How chickenpox begins and develops Chickenpox is an acute infectious disease characterized by a profuse itchy rash on the skin and surface of the mucous membranes. It does not appear instantly: the incubation period can range from 10 days to 3 weeks.
Chickenpox is highly contagious. The virus is transmitted through direct contact with a carrier. Children often get sick in entire groups (groups in kindergarten or classes at school). We will tell you how to recognize the disease in the shortest possible time to prevent its spread.
What causes chickenpox?
The causative agent of this disease is human herpesvirus type 3. It belongs to the subfamily of alphaherpesviruses, which have the following features:
- a wide range of hosts (humans and animals);
- short reproductive cycle;
- rapid reproduction;
- volatility;
- rapid decay of affected cells;
- death under the influence of UV rays.
When the chickenpox virus enters the human body, for the first three to four days it is contained within blisters covering the skin. On the eighth day it ceases to be detected. Outside a living organism, type 3 herpesvirus dies in 15 minutes.
The rash usually appears 48 hours after infection. The carrier remains infectious for another five days. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Contact-household infection is also possible.
How to recognize chickenpox?
To get sick, two conditions are enough: to be near someone with chickenpox and not have a history of it. Everyone gets infected with it, regardless of age and immunity strength. Nothing can be done during the incubation period. All we have to do is wait for the first signs:
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees;
- general malaise;
- decreased appetite;
- the appearance of a characteristic rash.
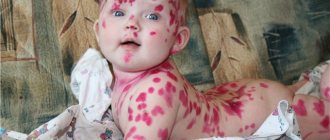
At first, the rash is rare and looks like spots or pimples. Under no circumstances should you squeeze them out: the scar will be very deep. The volume of the rash gradually increases, covering all parts of the body.
In the early stages, chickenpox can be mistaken for an allergic reaction. But contact dermatitis rarely spreads throughout the body and never develops into blisters.
In this case, the person feels severe itching. Scratching chickenpox is also not advisable. This will not bring relief, but there is a risk of getting a lot of scars on the skin or causing a secondary infection.
How long can you go for a walk?
the 5th day has passed from the last wave of blistering.
The period of elevated temperature ranges from 2 to 8 days; usually the baby himself does not show any desire to leave the house.
It would be wise not to go outside in unfavorable weather conditions: hypothermia is unacceptable these days.
It is important to know. A fashion for “chickenpox parties” has appeared in Russia. Parents take their children to visit their sick child so that they become infected at an early age and receive lifelong immunity. “Advanced” parents even offer others lollipops licked by a sick child. Doctors warn: there is a risk of overestimating the strength of the body's defenses and becoming seriously ill. It is better to get a vaccination, which most children tolerate easily. The famous doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky also expresses his opinion on the desirability of vaccinations.
Periods of chickenpox
Quite a long time passes between infection with the herpes virus and complete recovery. There are four periods:
- incubation (up to three weeks);
- prodromal (up to two days before the appearance of rashes);
- rashes (several waves for two to five days);
- crust formation.
During the prodromal period, the patient experiences general malaise. It is expressed in weakness, nausea, headache. Sometimes the temperature rises to 38-39 degrees, and vomiting occurs. In some patients, there is no prodromal period, and rashes immediately appear some time after infection.
Chickenpox in adults causes severe complications. They do not appear immediately. Some appear after the tenth day of the disease, others after a month.
How does chickenpox occur in children?
Chickenpox is considered a childhood disease, since it mainly affects children of preschool and primary school age. In children, the illness period is relatively short (about 10 days), while in adults it can last three weeks or more.
During this time, the rash goes through several stages:
- erythematous spots;
- nodular rash (papule);
- ulcers (pustules);
- crusts.
Recovery occurs when all the scabs fall off. Until this point, the person is still contagious and can pass the chickenpox virus to others. The first wave of rashes usually passes quickly, but it is replaced by several more.
As a rule, there are no complications in children. The main thing is that the baby does not scratch the rash to avoid secondary infection and scar formation. Severe disease occurs in newborns. When the first signs of chickenpox appear in an infant, you should immediately call a doctor.
Chickenpox: when can you walk and wash?
- Doctors' opinions on bathing with chickenpox vary significantly. In European countries, doctors are convinced that a child should not be prohibited from swimming. Clean water will wash away bacteria from his body that cause new rashes.
- Domestic doctors are of the opinion that it is better to refrain from swimming. They believe that taking a bath will only prolong the treatment time. If the child suffers from severe itching, you can wipe his body a little with a damp towel dipped in a weak manganese solution.
It is better to postpone a long bath after overcoming the illness.
As you can see, a child with chickenpox is allowed to walk in the fresh air. But, several rules must be followed. First, wait until your symptoms subside. Secondly, give preference to places where there are no heavy crowds of people. Remember that it is important to coordinate all actions with your doctor in order to maintain the child’s health. Be healthy.
Articles about children on the site:
- A child is angry: what to do, how to react
- Top 9 sports for children's development
- A child is bullied at school - what to do about it?
- Finger gymnastics, finger games for children 2-3, 4-5, 6-7 years old
- Fire prevention signs and reminders for children
Atypical forms of chickenpox in adults
In adults, chickenpox is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication of the body. Atypical clinical forms are also possible:
- Rudimentary. The rash is either absent or does not develop beyond the blotchy stage.
- Hemorrhagic. A bloody impurity appears in the blisters, and small hemorrhages appear on unaffected areas of the skin. Black crusts form.
- Bullous. Along with the usual chickenpox, other blisters appear. They are filled with a cloudy yellowish liquid and take a long time to dry. If such blisters burst prematurely, the area of skin underneath them becomes wet for a long time and does not heal.
