Skin rashes on babies: causes, treatment and prevention
In the first months of life, babies are prone to various types of irritation and rashes on parts of their body. This phenomenon is quite normal and in most cases is considered normal. This is due to the fact that the baby’s body is still very vulnerable, and it is just beginning to adapt to external and internal factors that can negatively affect the child’s condition. In addition, up to two or three months the baby is faced with hormonal changes, which often causes similar reactions. Consequently, a rash is not always a cause for concern and panic, but a specialist can best determine the nature of its occurrence and methods of treatment. There are a number of reasons that provoke the appearance of pimples, spots or redness on the skin of a newborn:
- hormonal rash;
- prickly heat;
- dermatitis;
- hives;
- food allergies;
- infections and viruses.
In 70% of cases, the rash occurs precisely on a hormonal background, which is completely normal and does not require treatment, especially medication. This is due to the receipt of maternal hormones while still in the womb, and subsequent adaptation to new conditions. Distributes on the forehead, temples, and on the back of the head under the hair. It goes away on its own, usually within a few days. In this case, the mother is recommended to simply bathe the baby daily in boiled water with the addition of a herbal solution (series). During the hot season, the baby’s delicate skin is doubly prone to various manifestations due to drying out in the sun. All areas exposed to sweat also become vulnerable. Miliaria is not life-threatening for the baby, but it can cause discomfort in the places where it is localized. You should bathe your child more often, ventilate the room, and, if possible, maintain optimal humidity where the baby spends most of his time. Of course, you should not dress your child in clothes that will make him hot and uncomfortable. It is useful to give the baby time to be without clothes and diapers so that the skin has the opportunity to breathe. In addition, it is recommended to always wash small items only using a special children's powder, and then iron them on both sides.
Which doctor should I contact?
A rash on a child’s legs is not the only symptom that occurs with skin pathology. The baby is bothered by itching, his general condition worsens, his appetite decreases, and his sleep is disturbed. You need to contact your local doctor, even if the child does not have a fever.
To find out the cause of the rash, you may need to consult a pediatric infectious disease specialist, allergist, or dermatologist.
Diagnosis of rashes on the legs in children
For differential diagnosis of a rash, medical history and examination will be needed.
Required:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- take an x-ray of the lungs.
If an allergy is suspected, special tests are performed. In the case of skin diseases, an examination by a dermatologist is sufficient. If necessary, scrape the surface of the rash elements. If the cause of the rash cannot be determined, in severe situations the cerebrospinal fluid is examined to rule out meningitis.
Allergic rash
In any case, parents are recommended to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the rash on the baby’s body. If a specialist discovers an allergy, then it is necessary to identify its form and irritant. Typically, the causative agent may be the following:
- the body's reaction to the weather (sun or cold);
- food allergies (in which the allergen product can be consumed by both the baby and the mother, if the former is breastfed);
- heredity (a child is at risk if at least one of his parents is predisposed to allergies);
- cosmetical tools;
- animal hair, dust, pollen;
- vaccination vaccines.
Once the cause of the rash is known, the next important step is to completely eliminate the irritant. It will be easier to do this in cases where the reason lies in external factors that they simply stop using (if they are creams, powders, detergents and other hygiene products). In the case where skin manifestations are the result of consuming certain products, it is important to exclude the product itself. The first signs may appear as early as an hour and a half after eating the allergen. Breastfeeding mothers must follow a diet and avoid spicy, fatty, chocolate, brightly colored fruits and vegetables, and alcohol. In such cases, it will be more difficult to get rid of the rash, since the product must be digested by the intestines, leave the baby’s body, and only after that the spots on the body will begin to disappear. You should know that when the pathogen reaches the baby through mother's milk, the process is delayed and recovery occurs after two weeks. Parents who themselves suffer from allergies should be extremely attentive to what their child is surrounded by and what he eats. Unfortunately, such babies are more prone to skin diseases than others. In this case, the irritant of an adult and an infant can be completely different. At the genetic level, only the predisposition itself is transmitted.
Almost always, allergies as a disease can be prevented. To do this, you will need to fulfill simple requirements:
- maintaining ideal cleanliness in the room, frequent wet cleaning and ventilation;
- introduction of complementary foods no earlier than four months from birth, and in some cases no earlier than six months. At the same time, it is important not to overdo it: if the introduced product is not suitable, then it should be offered to the baby again after one or two weeks;
- Diet compliance by a nursing mother. Drinking large amounts of liquid, broths and soups. Complete exclusion of harmful products;
- You should not self-medicate and try to prevent this or that reaction with the help of medications without appropriate doctor’s recommendations;
- maintaining hygiene and sharing a healthy lifestyle between mother and baby.
