Under the term dyshidrosis (Greek dyshidrosis
) understand two types of states:
1) this is the general name for sweating disorders;
2) as a synonym for “chickweed” - an eczema-like condition accompanied by blockage of the ducts of the sweat glands with the formation of small vesicles (bubbles); typical localization of rashes is the palms and soles, the lateral surfaces of the fingers and toes; the disease is accompanied by itching in 2/3 of cases [1, 2].
The medical literature separately describes dry lamellar dyshidrosis ( dyshidrosis lamellaris sicca
) is an abortive form of dyshidrosis, characteristic of a dry climate and manifested by small foci of fine-plate peeling in the absence of itching.
The etiology and pathogenesis of dyshidrosis and dyshidrotic eczema (DE) have not been sufficiently studied to date.
DE is spoken of in a chronic relapsing process represented by the rashes described above (vesicles with a dense covering ranging in size from 1 to 5 mm).
DE can occur against the background of emotional stress, in a humid and hot climate, in the presence of fungal-bacterial sensitization, pathology of the vegetative-vascular nervous system, and hereditary dyshidrotic conditions [3]. Hyperhidrosis worsens the course of this form of eczema [4].
Histological examination reveals an eczematous reaction around the sweat ducts, which is not associated with abnormalities of the sweat ducts. Dyshidrotic processes are characterized by ballooning degeneration of epidermal cells, resulting in the appearance of cavities filled with serous contents. A large number of such cavities resemble a foamy structure in the epidermis and are called “spongiosis.” The dermis contains perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates with an admixture of eosinophils [2].
Recently, the term “acute and recurrent vesicular dermatitis of the hand” was proposed to reflect the clinical features of DE.
Although the etiology of DE remains unknown, given the presence of metal allergy in patients with DE and improvement of symptoms after removal of the metal allergen, metal allergy can be considered as one of the important potential etiological factors of DE [2, 5].
Dyshidrosis Clinic
The bubbles are located deep in the epidermis. In severe cases, multi-chamber vesicles can form by the fusion of individual vesicles. This condition is characterized by severe itching [1, 2].
DE accounts for 20-25% of all cases of palm eczema. The peak incidence of DE occurs in women at 15-25 years, in men - at 30-40 years [4].
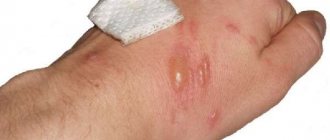
Most of the vesicles subsequently open, the serous fluid filling them flows out, after which a yellowish serous crust forms in place of the opened vesicle (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. DE of the palms, aggravation. Typically, most of the vesicles are grouped and form extensive lesions against the background of erythema [6].
Inflammatory lesions tend to spread peripherally, spreading to the dorsum of the hands, feet and other areas of the extremities. Often, as the process progresses, foci of weeping form in place of the opened vesicles [1].
Since DE is characterized by severe itching, when scratching the patient involuntarily tears off the covering of the vesicles, and then the phenomenon of “serous wells” occurs - these are depressions filled with serous discharge [6, 7].
Vesicles usually appear suddenly and are located symmetrically on the palms and soles [8]. The location of vesicles along the edges of the fingers or toes is characteristic of recurrent DE; if the vesicles are located predominantly on the very surface of the palms or soles, then this condition can be characterized as uncomplicated dyshidrosis (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. DE of the skin of the feet.
With frequent relapses accompanied by intense itching, lichenification (lichenification) occurs. The phenomenon of lichenification is characteristic of any area of the skin except the palms and soles [9].
When the acute process undergoes reverse development, some of the vesicles, especially those located more superficially, dry out, as a result of which brownish crusts form in place of the vesicles; upon palpation, a compaction is felt, reminiscent of a callus, sometimes with a recess in the center.
Typically, during the regression of the pathological process, the vesicles resolve within 1-3 weeks, which is often followed by a relapse and reappearance of the rash [4]. The number of elements during repeated spontaneous relapses, according to our observations, can be anything, even greater than during the primary manifestation. However, relapses that occur during successful treatment are usually characterized by a gradual decrease in the number of lesions with each relapse [8].
