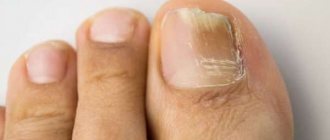
The mechanism of formation of emptiness under the nails on the toes and fingers.
Causes of onycholysis on the legs:
- Long toenails.
Often, when covering their toenails with gel polish, girls forget to file the length every 2-3 weeks. Due to the excessive length, there is a load on the nail plate from above and from the end.
- The shoes are the wrong size.
Shoes that are the same length as your foot or shorter put pressure on your big toe. The foot lengthens by 1 cm while walking, which is almost imperceptible to a person. But regular load from such shoes will lead to emptiness under the nail.
- The risk of nail separation from the nail bed increases in dress shoe wearers with a narrow forefoot.
When wearing such shoes, the big toe is severely compressed, the blood circulation of the matrix is disrupted and a void appears under the nail.
Symptoms of onychocryptosis
With onychocryptosis, the lateral part of the nail abuts the periungual fold and continues to grow inside it. At first, the patient feels general discomfort, redness of the skin around the nail is observed. It is also possible to change the shape of the nail. Preferences in shoes are gradually changing, the choice is given to open options, wearing tight, narrow, and over time, any closed shoes becomes difficult. In case of inaction, the symptoms of the disease become more pronounced, complications appear, and over time, surgical intervention becomes inevitable.
The main symptoms of an ingrown toenail include:
Painful sensations in the toe area resulting from injury, after wearing shoes, or for no apparent reason
· swelling and hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels of the circulatory system of any area of the body) of the periungual fold
formation of pus in the area of the nail plate
formation of excess connective tissue protruding from the wound, visually reminiscent of raw meat
In medicine, the development of onychocryptosis is characterized by three main stages - mild, moderate and severe.
Stages of onychocryptosis
First (mild) stage
characterized by redness of the periungual fold and moderate swelling. At this stage, the nail plate has no visual changes, and painful symptoms usually appear while walking in shoes.
Second (moderate) stage
accompanied by signs of inflammatory processes: the periungual fold becomes red, purulent discharge appears, and in some cases painful pulsation is observed. The nail becomes denser and dull.
Third (severe) stage
caused by hyperemia (increased blood supply) of the periungual ridges, the formation of hypergranulation (tissue growth in areas of inflammation), an increase in the volume of the phalanx, and the presence of purulent discharge. The nail becomes brittle and mobile, the skin around it visually resembles raw meat (this symptom is called “wild meat” in medicine).
Complications of onychocryptosis
Prolongation of the disease leads to the development of infections, which certainly aggravates the situation. Wounds that are open for a long time and do not heal are an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. An infected wound heals slowly as the body tries to heal the affected area, resulting in bright red granulation tissue forming at the site of the ingrown nail. If you do not start treatment or start the wrong treatment, the granulation becomes dense, the phalanx changes shape, and it becomes impossible to solve the problem with conservative methods. In addition, inflammation of the soft tissues of not only the fingers, but also the entire foot is likely to develop, which, if left untreated, can spread to the bones and lead to osteomyelitis.
Complications of onychocryptosis are associated mainly with the development of infectious and inflammatory processes and include:
· abscess
(limited inflammatory purulent focus causing intoxication) fingers. It is characterized by the presence of pronounced swelling and redness of the skin. Surgery required.
· lymphangitis
(acute or chronic inflammation of the lymphatic trunks and capillaries, occurring secondarily against the background of purulent-inflammatory processes). It is characterized by the spread of infection throughout the lymphatic system, affecting blood vessels. Complex treatment is required, including anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy.
· gangrene
(death of living tissue) of the finger. Characterized by processes leading to irreversible necrosis of soft tissues. Amputation of the affected phalanx or the entire finger is required.
· osteomyelitis
(purulent - inflammatory process that develops in the bones, bone marrow and surrounding soft tissues) of the finger. The infection affects the bones. Drug therapy is required. Amputation of the phalanx of the finger is possible if the patient comes too late.
