The incubation period for scabies is from 1 to 6 weeks, during which the parasites select and develop a “territory.” The immune system instantly reacts to their appearance and the emerging “waste”. The duration of the incubation period depends on the number of mites that have fallen on a person’s skin: the more there are, the faster the main symptom of scabies will appear - itching. The intensity and nature of skin rashes is not affected by the number of mites; the allergic reaction depends on the interaction of the human immune system and the waste products of the parasites. A sick person, constantly and vigorously scratching the bite sites, involuntarily introduces an infection, for example, staphylococcal; in this case, the bacteria “add” their own symptoms of the disease, giving the rash a pustular character.
When and where is it easiest to get scabies?
Scabies mites are inactive during daylight hours. The main peak of activity of the female tick, responsible for laying eggs, occurs in the evening and night. She lives only 4-6 weeks, but, under favorable conditions, during this time she can give birth to 50 million new individuals. The female mite digs a scabies burrow at the border of the stratum corneum and granular layer of the epidermis at a speed of 2-3 mm per 24 hours, and lays 2-4 eggs in one day. Female ticks make their way forward, males make their way wider; The saliva of males contains a large amount of proteolytic enzymes, and due to this, the keratin of the skin is dissolved, forming a nutrient, a lysate. Mites become active and crawl to the surface of the skin when the owner (person) falls asleep. Ticks use this time to fertilize a new female and develop new territories. The night speed of ticks moving along the surface of the skin reaches 25 mm/min.
Reasons for appearance
The lesions are caused by the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei. Any living creature that has been infected can carry it. And the more lesions on the patient’s body, the higher the risk that he can infect someone.
what does a scabies mite look like?
Infection is carried out by females and larvae. The female lives in the skin. During the daytime it is inactive, but in the evening it actively gnaws through passages, reproduces, feeds and secretes waste products. Consequently, the greatest risk of infection appears precisely in the evening and night time, when the tick is more active.
Everyone who comes into contact with the infected person is at risk. For example:
- family member
- roommate
- roommate
However, you can also become infected through indirect contact. For example in the following places:
- bathhouse
- public shower
- crowded places
Interesting. Outside a living organism, the female can live up to 3 days.
The disease spreads quickly due to the fact that the female lays eggs from which larvae hatch. After maturation, the latter crawl out to mate. The male dies and the female burrows back into human skin to continue the cycle of reproduction and spread.
Types of scabies
Typical scabies and its symptoms
- Itching
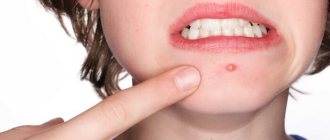
- Rashes are scattered or multiple, small reddish nodules merging into one line. After a while, they turn into bubbles that burst to form a crust. Crusts with purulent contents mean that when scratching a person acquired a bacterial infection.
- Winding scabies passages, which consist of segments 5-8 mm long (this is the distance that the female mite “travels” per day). They peel off over time and look like gray scratches ending in a transparent bubble in which you can see a dark dot - this is the body of the tick. Typical location of this form of scabies:
- fingers, more precisely, the lateral surfaces of the fingers and the distance between them,
- bends of the hands and elbows,
- mammary glands (especially nipple halos),
- lower abdomen, male genital organs, etc.
Complicated scabies (with pustules) and its symptoms
Specific additional symptoms: dermatitis or purulent skin lesions.
Scabies of clean people and its symptoms
With increased attention to hygiene and a healthy immune system, rashes are very rare, and itching intensifies only in the evening and at night.
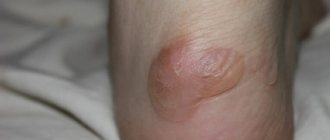
Nodular scabies and its symptoms
A few round skin lumps with a diameter of 2-20 mm, which are very itchy. They are colored red or brown, and scabies are visible on their surface. As a rule, they affect the penis, scrotum and inguinal-scrotal folds, circumference of the anus, nipple halos, inner thighs and buttocks.
Norwegian scabies and its symptoms
A very rare form, it appears only in those patients who, for various reasons, do not itch (do not feel itching or there is no allergic reaction due to weakened immunity). The skin thickens and becomes rough, rashes affect almost the entire surface of the patient’s body, even the skin of the face, hair and nail plates. The most unpleasant and characteristic symptom of Norwegian scabies is the formation of thick (up to 3 cm thick) crusts of a dirty yellow color over the entire surface of the body, under which extensive weeping erosions are exposed.
Features of scabies in children - signs and symptoms
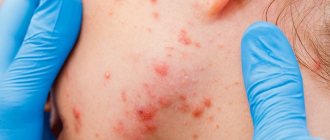
The possibility of contracting scabies in children is many times higher than in adults. The skin of a child is very delicate and thin, so it will not be difficult for a tick to penetrate into it. Parents often confuse a rash in a child with an allergic reaction and begin to self-medicate. Therefore, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor to make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment for scabies with medications. The initial signs of the disease are the same as in adults: mild itching and lobar rashes.