Differential diagnosis
dyshidrosis should be carried out with mycosis of the skin of the palms or soles, palmoplantar pustulosis, Andrews bacterid, atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis), punctate keratosis, acute phase of allergic contact dermatitis, bullous pemphigoid, in rare cases - with T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi's sarcoma [ 10].
Palmoplantar pustulosis
characterized by a monomorphic rash consisting of pustules against the background of an erythematous plaque with clearly defined boundaries; Often on the skin of other areas there are typical manifestations of psoriasis [11].
Nosological affiliation of the Andrews bacterium
(Fig. 3)
Rice.
3. Andrews Bacteride. a - pustular rashes on the palms without a tendency to merge; b - pustules on the palmar surface of the fingers. has not yet been determined. The disease manifests itself as multiple small pustules, usually round in shape, usually appearing in the central part of the palms or soles. Itching is not a constant symptom of this disease; it can be of moderate intensity or completely absent. In some cases, a pathomorphological examination is required to establish a diagnosis. With Andrews bacterid there are no typical psoriatic rashes, and the histological picture is typically characterized by a large spongiform pustule without significant changes around it. The correlation of rashes with exacerbation of chronic infections, mainly of the ENT organs, has been clearly established [12]. Atopic eczema
may manifest itself as vesicular rashes on the skin of the palms and soles during periods of exacerbation. The rash is usually accompanied by very intense itching. They are usually combined with symptoms of neurocirculatory (vegetative-vascular) dystonia: cold extremities, slight cyanosis, especially of the toes, poor tolerance of cold weather (below 0 °C) [7, 11].
Dyshidrotic rashes in idiopathic eczema
palms and soles clinically almost do not differ from those in atopic, with the only difference that they usually appear in adults or even elderly people, accompanied by clinical manifestations of dermatosis in other areas of the skin; the trigger mechanism is stress, endocrine diseases, intoxication [6, 8].
Bullous pemphigoid
- skin manifestations of this dermatosis are almost never limited to the area of the palms and soles. Moreover, in most cases, the rash begins on the torso, only then spreading to the limbs; represented by bullous elements. Bullous pemphigoid belongs to the group of non-acantholytic pemphigus, and IgG and complement fragment C3 antibodies are located at the dermal-epidermal border, along the basement membrane; the latter leads to detachment of the epidermis from the dermis [11].
Mycotic lesion of the skin of the soles
(and in some cases also the palms), as a rule, is accompanied by vesiculation. Vesiculation is characteristic of both the acute phase of the primary fungal disease and its exacerbation. The classic form of mycosis of the soles is a combination of dyshidrotic and intertriginous forms, when the rash is localized both in the center of the sole and along its edge, along the edge of the fingers and in the interdigital spaces. When localized in the area of the arch of the foot and along the edge of the sole, the vesicles are grouped, macerated, and form weeping surfaces surrounded by fragments of the epidermis [7]. Mycotic lesions differ from other forms of dyshidrosis in the severity of the process, the absence of a wave-like course, and the rapid addition of a secondary bacterial infection [9].
Isolated fungal infection of the interdigital spaces of the III-IV and IV-V toes should be differentiated from a peculiar epidermitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
) - punctate keratolysis; it is characterized by pronounced phenomena of maceration with detachment of the stratum corneum of the interdigital fold, sometimes with a light yellow or greenish tint to the scales (Fig. 4).
Rice.
4. Dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the skin of the feet. The mycelium of the pathogenic fungus is not detected in such cases. The diagnosis of the dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet must be confirmed by laboratory tests - detection of the mycelium of the pathogenic fungus (the detection of spores is not a diagnostically significant finding). The difficulty of laboratory diagnosis of such conditions lies in the phenomenon of lysis of the pathogenic fungus in areas of oozing, and it can be difficult to detect the mycelium of the fungus when taking scrapings from such areas. The fungus is more easily detected by scraping from a dry, flaky surface, usually close to the wet area.
The reverse development of rashes in the dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the soles is characterized by pronounced drying of the lesions, a rapid decrease in infiltration and, as a result, multiple cracks of varying depth and length, sometimes very painful. Especially often, such cracks occur due to irrational treatment of dyshidrotic mycosis, excessive use of drying agents and aerosols.