The risk of complications increases in the presence of concomitant diseases associated with disruption of blood vessels, for example, diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The risk group also includes people who are overweight and over the age of 60.
Why does a cavity form under the fingernail:
- nail injury;
- chemical burns resulting from the use of low-quality gel polishes or from contact with household chemicals and other aggressive substances;
- thinning of nails as a result of self-removal of artificial coating or sawing of the nail plate with a file (cutter) by a master;
- onychophagia, or a mental disorder in which a person bites or picks at the nail beds and the skin around them. As a result, the nail peels off from the nail bed;
- attempts to move the hyponychium or clean out dirt under the nails with something sharp;
- dermatological pathologies.
If you notice the first symptoms of onycholysis, contact the PODOLAB Podology Center in St. Petersburg. Podologists will advise you on this problem. And you will quickly restore the attractive appearance of your nails.
Diagnosis of the disease
First of all, a visual examination and history taking are necessary. It is important to identify the presence of concomitant diseases - to exclude or confirm fungal infections and diseases that are associated with disruption of blood vessels (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis).
Diagnosis of onychocryptosis includes
:
· collecting anamnesis (full collection of data about the patient and his diseases): identifying the causes of the disease, collecting complaints
· visual examination of the patient (diagnosing the stage of the disease and identifying complications): the condition of the nails, periungual ridges, skin of the fingers and feet; the presence of deformation of the fingers, swelling, purulent inflammation, granulation; comparison of two limbs
· general blood test (if complications are detected): carried out to identify or exclude a general inflammatory process. A blood glucose test is also performed to confirm or rule out diabetes.
· bacteriological examination of discharge from wounds (analysis of purulent discharge): the study is carried out to determine the type of pathogen and the severity of the inflammatory process
· X-ray examination (study of the internal structure of the foot): carried out to study the anatomical changes in the structure of the foot and to identify or exclude the transition of inflammatory processes to the bones
How to treat onycholysis?
The sooner you contact a podologist or dermatologist to identify the cause of nail detachment, the higher the chances of successfully eliminating the problem.
During the restoration of fingernails or toenails, there is a strict ban on any traumatic procedures, nail extensions, the use of decorative varnishes and aggressive chemical liquids.
If fungal spores have entered the cavity under the nail and onycholysis is infectious in nature, then treatment for onychomycosis is prescribed by a dermatologist.
If the nail plate on your ring finger periodically comes off, then there is a possibility that you need to seek treatment from an endocrinologist and adjust your hormonal levels.
Ingrown toenail and its treatment
“Beautiful from the tips of your hair to the tips of your nails!” This slightly modified Latin phrase expresses admiration for external beauty. Well-groomed lady. Generally a neat person. Staying like this from head to toe is an art. If you are a girl or woman who cares about her appearance, you have probably heard something similar addressed to you at least once. If you are a young man or a man who treats himself with purely masculine disdain, know that a neat manicure has never taken away anyone’s courage. Clean, properly cut and filed nails are not just visually pleasing. This, if you like, is one of the small bricks that make up the foundation of your health. Ingrowth of the nail plate into the body is a problem as old as time. It belongs to the category of those seemingly “little things” that can subsequently cause serious complications if you do not seek help.
Causes of ingrown toenails
- shoes that are too tight or narrow;
- traumatic injuries;
- mycotic (fungal) lesions of the skin;
- improper care of nails (sharp edges of the nail must be cut off and filed, repeating the rounded shape of the finger. But on the feet, unlike hands, the edges are not cut off clean, this is important!);
- weight gain, especially accompanied by stress on the legs (during pregnancy, when athletes build muscle mass);
- physiological characteristics and heredity.
In addition, there is a group of people who are more at risk of developing an ingrown toenail:
- people with circulatory problems
- people with diabetes
- people with flat feet
People suffering from diabetes and its complications should be especially attentive to their limbs. Due to decreased sensitivity, the likelihood of getting wounds, cuts, abrasions, and abrasions increases. And the slightest wounds with this by no means sweet illness tend to heal poorly. In order to prevent infection of injured areas, and, God forbid, the development of gangrene, a diabetic must be extremely attentive to himself.
