What is a cold allergy?
Allergy itself is a specific reaction of the body to the action of various irritants (allergens). It can be caused by various factors, including cold.
Hives that form on the skin under the influence of low temperatures are called cold dermatitis in medical terminology. Larisa Prokhorova, an allergist at the medical ]ON Clinic Kharkov[/anchor], will tell you more about the reasons for its appearance:
“It is mistakenly believed that cold urticaria occurs exclusively in winter at low air temperatures. However, this condition can actually be caused by swimming in cold water, drinking cold drinks, or staying in an air-conditioned room. True, in the latter case we are talking more about industrial premises, because for a reaction to occur, the ambient temperature usually must drop to at least 4°C.”
You can often hear the opinion that cold dermatitis is not an allergy in its typical manifestation. However, recent studies have shown that the body reacts to frost in the same way as other allergens, with increased production of histamine. This is what causes the appearance of allergy symptoms.
Heat urticaria: what is it?
Heat urticaria is an itchy rash (blisters) that occurs when the skin is exposed to high temperatures. The presence of this form of allergy can be determined using special tests. But there are more accessible and simpler diagnostic methods.
For example, it is enough to apply a hot object to the skin of the forearm for only 5-7 minutes. If redness, itching or swelling appears on the skin within 15-20 minutes, the diagnosis of “heat urticaria” can be considered confirmed. In children and adults, this allergic reaction may also occur in the form of fever.
Symptoms of cold urticaria
This type of allergy can manifest itself in different ways. Most often it is accompanied by excessive dryness and rash on the skin. Other symptoms of cold dermatitis include:
- a burning sensation on the affected skin when it is warmed;
- swelling and itching at the site of the rash;
- increased body temperature;
- headache and causeless fatigue;
- joint pain.
The exposed parts of the body suffer the most from the pathology. Yes, you just have to go outside without gloves, and you will most likely notice the appearance of an allergy to the cold on your hands. How exactly frost affects the skin will be explained by Elena Kaspruk, a dermatologist at the medical ]ON Clinic Mariupol[/anchor]:
“Cold air and harsh winter winds remove moisture from the skin. As a result, it becomes dry and may itch. In addition to dryness (xerosis), cold allergies can cause peeling, redness, cracking, irritation, tingling, burning and roughening of the epidermis. Symptoms of xerosis range from mild to severe depending on the severity of the body's reaction and the sensitivity of the skin. You can alleviate their manifestation with the help of moisturizing creams, but you should choose the optimal product after consulting your doctor.”
Also, the thin skin of the lips reacts strongly to frost. The reason is the same - increased histamine synthesis in the body and lack of moisture. In addition to their unaesthetic appearance, dry lips cause significant discomfort: they can crack and hurt while talking and eating. In addition, open bleeding wounds may form at the site of cracks, which can lead to infection.
You may have also noticed that your hair also becomes dry and brittle in winter. Natalya Rozhkova, a trichologist at the medical ]ON Clinic Sumy [/anchor], will tell you why this happens:
“The cause of dry and brittle hair can be that it does not receive or does not contain enough moisture. This causes the strands to lose their shine and become dull. Among other non-seasonal factors, such a situation can be caused by low or, conversely, too high air temperatures, so our hair needs special care and additional nutrition. And although dry strands are associated with the influence of cold, such a reaction in the body is not allergic and is typical even for people who are not prone to cold dermatitis.”
Paradoxical but true! If cold air negatively affects the condition of hair, then a cool shower does the opposite. It has been proven that cold water, unlike hot water, does not dry out the sebum layer, which acts as a protective barrier for the scalp. In addition, it “seals” and strengthens the hair cuticles, as a result of which they become stronger and healthier.
How does cold allergy manifest?
A person can acquire this form of allergy either by inheritance or during life. Acquired cold urticaria may appear in adolescence and completely disappear by the age of 20-25. But it also happens that the disease occurs in adult women over 30 years of age and occurs in an acute form.
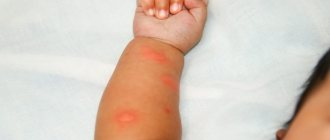
To diagnose an allergic reaction (urticaria) to cold, you will have to do special temperature tests: apply an ice cube to the skin of the forearm for 2-4 minutes. And then evaluate the results within 15-20 minutes:
- if blisters, swelling and redness appear within 10 minutes, this is primary/secondary cold urticaria;
- all similar symptoms appeared only after 20-30 minutes - this is an apathetic allergy to cold;
- if there is no reaction, but a rash appears on the skin area, this is reflex cold urticaria.
When is it time to see a doctor?
