Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity has its own microflora and its own specific diseases arise. Let's talk about one of them - fibrous epulis of the gums: what kind of disease it is, what are the causes of its occurrence, how is the treatment carried out.
Growth on the gum: why it appears and how to treat
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the cause
Infectious diseases
Non-communicable diseases
Types of growth
Gum cancer
Lump after crown installation
Growth on the gum: how to treat
Which doctor should I contact if a growth appears on the gum?
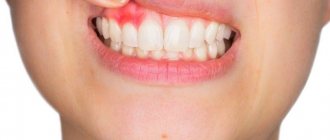
Normally, the gums have a smooth, pale pink texture. Any change, be it a thickening or a growth, signals problems in the body that cannot be ignored, as they pose a health hazard. Why lumps appear on the gums and how to treat them, we will tell you in the article.
Never do
You should never heat your gum or cheek, no warm compresses or salt or other “folk remedies”! It’s better not to do anything at all before going to the doctor. After warm compresses, pus may spread not only in the jaw, but also in the cheeks, throat, and neck. Situations arise that are dangerous not only to health, but also to life.
Contraindicated
- refusal to brush teeth;
- independent opening of the abscess;
- taking medications without the consent of a doctor (except for painkillers).
A growth has appeared on the gum: what is the reason?
A lump or growth is a compaction on the gum caused by damage to periodontal tissue, which may appear without any previous signs. Growths appear in people of any age, but mainly in young children, as they unknowingly introduce infection into their mouths. The first thing you need to do when you detect formations in your mouth is to determine the nature of their origin (only a doctor can do this). It comes in two types:
- Infectious. The appearance of cones is caused by the activity of bacteria.
- Non-infectious. Bumps and growths as a result of injury, mechanical or chemical damage.
If a lump has formed in your mouth, you should consult a doctor to rule out possible complications. The doctor will help diagnose the problem and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Folk remedies
The use of effective folk methods and recipes as a supplement to basic drug treatment can significantly speed up the healing process.
- Rinse with saline solutions. Per liter of boiled water - 4 tbsp. spoons of salt, leave to brew for an hour. Afterwards, warm the solution a little and sanitize the oral cavity. Salt disinfects, relieves swelling, and soothes.
- Gargling with herbal infusions. Chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, and yarrow are suitable for these purposes. 4 tbsp. l. herbs are brewed in 1 liter of boiling water and infused for half an hour. Herbs have a calming and antiseptic effect on the mucous membrane and promote the resorption of compactions.
- Kalanchoe juice. Nourishes and heals inflamed gum tissue, strengthens tooth enamel. Freshly squeezed juice is rubbed into the gums, or a washed leaf, freed from the outer skin, is simply chewed.
- Salt with honey. Healing tandem - salt softens inflamed tissues and helps remove purulent exudate, and honey disinfects, nourishes, and soothes. A mixture of honey and salt is prepared in a 2:1 ratio.
- Garlic tincture. It removes pus well and is a powerful antiseptic, but to avoid burns it should not be used for more than 3 days. The infusion is prepared from 4 heads of garlic, 5 lemons and 700 grams of vodka. The crushed ingredients are infused in alcohol for 3 days. Then rinse the mouth with the solution every 4 hours.
Important! Traditional methods are auxiliary methods of combating the disease, not a panacea, and will not replace drug treatment prescribed by a dentist.
Infectious diseases
| Gingivitis and periodontitis Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, often accompanied by the appearance of a red ball-shaped growth near the tooth. The next stage is periodontitis. With it, purulent discharge is observed, and the lump acquires a grayish or beige tint. |
| Granuloma or cyst When pulpitis is advanced, the inflammatory process reaches the apex of the root, where a granuloma forms. Often this process goes unnoticed by the patient, so he is in no hurry to see a doctor. Over time, the pathology can develop into a fistula - a white formation on the gum. |
| Flux Purulent inflammation on the gums occurs against the background of advanced caries or pulpitis, a poorly treated root canal. At the first stage, minor pain appears; on the second - swelling and redness; on the third, the temperature may rise and the cheek may swell; on the fourth – the pain becomes sharp and throbbing, swelling increases. |
Preventive actions
Monitoring the condition of the teeth and oral cavity will reduce the likelihood of tumors.
- Timely sanitation of the oral cavity. Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination and professional hygiene twice a year will prevent the growth of caries, the appearance of defects in fillings and the formation of tartar, leading to gum injury and the appearance of epulis.
- Prevention of gum injury. If systematic injury to soft tissue occurs as a result of poorly fitted orthopedic or orthodontic structures, consult your doctor about this problem. He will adjust the crowns or dentures.