Treatment of dyshidrosis of the skin of the soles (palms) should strictly correspond to the phase of the process [13].
Systemic therapy for dyshidrosis and DE
Prednisolone is prescribed orally at a dose of 0.5-1 mg/kg per day with a gradual dose reduction over 7-14 days; Dexamethasone in tablets of 0.0005 g is prescribed at a starting dose of 3-4 tablets per day, followed by a gradual dose reduction after obtaining a stable clinical effect [4].
If the patient’s condition remains severe, dyshidrosis takes on a bullous character (pompholyx), and a persistent course of the process develops, then weekly use of small doses of metrotrexate (10-15 mg intramuscularly once a week) or azathioprine (at a starting dose of 100-150 mg/day) is possible for an adult, until a clinical effect is achieved, followed by a dose reduction to 50 mg/day); this dose will be considered maintenance, and the patient will take the drug for 3-5 months [13].
Systemic therapy with synthetic retinoids is effective for dyshidrosis and DE [6, 11].
If the patient’s condition allows one to do without systemic glucocorticosteroids (GCS), then systemic antihistamines are prescribed, preferably combined action (simultaneously blocking H1 receptors and stabilizing mast cell membranes - cetirizine, fexofenadine).
External therapy.
In the acute period, tannin lotions, Burov's liquid, oak bark decoction are used with a further transition to steroid creams (clobetasol propionate), then a transition to tacrolimus ointment 0.1% or to a medium-strength corticosteroid cream (Advantan). This stage lasts 3-4 weeks [4].
In the phase of chronic inflammation, external corticosteroids should not be used.
The duration of use of very strong topical corticosteroids (clobetasol propionate) does not exceed 2 weeks (due to severe local immunosuppression with the subsequent addition of a secondary bacterial infection). Clobetasol accumulates in the epidermis, creating a depot after the first application for 4 days, and by the end of the 2nd week, the entire area of application is colonized by Staphylococcus aureus [14].
In case of persistent DE, it is possible to use photochemotherapy - psoralen at a dose of 0.6 mg/kg is taken orally in tablets 2 hours before UV-A irradiation; In total, the course includes 20-30 sessions of photochemotherapy with irradiation of the palms and soles.
Dupilumab is a newer biologic recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults who have not achieved adequate control with existing standard treatments. G. Weston et al. [15] reported two cases of persistent DE that were successfully treated with dupilumab at a standard dosage.
If the professional nature of dyshidrotic rashes is determined, and it turns out that they are caused by the ingestion of nickel salts into the body, then taking disulfiram can help: it is prescribed at 200 mg/day for 8 weeks [16].
If the dyshidrotic process is caused by a fungal infection, then a diagnosis is made of the dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the soles or palms. The presence of a large number of vesicles indicates the acute nature of the process, which is an indication for combination therapy. Combined treatment is the treatment of mycosis with the simultaneous use of systemic and external drugs [6].
Systemic antimycotics are prescribed in the following dosages:
- terbinafine - adults 250 mg 1 time per day;
— itraconazole — 200 mg 2 times a day for 7 days.
The duration of treatment with a systemic drug is determined by the presence or absence of nail mycosis. With isolated skin lesions of the soles/palms and the absence of onychomycosis, the duration of treatment with terbinafine is 20-30 days; in the presence of onychomycosis - on average up to 160 days.
If itraconazole is chosen as a systemic drug, then the duration of treatment is determined by the number of weekly cycles carried out in accordance with the scheme described above: if the dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the palms or soles occurs in isolation without affecting the nails, then 1-2 cycles of itraconazole are sufficient to eradicate the pathogen (interval 21 days between cycles); if onychomycosis is present simultaneously with the skin lesion, then the duration of treatment can be 4-5 cycles with an interval of 21 days; for isolated onychomycosis of the hands, 3 cycles of itraconazole are usually administered with an interval of 21 days [9].
When choosing external therapy in accordance with modern rules for the treatment of skin infections, it is preferable that the systemic and external drugs match the chemical group, and even better if it is the same molecule.
