December 5, 2020
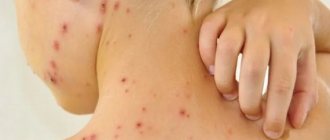
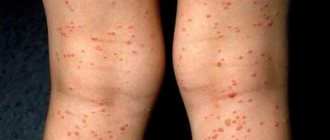
Most infections are caused by streptococci and staphylococci. They live in the environment, inhabiting the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and genitals. In 9–12% of cases, inflammation is provoked by corynebacteria, leprosy bacilli, tuberculosis, and campylobacter.
Healthy skin keeps germs out. This is prevented by the structure of the epidermis, the pH of sweat and sebum, and the antiseptic properties of the secretion of the sebaceous glands. When protection is violated, pustular rashes occur.
Superficial bacterial skin infections
Folliculitis
- inflammation of the hair follicle: abscess around the hair, redness of the surrounding area.
Pemphigus of newborns
- a severe contagious disease when inflammatory blisters cover the baby’s entire body, forming crusts and ulcers.
Impetigo
- against the background of redness, painless blisters with cloudy contents appear. Then the blisters shrink to yellowish crusts, leaving erosions.
Impetigo often occurs in children and young women. Localization: face, under the hair of the head, limbs. When staphylococcus attaches, the crusts become greenish or bloody. The disease spreads quickly in communities. If you suspect it, you need to isolate the child and bandage the wound.
Sores in the mouth as a sign of aphthous stomatitis
Wounds in the mouth can arise as a result of the development in a person of a separate independent disease of the oral mucosa, caused by the growth and development of pathogenic microorganisms. But, in addition, the cause of such wounds may also be hidden in the general somatic condition of an adult or child.
In most cases, mouth ulcers are symptoms of a disease such as canker sores. Stomatitis is a lesion of the human oral mucosa that occurs as a result of an atypical reaction of the immune system to foreign irritants. Depending on the nature and causes of the disease, stomatitis can be of various types: ulcerative, herpetic, allergic, vesicular, etc. But people most often have to deal with the aphthous form of this disease.
Let's name the main symptoms of aphthous stomatitis:
- The appearance of round ulcers (ulcers) in a person’s mouth, which are grayish in color and surrounded by a red, inflamed rim. Ulcers are located either separately or in groups and have different sizes.
- Painful sensations in the affected areas of the upper and lower palate of a person that occur during eating, drinking, or talking.
- Deterioration of a person’s general well-being, weakness.
- Temperature increase. But this is not a mandatory symptom; it occurs in most cases in children, since they are more difficult to tolerate aphthous stomatitis in the oral cavity.
- Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes. This symptom of aphthous stomatitis also occurs more often in children than in adults.
Bacterial infection of the deep layer of skin
Occurs when microbes enter deep into the dermis.
Furuncle
First, a painful node appears, then an abscess matures in its center. After 5–7 days it opens, a purulent-necrotic core is released, and the wound is scarred. When there is more than one lesion, they speak of furunculosis.
Carbuncle
These are several boils united into a common infiltrate. The place looks like a purple-bluish tumor. Pain increases, well-being suffers, body temperature rises. After opening the formation, a deep ulcer remains, healing with a scar.
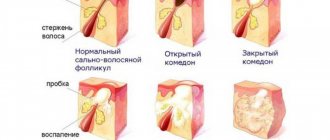
Acne (blackheads)
- inflammation of the sebaceous gland ducts due to blockage. Pustules form on the face, chest, and shoulders. Their contents dry out to crusts, after which, when rejected, scars or bluish spots remain.
Hidradenitis
Purulent inflammation of the sweat glands. The process often recurs. Favorite localizations are armpits, inguinal folds, under the mammary glands. Deep painful nodes appear, bluish-red on the outside. They are opened with the separation of liquid pus.
Erysipelas
Occurs in people who are individually predisposed. Foci of inflammation are clearly limited. The affected area is swollen, hot, bright red, with bursting blisters. The disease is accompanied by fever, intoxication, and severe pain.
Deep pyoderma can be complicated by inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and nodes, abscess, and sepsis.