If you find it difficult to trim your nails yourself, especially on your toes, do not hesitate to ask your family or a diabetic foot office for help. A podiatrist works there. It will not only help to get your nails in order, but will also determine the course of the underlying disease based on the condition of the foot. There is nothing humiliating in such requests and visits. And under no circumstances consider yourself a flawed person! There are the same people in the clinic, and they also have their own problems. Helping patients with diabetes is their responsibility.
The process of ingrown nails
There are several causes of ingrown toenails (onychocryptosis), but the main one is improper nail cutting. The nail begins to grow in width and thus grows into the finger. Ingrown nails mainly affect the toenails.
When a growing nail cuts into the delicate nail fold, a person begins to experience pain and discomfort. We often don’t pay attention to such trifles: you never know what will hurt you! But the nail is a living matter, although it does not have nerve endings. Metabolic processes constantly occur in it, causing renewal and growth. An embedded nail grows in the same way as a healthy one. And the more it grows, the more obvious the pain becomes. This local injury is also accompanied by inflammation, redness and swelling of the finger.
If the nail is ingrown on your hand, any, even the most insignificant, work will be accompanied by inconvenience. If you are on your feet, then even the calmest walking will become a test for a person. To withstand it, you have to limp. The presence of a permanent non-healing wound that often bleeds increases the risk of infection. It is accompanied by suppuration and necrosis (death) of adjacent tissues. The nail becomes deformed, thick, loose and brittle. There is nothing to think about open shoes. Any shoes will disturb the inflamed area, causing severe pain. Subsequently, it will have a sharp, pulsating character. There is only one way out: going to an appointment with a cosmetologist.
Traditional surgery
Not so long ago, it was impossible to eliminate the problem of ingrown toenails except through surgical intervention.
The procedure involved completely tearing off the nail plate under local anesthesia. A sterile bandage was applied to the open wound. The patient did not part with it for the next few months, observing all the necessary postoperative hygiene measures.
But the birth of a new nail takes a good six months. And the empty nail bed does not stand still. Lacking a hard cover, it becomes weaned from it and shrinks in size. The new nail grows reluctantly, because the old one is “pulled out by the roots” (the operation damages the growth zone). As a result, what grows has a deformed and thickened shape, an uneven surface and a porous structure. It becomes more difficult to care for such a nail than others. Some clinics still perform this operation to this day. In parallel with it, there is a modern, lightweight version of surgical intervention. When used, the nail remains in place. Only the ingrown edge of the nail and its growth zone are excised. And also everything that is damaged is removed: a diseased nail fold, dead tissue.
An experienced surgeon will perform this operation in the best possible way. But it, like the conservative option, is accompanied by heavy bleeding. This interferes with good visibility, and the doctor may not completely remove the growth zone. Suturing the wound, which completes the operation, forms a scar. The operated finger will have some external defect. He may also make himself known again. What to do to minimize the likelihood of relapse?
Nowadays, lasers are increasingly coming to the rescue.
Laser surgery
It is bloodless, as gentle and reliable as possible. The scope of medical applications of lasers is quite wide. It also includes treatment for ingrown toenails.
The treatment is outpatient (the patient comes to a cosmetic surgeon for a session and returns home after it). Local anesthesia. Moreover, its dose is significantly less than for surgical intervention.
Just like surgery, laser correction does not last long: 15-30 minutes. Since a laser is used on the patient instead of the usual surgical instruments, there is no bleeding or pain.
The big advantage of laser treatment for ingrown toenails is that the nail plate remains on the finger. Only its ingrown edge is removed. The growth zone is immediately cauterized.
The laser works successfully even in such difficult situations as acute inflammation and severe suppuration. Infected areas are sanitized (cleaned) with a laser. Diseased tissue simply evaporates. Healthy ones remain undamaged. This stops the inflammatory process.
The result lives up to expectations: the nail is preserved and the problem is gone. After laser treatment there are no relapses at all. Recovery (rehabilitation) occurs very quickly: within 5-7 days.
