December 5, 2020
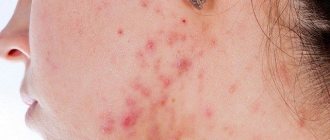
Most infections are caused by streptococci and staphylococci. They live in the environment, inhabiting the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and genitals. In 9–12% of cases, inflammation is provoked by corynebacteria, leprosy bacilli, tuberculosis, and campylobacter.
Healthy skin keeps germs out. This is prevented by the structure of the epidermis, the pH of sweat and sebum, and the antiseptic properties of the secretion of the sebaceous glands. When protection is violated, pustular rashes occur.
Superficial bacterial skin infections
Folliculitis
- inflammation of the hair follicle: abscess around the hair, redness of the surrounding area.
Pemphigus of newborns
- a severe contagious disease when inflammatory blisters cover the baby’s entire body, forming crusts and ulcers.
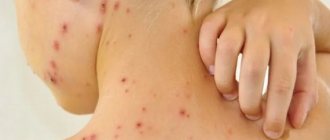
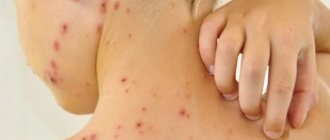
Impetigo
- against the background of redness, painless blisters with cloudy contents appear. Then the blisters shrink to yellowish crusts, leaving erosions.
Impetigo often occurs in children and young women. Localization: face, under the hair of the head, limbs. When staphylococcus attaches, the crusts become greenish or bloody. The disease spreads quickly in communities. If you suspect it, you need to isolate the child and bandage the wound.
Herpes simplex
Herpes simplex (lichen simplex) - most often appears as grouped blisters on a reddened area of the skin. Routes of transmission: contact (sexual) and airborne droplets. Approximately 90% of the world's population are virus carriers. However, not all of them have clinical manifestations.
At birth, antibodies are passively transferred from the mother to the child, which usually disappear by the 3rd year of life, and the child becomes susceptible to infection by the virus. Typically, in 80-90% of cases, primary infection occurs unnoticed and occurs without clinical symptoms, but sometimes pronounced manifestations of the disease are observed - primary herpes.
After the disappearance of the clinical symptoms of primary herpes or after a period of its asymptomatic course, the infection passes into a latent form, when the virus is in an inactive state. At this time, antibodies to the herpes virus appear in the blood, despite the presence of which, under the influence of various provoking factors (colds, stress, hypothermia, etc.), relapses of the disease occur, the intervals between which range from several days to several months and even years. People suffering from frequent relapses of the disease, if even minimal sensations occur, can themselves predict the appearance of rashes in the near future.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of blisters on a swollen, reddened background. The blisters can persist from several hours to several days, then the blisters turn into erosions that can become crusted. Often the appearance of rashes is accompanied by itching, enlargement of lymph nodes, and their pain. Often a new repeated attack is accompanied by headache, malaise, and dysfunction of the digestive tract. In women, relapses of herpes can have a clear connection with the menstrual cycle, usually occurring before the start of each menstruation.
Bacterial infection of the deep layer of skin
Occurs when microbes enter deep into the dermis.
Furuncle
First, a painful node appears, then an abscess matures in its center. After 5–7 days it opens, a purulent-necrotic core is released, and the wound is scarred. When there is more than one lesion, they speak of furunculosis.
Carbuncle
These are several boils united into a common infiltrate. The place looks like a purple-bluish tumor. Pain increases, well-being suffers, body temperature rises. After opening the formation, a deep ulcer remains, healing with a scar.
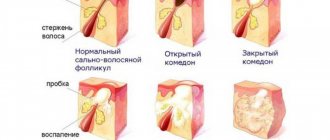
Acne (blackheads)
- inflammation of the sebaceous gland ducts due to blockage. Pustules form on the face, chest, and shoulders. Their contents dry out to crusts, after which, when rejected, scars or bluish spots remain.
Hidradenitis
Purulent inflammation of the sweat glands. The process often recurs. Favorite localizations are armpits, inguinal folds, under the mammary glands. Deep painful nodes appear, bluish-red on the outside. They are opened with the separation of liquid pus.
Erysipelas
Occurs in people who are individually predisposed. Foci of inflammation are clearly limited. The affected area is swollen, hot, bright red, with bursting blisters. The disease is accompanied by fever, intoxication, and severe pain.
Deep pyoderma can be complicated by inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and nodes, abscess, and sepsis.