Thus, in the combined treatment of mycosis of the feet with terbinafine, it is recommended to simultaneously prescribe drugs with this active substance externally and systemically; When treating mycosis of the feet with itraconazole (which does not have an external dosage form), it is recommended to use any external azole drug in the form of a cream.
If, as a result of examining the patient, it was possible to find out that the dyshidrotic process is caused by stress factors, then it should be borne in mind that usually in such cases the skin process proceeds from the very beginning as chronic DE and is accompanied in 2/3 of cases by neurocirculatory (vegetative-vascular dystonia). Such patients are recommended to consult a neurologist or psychiatrist [13].
In case of persistent neurocirculatory dystonia and, accordingly, persistent dyshidrosis, especially when the rash of blisters is not accompanied by severe itching, it is possible to use botulinum toxin preparations: the drug is administered intradermally in a dose of 100-160 IU. The toxin is capable of not only blocking facial muscles, but also, when used in the corresponding anatomical area in the form of injections, sharply reducing sweating (in the armpit, foot). The latter circumstance can be used to treat dyshidrosis. It is known that the number of vesicles (against the background of neurocirculatory dystonia) directly correlates with sweating activity [4].
External treatment
dyshidrotic lesions is a difficult task. And this is primarily due to the pronounced stages of the process. When starting treatment in the acute phase of the inflammatory process, we highlight the period of acute manifestations, when the fusion of opened vesicles forms a focus of weeping. In these cases, it is recommended to use aniline dyes - 1% aqueous solution of methylene blue, fucorcin in order to prevent infection. During this period, the use of aerosols of the “corticosteroid + antibiotic” type (even during a mycotic process) is justified in order to quickly, within a few hours, relieve the most acute phenomena.
In the next phase of the acute process, when weeping is no longer present, it is recommended to prescribe externally a combined drug of corticosteroid + antimycotic + antibiotic for 4-7 days, and only after the acute phenomena have stopped, switch to active external antifungal therapy.
When the skin process is transferred from acute to subacute, and then to the chronic phase of inflammation, a large number of cracks may appear, regardless of the etiology of dyshidrosis. And just in the subacute phase of the process, a transition is made from anti-inflammatory antifungal therapy (when combined corticosteroid + antimycotic + antibiotic creams are used) to antifungal therapy itself.
If there are a large number of cracks, creams containing epithelializing components are indicated - methyluracil, urea preparations, Shea butter, dexpanthenol, etc. [3].
The purpose of the study is to study the clinical effectiveness of Tetraderm
in the treatment of the dyshidrotic form of mycosis of the feet and DE.
Skin disease dyshidrotic eczema on the arms and legs - dyshidrosis: symptoms and causes
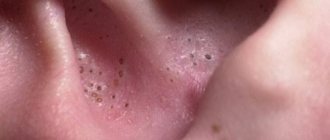
Dyshidrotic eczema is a chronic disease. It appears on the feet and palms in the form of small subcutaneous itchy blisters filled with fluid, which arise due to blockage of the sweat ducts. May also affect fingers and toes.
Usually the patient notices a new blister by chance: after scratching the itchy area, he discovers an unevenness on the surface of the skin.
Dyshidrosis of the hands
IMPORTANT: Blisters of dyshidrosis are located quite deep under the skin. The dimensions of the visible part of the visicles do not exceed 5–7 mm in width, and they are no more than 0.5 mm in height.
Elements of dyshidrosis can be collected in groups or appear singly. If several vesicles are located very close, they merge into one larger formation. The larger the bubble, the more painful it is and the longer it takes to heal.
Medium-sized vesicles “mature” for about 3 weeks. All this time, the skin in the affected area changes: it becomes dry, rough, flaky, and turns dirty yellow.
Dyshidrosis vesicle
IMPORTANT: When scratching or opening the blisters on your own, the disease may be complicated by the addition of a bacterial infection.
The cause of dyshidrosis may be:
- heredity
- decline in immunity
- metabolic disease
- regular exposure of the skin to allergens (detergents, cleaning products)
- endocrine diseases
- frequent stress and anxiety
- great fear
- increased sweating
- gastrointestinal diseases
- chronic infectious diseases “dormant” in the body
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and coffee
- long-term use of certain medications
- vegetative-vascular dystonia
- fungal skin infection
IMPORTANT: Dyshidrosis is a seasonal disease. It worsens in the warm season. It usually affects young people between 15 and 40 years of age. The disease is not contagious and cannot be transmitted through handshakes or in everyday life.
