Lipomas are benign tumors with the usual name wen. They appear on any part of the body except the palms and feet. Wen are usually painless, but cause aesthetic discomfort. Surgery will fix the problem, but is it necessary? Before thinking about surgical intervention, you need to find out why lipomas formed, whether it is worth removing them and how effective the procedure is.
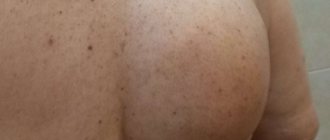
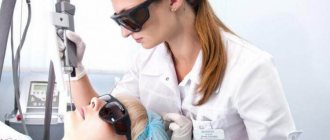
Rice. 1. Lipomas should be removed promptly
Why do lipomas occur?
To date, scientists have not been able to come to a consensus on why lipomas develop and why multiple lipomas are more common rather than single formations. Lipomatosis has nothing to do with the patient’s weight category or the amount of subcutaneous fat in his body, since formations can appear even in very slender people.
According to researchers, the appearance of wen is associated with a genetic predisposition. It can also be triggered by metabolic disorders in the body, hormonal imbalance, or thyroid disease. Some scientists are convinced that wen occurs due to malfunctions of the gallbladder and liver, as well as due to slagging in the body.
What to do if lipomas hurt?
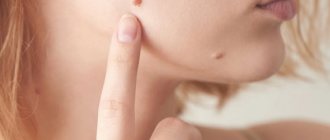
In its normal state, a lipoma has a spherical appearance (a round tumor with clear boundaries up to 5-7 cm in diameter). The lipoma is enclosed in a capsule. In most cases, it has a nodular structure, does not hurt, does not itch, does not bother palpation and practically does not grow. If the lipoma has become painful and is growing rapidly, then this may indicate not only inflammation, but also possible malignancy of the tumor. The catalyst for the inflammatory process in a lipoma can be injury and infection that has entered the body. Sometimes the cause of pain in a lipoma can be compression of nerves and blood vessels by the tumor. Pain in a lipoma is a signal for the patient to urgently seek advice and help from a doctor.
Rice. 2. If the lipoma hurts, it needs to be removed
When should lipomas be removed?
Most often, patients are interested in the question of whether lipomas should be removed immediately and whether it is possible to do without surgery.
It should be remembered that a lipoma is a benign formation that does not grow into the surrounding tissue. However, the problem is different: these formations tend to increase in size over time. At the same time, the lipoma “pushes apart” the tissues and organs located nearby in order to “win” a place for itself. Due to the pressure in them, metabolism can be disrupted, which is fraught with unpleasant consequences and pain.
In some cases, lipoma removal cannot be delayed. You should immediately consult a doctor if the wen has changed in appearance or you begin to feel physical discomfort. Redness of the skin over the lipoma, itching or peeling should also alert you.
Doctors recommend removing lipomas if they grow near a cluster of blood vessels or nerve cells. It is also better to “play it safe” and cut out a formation that is located in the so-called “high trauma zone” - in other words, in an area that is often exposed to external influences.
What does a lipoma look like?
The wen is located under the skin and is a semicircular convex growth. A person can detect it by touch or visually (for example, while bathing). Do not press, press or rub the affected area too hard. If a tumor is detected, immediately seek help from a surgeon.
Diagnosis of lipoma and its types
Before making a decision to remove a lipoma, a diagnosis of the neoplasm is carried out, which makes it possible to determine the optimal tactics of surgical intervention.
The doctor usually begins diagnosing a lipoma with a visual examination and palpation of the formation, which makes it possible to determine the shape, structure and approximate size of the formation. An ultrasound examination is also carried out, thanks to which it becomes clear what effect the lipoma has on surrounding tissues. If the formation is located in a potentially dangerous area, the doctor may prescribe a CT or MRI. A biopsy of the formation is also often performed to find out what tissue is part of it.
Lipomas are classified depending on where they are located and what tissues they contain. A serious problem is ring-shaped lipoma, which is a large subcutaneous tumor. It wraps around the neck like a collar, causing problems with breathing and swallowing. There are fibrous lipomas, which include connective tissue; angiolipomas containing adipose tissue and blood vessels; myolipomas, which contain muscle fibers; myelolipomas, consisting of adipose tissue and elements of red bone marrow; adenolipomas, including components of the sweat gland structure; very painful perineural lipomas. For each type of tumor, there are optimal removal tactics. Tumors can be removed by conventional surgery, using the endoscopic method, laser removal, or using the so-called “radio knife”. The final decision regarding how to remove the lipoma is made by the doctor, based on the general clinical picture of the disease, as well as the patient’s condition.
Clinical types of lipomas
- Perineural. Develops near nerve endings and is most painful and difficult to remove.
- Lumbosacral. It occurs predominantly in the spinal canal (usually underdeveloped), less often near the vertebrae.