Viral skin diseases
HERPES VIRAL DISEASES
Viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae (from the Greek herpes - creeping) are capable of causing dangerous infections, recurrent diseases, transplacental infections with the occurrence of congenital deformities, and potentially lethal lymphoproliferative diseases.
Of the more than 100 herpesviruses currently described, 8 cause human disease: herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV 1), herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV 2), varicella zoster virus (VZV), human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), Epstein-Barr (EBV), human herpesviruses type 6 (HHV 6) and type 7 (HHV 7) (isolated in HIV-infected people), type 8 (HHV (causes Kaposi's sarcoma).
Etiology.
Herpes simplex viruses are large DNA genomic viruses. The size of the virion can vary significantly (from 120 nm to 300 nm). The virion consists of 4 main structural elements: 1 - a core containing linear double-stranded DNA and shaped like a torus; 2 - capsid surrounding the core and including 162 capsomeres; 3 - tegumeite, located between the capsid and the virion envelope; 4 - a three-layer shell containing numerous projections or spines. Virus replication occurs relatively quickly and requires about 18 hours.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS OF HSV INFECTION.
Herpes simplex, herpes zoster of the skin and mucous membranes, is the most common disease in the population. There are primary, initial, recurrent and asymptomatic PG.
The herpetic process goes through 4 successive stages: 1) erythematous, 2) vesicular, 3) cortical/erosive, 4) clinical recovery, the total duration of which is on average 7-14 days.
According to clinical and morphological manifestations, genital herpes is divided into 4 types:
- first clinical episode of primary PG (primary herpes);
- first clinical episode with existing PG (initial herpes);
- recurrent HH (RGH);
- asymptomatic GG.
LABORATORY DIAGNOSTICS OF HSV INFECTION
Laboratory diagnosis of diseases caused by HSV includes a set of methodological approaches, the purpose of which is to detect markers of herpesvirus infection. These include: the genome of the virus, viral proteins (antigens), infectious viral particles, cytopathogenic effects on cells, the specific immune response of the patient’s body (antibodies).
Shingles
Varicella zoster virus (VZV) is the cause of two clinically dissimilar diseases: chickenpox (VZ), which affects almost all children, and herpes zoster (HZ), or herpes zoster, the clinical manifestations of which are usually observed , in people of mature age.
Skin lesions are often preceded by prodromal phenomena: fever, feeling of malaise, general weakness, headache, etc. In parallel with this, unilateral neuralgia of a certain innervation zone often develops. The clinical picture is characterized by pronounced polymorphism. During the first day after the onset of neuralgia, single vesicles appear on hyperemic and somewhat swollen skin along the sensory nerve and its branches. The localization of lesions can be varied; they are usually unilateral. The contents of the vesicles quickly become cloudy, pustules, erosions, and crusts form.
ETIOPATHOGENETIC THERAPY OF HUMAN HERPES VIRAL DISEASES
Currently, there are no specific therapies for herpesvirus infections that can eliminate the causative agent of the disease. Antiherpetic chemotherapy.
The most effective antiviral drugs are from the group of synthetic nucleosides (acyclovir, famvir, valtrex).
For herpes in the acute period, adults are recommended to take groprinosin 2 tablets (1000 mg) 3 times a day (50 mg/kg per day) for 5 days, and during the period of remission with recurrent infection - 2 tablets 1 time a day for up to 6 months.
Today it is customary to distinguish three main immunocorrective areas: immunomodulation (interferon inducers), replacement (recombinant genetically engineered interferons) and stimulation (herpetic vaccine).
PAPILLOMOVIRUS INFECTION
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection occurs through direct contact. HPV belongs to genus A of the papovavirus family, the genome is represented by circular double-stranded DNA, does not have an envelope, the bulk is represented by structural proteins. A wide range of HPV types (more than 60 types of HPV DNA) causes a variety of lesions on the skin and mucous membranes.
Clinical forms
- Vulgar warts on the hands
- Plantar warts
- Flat warts
- Filiform warts (acrochorids)
- Epidermodysplasia veruciformis (Lwandowski-Lutz epidermodysplasia veruciformis)
- Laryngeal papillomas
- Papillomas of the oral mucosa (local epithelial hyperplasia - Beck's disease, papillomatous nevus
- Anogenital warts (genital warts) Intraepithelial neoplasia: Bowenoid papulosis and Bowen's disease.
- Giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma.
HPV diagnostic methods
Modern methods for diagnosing HPV can be divided into classical ones, including the cytological method, histological examination of biopsy specimens, colposcopy, determination of antibodies to HPV and molecular genetics.
Treatment.