Walking in the fresh air, swimming, and hardening will have a positive effect on the health of all family members.
Urticaria and dermatitis are also types of allergic reactions. In the first case, there is a sudden appearance of itchy blisters on any part of the body. Such symptoms can occur from insect bites, from interactions with chemicals, and from eating strong allergens such as cow's milk, nuts, and honey. It is important to consider that prolonged exposure to the pathogen can worsen the baby’s condition, develop into edema and, at the same time, complicate breathing. Therefore, it is necessary to get rid of the presence of the irritant as quickly as possible and consult a doctor. Treatment occurs with the help of antihistamines and sedatives.
Dermatitis , like other types of allergies, is provoked by prolonged exposure to an irritant, increased sensitivity and predisposition to similar manifestations. Symptoms include inflammation of certain areas of the child’s skin (most often the hands, groin, cheeks), possibly burning and discomfort. Dermatitis is divided into several types:
- diaper (long-term interaction of delicate skin with irritants, such as wet diapers, diapers. Here you should change the diaper more often and wash the baby with running warm water before each change.
- Use wet wipes only when necessary, and apply a special protective cream under the diaper.);
- atopic (an outbreak occurs at the immune level, as the body’s response to respiratory and contact irritants. Localized on the cheeks, thighs, arms. Characterized by peeling lesions.);
- allergic (lack of vitamins in the body, consumption of allergic pathogens in food, lack of fresh air, moodiness, hyperactivity).
As in other cases, it is very important to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin treatment in order to prevent transition to a chronic form. All allergenic foods should be excluded from the baby's diet; to reduce itching, the doctor will prescribe the use of a cream or ointment, and also prescribe the necessary medications to eliminate the causes. It is worth understanding that the problem always lies inside, and it is important not only to eliminate external symptoms, but also to completely destroy the original cause of the disease. When an allergy manifests itself against the background of vaccinations for a child, it is important to take into account the child’s predisposition in advance, notify the doctor about this and follow a number of measures prior to vaccination. Such events include the following:
- taking tests;
- use of antihistamines two to three days before vaccination;
- close observation on the day of vaccination and refusal of new products.
Parents need to know that any vaccine contains a potential pathogen. It can be chicken egg white, gelatin and other components that make up the drug. Therefore, after the vaccination has already been done, you need to stay with the child in a medical facility for about half an hour, in order to observe and take measures, if necessary. Most often, doctors do not recommend going for walks on the day of vaccination, especially if the baby is still very small and fragile. It will be necessary to monitor the general condition and possible changes for two weeks.
Rash caused by infections and viruses
Only a specialist can recognize the etiology of the formation of a rash on the baby’s skin and prescribe the need for treatment. But in cases where skin manifestations are accompanied by fever, stool disturbances, vomiting, and difficulty breathing, then most likely the nature of the disease is directly related to infection. Infectious rashes are caused by diseases such as:
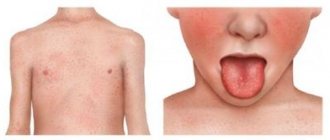
- chickenpox (caused by the appearance of blisters containing liquid inside. The areas of spread itch and itch, and the temperature rises to critical levels. Throughout the maturation of the blisters, the child is a carrier of the infection. The affected areas are treated with brilliant green. If all the doctor’s instructions are followed, recovery occurs after 21 days.);
- rubella (this type of infection is characterized by cough, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, intestinal dysfunction, and, as a result, diarrhea and vomiting. The rash is usually not palpable, but appears in the form of redness of the skin. Most often, this disease occurs in children older than two years, but infants can also be infected, especially those who do not have the appropriate vaccination. The disease proceeds without complications and does not require special measures. It is only important to maintain bed rest and reduce the risk of rubella infection for other small family members, since five to seven days, an infected infant can infect unvaccinated children.);
- measles (the main reason for its appearance is the lack of vaccination. Infection occurs by airborne droplets, and symptoms begin to appear no earlier than a week later. As a result, it is not possible to notice the disease in time. Only after a few days do the symptoms of the disease make themselves felt : the temperature rises, a small rash appears first on the inside of the cheeks, head, and then throughout the body.The child’s immunity weakens, so it is necessary to feed it with vitamins during this period, and allow the body to cope with the disease on its own.
