SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
Intimate discharge (“leucorrhoea”) and itching are the most common reasons why women turn to a gynecologist for examination and treatment. Why is vaginal discharge normal and does not cause concern to doctors, and what symptoms indicate trouble in this area?
Before you begin to treat vaginal discharge, you need to find out what caused it and provoked its appearance. A gynecologist deals with similar complaints in adult women; if there are problems in young girls and adolescent girls - a pediatric gynecologist. Self-medication at home using advice gleaned from reviews on the Internet or from “unfortunate” friends is fraught with unpleasant health consequences!
The causative agent of the disease and risk groups
The content of the article
Fungal infections of the vagina in women most often include fungal infections and ringworm of the vulva. The most common pathogen that causes this disease is a fungus called Candida albicans. Therefore, fungal infections are defined as candidiasis. Vaginal mycoses can also be caused by other species of the genus Candida.
The occurrence of dermatophytes in the vagina is a rare case, most likely the result of external contamination.
Vaginal candidiasis
About 70% of women suffer from vaginal and vulvar fungus at least once in their lives. There are groups of people who are more prone to candidiasis. These include: women, after antibiotic therapy, steroid treatment, pregnant women (vaginal itching during pregnancy).
Also susceptible to the disease are women taking hormones and their derivatives, as well as patients with hormonal dysfunctions. It often happens that recurrent vaginal yeast infections are one of the first signs pointing to diabetes.
Symptoms of the disease in women and men
Symptoms of vaginal mycosis are usually quite severe. Manifestations of the disease are quite typical. A woman is bothered by vaginal discharge that is white or grayish in color.
Vaginal discharge appears with varying intensity. Some women may have few symptoms and little or no vaginal discharge. And for others, especially pregnant women, they are pronounced and cause severe anxiety; the volume of vaginal discharge can be quite large.
Another characteristic symptom is itching in the vaginal and vulvar areas. Burning and itching of intimate areas is very annoying. In addition, changes occur in the epithelium, the affected areas develop in the vestibule and the vagina itself.
Itching of the intimate area
In the case of a fungal infection, men develop the following symptoms: flaky discharge from the foreskin, redness, itching, burning, swelling, rashes in the form of blisters on the head of the penis.
Rashes that are considered normal
Healthy female genital organs have smooth skin and a uniform color from light pink to dark brown. When deviations from the norm occur, suspicions about the presence of diseases arise, but some rashes in the intimate area are considered a normal consequence of physiological changes.
Parents often wonder why the labia minora darken in girls?
During puberty, blood flow increases, the mucous membranes in the groin area begin to swell and darken. During adolescence, girls may develop skin formations in the form of white dots on their genitals. They are called Fordyce granules and are a consequence of hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands. They occur in the groin, face, lips, and mouth. They are not dangerous and do not require treatment.
READ ALSO: Acne vulgaris (acne) in adolescents - treatment of juvenile acne, causes in boys and girls
White genital rashes may be a type of common acne, which is also normal during hormonal changes during puberty in teenage girls.
During pregnancy, swelling and redness of the intimate organs is observed - this is a consequence of an increase in the hormone estrogen, which increases blood flow in the pelvis.
Skin pigmentation in older women is also not a deviation and should not be a cause for concern. In the post-climactic period, all women are faced with the fact that the vagina secretes less secretion, the mucous membrane of the genital organs changes structure and shade.
Allergic reactions and irritations in the groin area to external pathogens in the form of underwear or soap are not considered a pathology; you just need to stop using them to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment of vaginal thrush
The main element of the treatment of mycotic infections of the vagina and vulva is the use of antifungal drugs. Therapy is recommended not only for the woman herself, but also for her partner.
It is not possible to completely get rid of Candida fungi in the vagina. The goal of treating vaginal mycosis is only to relieve the symptoms. The most affordable medicine for vaginal fungus is clotrimazole. It is active against yeast-like and dimorphic fungi, dermatophytes, some pathogens of lichen, erythrasma, Trichomonas vaginalis (in high concentrations).
Vaginal tablets (at night for 6 days) and a cream that can be applied to the vulva are available for treatment. The cream is prescribed to a partner: lubricate the head of the penis twice a day for at least 1-2 weeks.