- Gangrenous. The tissues inside the blisters die, and ulcers form underneath them. Cleaning of pus is often required.
The generalized form of chickenpox is considered separately. It is characterized by damage to internal organs. It is difficult to tolerate and there are deaths. At risk are patients taking steroid hormones.
Treatment
Treatment of chickenpox in its standard course occurs at home after consulting a doctor. It is aimed at improving the general well-being of the patient: drugs whose active ingredient is paracetamol are used to reduce elevated body temperature.
In the vast majority of cases, patients suffer from unbearable itching of the skin. To alleviate the condition, special ointments and solutions are prescribed based on zinc and potassium permanganate, with the addition of tea tree oil. Antihistamines may be recommended. Often, a specialist will prescribe ointments whose action is aimed at destroying the viral pathogen.
In more serious cases (especially if there is concomitant shingles), the doctor will prescribe analgesics. In case of extremely reduced immunity, the patient is given immunoglobulins, and in case of intense intoxication of the body, detoxification solutions are administered.
How to help with chickenpox?
There is currently no cure for chickenpox. Usually the disease goes away on its own, and therapy is limited to smearing the rash with aniline dyes with bactericidal properties. A solution of brilliant green (“zelenka”) is usually used. You can take an antipyretic to relieve your general condition.
To relieve itching use:
- solution of iodine tincture (2-3%);
- solution of potassium permanganate (1:5000);
- hydrogen peroxide (3%);
- glycerol.
In some cases, antihistamines can help relieve itching. But you should not take them uncontrollably: it is better to call a doctor at home and determine acceptable medications. Showering is allowed, but without a washcloth to avoid damaging the bubbles. The same applies to the use of towels - after water procedures, you need to carefully pat your body dry with a cloth.
The benefits of being outside
It is quite difficult for a baby to stay at home for 2-3 weeks; confinement at home quickly becomes unbearable. If the room is hot, the itching of the skin becomes unbearable. Ventilation gives relief only when the window is open. Fresh air will reduce symptoms of the disease and improve the mood of mother and child.
If the general condition of the small patient does not cause concern, walks in the fresh air can begin in the absence of fever. Usually the child returns to normal on the tenth day from the onset of the disease. However, he remains a carrier of the virus and is dangerous to others.
It is important to know. A mask worn on a child to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to other people is useless for chickenpox: tiny particles of saliva easily penetrate through it.
Complications of chickenpox
In most cases, this disease is not dangerous; children tolerate it easily. The only threat is infection of the wound when combing with dirty hands. In such cases, staphylococci or streptococci may be ingested and a purulent infection may develop.
The chickenpox virus does not disappear from the body after recovery. Temporarily neutralized, it is localized in the spinal cord. As years pass, it can become more active and cause shingles.
In adults, complications may include:
- stomatitis (if a rash appears in the mouth);
- conjunctivitis (on the eyelids);
- inflammation of the middle ear.
The greatest danger is chickenpox pneumonia with a mortality rate of 40%. The consequences of infection with the chickenpox virus can manifest themselves in the form of neurological disorders, heart disease, and joint damage. A month after recovery, there is a risk of developing retinal inflammation and cranial nerve palsy.
Symptoms of the disease
The appearance of the first symptoms of chickenpox occurs after the incubation period. On average, it lasts from 7 to 21 days after the pathogen enters the human body.
In most cases, the initial manifestation of the disease is a high fever, which persists for 3-7 days and can be accompanied by body aches, headache, insomnia, restless sleep, and loss of appetite.
This is followed by the main symptom of chickenpox - a rash that appears on the torso and head (up to the scalp) and spreads to the limbs. Rashes can be found in the most unexpected areas, for example, in the vaginal area, on the mucous membrane of the mouth and the cornea of the eyes.
The diameter of one such formation is 1-4 mm. At first they look like bubbles surrounded by reddened tissue, inside which clear liquid accumulates. Then the bubbles become drier and form crusts instead.
At this stage, most people with chickenpox suffer from unbearable itching. However, scratching the papules is strictly prohibited: otherwise, they will leave marks in the form of scars.
In some cases, patients may experience enlarged lymph nodes, either selectively or all at once, among the symptoms of chickenpox.
Are you experiencing symptoms of chickenpox?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
What is chickenpox pneumonia?
This is a lung lesion that occurs in 16% of cases of chickenpox and in almost all cases if the disease occurs in a generalized form. The first symptoms may appear simultaneously with the rash:
- dyspnea;
- chest pain;
- cough with sputum (often with blood);
- bluishness of the skin.
Multiple focal nodules spread in the lungs, which on x-ray look like tuberculosis. Antibiotics do not help in this case. Against the background of chickenpox pneumonia, bronchitis often develops; in severe cases, pulmonary edema is possible.
Pneumonia that develops in the later stages of chickenpox is considered separately. It is caused by a secondary coccal infection and is a common pneumonia. The disease is treated according to the standard regimen - penicillin.
Neurological complications of chickenpox
The consequence of infection with a herpes virus in an adult can be secondary encephalitis. Inflammation develops from the fifth to tenth day of the rash, sometimes even after recovery. The pathological process can be localized in different places:
- membranes of the brain (meningitis form);
- cerebellum (atactic form);
- spinal cord (myelitic form).
- Combined damage to the brain and spinal cord (encephalomyelitis, meningoencephalitis) is also possible.
In mild cases, damage to the central nervous system by the chickenpox virus leads to loss of coordination, involuntary eye movements, hand tremors, and dizziness. In more severe cases, vision suffers (up to its complete loss). The most dangerous complication is paralysis. Mental damage, even mental retardation, is also possible.