We are unlikely to be wrong if we say that most people with symptoms of cold urticaria have never consulted a doctor. But in vain, because this allergy can be no less dangerous than, say, due to a bee sting.
The fact is that an acute reaction to cold, like any acute allergic reaction, can have serious consequences, including anaphylactic shock. That is why at the first signs of cold dermatitis it is better to consult a doctor. He will prescribe the necessary tests to rule out pathologies with similar symptoms and may conduct an ice cube test to track the body's reaction to cold. After this, your specialist will likely recommend antihistamines and skin care products to help ease your allergies.
If, after being in the cold air, you have trouble breathing, your blood pressure has decreased, your heart rate has increased, or swelling of your throat or tongue has appeared, you should urgently call an ambulance.
General notes on therapy
Treatment Goals
- regression of rashes;
- no relapses.
Diet.
- In case of a proven food allergy, it is recommended to avoid eating foods that provoke the development of the disease. Eliminating identified allergens from the diet leads to an improvement in the condition of the skin after 24-48 hours.
- In patients with daily or almost daily urticaria, it is recommended that a hypoallergenic diet be included in the extensive evaluation plan. In the case of a pseudo-allergic reaction, improvement with a hypoallergenic diet occurs after 3 weeks.
Pharmacological drugs
.
- Non-sedating 2nd generation H1-histamine blockers are recommended as basic first-line therapy for acute and chronic urticaria.
- The use of 1st generation H1-histamine blockers is currently limited due to their low effectiveness and the risk of side effects (sedation, anticholinergic effects, sleep disorders, etc.) and is indicated only in a number of exceptional cases.
- Treatment of acute urticaria with glucocorticosteroid drugs is not recommended. Indications for the use of systemic glucocorticosteroids are: lack of effect when treated with H1 receptor blockers, delayed urticaria due to pressure, angioedema.
- It is not recommended to use, due to very low evidence of effectiveness: H2-receptor blockers (both monotherapy and in combination with H1-histamine blockers), montelukast, zafirlukast, tranexamic acid, sodium cromoglycate, topical corticosteroids, colchicine, indomethacin, nifedipine.
Indications for hospitalization
to the dermatological hospital: widespread urticaria, accompanied by intense itching and a disturbance in the general condition, as well as lack of effect at the outpatient stage of therapy. to the intensive care unit: concomitant angioedema in the larynx, anaphylactic reactions
Requirements for treatment results
- stopping the appearance of fresh rashes;
- complete resolution of existing rashes;
- absence of subjective manifestations of the disease.
Prevention
Prevention of urticaria involves a thorough analysis of the allergy history before prescribing drug treatment. Particular attention should be paid to the manifestations of atopy in patients with urticaria. For preventive purposes, the use of 2nd generation H1-histamine blockers is recommended [8]. For patients with chronic urticaria, it is important to sanitize foci of chronic infection, treat concomitant pathologies, and also limit the effect of potential allergens.
Acute urticaria
- Eliminate exposure to trigger factors.
- Carry out drug therapy aimed at relieving the symptoms of the disease:
- treatment with H1-histamine receptor blockers;
- if there is no effect, treatment with systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs;
- urgent measures to relieve angioedema.
Chronic urticaria
- Elimination of exposure to factors that cause exacerbation of the disease (if possible).
- Hypoallergenic diet with the exclusion of suspected allergens and/or obligate allergens. When eliminating a food allergen from the diet, the condition improves after 1-2 days. When the rashes disappear, a gradual introduction of excluded or new foods begins, one at a time, one every other day, until new rashes appear. The ineffectiveness of the elimination diet for 1 month indicates the absence of a connection between urticaria and food products and serves as an indication for canceling the elimination diet.
- Drug therapy aimed at reducing symptoms of the disease.
Algorithm for drug treatment of patients with chronic urticaria.
| First line of therapy: | H1-histamine blockers 2nd generation |
| Symptoms persist for 2 weeks | |
| Second line of therapy: | Increasing the dose of 2nd generation H1-histamine blockers by 4 times* |
| Symptoms persist for 1-4 weeks | |
| Third line of therapy: | Omalizumab |
| A short (maximum 10-14 days) course of glucocorticosteroid drugs can be administered at any time. Indication: severity of exacerbation | |
* it is required to justify the prescription in doses exceeding those specified in the instructions for the use of drugs, to invite the patient or his legal representative to sign an informed consent, explaining the benefits and risks of such a prescription, to approve the prescription by a medical commission.
2nd generation H1-histamine blockers are effective in 40-60% of patients with chronic spontaneous (idiopathic) urticaria. If there is no effect from treatment with them for 2 weeks, a 4-fold increase in the dose of drugs is possible. Increasing the dose of H1-histamine receptor blockers allows you to limit the use of glucocorticosteroid drugs and, thus, avoid side effects of therapy and steroid resistance.