If these preventive measures are followed, the prognosis is favorable and epulis does not recur.
We hope that our article about epulis will be for informational purposes only. And if you want to soothe your gums, make them strong and strong, try the unique two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE.
This is the only rinse with a combination of chlorhexidine + benzydamine for the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases. The product has a combined effect: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic. Instant anesthetic effect allows you to quickly reduce pain.
Non-communicable diseases
| Epulis This is a benign formation. It has a stem and a cap. Most often it occurs due to malocclusion, improper prosthetics, and hormonal changes. In the absence of adequate treatment, the tumor can develop into a malignant one. |
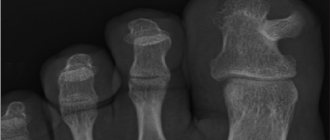
| Exostosis A bone growth that occurs against the background of a jaw abnormality - the bone extends beyond its usual boundaries, forming a lump. Most often, the reason lies in a genetic predisposition, less often - as a result of injury or complex tooth extraction. |
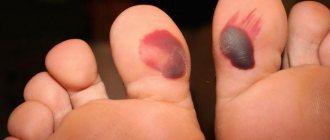
| Hematoma As a rule, it is formed as a result of an impact and goes away on its own over time. If there is damage to the tissue, then surgical intervention is necessary. |
Treatment
How to get rid of a lump that appears on the gum? Treatment is based on eliminating the causes and symptoms of the underlying disease.
Fistula.
When a fistula occurs, the main goal is to eliminate the source of infection and remove the pus. To do this, rinse the mouth with a solution of soda and salt in a 1:1 ratio (half a teaspoon per glass). The procedure is repeated daily every 1.5-2 hours until the seal completely disappears.
Exostosis.
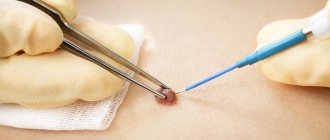
Exostosis is treated only surgically if there are indications for removal of the lump: pain, rapid growth, or the presence of a cosmetic defect. During surgery, overgrown areas of tissue are removed with a chisel, then the bone is smoothed out.
Worth knowing!
In children, exostoses often disappear on their own over time, so there may be no need for surgery.
Epulis.
Treatment of epulis begins with eliminating the causes that caused it - removing tartar, treating caries, adjusting prosthetic structures. Then observation is carried out and, if necessary, surgical excision of the cones to healthy tissue.
Periodontitis.
To treat periodontitis, the filling is removed from the diseased tooth, the canals are sanitized and widened (to allow pus to escape) and the affected periodontal tissues are removed. Antiseptic treatment is carried out and antibiotics are prescribed. Then a temporary filling is placed, which is later replaced with a permanent one.
Periostitis.
Treatment for periostitis is similar to the sanitation of periodontitis, with a difference in the duration of the procedure due to the more serious consequences of the disease. The tooth is unfilled, the canals are cleaned and expanded. Medicine is placed under the temporary filling and it is removed after 2 months. The tooth is washed with antiseptics, then the temporary filling procedure is repeated again. When the symptoms of the disease are eliminated, a permanent filling is applied; if there is no result, the tooth is removed.
Periodontitis.
Treatment takes place on an outpatient basis. The doctor removes tartar and performs antiseptic treatment of dental pockets. For serious lesions, treatment is performed surgically.
Gingivitis.
Gingivitis can be treated at home, using ointments, gels and rinses prescribed by your doctor. But the main thing is proper oral hygiene.
Important!
Treatment of diseases, depending on their complexity and nature, can be carried out on an outpatient basis or at home. One thing is certain: only a specialist should make a diagnosis and prescribe procedures (even at home!)!
Types of growth
New growths on the gums vary in shape, size, and method of formation.
- Angiomatous growth. A soft, bumpy, pink growth that grows very quickly. Often reappears after removal. This growth is diagnosed in children aged 10-12 years; as a rule, it does not occur in adults.
- A fibrous growth is a gum-colored lump. It grows slowly and does not cause pain, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor.
- Giant cell growth. A rapidly growing neoplasm of red-blue color, from which serous fluid is secreted. The lump is easy to injure.
Ball in mouth - what is it?
When the inflammation begins to gradually progress, a blister appears on the gum. The main reason for the formation of a lump is poor oral hygiene and prevention. But the ball can also form under the influence of other factors: inflammation occurring in the roots of the teeth, gums, mucous membranes, and periosteum.
