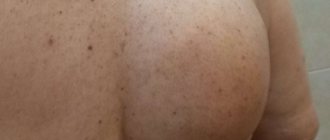
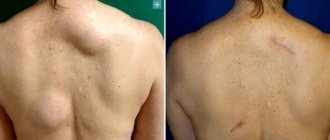
Benign neoplasms can appear in different places on the human body, which are called lipomas in the medical community, and wen in the common people. Usually a lipoma is a single fatty tumor on the body, but if many fatty tumors appear, a disease such as lipomatosis is diagnosed. Most often, lipomas are found on the face, head, back, neck, chest and upper limbs. Most doctors agree that the cause of this pathology is metabolic disorders and a genetic defect.
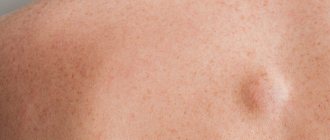
Rice. 1. If lipoma hurts, then you need to see a doctor
Lipomas usually do not cause discomfort or pain. A person can live with her all his life and not attach much importance to it. But it happens that the lipoma begins to increase in volume, changes color, and hurts when touched. In this case, you should pay close attention to your health and go to a specialist to find out the cause of the changes and get competent recommendations.
Services and prices
Removal of lipoma more than 3 cm
7000 ₽
Sign up
Removal of lipoma up to 3 cm
4000 ₽
Sign up
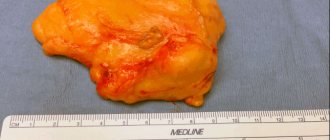
Lipoma is the most common soft tissue tumor and consists of fat cells surrounded by a thin fibrous capsule. Popularly, such a neoplasm is called a wen.
Often, a person who is attentive to his body may stumble upon such a subcutaneous formation. Such a finding can cause, at a minimum, caution, and sometimes fear of the oncological process. The unknown is always scary. If you have any concerns, you should consult your doctor. In most cases, subcutaneous neoplasms in soft tissues are benign and do not pose a threat to the owner of the wen. However, lipomas still require the supervision of a specialist who must recognize a malignant process, if one occurs.
Peculiar red flags, signs that make you wary, are rapid tumor growth, pain, and the presence of two or more similar formations on the body.
By external signs, lipoma is little distinguishable from liposarcoma, hygroma, subcutaneous cyst, hematoma, parasitic invasion, inflammation or consequences of injury. Therefore, it is important that any neoplasms be examined by a doctor.
First of all, the question of the malignancy of the tumor is decided at the appointment. Liposarcoma occurs more often in middle-aged and elderly people. This is an aggressive and fast-growing tumor that can put pressure on surrounding organs and tissues and cause pain. Situations when an existing lipoma degenerates into a malignant tumor rarely occur. However, the oncological process requires a radically different approach to diagnosis and treatment, so it is important to diagnose it as early as possible.
Lipomas may have a hereditary predisposition. This fact, combined with the spread of wen to other parts of the body, makes the doctor suspect lipomatosis. Lipomatosis accompanies a number of hereditary syndromes such as Madelung's disease and Dercum's syndrome. Diseases with a family history require a special approach to therapy.
When should lipomas be removed?
Most often, patients are interested in the question of whether lipomas should be removed immediately and whether it is possible to do without surgery.
It should be remembered that a lipoma is a benign formation that does not grow into the surrounding tissue. However, the problem is different: these formations tend to increase in size over time. At the same time, the lipoma “pushes apart” the tissues and organs located nearby in order to “win” a place for itself. Due to the pressure in them, metabolism can be disrupted, which is fraught with unpleasant consequences and pain.
In some cases, lipoma removal cannot be delayed. You should immediately consult a doctor if the wen has changed in appearance or you begin to feel physical discomfort. Redness of the skin over the lipoma, itching or peeling should also alert you.
Doctors recommend removing lipomas if they grow near a cluster of blood vessels or nerve cells. It is also better to “play it safe” and cut out a formation that is located in the so-called “high trauma zone” - in other words, in an area that is often exposed to external influences.
Reasons for appearance
There are many factors that influence the formation of lipomas. Among the reasons are hereditary predisposition, impaired metabolism of fatty acids in the body, liver disease, pancreatic disease, non-compliance or violation of hygiene rules.