Features of the treatment of individual forms of urticaria
- Cold urticaria
. Patients should avoid sudden exposure to cold temperatures. 2nd generation antihistamines (rupatadine) can be used. Systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs are ineffective. - Delayed pressure urticaria
. Pressure on the skin should be avoided. For severe delayed urticaria from pressure, the most effective are systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs, which are prescribed for a short period of time with a gradual reduction in dose. Histamine H1 receptor blockers are usually ineffective. - Solar urticaria
. Antihistamines and ultraviolet light irradiation in gradually increasing doses are effective (tolerance induction). Adequate photoprotection (UVA+UVB) is important. - Urticarial dermographism
. No treatment is required unless the patient consistently responds to minimal trauma. 1st generation H1-histamine receptor blockers are effective. In some cases, the disease is severe and continuous therapy with 2nd generation antihistamines is required. - Cholinergic urticaria
. Patients should avoid intense physical activity. 1st and 2nd generation H1-histamine receptor blockers are used. Belladonna alkaloids/phenobarbital/ergotamine and radobelin/phenobarbital/ergotamine are indicated for the treatment of cholinergic urticaria. - Contact urticaria.
Avoid contact with provoking factors. Antihistamines are effective methods of therapy. Preventive administration of 2nd generation H1 histamine blockers is acceptable in cases of possible contact with trigger factors (for example, insect bites). Topical glucocorticosteroid drugs may be prescribed. For severe manifestations of the disease, systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs are used. - Thermal, aquagenic, vibration urticaria.
Antihistamines are not always effective. - Angioedema
. With the development of angioedema, epinephrine is administered parenterally (intravenously, intramuscularly or subcutaneously, depending on the severity and location of the lesion) and H1-histamine receptor blockers (intravenously or intramuscularly). If this therapy is ineffective and in cases of the development of severe angioedema with a violation of the general condition, systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs are used. In cases of difficulty breathing, aminophylline is used. - Adrenergic urticaria.
Avoid contact with provoking factors, oral propranolol. Nonspecific therapy, including tranquilizers and antihistamines.
Treatment regimens
1. 2nd generation H1-histamine receptor blockers
- Loratadine 10 mg orally 1 time per day until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears
- desloratadine 5 mg orally once a day until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears
- fexofenadine 180 mg orally 1 time per day until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears
- Cetirizine 10 mg orally once daily or 5 mg orally twice daily until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears
- Levocetirizine 5 mg orally once a day until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears
- ebastine 10-20 mg orally 1 time per day (depending on the severity of symptoms) until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears
- Rupatadine 10 mg orally once a day until the rash disappears and 4 weeks after the rash disappears.
2. First generation H1-histamine receptor blockers
- diphenhydramine 25-50 mg orally 4-6 times a day or 20-50 mg intramuscularly 1-2 times a day for 7-10 days
- clemastine 1 mg orally 2 times a day or 2 mg intramuscularly 2 times a day for 7-10 days chloropyramine 25 mg orally 1-2 times a day or 20-40 mg intramuscularly 1-3 times a day for 7-10 days
- cyproheptadine 2-4 mg orally 3-4 times a day for 7-10 days
3. Glucocorticosteroid drugs
- betamethasone 1-2 ml intramuscularly with an interval of 7-10 days, 1-2 injections
- dexamethasone 4-16 mg per day intravenously or intramuscularly until pronounced clinical improvement occurs, with further transition to oral administration (except for the treatment of angioedema)
- dexamethasone 1.5-4.5 mg per day orally until pronounced clinical improvement occurs, with a further gradual dose reduction of 0.125-0.25 mg once a week until complete withdrawal
- prednisolone 30-100 mg per day intravenously or intramuscularly until pronounced clinical improvement occurs, with further transition to oral administration (except for the treatment of angioedema)
- prednisolone 10-30 mg per day orally until pronounced clinical improvement occurs, with a further gradual reduction in dose by 2.5-5 mg once a week until complete withdrawal.
4. Adrenergic agonists
For severe urticaria and/or angioedema (laryngeal edema, exercise-induced anaphylaxis, severe cold allergy), epinephrine, a solution of 0.1% (0.1 to 0.3 ml), is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly, if necessary, the administration is repeated after 10 -20 minutes up to 3 times.
5. Omalizumab
The drug is indicated for the treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria, resistant to therapy with H1-histamine receptor blockers, in patients aged 12 years and older. The recommended dose of the drug for chronic idiopathic urticaria is 300 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks. It is recommended that the attending physician periodically evaluate the need for continued treatment. The effect of omalizumab, as a rule, can be observed already in the first day, with its subsequent increase over a number of weeks. According to clinical studies and real clinical practice, the effectiveness of omalizumab reaches 90%.
