes and other public catering establishments.
Nut allergies - Brazil nuts, hazelnuts, walnuts, pecans, cashews, almonds, etc. to all hard-shelled nuts—can be as severe as a peanut allergy. In some cases, the allergy is only to a certain type of nut, in others - to all. To avoid accidents, people with such allergies usually avoid any nuts, so as not to take unnecessary risks. Warn all family members, caregivers, teachers and friends that your child should not be given foods that contain even traces of nuts and peanuts, because. Nut allergies are the most severe of all food allergies.
Soybeans
An allergy to soy protein in children when using a soy formula manifests itself in the same way as an allergy to cow's milk protein - a rash, runny nose, wheezing (obstructive syndrome), diarrhea or vomiting may appear. Moreover, some children with an allergy to cow's milk also have an increased sensitivity to soy. In this case, discuss with your pediatrician the choice of a special hypoallergenic mixture in which the protein is maximally broken down or which contains individual amino acids.
However, children with soy allergies usually tolerate soy oil and soy lecithin well because they contain minimal amounts of protein.
Wheat and Gluten
Usually, rice and oatmeal are the first to be introduced into a baby’s diet, since they are much less likely than others to cause allergies. If there are no problems with oatmeal, move on to wheat. Wheat is the grain that most often causes allergies, but despite this, food allergies to wheat are quite rare. And this is great, because... Wheat is included in many prepared foods.
There are 2 types of negative immune reactions to wheat. The first is a classic food allergy with symptoms such as hives or difficulty breathing that occur immediately after a child eats foods containing wheat. The second is called celiac disease. It is related to gluten, a protein found in grains such as wheat, rye, and barley. In children with celiac disease, gluten damages the lining of the small intestine and interferes with the absorption of nutrients. This may go unnoticed for some time. Typical symptoms of celiac disease are abdominal pain, diarrhea, irritability, poor weight gain, and slow growth. Celiac disease usually appears soon after cereal is introduced, but in some cases the symptoms are so mild that a diagnosis may not be made until adolescence or even beyond.
Food allergies. Note
- If your child develops symptoms that indicate an allergy after eating certain foods, eliminate these foods from the diet and consult a pediatrician.
- Some children with milk or egg allergies can tolerate small amounts of these products found in baked goods. But there are children in whom even a small amount of thermally processed allergens causes allergies.
- Children who have several foods excluded from their diet due to food allergies may be at risk of malnutrition. Discuss with your doctor the possibility of consulting a nutritionist to organize adequate nutrition for your child.
- Children with food allergies should be able to do everything that children without allergies can do, except eat foods that cause allergies. Discuss with your pediatrician or allergist the issue of eliminating the allergen, as well as dietary and therapeutic measures to lead a full, safe and healthy lifestyle.
Source
published 25/11/2014 13:56 updated 02/08/2021 — Nutrition, Allergic diseases, Allergology and immunology