The types of lasers used in laser surgery are determined depending on the laser materials (active media). The most commonly used is carbon dioxide laser (CO2 laser), which can be read about in the article “Carbon dioxide laser as the most common laser in cosmetology.” It produces infrared radiation. This is one of the most powerful lasers operating in continuous flow mode. It literally heats living tissue. Under its influence, it is evaporated or excised. There is no burn in this case.
However, laser treatment also has some disadvantages:
- nail growth may be impaired
- because of this, fungus (mycosis) may occur
- there is a possibility of late complications (5-7 years after treatment)
Together with your doctor, you will choose the most suitable treatment option for yourself. And, most likely, it will be laser correction. Because, although there is a possibility of late complications with it, in any case, relapses are excluded.
As we know, there are no absolutely healthy people. And yet, we can avoid many health problems. Even very serious ones. If you still haven’t escaped, don’t despair. Fight for your health. Fight illnesses - and your own unbelief. Stay healthy and charming to the very tips of your nails!
Ingrown toenail – cost of treatment
| Difficulty categories | Price |
| Ingrown nail (unilateral removal) category 1 | 4,650 rub. |
| Ingrown nail (unilateral removal) category 2 | 6,550 rub. |
| Ingrown nail (unilateral removal) category 3 | 7,250 rub. |
| Ingrown toenail (bilateral removal) | 8000-10000 rub. |
The nail has turned black
03. How long does it take to completely cure nail fungus? Is there a way to speed it up somehow?
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis, is an infectious disease of the nail plates of fungal etiology, caused by dermatomycetes, yeast or mold fungi, which affects any component of the nail complex, including the growth zone, bed or the plate itself. In all countries of the world, this is one of the most common diseases of the skin and its appendages. The disease can be accompanied by discomfort, changes in the appearance of the nails, which in some cases leads to serious physical and professional limitations, aesthetic anxiety for patients, and also reduces their quality of life. Diseases such as flat feet, varicose veins of the lower extremities, and hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating of the feet) increase the likelihood of developing onychomycosis. Excessive dryness of the skin, which develops as a result of endocrine disorders (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus) or as a natural condition in old age, also creates a favorable environment for the development of the disease.
Diagnosis of onychomycosis:
— clinical picture, anamnestic data (changes in nail plates)
– microscopic examination (examination of a wet preparation in potassium hydroxide)
— cultural examination (culture with identification of the pathogen).
Treatment of onychomycosis is possible at any time the disease manifests itself, but the most rapid and effective treatment is with minimal damage and modification of the nail plate. The main method of treating onychomycosis is the complex prescription of drugs, both systemic (in the form of tablets by mouth) and external agents (solutions, drops). Patient management tactics depend on the area of the lesion and the duration of modification of the nail plates. Treatment rates can be improved by the additional use of laser treatment of nail plates, which contributes not only to the antifungal effect, but also to improved trophism of the nails with their speedy recovery. Topical (local) application of antifungal varnishes containing ciclopirox 8% or amorolfine 5% can also help to quickly get rid of a fungal infection, as an additional remedy to oral medications, especially for resistant infections.
Descriptions of diseases
Simultaneous diseases of the fingernails and toenails are quite rare; usually the nails of the upper extremities are affected.
Hippocrates nails
The extreme phalanges of the fingers thicken, the nails become convex and round. Hippocrates was the first to describe this phenomenon affecting the hands, which is why it got its name. It is not an independent disease, but may appear as a symptom when:
- emphysema;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- long-term endogenous intoxication;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- cancer, especially in the lungs.
Sometimes Hippocratic nails can be a hereditary or congenital pathology. In cancer, it develops rapidly over months or weeks; in other cases, the process of change can last for years.
Scleronychia
Hypertrophic changes occur in both the arms and legs. Nails harden, become transparent, taking on a yellowish-gray tint, and over time may separate from the nail bed. This is considered a manifestation of endocrine diseases, although the main causes of scleronychia are still not known.
Onychogryphosis
Another name is “bird's claw”. It can develop as a result of frostbite or severe bruising.