Treatment of angioedema (Quincke's edema)
- epinephrine, solution 0.1%: 0.1-0.5 ml intravenously or intramuscularly, or subcutaneously once;
- chloropyramine, or clemastine, or diphenhydramine 1-2 ml intravenously or intramuscularly once;
- prednisolone 60-100 mg intravenously or intramuscularly or dexamethasone 8-16 mg intravenously or intramuscularly until pronounced clinical improvement;
- aminophylline 10 ml of 2.4% solution intravenously, slowly, once.
Related treatments
In the treatment of urticaria, drugs that affect the central nervous system are used as concomitant therapy: anxiolytics (tranquilizers) and antidepressants.
1. Anxiolytics (tranquilizers) for cholinergic urticaria:
- Hydroxyzine 25 mg orally 4 times a day with meals for 7-10 days
- belladonna alkaloids/phenobarbital/ergotamine 1 tablet orally 2-3 times a day for 1 month
- radobelin/phenobarbital/ergotamine 1 tablet orally 3 times a day for at least 1 month.
2. Antidepressants as concomitant therapy for patients with urticaria in the presence of depression and anxiety.
- amitriptyline 25-50 mg orally 1 time per day for at least 1 month.
3. External therapy. To reduce itching and burning, use warm showers and baths, lotions, shaken suspensions with menthol, anesthetics that do not contain glucocorticosteroid drugs.
Open recommendations
- Some experience has been accumulated in the use of cyclosporine A in combination with 2nd generation H1 histamine blockers for chronic urticaria.
- There are few studies showing the effectiveness of plasmapheresis in chronic urticaria of autoimmune origin.
- The latest consensus documents on the treatment of urticaria also recommend leukotriene receptor blockers, 2nd generation H1 histamine blockers in combination with omalizumab, ketotifen, dapsone, sulfasalazine, oxatamide, nifedipine, warfarin, intravenous gammaglobulin, autologous plasma, montelukast. However, this therapy has low-quality evidence, with no efficacy data from high-quality randomized clinical trials (CDs) [26–29, 34–43].
Treatment of pregnant women and during lactation
When managing pregnant and lactating women, you should adhere to rules similar to those when managing children. It is important to avoid the use of any systemic drug during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, but the most effective treatment should be ensured. There are indications of an increase in histamine levels in pregnant women, which determines the need for the use of antihistamines. Prescription of 2nd generation H1-histamine blockers during pregnancy should only be used if necessary, when the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus. In the first trimester, medications should be avoided.
A low dose of loratadine may be used for a short time. Use of 1st generation H1-blockers immediately before birth may cause respiratory depression and other side effects in newborns.
To date, there is not a single indication in the world of congenital pathology in children born to women who took 2nd generation H1-histamine blockers (cetirizine, loratadine) during pregnancy. It is advisable to prescribe loratadine to pregnant women with urticaria; recommendations for loratadine can be extrapolated to desloratadine. Recent clinical observations have shown that the safest drugs during pregnancy are loratadine, and during lactation, loratadine and cetirizine [45].
Treatment during lactation.
It is necessary to avoid taking medications during breastfeeding. If necessary, loratadine and cetirizine can be used.
Treatment of children
In children, acute urticaria is more often recorded, which can manifest itself as an allergic reaction, for example, to food. The disease usually develops within an hour after eating food and resolves within 24 hours. Chronic urticaria is less common among children than among adults. In childhood, the most commonly reported urticaria are pressure urticaria and cold urticaria, which are often combined with dermographic or cholinergic urticaria. In most cases, the positive effect of therapy is achieved by taking antihistamines and eliminating trigger factors. For children, 1st line of therapy is recommended, similar to that for adults. It is important to consider the age restrictions and age dosages of each of the H1-histamine blockers:
- loratadine: children aged 2 to 12 years with body weight less than 30 kg - 5 mg 1 time per day, children over 12 years old, and also with body weight more than 30 kg - 10 mg 1 time per day;
- Levocetirizine: children aged 2 to 6 years - 2.5 mg per day, children over 6 years - 5 mg per day;
- Cetirizine: children over 6 years of age (weighing more than 30 kg) - 1 tablet 1 time per day.
Desloratadine, fexofenadine, rupatadine are approved for use in children aged 12 years and older. In infants and children under 2 years of age, first generation H1-histamine receptor blockers can be prescribed. In rare cases, the use of systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs is allowed (for 3-5 days ) .