- Intermuscular. They affect muscles by growing through them. After removal they often appear again.
- Myolipoma. It affects soft tissues and almost never develops under the skin, being located directly on it.
- Angiolipoma. It appears in the form of a dense subcutaneous node, typical for men.
- Adenolipoma. In many ways it is similar to atheroma, affecting not only fatty tissue, but also the sweat glands.
- Articular. It affects the synovium of the joint, as well as the vagina and tendons.
Surgical removal of lipoma
Surgical removal of lipoma is one of the most popular methods of getting rid of lipomas. If the formation is small in diameter, surgical excision is performed under local anesthesia; if the lipoma is large, then general anesthesia is recommended.
No preliminary preparation is required before surgical removal of a lipoma. The patient, as a rule, also does not need a preoperative course of medications. Surgery is performed after an ultrasound has been performed.
After administering anesthesia, the doctor makes a small incision into the lipoma - the so-called excision. After this, he cuts out the fatty tissue and the capsule that contains it. It is the removal of the capsule that ensures that the disease does not recur. After this, the tissues are sutured in layers. In this case, self-absorbable threads can be used. An antiseptic bandage is applied to the scar. If the formation was of significant diameter, thin drainages can be used.
Depending on the complexity of the operation, the location of the lipoma and its size, the length of hospital stay ranges from one to three days. In order to relieve discomfort, painkillers are used.
Sutures are removed approximately seven to ten days after surgery. After surgical excision of the lipoma, a scar remains. Special creams and ointments will help make it less noticeable, the use of which must be agreed with your doctor.
Features of pathogenesis
There is no consensus among specialists about the neoplasm. Some sources consider it to be hypertrophied fatty tissue, others - a true tumor. If the process occurs in a place where there is no fatty tissue, then it is associated with a change in the structure of connective cells.
One theory states that the accumulation of adipocytes in a certain zone is due to chromosomal gene abnormalities responsible for the production of TAG lipase. The enzyme is responsible for providing energy through the breakdown of fats.
Some experts are confident that the appearance of subcutaneous wen is explained by the active deposition of lipids in adipose tissue. The prerequisites for the formation of a lipoma appear during embryonic development, during its formation. In adult patients, wen can form anywhere. In rare cases, massive development of benign neoplasms is observed.
Contraindications for surgery
Surgical removal of a lipoma, like any other surgical intervention, has a wide range of contraindications.
- Thus, surgical removal of wen is not performed on women in an “interesting” position, or during breastfeeding. Doctors recommend refusing surgery during “critical days.”
- Herpes, recent colds or infectious diseases are also reasons to undergo surgery.
- It is highly undesirable to perform surgical removal of a wen if the patient has been diagnosed with diabetes.
- Surgical removal is also fraught with complications due to secondary immunodeficiency - in other words, reduced body resistance.
Is it possible to treat lipoma on your own?
This is not recommended to avoid injuries and various complications. It is also important to consider the following facts:
Lipoma does not go away on its own. If you do not pay due attention to the pathology, it can grow and change, which makes it more dangerous. Treatment of lipoma in the early stages brings the greatest effect.
Removing the lipoma is the only treatment option. Treatment of pathology with conservative methods, including the use of diets and/or physical activity, does not give the desired effect and is fraught with relapses.
In the case of lipoma, surgery is necessary. Do not try to replace it with a course of medications, especially without consulting your doctor.
Modern types of operations to eliminate lipomas do not injure the body and can be performed even on children. Pathology can be treated using laser and radio wave technologies. The technology used affects the cost of the operation. The choice of treatment method is made in consultation with a doctor.
Diagnosis of lipoma
Typically, an experienced professional will diagnose a lipoma during a physical examination. If the lipoma is large or painful, the doctor may prescribe a histological examination or ultrasound to rule out malignancy of the tumor.
Differential diagnosis of lipomas is carried out mainly with malignant tumors; in doubtful cases, cytological examination of punctate and angiography are used.
X-ray diagnosis of soft tissue lipomas is based on the use of long-wave (soft) X-ray radiation.
Other lipoma removal methods
In addition to surgical excision of the lipoma, there are other methods for removing the tumor. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Laser removal
Laser surgery is one of the most innovative methods for removing fatty tissue. Most often, this option is used to remove formations on the face and neck, since the procedure leaves virtually no scars. Moreover, since the fatty tissue is removed along with the capsule, the likelihood of relapse is reduced to almost zero.
During this operation, the laser simultaneously performs two functions: a scalpel and a coagulator, cutting tissue and at the same time preventing the development of bleeding. Therefore, laser removal is bloodless, due to which healing occurs quickly and swelling and suppuration do not develop. Since laser removal is a non-contact method, it is completely sterile. The duration of the laser removal operation is about thirty minutes, manipulations are carried out using local anesthesia.