The nail becomes dense and uneven, taking on an unnatural color from gray-yellow and brown to almost black. In addition, its free edge is bent, like a bird's, or twisted into a spiral.
Treatment consists of softening the surface of the nail with a salicylic patch or ointment; in advanced cases, it can be scraped off or surgically removed.
Onyhauxis
Overgrowth of the subungual cornea, which is accompanied by darkening of the nail and inflammation of the nail fold. It affects 1-2 fingers; in rare advanced cases, it can be observed on all fingers and toes. Usually manifests itself as a consequence of insufficient nutrition of the nail in diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- varicose veins;
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels of the lower extremities;
- elephant disease.
It can also be caused by injury or poor-quality manicure; sometimes onychauxis warns of a lack of certain vitamins and minerals in the body. For correction, medications that thin and activate blood circulation are prescribed; in case of vitamin deficiency, the menu is enriched with essential nutrients and multivitamins.
Onychomadesis
Sometimes accompanies fungal or bacterial diseases of the fingernails and toenails, often resulting from mechanical damage or regular nail biting (onychophagia). The nail bed becomes inflamed, the nail matrix itself darkens and after a short time comes off the finger completely. This happens both from the free edge and from the internal one, depending on the cause of the disease.
Treatment is aimed at improving blood circulation in the sore finger through massage, vitamins and medications. If onychomadesis is of infectious origin, the disease that caused it is treated accordingly. In addition, they try to protect the exposed nail bed from fungi and bacteria, otherwise the affected nail will never grow back.
Transverse furrows of Beau (lines of Beau-Reil)
They appear due to inhibition of the growth zone of the nail due to metabolic disorders, injury or unsuccessful manicure, and quite often appear in children as a reaction to a viral infection. Depending on the course of the disease, there may be one or several, which makes the nail look wavy (see photo above).
Bo's line looks like an arc extending across the entire surface of the nail from one side roller to the other. Its depth can reach 1 mm and directly depends on the severity of the disease. In difficult cases, the groove can tighten the nail so much that its free edge ceases to receive enough nutrition, gradually atrophies and comes off the finger.
After eliminating the factor that provoked the appearance of Bo's line, the defects on the nails go away on their own over time.
Longitudinal furrows
They are also called vertical. Possible reasons for their appearance:
- age-related changes;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- psoriasis;
- spinal cord damage;
- gout;
- defects in the functioning of the intestines or pancreas;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- lichen planus;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- damage to the root of the nail plate;
- lack of iron and vitamin B12.
After eliminating the cause, the nails themselves return to their original appearance. During treatment or with age-related changes, to improve the appearance, longitudinal furrows can be hidden under a layer of special varnish.
Leukonychia
White spots appear on the nails. Their shape, quantity and location vary with different dysfunctions of the body. The appearance of spots on the nails indicates the presence of the following problems:
- protein deficiency;
- deficiency of vitamins (especially C, E, A) and microelements (calcium, zinc, iron);
- fungus;
- disorders of metabolic processes in the body;
- heavy load on the nervous system: stress, depression, anxiety;
- bowel problems;
- frequent contact with household chemicals, low-quality varnishes;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- kidney disease;
- skin diseases.
If there is no suspicion of disease, then this defect can be corrected independently. It will be enough to establish a rest and work schedule, supplement the diet with foods with essential nutrients, and wear gloves when coming into contact with household chemicals.
Onychodystrophy
Changes occur in the periungual fold, nail plate and bed. The nail becomes less transparent, its thickness changes, and growth slows down. It is also possible that longitudinal furrows may appear and the color may change to greyish-yellow. The causes of this fingernail disease may be:
- mycoses;
- injuries;
- skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, lichen planus);
- avitaminosis;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine system;
- problems with the heart and lungs;
- interaction with alkalis, acids, chemicals with unprotected hands.
