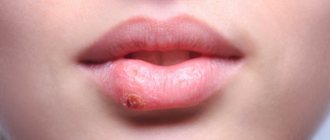
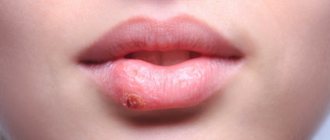
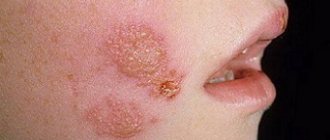
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that can cause small, raised papules to grow anywhere on the body, particularly on the genitals (lips, clitoral area, vaginal opening), as well as the perineum and anal area. There may be just one or a whole group, and although they are usually painless, they can become quite itchy.
Molluscum contagiosum papules on the labia are usually smooth and firm with a dimple in the center, but may be pink, white, or flesh-colored in appearance. The infection is spread through sexual or non-sexual skin-to-skin contact and is most common in children, sexually active adults, and immunocompromised people.
Causes
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus of the poxvirus family, close to the causative agents of smallpox. The rash on the genitals, buttocks and other parts of the body usually lasts for several months, but sometimes lingers for up to two years before disappearing spontaneously.
This skin condition can be spread from skin to skin or through close contact, shared towels, clothing, shaving equipment, swimming pools, or by scratching the affected area, etc. This skin condition can be sexually transmitted and occurs in the genital and anal areas. In this way they are similar to genital warts. Avoid self-contamination or passing the molluscum to a partner by practicing safe sex or abstaining from sexual contact altogether until the outbreak is treated or eliminated.
Relapses
Unlike the varicella zoster virus (chickenpox), which never truly goes away and can cause herpes zoster (shingles) years later, the molluscum contagiosum virus does not remain after recovery. However, if you come into contact with someone with molluscum contagiosum, you may become infected with the virus again. There is no immunity against molluscum contagiosum.
Prevention
Among adults, the most common method of transmission of shellfish is through sexual contact. Therefore, avoiding sex with someone infected with molluscum contagiosum is a good idea. It should be noted that molluscum contagiosum is considered a less severe sexually transmitted infection, but it is still an STI.
It is difficult to prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum among children, so this infection is much more common among children.
Medical methods for removing nodules
Unlike laser coagulation, cryotherapy, electrocoagulation and mechanical curettage of nodular formations in molluscum contagiosum, medicinal treatment using ointments and solutions is the most gentle. Although, of course, some substances used for removal can also leave a significant mark after their impact - this is especially true for alkaline and acid-containing solutions.
According to the degree of increase in effectiveness (but also pain in use!), such remedies can be arranged in the following order:
- Oxolinic ointment. Harmless in case of overdose, has a mild antiviral effect
- Fluorourocyl ointment. Antimetabolite of nucleic acid metabolism. Effective when affecting mucous membranes.
- Preparations with benzoyl peroxide. Belongs to the series of diacetylperoxyls. Reduces the production of sebaceous gland secretions, thereby impoverishing metabolic processes in the epidermis, which deprives the virus of material for reproduction.
- Kondilin or Vartek. The ointment is applied pointwise to nodular accumulations 2 times a day, then, after half an hour of exposure, it is washed off.
- Salicylic acid. Apply generously with a swab to areas of accumulation of nodules at any stage. Do not wash off after exposure. Has a cumulative (accumulative) effect.
- Tretinoin (medicinal synonyms and analogues - Retin-A, Lokacid). Apply directly to the nodules no more than 2 times a day. Keep it on for about 6 hours, then wash it off. The nodules are lubricated until they disappear completely.
- 3% trichloroacetic acid solution. The solution involves spot application on the nodules 1-2 times a day for 30-45 minutes. After exposure, rinse with warm water.
- Extract of celandine using caustic alkali. They act on the blisters once a day, after first applying any oily cream to the skin surrounding the nodule to protect it. After 20-30 minutes of exposure to the pathological area, rinse thoroughly with warm water.
How long to use the listed remedies becomes clear as the nodules and their contents disappear. This usually requires a minimum of 3 weeks. Although if the mildest means are used, the treatment is delayed up to 4 months.