Dyshidrosis of the feet
Possible complications
When scratching or opening the rash on your own, there is a high risk of pathogenic microorganisms getting inside. This leads to an inflammatory process: the blisters turn into pustules. The liquid inside them loses its transparency, acquiring a yellowish color. The discomfort intensifies, severe swelling appears. In some cases, the patient experiences an increase in body temperature.
Other complications of hand dyshidrosis include panaritium and lymphangitis: purulent inflammation of the finger and lymphatic vessel, respectively. In the latter case, a painful cord forms under the skin.
Types of dyshidrosis: dry lamellar, allergic
A type of dyshidrosis is dry lamellar dyshidrosis. Its difference is that bubbles filled with liquid do not develop under the skin, but the patient’s palms and feet are covered with flaky skin, which can be removed in layers.
IMPORTANT: Treatment of dry lamellar dyshidrosis has its own characteristics and should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Allergic dyshidrosis occurs as a result of an increase in allergy levels. It manifests itself in a standard way for dyshidrosis: bubbles appear suddenly, in an “attack.” They itch and cause discomfort. It often begins after contact of the skin of the hands with low-quality cleaning agents and detergents.
IMPORTANT: Taking antihistamines will help relieve the symptoms of allergic dyshidrosis.
Dry lamellar dyshidrosis of the hands
Main symptoms
The first signs of the disease are a slight burning sensation, tingling sensation and a desire to scratch the palms, the skin on which changes its normal temperature, becoming much warmer, and the skin swells.
After a short time, small, match-shaped tubercles—vesicles—that are dense to the touch form in the deep layers of the dermis. A clear liquid is visible inside them.
We recommend reading: Treatment of bedsores in bedridden patients and the elderly
Treatment of dyshidrosis with drugs, ointments
Treatment of dyshidrosis is prescribed only after determining the cause that caused it:
- If the disease “gains momentum” in the hot season and is explained by increased sweating of the patient or confirmed vegetative-vascular dystonia , an atropine solution (0.1 – 0.25%) is used for its effective treatment. The drug is used for 12 days, starting with 4 drops. Every day the dose increases by 1 drop, then decreases. Novocaine (0.5%) is taken orally three times a day before meals
- When the cause of the development of dyshidrosis is nervous shock , the main drugs in therapy are sedatives: valerian, motherwort, peony tincture, St. John's wort and others
- If dyshidrosis is caused by fungal diseases , then they are treated first, and only after that, if necessary, dyshidrosis itself
- For allergic dyshidrosis, long-term use of antihistamines and adherence to a hypoallergenic diet are prescribed. Of course, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the allergen
Local treatment for any of the above types of dyshidrosis consists of using baths with string, chamomile, St. John's wort, black and green tea for the hands and feet.
IMPORTANT: Before placing the affected limb in the decoction, the bubbles are pierced and treated with medical alcohol.
Dry lamellar dihidrosis is treated with ointments: dermatol (5%) and ichthyol (5%), boric alcohol and retinol.
Ichthyol ointment is used to treat dry lamellar dyshidrosis
IMPORTANT: When treating any form of dyshidrosis, you should be patient. The disease may not respond to treatment for some time and may recur.
Often, complex treatment of dyshidrosis includes physiotherapeutic procedures, such as:
- electric shock treatment
- ozone therapy
- laser cauterization
- ultraphonophoresis
Folk recipes
In the complex treatment of skin pathologies, in particular dyshidrosis, “old-fashioned” methods can also be used. Before using folk recipes for this category of patients, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist.
This is due to the fact that many medicinal herbs have contraindications, so it is extremely important to determine before starting treatment whether they can be used by the patient
If the patient does not have individual intolerance to medicinal herbs, then they can use the following recipes when carrying out complex therapy for dyshidrosis:
- You can take baths with herbal infusions. Chamomile inflorescences, sage grass or strings are excellent for these purposes. You should pour a mixture of these medicinal plants (6 tbsp) into a saucepan and pour boiling water (1 l) over it. After this, place the container on low heat and bring its contents to a boil. Next, remove the saucepan from the stove and cool. The liquid that has been infused for half an hour must be filtered and its volume brought to 3 liters.