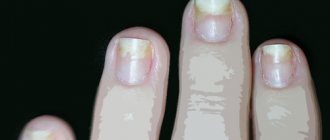
Onycholysis
Refers to onychodystrophy. With onycholysis, a change in the color of the nail plate from yellow to brown is observed. The nail becomes brittle and moves away partially or completely from its bed. Possible reasons:
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- skin diseases;
- taking antibiotics;
- dysbacteriosis;
- injuries;
- contact with allergens;
- some chronic diseases.
Ingrown nail
This type of toenail disease occurs because the main causes are too tight shoes and improper trimming. The nail grows into the side cushion, which causes swelling of the finger, pain when walking, and inflammation of the soft tissues.
In mild cases, you can get by with foot baths and softening compresses; in advanced cases, only a surgeon can correct an ingrown toenail.
Onychorrhexis
Brittleness and fragility of nails, which leads to their separation. Usually accompanies diseases and conditions that cause impaired microcirculation in the fingers. A harsh diet and frequent contact with an alkaline environment may also be the cause. Onychorrhexis is extremely rare on the legs.
Anonychia
Lack of nail plate. It can be either congenital or acquired after injury, diseases of the nervous system of an organic nature, or some dermatoses.
Koilonychia
The nail becomes thinner and becomes concave like a spoon. Possible reasons:
- heredity;
- anemia;
- constant destructive effect of acetone or household chemicals;
- some infections;
- incorrectly done manicure.
Micronychia
Pathologically small, shortened nails. It may be congenital or develop as a result of nail biting. Micronychia also sometimes manifests itself as a symptom in diseases such as:
- progressive scleroderma;
- Trenaunay syndrome;
- flat angioma;
- Genuine epilepsy;
- malnutrition of the hand.
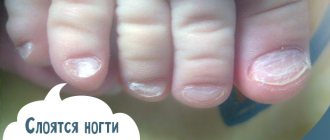
Onychoschisis
Transverse separation of the nail plate. It often occurs due to the aggressive influence of substances in household chemicals and decorative nail products. It often occurs in representatives of professions with increased mechanical stress on the fingers: musicians, printers. Onychoschisis also appears with vitamin deficiency.
Onychomycosis
Fungal nail diseases can most often be found on the feet and there are quite a lot of their varieties, so for more effective treatment it is better to consult a dermatologist.
You can get the fungus anywhere, but it requires a warm, moist, dark environment to thrive, which is why it mainly affects the feet. The disease takes a long time to develop, the first symptoms may appear only after several months.
First, itching is felt in the infected area, the skin begins to dry and peel. Next, the nail itself is affected, its color changes, cracks appear on the surface and a putrid odor appears. If left untreated, over time the mycosis will spread throughout the body and cause various kinds of complications.
Gapalonychia
The nail plates become soft, break and split. It occurs due to diseases of the endocrine system, metabolic disorders in the body, and regular exposure to aggressive chemicals.
Platonychia
The surface of the nail is completely flat (see photo). It can be congenital or acquired as a result of professional activity. Also, some chronic inflammatory processes can provoke this defect.
Causes of unhealthy nails
Normally, the nail should be smooth, non-compacted and pink in color. If it changes color, shape, becomes brittle and fragile, the nail plate partially or completely moves away from the phalanx of the finger, this may indicate the presence of the following problems:
- improper care of fingernails and toenails;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- the presence of infectious or parasitic diseases in the body;
- injuries;
- regular destructive effects of harmful substances;
- a congenital anomaly that can only manifest itself over time;
- diseases of organ systems - cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine;
- development of a low-quality tumor.
In addition, nails are also subject to age-related changes. As they age, they may turn yellow and become hard or brittle.
Prevention
The following list of simple rules will help you prevent many possible diseases of the toenails and fingernails.
- You can't bite your nails.
- File your nails with a glass or cardboard file.
- Manicure should be done on steamed hands, this reduces the risk of microtrauma and, as a result, infection of the wound.
- If you use the services of a salon to care for your nails, make sure that the technician disinfects the tools before use.
- Dry your hands and feet.
- Your diet should include enough foods containing vitamins and minerals.
And most importantly, do not be lazy to contact doctors and undergo additional examinations by specialists. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of defeating it.