Symptoms
Infection with the molluscum contagiosum virus causes fluid-filled bumps to appear on the skin.
These bumps range from the size of a pinhead to the size of a pencil eraser. They usually have a small dimple or dimple in the middle. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, may develop large bumps. They may grow to the size of a ruble coin, or they may have clusters of atypical bumps. In most people, lesions caused by molluscum contagiosum are painless. However, they may become itchy, irritated, swollen, or inflamed.
Photo of molluscum contagiosum
If you have molluscum contagiosum on your genitals or other intimate places, it is important to avoid injuring them. Scratching or scratching can spread the virus. Scratches can also make your skin susceptible to secondary infections caused by other bacteria. Molluscum contagiosum infections are usually easy to treat in people with healthy immune systems.
Because molluscum bumps are painless, you may not notice an infection. Visual examination of the genital area, perineum, buttocks and anus is the main way to identify signs of this disease. Molluscum contagiosum cannot be detected by smear or blood tests.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact: a urologist, dermatovenerologist. The main thing is not to comb the growths or try to squeeze them out. The doctor knows how to do it correctly and how to treat it. If the molluscum has spread to the eyelids, you should consult an ophthalmologist.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Visual inspection.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Scraping of the contents of the papule, its microscopic analysis, PCR examination.
- Urethral swab for STIs.
The appearance of molluscum contagiosum may be a marker of decreased immunity, so doctors recommend donating blood for HIV. This is a preventive and recommended measure - there is no need to be alarmed. As confirmation, we present the answers of specialists to a man who is worried about this. From the site https://sprosivracha.com/questions/92218-kontagioznyy-mollyusk:
On the question of the effectiveness of “Stopmollusk” from the site https://sprosivracha.com/questions/300216-kontagioznye-mollyuski-kak-lechit:
When diagnosing, it is important to differentiate molluscum contagiosum from dermatofibroma, scabies and basal cell carcinoma. If necessary, the doctor performs a biopsy of a suspicious papule. The same procedure is carried out for atypical forms of molluscum contagiosum. There may be no depression in the center of the papules; sometimes they are pedunculated or covered with a keratinized layer of skin.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
There is no cure, but molluscum contagiosum growths from the labia will eventually go away on their own. In most people, the lesions or growths usually disappear between 6 and 12 months of age. However, sometimes the infection can take years to clear up and this is the main reason why people get treatment.
Growths from the intimate area can be removed by a doctor. In fact, your doctor may recommend removal of the molluscum contagiosum to limit its spread to other people. Remember that molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious!
Cryotherapy and radiosurgery are considered among the most effective treatments, although they have received some criticism due to the risk of blistering, scarring, or hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin). A type of non-invasive surgical curettage, otherwise known as molluscum contagiosum “plucking,” is also effective in physically removing papules from the labia and other private parts of women, although it can also cause scarring. Two other ways your doctor can remove lesions secondary to molluscum contagiosum are scraping and laser.
Prevention of infection
Molluscum contagiosum of the genitals is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. It can also be spread by contact of the labia with objects, such as clothing or towels, that have been contaminated with the virus. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid sharing clothing, towels and sex toys with infected people. Finally, wash your hands after touching any of your own molluscum contagiosum rashes. This may help you avoid spreading the virus to other areas of the skin.
Because labia molluscum is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, safe sex cannot completely prevent transmission. However, reliable condom use can reduce transmission of the virus. Additionally, there is some evidence that having pubic hair may reduce the risk of shellfish transmission. At least two studies have found evidence of more infections in people who shave or epilate their pubic hair.
Where to go in Moscow
Two different types of medications can be used to treat molluscum contagiosum.
First, topical medications containing retinoids can be applied to the lesions. Second, irritants containing salicylic acid can be applied to the lesions to dissolve them over time. Immunomodulatory and antiviral methods, in particular oxolinic ointment and other drugs, can also be considered. As always, treatment for molluscum contagiosum should be prescribed by a doctor. Clarification:
✔ If you want to get rid of this problem, sign up for a preliminary consultation with a leading specialist at our Moscow clinic!