In the photo, how scabies manifests itself in children (symptoms and first signs of the disease are the same as in adults, but may be more pronounced):
Severe itching does not allow the child to sleep; he begins to act up and scratch the itchy areas, spreading the infection throughout the body. As a result of scratching, crusts appear, which, when stretched, burst and become wet, which can provoke eczema. It is necessary to constantly examine the child’s skin and immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms.
At the first symptoms of scabies in children, treatment should be started immediately. The photo shows an ointment that all parents should know about
How long is the incubation period for scabies?
Laboratory studies have found that the incubation period for scabies lasts from one to 6 weeks. During this period of time, the human immune system also begins to react to the pathogen. From this we can conclude that the signs of the disease will appear the faster the more parasites get on the skin.
When it comes into contact with the skin of females, there is no incubation period, so they immediately begin to parasitize, gnawing through canals and laying eggs. When infested with larvae, it lasts more than 2 weeks until the larva matures and begins to invade.
It is not possible to determine the incubation period of scabies in practice, because the first signs do not always appear immediately. In some cases, a long time passes after contact with an infected person and infection does not always occur through direct contact. After all, scabies can be contracted through a door handle in a public place or through handrails on public transport.
What is polycystic ovary syndrome, its symptoms, diagnostic methods and treatment?
How to cure cervical erosion using traditional methods? You can read it here.
About the manifestations of leukoplakia in women: .
How to treat
For proper treatment, specific therapy must be carried out to confirm scabies. If the doctor was unable to identify the mite and scabies, a trial treatment will be prescribed. In addition, preventive treatment is prescribed to all family members and people in contact with the patient.
The doctor will prescribe medications that kill ticks. Most often they are:
- aerosols
- ointments
- creams
- suspensions
- emulsions
The prescribed drugs will be based on the following substances:
- benzyl benzoate
- permitrina
- sulfur
- piperonyl butoxide
- esbiola
Sometimes treatment includes washing with soap or treating the skin with emollient ointments before using the drug.
Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine and treatment method. It is based on the following criteria:
- clinical picture
- complications
- person's age
- pregnancy
Self-medication can cause complications, apathetic forms of infection or a protracted course of the disease.
Diagnostics
To determine the clinical picture, you need to do the following:
- Explain your symptoms to your doctor in detail. For example, itching only bothers you at certain times
- get tested
- examine the patient's body
- determine the source of infection
- find traces of the tick itself or its larvae
Typically, the disease is determined by the following criteria:
- purulent blisters
- dry crust
- redness on the buttocks
- scabies (the most important criterion)
To determine the itch, the lesion can be stained with iodine, oil containing minerals, or simply pressed on the epidermis with a glass slide. This will block blood from reaching the affected area and allow you to clearly see the affected area. It can also be detected using dermatoscopy (during the procedure the tick itself is detected).
Ticks can be detected using lactic acid. One drop (40%) should be applied to any lesion and wait 5 minutes. The loosened skin can then be scraped off with a sharp spoon until capillary bleeding appears. The resulting epidermis must be applied to a glass slide and looked at under a microscope. The method will allow you to identify most parasites and the products of their activity.
Scabies: treatment at home
Medicines for scabies can be replaced with homemade ointments and decoctions. Local treatment of scabies is possible using the following recipes:
- Celandine juice. The celandine grass must be chopped. Through gauze, or using a press, squeeze out 1 tbsp. l. juice Apply the resulting liquid to the areas on the body.
- Celandine ointment. Dry the celandine bush in the sun. Grind into dry powder. 1 tbsp. l. Mix dry herbs with two tablespoons of cream and leave for a day in a cool place. The ointment is ready for use.
From celandine
- Elecampane ointment. Grind the elecampane root into a paste. Heat the lard over the fire. Mix with herbal preparation. Add liquid tar soap at the rate of 30 ml per 100 g of mixture. Mix well and apply to rashes. After drying, wash off the crusts with laundry soap.
- Gunpowder ointment. To prepare the ointment you will need 3 tbsp. l. fat sour cream and 1 tbsp. l. gunpowder Stir until smooth. Close the container with ointment and wrap it in heat. Stir the ointment every 30 minutes for several hours. After applying the ointment, you must wait until it is absorbed. Then wash off with laundry soap.
- Turpentine-based product. Bring 30 ml of refined vegetable oil to a boil. Add 1 tsp. turpentine. Treat areas of tick infestation.
- Bay leaf remedy. Grind the bay leaf into powder. Mix 50 g of soft butter with fragrant powder. Apply to rashes.
- During the treatment period, bath procedures are carried out using laundry and tar soap.