None of the modern methods leads to a complete cure or guarantees the absence of relapses. The relapse rate is 20-30%. Known treatment methods can be divided into several main groups: destructive (electrocoagulation, laser destruction, chemodestruction), cytostatic (5-fluorouracil, prospidine, podophyllin, podophyllotoxin), antiviral (groprinosin, epigen), immunological (groprinosin, interferons and interferon inducers), combined .
Molluscus contagiosum
Etiology. Molluscum contagiosum is a viral dermatosis, the causative agent of which is the dermatotropic molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), similar to the causative agent of smallpox, belongs to the family of smallpox viruses (Poxviridae), to the subfamily of vertebrate poxviruses (Chordopoxviridae) genus Molluscipoxvirus.
Clinic. The disease can occur at any age, but children between 1 and 5 years of age are most often affected. A greater number of cases are observed in regions with a warm, humid climate. On the skin of the torso, in the area of the inguinal folds, on the face, in the buttocks and other areas, papular rashes of pearly white, pink and normal skin color 1-2 mm in diameter or nodes 5-10 mm with an umbilical depression in the center appear, filled horny masses.
Treatment. There is no etiological treatment. Symptomatic treatment includes squeezing out the horny masses with tweezers, followed by lubrication with a 5% alcohol solution of iodine. Modern methods of therapy are electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser therapy, chemical destruction followed by lubrication with antiviral ointments. In case of extensive and recurrent lesions, it is necessary to study the immune status of patients and carry out differentiated immunocorrective therapy.
UZ City Clinical Dermatovenous Dispensary
Head of Far Eastern Educational Institution No. 3 Tarasevich Svetlana Mikhailovna
Work phone: 372-73-90
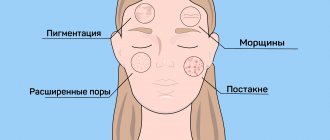
Features of facial skin infections
The blood supply to the organs of the head, face, and membranes of the brain is closely connected. Incorrect treatment and squeezing of pimples is dangerous due to the spread of bacteria through the blood and lymph. You can achieve an increase in the area of the affected area, such dangerous complications as meningitis, abscesses and phlegmon, and inflammation of the eyes.
Before deciding on cosmetic procedures - cleansing, peeling, mesotherapy - undergo an examination by a dermatologist to determine the cause of the pustular rash and receive treatment.
Treatment of bacterial skin infections
It should start from the early stages and be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. In some cases, local treatment with antibacterial ointments and wiping with antiseptics is sufficient. Widespread rashes, deep pyoderma, require the prescription of systemic antibiotics. In chronic cases, the doctor may recommend autohemotherapy and immune drugs.
Surgical treatment is carried out if the abscess does not open on its own or if a rough scar must be avoided. Laser coagulation and physiotherapy are used to restore tissue.
It is important to identify and treat concomitant diseases, eliminate adverse external effects on the skin, and select nutrition.
Lichen
Shingles (herpes zoster) is an acute viral disease. It manifests itself as grouped rashes along the nerve trunks and is accompanied by neuralgic pain. Shingles is considered as a secondary infection against the background of a partial decrease in immunity, which developed as a result of contact of the body with the virus in the past. In typical cases, the disease begins with pain and itching at the site of the future localization of the rash. Quite often, rashes of herpes zoster are accompanied by general phenomena in the form of weakness, malaise, headaches, and increased body temperature.
Prevention
Observe the following rules:
- After visiting the gym, wipe the areas that came into contact with the equipment with an antiseptic.
- Treat cuts and wounds with antibacterial drugs (iodine, salicylic alcohol, hydrogen peroxide) immediately after they occur.
- Do not share hygiene items or cosmetics with other people.
- Places of abscesses and impetigo should not be washed with water, combed, or pressed.
- Avoid spicy fatty foods and sweets.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist on time.
The doctor will help you identify the cause of the inflammation, do the necessary tests, and select a treatment that suits the type and stage of pyoderma. December 5, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus through direct contact or through the use of shared hygiene items (washcloths, sponges, towels).
Children get sick more often! Epidemic outbreaks of the disease are possible in children's groups.
The incubation period ranges from 2 weeks to 2-3 months.
These are usually smooth, shiny, translucent pink or grayish-yellow nodules ranging in size from a millet grain to a pea with a characteristic depression in the center. Their number can vary - from single ones, most often located on the face, neck, back of the hands, to numerous, distributed throughout the body.
Sometimes the rashes can coalesce into large, uneven tumor-like formations “giant clam”.