Why patients choose our clinic
The Kuntsevo Medical Center has doctors of the highest category and doctors of medical sciences. We invite you to our clinic for removal of molluscum contagiosum. A dermatologist will conduct a diagnosis and select an effective method of eliminating the virus that is right for you. Prescribe further therapy to treat the infection.
The medical center has modern devices and innovative equipment. Sterile rooms and friendly staff. You can see the full range of services in a special section of our website. Our clinic has average prices for Moscow. Call us and make an appointment!
Question answer
Most often, preschool children, adolescents and elderly people (after 60 years) become ill with molluscum contagiosum. The surprising thing is that babies under one year of age never get sick with this, and this is due to the presence in the body of special antibodies that come from breast milk and are partially transferred from the mother's placenta.
Papules can appear singly or in groups, gradually merging together.
Such neoplasms on the face do not cause pain, but sometimes itching may occur. Inflammation progresses only if another infection occurs.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made by a doctor after a thorough examination and study of the general clinical picture of the patient. In case of controversial nuances, a histological examination of the contents of pimples is prescribed. It is studied under a microscope to detect mollusc-like bodies.
External symptoms of molluscum contagiosum are identical to many other diseases:
- lichen planus;
- syphilis;
- warts;
- chicken pox;
- allergic rashes;
- tumors.
For an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a dermavenerologist.
Folk remedies for fighting shellfish (4 recipes)
Treatment of molluscum on the face with folk remedies is possible in different ways, for which there are many effective recipes. They include both individually and in combination herbal and medicinal products.
The most promising options are presented in the table:
| An approach | Photo | Instructions |
| Garlic | Grind the garlic to a paste and mix with softened butter. The proportions are maintained at 1:1. Distribute the mass over gauze and apply it to the papules, fixing it with an adhesive plaster. Change the lotions to fresh ones three times a day. You can wipe the affected areas with garlic alone (cut into a clove). The course of treatment is a week. | |
| Potassium permangantsovka | Cauterization is carried out with a manganese solution. | |
| Iodine, hydrogen peroxide, calendula tincture | Apply any product directly to the tumors with a cotton swab, being careful not to infect healthy skin. Medical alcohol is applied around the papules. Then the nodules are carefully squeezed out and treated with alcohol. Cauterize with iodine, hydrogen peroxide or calendula. It is advisable to wash clothes and bedding to prevent re-infection. After the procedure, you should not wet the wounds and carry out disinfection with iodine every day. As soon as crusts appear, use oxolinic ointment. | |
| Celandine juice | Lubricate the rash with freshly squeezed juice of celandine or dandelions. Eucalyptus also helps a lot. |
Expert opinion
- Cosmetologist
- Surgeon
Michelle Ellern
practicing cosmetologist-dermatologist
Do not scratch papules on the face, as this will lead to the spread of infection to other parts of the body. In men, infection often occurs during shaving, as a result of which nodules migrate to the chin and cheeks.
Theda Contis
plastic surgeon
During the recovery period (4–18 months), it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, harden, eat a balanced and nutritious diet, including fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet. It would be a good idea to play sports and often take walks in the fresh air. A periodic stay in a pine forest will be especially useful.
Whether to remove mollusks on the face is up to each person to decide for themselves. One thing is certain: these formations spoil the appearance and add complexities. This is why many doctors advise not to wait until the problem goes away on its own.
How to be treated
Only the doctor explains how to treat molluscs on the face after making a diagnosis. Typically, specialists do not resort to drug therapy if the body as a whole is strong and the immune system is in order.
Over time, all symptoms gradually disappear. If immunity is reduced, then without taking certain measures there is a high probability of transformation of the initial stage into a chronic one.
If the body is extremely weakened due to any diseases or for other reasons, it is vitally important to constantly take measures to strengthen the immune system.
In such a situation, medications are prescribed depending on a number of indications: the patient’s age, general well-being, and the stage of the disease.
List of commonly prescribed medications:
- Cycloferon.
- Amexin.
- Antibiotics: Metacycline, Tetracycline.
For external treatment of the affected areas, ointments are used - oxolinic, Acyclovir.