Preventive actions
The causes and prevention of scabies are close by. After all, you can only become infected through contact with an already infected person or objects after using it, so for prevention, experts recommend washing your hands as often as possible, preferably wiping them with a liquid antiseptic. Chlorhexidine would be an excellent option - a convenient bottle can easily fit into a purse or glove compartment of a car, and washing your hands several times a day will be an excellent prevention of scabies.
Related services: Consultation with a dermatologist Dermatovenereology
Effective treatment of scabies with medicinal herbs
It is recommended to wipe areas of scabies mite infestation with herbal tinctures. At home, you can use several recipes for scabies:
- A tablespoon of crushed fume is poured into 100 ml of vodka. Let it brew for a week. Wipe the affected areas.
- 100 g of buckthorn fruit into 1 liter of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes. Let it brew until it cools completely. Soak a cotton swab in the broth and wipe the affected areas.
- Take 2-3 nuts in green skins and 5-7 young leaves, pour 300 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Wipe the affected areas with cooled tincture.
Treatment of scabies at home can begin with taking a bath of medicinal herbs. A concentrated decoction is prepared from the medicinal herb and poured into a filled hot bath. For medicinal purposes they use ragwort, verbena, burial ground, and juniper.
Treatment of scabies with folk remedies
Let's consider several folk remedies that have a beneficial effect on the treatment of scabies:
- Grind 0.5 kg of tomatoes. Add 1 cup vegetable oil. Fry the resulting mixture well in a frying pan. After cooling, apply to affected areas.
- For bath procedures, prepare garlic soap . Grate the bar of soap, pour it into a saucepan and melt it over the fire. Add the pulp of one onion and two cloves of garlic. Mix thoroughly, pour into the mold and let harden. After the first wash, monitor the skin's reaction for allergies.
- Prepare bread kvass. Salt it and warm it up slightly. Moisten the affected areas with a cotton swab.
- a glass of mustard oil with the pulp of half a head of garlic. Bring to a boil and keep on low heat for a quarter of an hour. Strain and cool. Lubricate the rash areas. Store the remaining mixture at a cool temperature.
- 2 cloves of garlic into a paste and add 1 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar. The resulting product is applied to the areas of infection until the itching is completely eliminated.
Garlic for scabies
- 100 ml of body lotion with 25 drops of tea tree oil. Apply to affected areas of the body.
WHO activities
WHO works with Member States and partners to develop scabies control strategies and outbreak response plans. WHO recognizes that the burden of disease and the risk of long-term complications need to be better defined and that scabies control strategies need to be linked to interventions to facilitate rapid and cost-effective implementation. WHO is working to ensure that ivermectin is included in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines at its next update. In addition, WHO is working to ensure that quality and effective medicines are available to countries that need them.
Features of infection
A sexually mature female is about 0.3 mm in length. Its lifespan is 1 month - this time is enough to lay eggs and for new mature females to develop from the hatched larvae.
Interesting:
Only female parasites parasitize the human body - they have specific “hooks”, with the help of the skin they make passages in the epidermis. They need this to reproduce; it is in these passages that tick eggs turn into larvae.”
The parasite is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person during close contact - this can be facilitated by promiscuous sex, being in crowded places with sick people, and unsanitary living conditions. In rare cases, infection can occur through household items such as washcloths and towels, which is why the parasite can be picked up in a public bath or swimming pool.
Interesting:
Children get scabies much more often than adults and they become infected mainly in children's groups. This is due to the fact that children do not always observe the rules of personal hygiene and often exchange toys and other personal items with each other.
Scale of the problem
Scabies is one of the most common skin diseases and accounts for a significant proportion of skin diseases in developing countries. It is estimated that more than 200 million people worldwide are infected with scabies at any given time, but more efforts are needed to more accurately estimate this burden. According to recent publications on scabies, prevalence rates range from 0.2% to 71%.
Scabies is endemic in many resource-limited tropical areas, where average prevalence rates among children are estimated to be 5–10%. Re-infections are common. The heavy burden of scabies and its complications imposes significant costs on healthcare systems. Scattered cases occur in high-income countries, but outbreaks of scabies in health care settings and vulnerable communities result in significant economic costs to national health services.
Scabies is common throughout the world, but the most vulnerable populations—young children and older adults in low-resource communities—are particularly susceptible to scabies infection and the development of secondary complications. The highest rates of infection are found in countries with hot tropical climates, especially in communities where people live in conditions of overcrowding and poverty and access to treatment is limited.
Transmission of infection
Scabies is usually spread from person to person through close skin-to-skin contact (for example, living together) with an infected person. The risk of transmission depends on the level of infestation, with contact with persons with crusted scabies presenting the highest risk. The likelihood of transmission through contact with contaminated personal items (such as clothing and bedding) is low for normal scabies, but may be high for crusted scabies. Given the asymptomatic period of infection, transmission may occur before symptoms appear in the initially infected person.