For a long time it was believed that soft tissue injury predisposes to the development of lipomas, but this fact was subsequently refuted in research. Thus, doctors agree that one reason that would explain all the processes has not yet been found. However, predisposition to gastrointestinal lipomas has a proven connection with a gene mutation on chromosome 12. In other cases, the reasons remain unknown.
Why do lipomas occur?
To date, scientists have not been able to come to a consensus on why lipomas develop and why multiple lipomas are more common rather than single formations. Lipomatosis has nothing to do with the patient’s weight category or the amount of subcutaneous fat in his body, since formations can appear even in very slender people.
According to researchers, the appearance of wen is associated with a genetic predisposition. It can also be triggered by metabolic disorders in the body, hormonal imbalance, or thyroid disease. Some scientists are convinced that wen occurs due to malfunctions of the gallbladder and liver, as well as due to slagging in the body.
Symptoms and classification
Lipomas are distinguished by anatomical location into lipomas of the head, face and neck, lipomas of the trunk, extremities, chest (mediastinum), mammary gland, gastrointestinal tract, internal organs, retroperitoneal tissue, spermatic cord. There are also rare localizations in the myocardium, lungs, and meninges.
Another classification of adipose tissue tumors involves a clinical division:
- Lipoma surrounding nerve structures is called perineural . Due to compression of the nerves it can cause severe pain. Removal of perineural lipomas differs from subcutaneous lipomas and requires a highly qualified surgeon;
- A tumor growing in the spinal canal (usually in the lumbar region) is called lumbosacral lipoma; Mostly occurs in children and is combined with underdevelopment of spinal structures;
- Lipoma of the joint and its structures (synovium, vagina, tendons);
- Intermuscular lipomas are formed from areas of adipose tissue between muscle fibers;
- Angiomyolipoma is a tumor of fatty and muscle tissue, which in most cases grows in the kidneys and pancreas. Middle-aged and mature men are more predisposed to its formation;
- Subcutaneous lipoma is a formation of varying sizes in the subcutaneous fat tissue. In everyday life it is usually called wen.
Lipomas usually occur alone. However, some patients discover several tumors at once. Such cases are most often associated with hereditary diseases and require careful study by specialists. The most common places for lipomas to form are the neck, back and limbs.
A subcutaneous lipoma is a mobile, elastic seal in the form of a lump or ball, which does not cause pain when pressed. A neoplasm can cause pain if it grows beyond its capsule into healthy tissue or due to compression of adjacent nerves.
For example, a wen located on the head can cause headaches, and the same formation on the neck can cause hoarseness and difficulty swallowing.
Gastrointestinal lipomas differ from their subcutaneous counterparts. Small formations in the intestine do not cause symptoms and are often discovered incidentally during an instrumental examination of the gastrointestinal tract. However, if it increases in size, this happens when the tumor reaches 2 or more centimeters in diameter, the lipoma can block part of the intestinal lumen and cause intestinal obstruction, intussusception, stool problems, abdominal pain and even bleeding.
Osteochondroma
Osteochondroma
- a benign formation over the bone in the form of a smooth protrusion of cartilage tissue up to 12 cm in size with bone marrow contents. Osteochondromas can be multiple or single.
The reasons for the appearance of such formations are not fully understood. The risk of developing osteochondromas is believed to increase:
- Intrauterine anomalies of skeletal formation;
- Hereditary factors;
- Irradiation.
Osteochondroma of the bone occurs:
- In the area of the joints, eventually spreading to the middle of the bone;
- Localization occurs on the ribs, femur, vertebrae, tibia, foot and scapula;
- Less commonly, the hands, heel bone and humerus are affected.
The bones of the skull are not affected. There is no pain or mobility. The tumor has clear boundaries. If the tumor is small, it does not bother you; pain may occur when the blood vessels are compressed.
How is the diagnosis done?
- After an external examination, the patient is sent for an x-ray, which will show the formation and its connection to the bone.
- MRI or CT is used if the situation is unclear.
- Morphological analysis may be performed.
Treatment
The only method used is surgery - removal of the formation with its base and stem. The removal process is necessary if:
- Education is increasing;
- Has large sizes;
- Accompanied by pain;
- Causes skeletal deformation.
In other cases, the patient is observed and monitored using x-rays.