Contraindications to laser removal of a wen are a history of cancer, diabetes, pregnancy and inflammatory processes.
Radio wave method
The radio wave method or the so-called “radio knife” is excellent for getting rid of lipomas of small diameter. Its essence is the impact on formation of intense electromagnetic radiation. High-frequency waves perform the duties of a scalpel, cutting tissue. Under the influence of the “radio knife”, heat begins to be generated in the cells, as a result of which they self-destruct. In this case, under the influence of radio waves, the wound is disinfected and coagulated.
The undeniable advantage of removing lipomas using a “radio knife” is that such an intervention is bloodless. In addition, thanks to the use of local anesthesia, the manipulation is painless. Radio wave removal of a tumor eliminates the possibility of complications: in particular, wound infection, swelling, and suppuration.
Postoperative rehabilitation requires minimal time - within a week or two the wound heals completely, leaving no scars. There is also no need for a hospital stay.
Puncture-aspiration method
The puncture-aspiration method of lipoma removal is also effective. During this procedure, a needle is inserted into the tumor, after which the entire contents of the tumor are drawn out with a special syringe-pump. However, this method has one significant drawback - since the capsule remains in the same place, a relapse may develop. Also, an even larger wen may appear if, after “sucking out” the tumor, at least a tiny fragment of the formation remains under the skin.
And since such liposuction is performed blindly, without visual control, it is impossible to guarantee complete removal of the tumor.
Endoscopic surgery
One of the innovative methods, characterized by low trauma and excellent cosmetic effect, is endoscopic removal of lipoma. In this case, the incision is made not on the tumor itself, but at some distance from it: as a rule, in the folds of the skin, in areas hidden from prying eyes. After this, an endoscope and instruments are inserted into the incision, with the help of which the wen is removed.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
The cause of lipoma formation is unknown. The risk of developing a tumor increases with a family history. Other risk factors include:
- morbid obesity (adirositas dolorosa) is a rare disease characterized by multiple lipomas);
- Cowden's syndrome;
- Gardner's syndrome;
- Madelung syndrome.
Atheromas are formed when the outflow of sebum is obstructed. Provoking factors are considered:
- compaction/thickening of the epidermis;
- hyperhidrosis – increased sweating;
- hormonal imbalances;
- use of antiperspirant deodorants;
- incorrect personal hygiene.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma
- a benign tumor that most often appears on the head and neck in girls. As a rule, vascular formation is detected in newborns.
The reasons for the formation are not clear. Presumably, this is a viral infection carried by a pregnant woman.
Symptoms of pathology
- Superficial formations are red or purple in color and have clear edges. When pressed, the formation turns pale.
- Cavernous hemangiomas are located under the skin in the form of blood-filled nodules.
- Combined hemangiomas are a combination of superficial and subcutaneous.
- Mixed formations consist of different tissues.
- Hemangiomas of the perineum and genital organs are prone to ulceration.
How is the diagnosis done?
- The problem is diagnosed by a surgeon using an external examination and laboratory data.
- Using ultrasound, the depth and location are determined, the speed of blood flow and the volume of the tumor are measured.
- For large tumors, angiography is used.
Hemangioma in adults is a rare phenomenon. Most often, localization occurs on the neck and face, less often - on the arm, on the finger, on the hand, in the anus, on the external genitalia. It does not degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
The disease is often treated by surgeons. Hemangioma should be treated immediately after detection:
- For deep-lying formations, surgical excision is used;
- For large areas, radiation therapy is used, acting in small fractions;
- Cauterization (diathermoelectrocoagulation) is used for point formations.
- For small complex formations, sclerosing treatment is used - alcohol injections.
- Treatment of combined hemangiomas requires the sequential use of cryogenic and injection therapy.
- Hormonal treatment is indicated for children.
- All simple small hemangiomas must be cauterized with liquid nitrogen.
- Over a large area, the use of hormonal and radiation exposure is indicated.
- For cavernous and combined lesions, surgical, cryogenic and sclerosing methods are effective.
- For formations in the parotid region, complex treatment using angiography and embolization is used.
The disease is often treated by surgeons.
If left untreated in young children, the formation may resolve over time. If the formation increases or complications arise, then it is not recommended to delay. Vascular tumors on the face should be removed early, as the risk of complications is too great.
How is a lipoma removed?
Wen is removed surgically, laser or radio wave. The most common procedure is surgical removal of the lipoma (a small micro-incision is made at the site of the wen formation, after which a scar may remain). The minimally invasive procedure takes place on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia and does not affect healthy tissue. The risk of blood loss and rehabilitation period are also reduced (after the procedure the patient can go home).
To speed up the healing of the lipoma removal site, you need to regularly change the bandage and prevent it from getting wet and dirty. During this period, the patient is not recommended to play sports, visit the bathhouse or solarium.