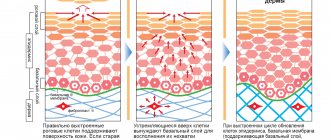
Fast wound healing
CONDITIONS
- The wound must be clean, free of foreign matter, dirt, particles, and non-viable tissue;
- The wound should not be infected;
- The wound should not remain open and in contact with the environment;
- Healing should occur in moderately
moist environment.
And now, in order: Condition of the wound.
It should not contain foreign particles, dirt, or non-viable tissue.
Any dirt, clotted blood and pus must be removed, that is, the wound must be treated and washed. Hydrogen peroxide, saline solution, or, in extreme cases, just clean water will do. If the wound is chronic, poorly healing with a dry, poorly detachable bottom (eschar), it is necessary to use a special gel ( Fibrogel Ag
or
Intrasite gel
) in combination with a secondary absorbent dressing (Allevyn Adhesive, Non Adhesive), or in combination with a breathable film dressing (Opsite FlexiFix , Opsite Flexigrid). However, if you have a deep chronic wound, we recommend that you first seek help from specialists.
Presence of infection.
The presence of an infectious process in the wound negatively affects the healing process.
If measures are not taken, the wound may become chronic, as a result of which the healing process may take a long period. It has long been proven that silver has a pronounced antibacterial effect, due to which the use of silver-containing dressings significantly helps to block the growth of bacteria and the development of infection in the wound. If there is an infectious process, it is necessary to use a bandage with silver nanocrystals (Acticoat or Acticoat 7); Neofix Fibrotul Ag
. Matching headbands are here.
Closing the wound.
The wound must be protected from environmental influences and infection. If the wound is small, an abrasion or a scratch, it is enough to treat it with a special film spray (Opsite Spray) or cover it with a breathable film bandage (Opsite FlexiFix, Opsite Flexigrid). The dressing for wounds of medium size and depth should be sterile, impervious to moisture and microorganisms from the outside, and also facilitate the absorption of exudate and removal of excess moisture (Neofix Post, Opsite Post Op, Opsite Post Op Visible).
Humid environment.
It was previously believed that for a wound to heal quickly, it should be as dry as possible, but modern experience shows that for successful and rapid wound healing, a moderately moist environment must be maintained in it. In a humid environment, enzymes and growth factors are most active and cell growth and reproduction are more active, but excess moisture must be removed. Optimal moisture in the wound is maintained with breathable patches (Neofix Post, Opsite Post Op, Opsite Post Op Visible) when there is little exudate, or sponge dressings when there is a lot of discharge (Allevyn Adhesive, Non Adhesive).
WHAT TO DO?
- Assess the wound. Large, deep, bitten, scalped, lacerated wounds and wounds with heavy bleeding require qualified medical care; self-medication in this case is dangerous.
- Clean the wound - rinse with hydrogen peroxide, it will help remove small foreign objects, particles of dirt, non-viable tissue, and blood clots from the wound. If there is no hydrogen peroxide, then you can simply wash the wound with water or saline;
- Treat the edges of the wound. In this case, iodine or a solution of brilliant green (brilliant green) is suitable. To prevent wound infection, you can use a silver-containing dressing, Neofix Fibrotul Ag, fixing it on the wound with a patch or film type bandage (Opsite FlexiFix, Opsite Flexigrid);
- You can also simply cover the wound after treatment with a non-stick, breathable, moist dressing. Or a patch with the same properties. In this case, any adhesive bandage on a non-woven or film base (Neofix Post, Opsite Post Op) is suitable.
If the wound is small, then you need to do the following:
CONCLUSION OF WOUND EDGES
For additional fastening of the edges of a sutured wound, as well as for bringing together the edges of an incised wound after treatment, you can use LEUKOSTRIP adhesive strips. They reliably fix the edges of the wound, allow air to pass through, and remove excess moisture.