Forecast
The disease has a favorable prognosis - its growth stops with the end of the formation of the skeleton. Degeneration into a malignant state ranges from 1 to 10% (more often with multiple formations).
Recovery after surgery is quick. Patients are prescribed physical therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment methods
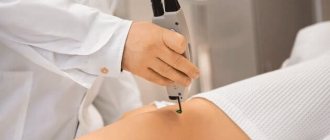
The treatment method is selected based on the location of the tumor, size and medical history of the patient. First of all, the doctor must make sure that the patient’s neoplasm is benign. To do this, the doctor carefully examines the patient, collects anamnesis and, if necessary, refers him to the necessary tests. For the differential diagnosis of lipomas, ultrasound examination of soft tissues, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging are used and, if a malignant tumor is suspected, a tumor biopsy is taken.
The most common type of tumor from adipose tissue is a subcutaneous lipoma, which does not cause dysfunction of organs, systems and does not threaten the patient’s life, and removal is performed only for cosmetic purposes.
Also, indications for surgical treatment of lipoma are large tumor sizes, 5 cm or more, and the presence of symptoms caused by the tumor.
There is no effective conservative treatment for lipomas. It is also worth noting that traditional methods such as heating and applying ice do not affect tumors from adipose tissue. However, they can cause serious complications if the neoplasm is of a different nature. For example, when atheroma is heated (atheroma is an accumulation of sebaceous secretion that clogs the duct of the sebaceous gland and causes inflammation), inflammation may spread and infect healthy tissues that are nearby.
Among the surgical methods for treating lipomas are:
- lipoma excision
- liposuction
- laser removal
- endoscopic method (for gastrointestinal lipomas)
Mesenchymoma
Mesenchymoma
– a malignant formation related to sarcoma. Angiosarcoma and liposarcoma can be found in its composition.
The exact causes of the occurrence have not been clarified. Perhaps this is the effect of carcinogens on the fetus. Risk factors are:
- Vibration, hypothermia and ionizing radiation;
- Chemical exposure – toxic substances, drugs;
- Bacterial and viral infections.
The location is predominantly the chest and abdominal cavity, mediastinum and retroperitoneal space. The formation is manifested by pain, cough, heartburn, shortness of breath and a feeling of fullness.
Diagnosis is carried out using radiography, ultrasound, MRI, biopsy and endoscopic examination. Treatment is carried out surgically. Auxiliary methods are radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Advantages and disadvantages of various methods
- Lipoma excision.
Excision of a lipoma is the simplest and most affordable way to remove a wen. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon injects the lipoma with an anesthetic and removes the tumor along with the capsule through an incision in the skin. Removal of the fibrous capsule is an undeniable advantage of this method. This prevents the re-formation of lipoma in the old place, which means it reduces the risk of relapse to a minimum. This method also allows one to examine the histological structure of the tumor. In general, the operation lasts no more than half an hour.
- Liposuction.
Liposuction allows the tumor to be removed through a small hole. A special device is inserted into the cavity of the wen, which destroys the lipoma. Many doctors and patients love this method for its minimal invasiveness and good cosmetic results. However, the disadvantage is the inability to remove the fibrous capsule of the wen, which creates the possibility of future relapse of the tumor.
- Laser removal.
Laser techniques are used to eliminate tumors larger than 3 cm. The method is gentle, carries minimal risks of bleeding and infection, and does not leave wounds or scars.
Preparation for the procedure
In case of subcutaneous lipoma removal, no special preparation is required. The mini-surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, meaning it does not require hospitalization. The surgeon performs all necessary manipulations under local anesthesia. Thus, the procedure is painless for the patient.
Giant subcutaneous lipomas, as well as neoplasms of the intestines, internal organs, and peritoneum require more serious and thorough preparation. Operations of this type are carried out with hospitalization of the patient. Before the intervention, samples are taken and, if necessary, additional studies are done. Operations performed under general anesthesia require restriction of water and food on the eve of the operation.
What pathologies have symptoms similar to lipoma in the heart
Rhabdomyosarcoma in children
— Fibroma: single, ventricular, calcified, has different contrast characteristics in CT and MR studies
— Rhabdomyoma: multiple formations
— Tubular sclerosis
Fatty infiltration of the interatrial septum
— Fatty infiltration more than 2 cm in transverse diameter
– Often overweight patients with atrial fibrillation
— Additional oval window