It is recommended to help the baby during this period, based on the symptoms that appear: antipyretics, throat sprays, nasal drops, as well as bed rest and frequent fluid intake. Treatment can take place both at home and in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor, in order to eliminate the possibility of complications). A dermatologist or allergist will help you make the correct diagnosis. To do this, you need to undergo tests and, if necessary, skin scraping. An important role is played by external factors, the nature of the rashes, their localization, as well as the accompanying deterioration of the baby’s condition. In any case, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions regarding treatment and compliance with certain rules. The duration of allergies is also particularly influenced by the child’s immunity: the stronger it is, the sooner it will cope with the disease. Parents are required not to panic, but to notice the slightest manifestation of symptoms in time and contact a doctor as soon as possible.
Preventing rashes
There are simple rules that will help avoid skin infections. What you should do is:
Exercise caution when in contact with sick people (for example, avoid shaking hands). Use personal hygiene products. Take sunbathing in doses. Ultraviolet light is good for the skin: it dries the epidermis and kills pathogenic microbes. Regularly care for your body skin by cleansing it with scrubs
If a ready-made cosmetic product is not available, you can use improvised means - sea salt, ground coffee. Vegetable oils, honey, and sour cream are suitable as bases. By cleansing the body, the scrub rids the skin of pathogenic microorganisms.
Of course, these recommendations will not provide complete protection, because the cause of the rash may be pathologies of internal organs or hormonal imbalance. Nevertheless, such preventive measures will significantly reduce the risk of disease and prevent the development of watery acne.
Skin rashes on babies: causes, treatment and prevention
In the first months of life, babies are prone to various types of irritation and rashes on parts of their body. This phenomenon is quite normal and in most cases is considered normal. This is due to the fact that the baby’s body is still very vulnerable, and it is just beginning to adapt to external and internal factors that can negatively affect the child’s condition. In addition, up to two or three months the baby is faced with hormonal changes, which often causes similar reactions. Consequently, a rash is not always a cause for concern and panic, but a specialist can best determine the nature of its occurrence and methods of treatment. There are a number of reasons that provoke the appearance of pimples, spots or redness on the skin of a newborn:
- hormonal rash;
- prickly heat;
- dermatitis;
- hives;
- food allergies;
- infections and viruses.
In 70% of cases, the rash occurs precisely on a hormonal background, which is completely normal and does not require treatment, especially medication. This is due to the receipt of maternal hormones while still in the womb, and subsequent adaptation to new conditions. Distributes on the forehead, temples, and on the back of the head under the hair. It goes away on its own, usually within a few days. In this case, the mother is recommended to simply bathe the baby daily in boiled water with the addition of a herbal solution (series). During the hot season, the baby’s delicate skin is doubly prone to various manifestations due to drying out in the sun. All areas exposed to sweat also become vulnerable. Miliaria is not life-threatening for the baby, but it can cause discomfort in the places where it is localized. You should bathe your child more often, ventilate the room, and, if possible, maintain optimal humidity where the baby spends most of his time. Of course, you should not dress your child in clothes that will make him hot and uncomfortable. It is useful to give the baby time to be without clothes and diapers so that the skin has the opportunity to breathe. In addition, it is recommended to always wash small items only using a special children's powder, and then iron them on both sides.
Associated diseases
Prickly heat
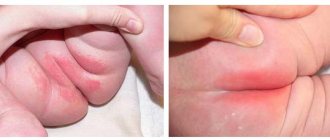
A disease characterized by the formation of small blisters or pimples. It is provoked by elevated temperature, steaming the body with warm or synthetic clothing that does not allow air to pass through. It often occurs in the groin area, in the folds under the knees, and in the armpit area.
Miliaria is distinguished:
- papular (associated with the appearance of papules: the skin dries very much, peels and itches);
- red (distinguished by red blistering and nodular formations up to 2 mm with cloudy liquid inside, itching);
- crystalline (characterized by the presence of white and transparent bubbles with a diameter of up to 1 mm.).
Treatment of the disease is associated with the elimination of provoking factors (overheating) and compliance with the necessary hygienic conditions.
You can relieve the symptoms of the disease with the help of creams and gels: “La-Cri” (safe for infants, pregnant women), “Bepanten”, etc.
Hormonal imbalance and vitamin deficiency
Changes in hormonal levels (during puberty, in case of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs involved in the production of hormones) can cause acne to appear on the legs. The disease manifests itself individually, and peeling of the skin may occur.