The problem is that the disease can be diagnosed in the later stages, with the development of a purulent process. This happens because the patient does not visit the dentist. For patients who experience fear while in a chair, the doctor can give sedative anesthesia, in which the receptors are turned off and the patient falls into a shallow sleep.
Attention! It is better to diagnose the disease early in order to prevent more dangerous consequences, including blood infection and inflammation of the entire jaw.
Gum cancer
This dangerous neoplasm is worth highlighting separately. Mutation cells begin to divide uncontrollably, which is why a red tumor forms on the gum. The disease progresses quickly and over time can develop into jaw cancer.
What are the symptoms?
- General weakness;
- increased body temperature (37 C°);
- loss of appetite;
- constant drowsiness.
The doctor makes an accurate diagnosis after a detailed examination. As a rule, treatment is long and painstaking. With timely medical intervention, the outcome is favorable.
Classification of fibroids
Pathology is divided into several types according to criteria. This includes the density of the benign neoplasm, the nature of its origin, as well as the severity of clinical manifestations.
Dense fibroma
Characterized by a solid consistency. This is due to the fact that the contents are quite hard fibers of connective tissue. They include a small number of cores. Formations of this type are most often found on the gingival surfaces and palate.
Soft fibroma
The fibrous structures are thin and freely located, so their clusters are characterized by a high degree of softness. This type is most often observed on the tongue and the inside of both cheeks. Benign neoplasms of a mixed type, combining the signs of all the varieties listed above, can be found on the sublingual part and on the mucous membranes of the floor of the oral cavity. For example it could be:
- Fibrolipoma. It is hard to the touch because it contains fibrous fibers. It can be eliminated surgically, with laser, or radio waves.
- Fibrohemangioma. As a rule, it is provoked by infectious processes occurring in the child’s body. It is extremely rare in adults. It never degenerates into malignant tumors. Most often it is treated surgically, in some cases it can resolve on its own.
Fibroma from irritation
This is not a tumor formation in its usual form, but the result of reactive hyperplasia. Chronic pathology is characterized by the development of focal lesions, which are caused by systematic mechanical action and subsequent injury.
The most common cause is installed crowns, fillings, and dentures. In the latter case, the disease is called prosthetic granuloma. The orthopedic structure exerts continuous pressure on the alveolar process, leads to its resorption, moves forward and contributes to the formation of compactions, which are associated with the inflammatory process.
The risk group includes not only patients who have undergone prosthetics, but also people with untimely cured caries, in adulthood, with foreign objects in the oral cavity (for example, with piercings). Studies have shown that women are more prone to such hypertrophic transformations than men.
Symmetrical fibromas
Doctors diagnose such tumors in the area of the third molars in the areas between the gums and the roof of the mouth. The tumor is hard to the touch and resembles a bean in shape.
It should be noted that this type of compaction does not apply to true fibromatosis. These are just overgrown tissues in the gingival membranes, accompanied by the process of scarring and other changes of a similar nature.
Lobular fibroma
It occurs as a result of reactive hyperplasia with systematic trauma to delicate sensory fibers with prostheses or other orthopedic structures. The main distinguishing feature of such formations is their rough, textured surface. When palpated, tubercles are felt.
Fibrous epulis
This is a dense growth of pinkish tissue that does not cause pain or other discomfort. The edges are often hyperemic, have clear boundaries and irregular shape. The base is quite wide.
The vestibular part of the gums is usually affected. There are cases of neoplasms occurring in the interdental spaces in the form of a saddle with spread to the intraoral surface.
Quite often, a dental unit located in a pathological area has a poorly fitted metal crown, extensive carious lesions, or a prosthetic clasp. It is these structures that are the provoking factor in the occurrence of a chronic inflammatory process with the formation of granules, which over time are transformed into mature connective fibrous fibers.
In dentistry, there are also angiomatous epulis. They are brighter in color, somewhat softer to the touch and bleed. In this case, blood appears not only at those moments when the surface is affected mechanically, but regardless of the presence or absence of a traumatic factor. When conducting diagnostic studies, many vascular branches are detected in the pathological area.
Growth on the gum: how to treat
The treatment plan is developed by the doctor based on the nature of the growth, so in no case should you self-medicate. It is important to understand that if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, serious complications can arise.
If the cause is an infection, then it must be removed. In case of periodontal inflammation, professional oral hygiene is performed. If the cause is periodontitis and complicated pulpitis, then first the lump is opened and pus is pumped out of it, and then conservative or surgical treatment is carried out.
If there is no pain, for example, with epulis or ecostosis, then the decision about surgical intervention is made together with the patient.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.