SUPERFICIAL WOUNDS, EXTENSIVE Abrasions
To ensure healing of a superficial wound, non-adhesive mesh dressings containing paraffin (Jelonet) are used as the primary wound covering. If there is a risk of wound infection, as well as to prevent infectious complications, a mesh dressing containing soft paraffin and an antiseptic (Bactigras) can be used as a primary wound covering. To remove excess fluid (exudate), an absorbent secondary layer is applied over the mesh bandage - a sponge bandage (Allevyn Adhesive, Allevyn Non Adhesive). Fixation can be achieved using a breathable film bandage (Opsite Flexifix, Opsite Flexigrid).
WOUNDS ON THE FACE
Wounds on the face require a special approach, since wound healing should lead to minimal cosmetic defects. For additional reduction of the edges of the wound, if the wound is sutured, or as a primary dressing, you can use special adhesive strips - strips (Leukostrip). The range of leading manufacturers of plasters includes a large number of simulated bandages (cut to size), with which you can carefully close the wound. If a scar has formed after healing, you can use a special silicone bandage that is designed to reduce and eliminate scars (Cica-Care). You can buy Cica-Care silicone patch here.
POST-OPERATIVE WOUNDS
We recommend covering postoperative wounds with specialized dressings. The structure of the dressing provides a favorable environment for healing and its painless change when dressing. Thanks to the inner layer, the bandage is securely fixed to the skin, but later it can be easily and painlessly removed. The middle, absorbent layer, consisting of viscose or polyurethane foam, ensures quick and reliable removal of exudate. The outer film or non-woven layer ensures rapid and constant evaporation of excess moisture. Among non-woven based dressings, we recommend using Neofix Post and Primapore. Among film-based dressings, Opsite Post Op and Opsite Post Op Visible have proven themselves to be excellent.
PURPUS WOUNDS
The presence of pus in the wound indicates that an infectious process has begun. Treatment of purulent wounds, especially large and deep ones, requires qualified medical care and an integrated approach. For such a case, we can recommend the following dressings: - For cleaning a wound with a dry, poorly detachable bottom (scab), or in the presence of a dense fibrin film at the bottom of the wound, hydrogel (Intrasite Gel) has proven itself very well. It must be applied to the surface of the wound, and then covered with a secondary film or sponge bandage. After 48 hours, the wound needs to be washed and cleaned. — For the treatment of purulent wounds, dressings with silver nanocrystals (Acticoat and Acticoat 7) have proven themselves to be excellent. Silver, acting as an antiseptic, is released gradually, providing a long-lasting and permanent effect. Acticoat dressing can be left on the wound for up to 3 days, Acticoat 7 for up to seven days. These dressings are primary; after application to the wound, they must be covered with a secondary absorbent dressing. Before use, silver-containing dressings must be moistened with distilled water or water for injection. Go to CATALOG OF BANDAGES
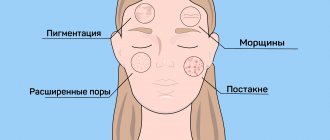
Features of facial skin infections
The blood supply to the organs of the head, face, and membranes of the brain is closely connected. Incorrect treatment and squeezing of pimples is dangerous due to the spread of bacteria through the blood and lymph. You can achieve an increase in the area of the affected area, such dangerous complications as meningitis, abscesses and phlegmon, and inflammation of the eyes.
Before deciding on cosmetic procedures - cleansing, peeling, mesotherapy - undergo an examination by a dermatologist to determine the cause of the pustular rash and receive treatment.
Treatment of bacterial skin infections
It should start from the early stages and be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. In some cases, local treatment with antibacterial ointments and wiping with antiseptics is sufficient. Widespread rashes, deep pyoderma, require the prescription of systemic antibiotics. In chronic cases, the doctor may recommend autohemotherapy and immune drugs.
Surgical treatment is carried out if the abscess does not open on its own or if a rough scar must be avoided. Laser coagulation and physiotherapy are used to restore tissue.
It is important to identify and treat concomitant diseases, eliminate adverse external effects on the skin, and select nutrition.
Why does aphthous stomatitis occur?
As noted above, the causes of aphthous wounds in a person’s mouth can be both local and general somatic in nature. Let's look at the main ones.