Treatment of thrush
Preparations that contain econazole are also used. Econazole is active against a large number of strains of microorganisms: fungi of the genus Candida, molds, all dermatophytes, corynebacteria. Trade name: Gino-pevaril. More convenient to use. 150 mg suppositories are used at night for three days, sometimes treatment is extended or repeated after 10 days.
In case of recurrent mycoses, oral therapy is used - fluconazole, itraconazole.
Pregnant women are recommended to use topical medications; oral medications are not used. Clotrimazole drugs are often prescribed (from the second trimester). Natamycin is also used (Pimafucin suppositories 100 mg, 3-6 days).
It is prohibited to use any medications on your own, especially during pregnancy. Each medicine has its own spectrum of action, that is, it acts against certain pathogens. Only a doctor can determine the specific pathogenic microorganism that caused the fungal disease based on test results.
Self-medication will not bring positive results, since no folk remedies for vaginal fungus help. The more aggressive. Douching with a solution of potassium permanganate will result in a burn to the mucous membrane. Using garlic inside the vagina can cause irritation and burns.
All “homemade” drugs lack sterility; their use will lead to even greater infection, adding bacterial infection to the fungal disease. The risk of damage to the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix threatens the development of pathological cell formations, including malignant ones.
What diseases can cause rashes and spots
In addition to physiology, there are serious reasons for the formation of rashes in the intimate area in women. Endocrine disorders of the body lead to the fact that the female body is covered with large red painful purulent pimples. They appear on any part of the body, including the groin. Hormonal imbalances require proper treatment.
When small papules form on the labia, this indicates micropapillomatosis , that is, the presence of the human papilloma virus in the body. They are painless, asymptomatic, and do not interfere with life in any way, but it should be remembered that with any changes in the state of the immune system, there is a risk of HPV developing into cancer cells.
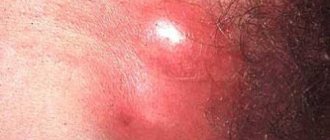
A disease of the Bartholin glands of infectious etiology - bartholinitis - provokes rashes in the groin of women at the entrance to the vagina, where these glands are located. Their inflammatory process leads to the formation of blisters with pus inside. After some time, they burst and ulcers form in their place. Without treatment it will lead to a chronic form.
White pigment spots on the labia indicate the rare disease vitiligo. This little-studied, acquired skin disease of the genitals and the entire body manifests itself in the formation of large white spots. The origin and methods of treatment are still being studied, but it is absolutely clear that apart from an external defect, this disease does not threaten anything else. It appears and disappears on its own, but the use of certain cosmetics and certain dermatological drugs is not prohibited.
Sexually transmitted diseases and rashes on the labia always accompany each other; they can be accompanied by symptoms such as: itching, burning, painful urination, colored discharge (yellow, green, brown) of unusual consistency with a foul odor, pain during sex. The rashes are localized on the vulva and in the vestibule of the vagina, mostly small in size, red, protruding above the skin. The most common diseases include chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and gonorrhea .
An unpleasant viral disease, cytomegalovirus , causes the formation of red spots throughout the body, including rashes on the genitals. The resulting inflammatory processes affect internal organs, so the pathology should not be ignored.
The development of skin diseases of the genital organs in women is provoked by fungal diseases, parasitic diseases, and chronic dermatitis .
Fungal vulvovaginitis and pediculosis pubis
The occurrence of a vesicular rash in the intimate area in women may be a fungal disease - vulvovaginitis . After a disturbance in the bacterial balance in the vaginal environment, rashes appear on the lips of the female genital organs, in the vestibule, inside the vagina, and spread to the anus. The symptoms accompanying dermatitis are the following: itching, light discharge with a cheesy consistency, burning sensation.
READ ALSO: Lump in the groin in men, left or right - photo and 4 reasons
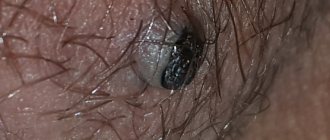
The causative agent of lice pubis are parasites - pubic lice. Their habitat is the part of the pubis and genitals covered with hair. Insect bites are very itchy and require constant scratching. From small pinpoint bites, after scratching, large red spots appear, on which crusts and ulcers form, with subsequent mechanical damage to which a secondary infection can occur.