- Experts recommend making baths from a decoction of oak bark. To prepare it, you need to take a saucepan, pour oak peels (5 tbsp) into it, and pour boiling water (1 l) over them. The contents of the container must be brought to a boil over low heat, then simmer for 20 minutes. The mixture should infuse for 30-35 minutes, after which it should be strained.
Preventive actions
People who have encountered this skin pathology should carry out its prevention, which will prevent relapses:
- Experts recommend that patients follow a daily routine.
- You should find time for proper rest.
- Patients should minimize stressful situations.
- When contacting household chemicals, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment.
- You need to take vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Cosmetics used by patients must be of high quality and contain natural ingredients.
Dyshidrosis is characterized by damage to the human skin; the disease is especially pronounced on the arms, palms and fingers, legs and soles of the feet.
The cause of its occurrence is obstruction of the sweat glands.
As a result, the skin becomes covered with blisters that itch and hurt. When the blisters open, crusts and cracks form, and open wounds can become infected.
When making a diagnosis, other dermatological diseases that have similar signs and symptoms must be excluded.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively, and physiotherapeutic methods are widely used.
Correct diagnosis, early therapy and regular prevention help to completely get rid of the problem and eliminate the risk of relapse.
Zinc ointment for the treatment of dyshidrosis
Zinc ointment consists of zinc oxide diluted with petroleum jelly in a ratio of 1:10. Due to its anti-inflammatory, drying and astringent properties, it is widely used to treat various skin diseases, including dyshidrosis.
IMPORTANT: Zinc ointment, applied in a thin layer to damaged areas of the skin after hygiene procedures, will relieve irritation, relieve itching, and have a drying effect. You can use the ointment up to 4 times a day.
Zinc ointment for the treatment of dyshidrosis
Medicines
Photo: med-look.ru
A skin pathology accompanied by the appearance of blisters with fluid is called dyshidrosis or pompholyx. The disease is painful with constant itching of the hands and feet. The skin disease is not contagious and is mostly chronic. Therefore, patients register at the dispensary and are observed by a doctor. Treatment of dyshidrosis is rather symptomatic, aimed at eliminating external manifestations on the skin. It must be comprehensive, only in this case there is a chance of recovery. Therapy is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the nature of the disease and its stage.
Drugs to combat skin disease
Complex treatment of the disease involves undergoing various types of therapy. At the same time, the patient must take medications prescribed by the attending physician. The patient is prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antihistamines;
- hyposensitizing drugs;
- glucocorticosteroid drugs (in severe forms).
The affected areas of the skin are treated with various antipruritic, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic ointments and creams. These drugs include:
- triderm;
- diprosalic;
- advantan;
- zinc ointment;
- salicylic ointment.
Ointments are prescribed for the normal course of the disease, its dry form, secondary manifestation, and at the exfoliation stage.
Triderm for dyshidrosis
The drug is available in the form of a cream or ointment. It is an excellent antimicrobial agent. The antibiotic gentamicin included in the composition is absorbed into problem areas of the skin when applied. It has a systemic effect. The drug is highly effective for all forms of eczema, dermatitis, lichen, and dermatomycosis.
The cream is applied to the surface of the affected areas twice a day in the morning and evening. Triderm should be used daily as prescribed. This medicine has its contraindications, so you should carefully read the instructions before use.
Diprosalik
Like Triderm, Diprosalik is a combination drug. It contains substances such as salicylic acid and betamethasone dipropionate. The ointment has an anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, vasoconstrictor effect. Prescribed for people of any age group, starting from two years. The ointment is used twice a day in the morning and evening. Apply the drug to the affected areas in a thin layer. Diprosalic is not recommended for use if there is increased sensitivity of the body to any substance included in the composition. Reviews from patients using Diprosalic for dyshidrosis indicate that the medicine copes well with the disease in the initial stages of its manifestation.