Local causes of aphthous stomatitis:
- Mechanical damage to the human oral mucosa. Such injuries occur as a result of a person eating hard and tough foods. Often, even a small scratch on the roof of the mouth can cause aphthous stomatitis.
- Thermal lesions of the human oral mucosa. The occurrence of wounds and the development of aphthous stomatitis in this case provoke burns of the mucous membrane, which a person could receive by consuming hot drinks or food.
General somatic causes of wounds in the human oral cavity:
- Heredity factors. The predisposition to the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis in the mouth may be determined by genetic reasons. Therefore, there is a risk of developing this disease and the manifestation of a chronic form of stomatitis (when ulcers on the mucous membrane appear regularly) in people whose parents also suffered from this disease.
- Somatic diseases. Aphthous stomatitis often develops in people who suffer from any secondary somatic diseases. For example, these could be diseases of the digestive system and gastrointestinal tract.
- Weak immunity. For this reason, children are susceptible to oral ulcers because their immunity is not yet fully developed. In a child, aphthous stomatitis is more severe than in an adult and is accompanied by an increase in temperature and a deterioration in general well-being. Against the background of colds, immunity is also often reduced, and aphthous stomatitis occurs in the person’s mouth.
- Avitaminosis. With an incorrect diet, a person does not receive enough substances necessary for the successful functioning of the body. Due to a lack of vitamins C and B or microelements such as selenium, folic acid, zinc or iron, in some cases aphthous stomatitis occurs in a person’s mouth.
- Allergy. An allergic reaction associated with eating foods such as citrus fruits, nuts (especially peanuts), chocolate, red berries (strawberries, wild strawberries) or foods containing gluten (cereals, pasta) in some cases leads to the appearance of canker sores. wound in a person's mouth.
- Stress. When a person finds himself in a stressful situation, he spends significant resources to cope with the current problem. This leads to a loss of strength, decreased immunity and a general weakening of the body, as a result of which wounds form in the person’s mouth and he develops aphthous stomatitis.
Prevention
Observe the following rules:
- After visiting the gym, wipe the areas that came into contact with the equipment with an antiseptic.
- Treat cuts and wounds with antibacterial drugs (iodine, salicylic alcohol, hydrogen peroxide) immediately after they occur.
- Do not share hygiene items or cosmetics with other people.
- Places of abscesses and impetigo should not be washed with water, combed, or pressed.
- Avoid spicy fatty foods and sweets.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist on time.
The doctor will help you identify the cause of the inflammation, do the necessary tests, and select a treatment that suits the type and stage of pyoderma. December 5, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
How to get rid of sores in the mouth?
Stomatitis wounds that occur in the human mouth, in most cases, heal on their own within 7-10 days after formation. But timely treatment of aphthous stomatitis is necessary in order to prevent the formation of ulcers on the human oral mucosa again. The fact is that the acute form of stomatitis, which is characterized by the sudden appearance of wounds of various sizes on the upper and lower palate in a person’s mouth, if the problem is ignored or the wrong treatment is carried out, tends to develop into a chronic form of the disease. Wounds in the oral cavity with chronic stomatitis appear periodically and bother a person from time to time throughout life.
To exclude the possibility of aphthous stomatitis ulcers reoccurring, dentists perform the following treatment:
Local therapy
. It involves treating wounds on the oral mucosa with antiseptic agents: gels, ointments or sprays. During this treatment of stomatitis, a person is prescribed daily rinses with solutions such as furatsilin, chlorhexidine, miramistin, etc.
General therapy.
It includes a set of measures to cure this disease and at the same time strengthen the body. To strengthen the body, the doctor prescribes immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin courses to the person. To combat aphthous stomatitis, different drugs are used, depending on the nature of the disease and the causes of its occurrence: antihistamines, antivirals, steroids or antibiotics.
The selection of funds for the treatment of wounds with aphthous stomatitis is carried out only by a doctor and occurs after a visual examination of the person’s oral cavity, conducting the necessary diagnostic tests and making a diagnosis. The LeaderStom Clinic offers to use the services of our experienced doctors to carry out these operations.