Scabies and molluscum contagiosum
Scabies is an infection caused by a parasite, the scabies mite. In the genital location, the pubis and labia majora are most densely deposited. It is characterized by a rash in the form of a scattering of small paired red dots. Between them you can see thin lines - the passages of the parasites, and black dots - the exit holes. After scratching they become sores. Like all parasites, the scabies mite actively reproduces, laying eggs. A striking symptom is incessant itching that cannot be tolerated. The carrier of a contagious disease must be isolated during the period of treatment.
The disease molluscum contagiosum is viral in nature and is transmitted through household contact. After a woman is infected, fleshy, spherical rashes appear on the labia majora, labia minora, and thighs. When pressed, crumbly contents come out, the small particles of which, under a microscope, resemble mollusks, hence the interesting name. The formations are arranged in such a way that they form a ring. When infected, mild itching is sometimes observed, but more often the disease is asymptomatic and goes away on its own. But the virus remains to live inside the body, taking a latent form; if the immune system is disrupted, a recurrence of genital rashes or other parts of the body will occur.
Syphilis, psoriasis
Treponema virus is the causative agent of the venereal disease syphilis , which causes great harm to health, including death. The first sign of infection in women is the appearance on the genitals of a small red spot with a marked edge and a smooth shiny center, otherwise called a chancre. It doesn’t hurt, doesn’t itch, and is slowly developing into an ulcer. By this time, a secondary symptom appears - a pink rash all over the body. It should be noted that if treatment has not been carried out, and the rash has disappeared, this is not a reason for joy, it means that the disease is in an advanced stage, when internal organs are affected, bone tissue is destroyed, the consequences of which are the saddest. Syphilis is transmitted sexually, some of its types are transmitted through household contact. It is important to understand that all sexual partners of the patient should be treated; this issue cannot be treated irresponsibly, since syphilis is a serious disease that threatens human life. Deliberate spread of infection is criminally punishable.
Psoriasis is an autoimmune chronic skin disease. It is characterized by the appearance of rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. Small pink papules with characteristic peeling form on the female genital organs; they are painful and with severe itching. If the disease has taken an atypical form, in which the inner layers of the epidermis are affected, there is no peeling, and the disease manifests itself by the formation of red spots, sometimes reaching large sizes. With an atypical form, it is much more difficult to diagnose the pathology; histological analysis is necessary.
Psoriasis, contrary to popular belief, is not contagious and is not transmitted either sexually or through household contact. The causes of the disease are determined by a combination of internal and external factors, such as genetic predisposition, impaired immune function, stress, and concomitant diseases. Once it occurs, psoriasis cannot be treated; its symptoms appear during exacerbations.
READ ALSO: Treatment of ear eczema. Noma of the auricle and external auditory canal
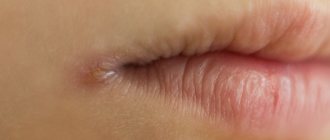
Inguinal athlete's foot and genital herpes
Genital herpes has a viral etiology, and after infection of the body it becomes chronic. It is impossible to get rid of it completely; treatment is mainly carried out to relieve symptoms, and the virus continues to exist in a passive state and is activated when immunity decreases. Almost always, genital herpes occurs in combination with concomitant diseases that provoke its appearance. An active virus in the female body is expressed in the appearance of vesicular rashes with cloudy, liquid contents on the vulva and labia minora. Over time, ulceration occurs and a wound with a crust forms in place of the vesicle, which gradually heals. The formation of wounds is a rather painful process that affects overall well-being. It is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, redness of the genitals, burning, painful itching, fever, aches in the muscles and joints.
Athlete's groin is caused by a fungus called Hebra's eczema. The itchy rashes characteristic of the disease are localized in places with poor air circulation and large accumulations of sweat - the intimate organs of women are a very favorable environment in this regard. The formations are ring-shaped with small bubbles around the perimeter and are pink in color. They gradually increase in size, occupying the entire groin area and even the thighs. Like all fungal diseases, it causes severe discomfort to the owner and requires immediate treatment.