Advantan for dyshidrosis
Itching, pain and irritation are effectively suppressed by Advantan. Available in the form of ointment and cream. Apply externally once a day. The course of treatment is no more than 14 days. Medical practice shows that Advantan is widely used in dermatology for the treatment of severe forms of pathologies. The ointment is contraindicated in children under 4 years of age.
The instructions indicate precautions and contraindications that should be strictly observed.
Zinc ointment
Zinc ointment is an anti-inflammatory agent that has been known since ancient times. This is a simple and effective remedy for many inflammatory skin diseases. The ointment contains zinc oxide. You can purchase the drug at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.
The effect of zinc ointment for dyshidrosis is aimed at reducing irritation, drying out skin areas, and reducing inflammation. Apply to damaged skin two to three times a day with light movements. Before use, you must read the instructions for use. The medicine has no contraindications, but long-term use can cause allergic reactions.
Salicylic ointment
It is used for the dry form of dyshidrosis or the exfoliation stage. Has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. The correct effect in treatment is achieved when used according to the instructions. Ointment for dyshidrosis is applied to the affected skin 1-2 times a day. To improve the result, apply a sterile napkin on top. The course of use of the drug depends on the stage of the disease, but it should not exceed 21 days. Salicylic ointment has contraindications, so you need to read the instructions.
It is not recommended to treat dyshidrosis on your own. Each drug should be selected by a dermatologist. The doctor prescribes medicine depending on the stage of the disease and its course.
Treatment of dyshidrosis folk remedies
In almost all folk recipes for dyshidrosis, celandine juice is an obligatory component.
Recipe No. 1. Mix 0.5 tsp. homemade full-fat sour cream with 7 drops of celandine juice. Apply to cleansed, affected skin of the hands and feet 2-3 times a day for a few minutes, then rinse with warm water.
Recipe No. 2. Add 10 drops of celandine juice to a strong chamomile decoction (100 g). Wipe your palms with this product several times a day.
Recipe No. 3. Open the bubbles of dyshidrosis and thoroughly treat with alcohol tincture of calendula. After they dry, apply a mixture of aloe juice and celandine juice (1:1) to each of the bubbles, trying to get as deep as possible.
It can also be used in its pure form. To do this, each individual element of dyshidrotic eczema is “cauterized” with the juice released from the cut stems of a fresh celandine plant. First, the bubbles are carefully opened with a thin, sharp needle treated with alcohol.
Celandine juice is used to burn dyshidrosis blisters
IMPORTANT: When using celandine juice, difficult to remove yellow-brown stains remain on the skin.
The most famous drugs in therapy
The options for ointments used in the treatment of the disease are very diverse, however, the choice of drug should be approached responsibly: dyshidrosis can occur in different ways and a medicine suitable for one form of the disease will be contraindicated for another.
The most commonly used means in this case:
- Levomekolev ointment: suppresses inflammation in the skin, contains a strong antibiotic that creates a powerful barrier to infection.
- Tetracycline: recommended for use in case of secondary infection, in the presence of deep wounds, severe itching.
- Amyclone: an antifungal drug used for mycoses of the dermis.
- Zinc: suppresses the activity of pathogenic bacteria in skin cells, has a drying, disinfecting effect.
You may be interested in an article about the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis.
You can also read an article about thyroid treatment.
You can learn about the treatment of pityriasis rosea in humans in this article.
Baths for dyshidrosis
Baths with medicinal herbs help reduce the symptoms of dyshidrosis, relieve itching and relieve swelling. For dyshidrosis, the following are effective: string, sage, chamomile, yarrow, calendula, valerian root, St. John's wort and oak bark.
To prepare the decoction, take 10 tsp. dry pharmaceutical herb , place in an enamel bowl, pour boiling water ( 0.5 l ) and place on low heat for 5-10 minutes . As soon as the broth has cooled a little, use it as a bath, placing limbs damaged by dyshidrosis in it until the liquid cools completely.
Baths for dyshidrosis relieve itching and relieve swelling
What is the difference between dyshidrosis and dyshidrotic eczema?
The difference between these two diseases is visible in the symptomatic manifestations:
- With true dyshidrosis, blisters form only on the palmar surface of the hands. The rash lasts up to 10 days, then the blisters dry out and subside. When the covers of dried blisters are damaged, superficial erosions form and moderate pain occurs.
- In the case of dyshidrotic eczema , swelling, a blistering rash occurs, and the number of blisters increases. After a few days, the covers of the bubbles open and weeping begins. The temperature often rises, the area of the rash swells, itches and hurts.
Treatment of dyshidrosis in children
Treatment of dyshidrosis in children has one peculiarity: children will most likely scratch the itchy rashes, so it is unlikely that it will be possible to avoid the addition of a bacterial infection. The therapy will include an antibacterial ointment.
In any case, before starting treatment, it is necessary to find out the cause of dyshidrosis.
- Dyshidrosis usually affects the skin of the palms and feet in children in cases of severe decline in immunity or is a kind of allergic reaction of the body.
By improving your health or eliminating the effect of the allergen, you can prevent new rashes, and with the help of ointments and herbal baths, you can speed up the healing process of existing ones.
- If dyshidrosis affects the delicate skin of a breastfed , the mother should reconsider her diet. Most likely, the reason lies in her poor diet.
IMPORTANT: In adolescent children, dyshidrosis can develop against the background of strong experiences. In this case, sedatives will help.
Dyshidrosis in a breastfed infant can be a consequence of poor nutrition of the mother
Course of the disease
Every day, the tubercles change their appearance: merging into a common mass, opening spontaneously, they provoke the occurrence of unpleasant painful sensations.
The skin of the palms peels off, cracks, becomes rough, and erosions form.
At the same time, the patient’s well-being worsens, since these phenomena are very painful. When they open, the tubercles can become infected and fester. A concomitant symptom is enlarged lymph nodes in the armpits.
As the disease progresses, symptoms can become severe:
- general deterioration of health, depression;
- dizziness, migraine;
- lack of appetite;
- the occurrence of lymphangitis;
- high body temperature.
These signs are characteristic of an advanced case - when the disease has progressed to the eczematous stage, which is very dangerous for the patient’s health.
Throughout the entire cycle of dyshidrosis, careful observation by a specialist, regular examinations, treatment procedures and relevant tests are necessary. The attending physician will help monitor what stage the disease is at and prevent the occurrence of associated complications.
Treatment of dyshidrosis during pregnancy
The doctor treats dyshidrosis in pregnant women with extreme caution. After determining the cause of the disease, he prescribes only those drugs that will not harm the health of the unborn child.
The use of antihistamines is mandatory. You can relieve itching and swelling with zinc ointment and herbal baths.
IMPORTANT: Pregnant women should not try to treat dyshidrosis on their own, as the wrong medications can only worsen the situation.
Treatment of dyshidrosis in pregnant women should be under the supervision of a doctor.
To successfully get rid of dyshidrosis, drug treatment alone is not enough. It is important for patients to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition, or at least exclude spicy, fried, smoked and salty foods from the diet. You should also be careful when consuming coffee, chocolate, honey, berries, eggs, citrus fruits and dairy products.
Rules for applying ointments
When using ointments, you must adhere to certain recommendations:
- Before manipulation, clean the affected area. In this case, the wound can be washed with Chlorhexidine. Wash and disinfect hands.
- A little ointment is evenly distributed on a sterile napkin. Sometimes it will be more effective to apply the drug using your fingers.
- Cover the affected area of the skin with a napkin.
- You must wait until the ointment is absorbed. Do not rub or rub in the medicine. Such movements can damage the top layer of inflamed skin.
What products can
With dyshidrosis, the most important thing is the timely removal of toxins from the body, because cleansing the body is one of the conditions for recovery. For this purpose, drugs are prescribed - sorbents, but no less important is the good functioning of the digestive tract, which is facilitated by a diet rich in fiber.
- Pasta from durum wheat;
- Dairy products, preferably low-fat (kefir, sour milk, cottage cheese, natural yogurt);
- Sunflower oil.
- Vegetables;
- Vegetarian soups;
- Lean meat (veal, poultry) in limited quantities;
- Various oatmeal (except semolina), boiled in water;
- Fresh cucumbers, salads;
- Boiled or baked potatoes;