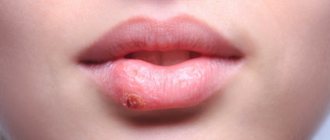
Urticaria is a skin disease associated with the appearance of an allergic rash. In shape and size, it resembles the blisters that appear after being struck by nettles, hence the name. In the acute form, rashes appear literally in the first minutes after interaction with the provoking factor, they pass quickly - within a few hours. If the effect of the allergen is not eliminated, a recurrent form of the disease occurs. A single episode does not require treatment, but chronic urticaria will not go away without treatment. If you experience symptoms of hives, you should definitely consult a doctor.
At CELT you can get advice from a gastroenterologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Reasons for appearance
The causes of urticaria in children and adults , as a rule, are the consumption of food allergens and certain medications, as well as direct contact with household chemicals (powders, detergents, etc.). In addition, hives can appear due to insect bites, animal hair, and house dust. All these factors are the causes of allergic urticaria .
In the case when the disease is not associated with allergies, it can occur as a result of any chronic diseases. Due to exposure to cold, sun, and mechanical pressure on the skin, this pathology can also develop.
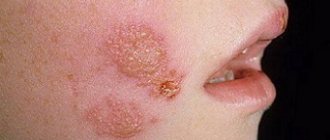
Urticaria in an adult photo
Causes of development and forms of urticaria
The main cause of hives is contact with an allergen. There are many factors that can provoke a pathological response of the immune system (this is an allergy). Most often, urticaria is caused by contact with such groups of substances as:
- Medicines, especially antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
- Dust.
- Animal fur or feathers.
- Plant pollen, poplar fluff.
- Substances that get under the skin from insect bites.
- Compounds that parasites secrete are most often caused by Giardia.
- Some substances contained in food products.
For the development of acute urticaria, short-term contact with the allergen is sufficient. The chronic form is characterized by frequent relapses and is associated with prolonged proximity to the substance causing the pathological reaction. Therefore, at the first manifestations of an allergy, it makes sense to conduct special tests, find out what exactly caused the rash, and exclude any contact with this substance.
In the chronic form, the rash and inflammation are less pronounced. After an exacerbation, the symptoms disappear for a while. Recurrent urticaria may be associated with the presence of a source of infection in the body and requires consultation with a specialist.
Symptoms of urticaria
Symptoms of urticaria are blisters appearing on the body, accompanied by severe itching. They can periodically disappear and appear, affecting more and more new areas of the skin. In this case, the patient may experience an increase in body temperature, redness of the skin, and swelling.
What does hives look like? The blisters that form with urticaria resemble nettle burns and are located in various areas of the body. Hives most often occur on the arms, face and chest.
Hives
Acute and chronic urticaria
Numerous bright pink blisters suddenly appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
With urticaria, the main part of the rash appears within an hour, when the concentration of histamine in the blood is still quite high, but a little later a few more blisters may appear, while the main part of skin diseases begins gradually with several elements. After a few hours, the blisters either disappear without a trace, or a second wave of hives occurs with the formation of new blisters. Chronic urticaria lasts for months and sometimes years. The blisters are itchy and painful to the touch, and the skin around them is swollen and hyperemic. Depending on the size of the lesion in urticaria, the general condition may not change, or there may be a rise in temperature, malaise and headache.
Chronic forms of urticaria are associated with autointoxication and occur in diseases of the digestive organs and liver. Foci of chronic infection in the tonsils and gall bladder, caries and various helminthic infestations can also sensitize the body and cause chronic urticaria. When urticaria recurs, patients may experience headache, nervousness, nausea and vomiting, sleep disturbances, and in some cases, urticaria may be complicated by swelling of the membranes of the brain.
Pediatric urticaria
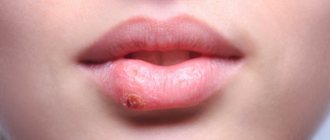
Children's urticaria, or strophulus, refers to allergic skin diseases that develop due to food sensitization against the background of exudative diathesis. In children who are bottle-fed and in children whose diet is not appropriate for their age, a nodular-vesicular rash occurs. Constant contact with allergens, insect bites and the presence of infectious diseases and parasites in the body contribute to the development of urticaria.
The resulting blisters quickly transform into pink-brown nodules up to 3 mm in diameter with a small bubble at the top. Since urticaria causes blisters to itch, the affected skin quickly macerates, scratching, erosions and bloody crusts appear. Urticaria affects large folds of the body, the upper limbs and sometimes the elements spread throughout the body. In young children, especially under the age of three, dyspeptic disorders are observed: vomiting, diarrhea, or, conversely, constipation. If urticaria takes on a chronic, sluggish nature, then children become lethargic, moody, and there is loss of appetite and sleep disturbances. Due to maceration, urticaria elements become infected with pyococcal flora. Urticaria in children must be differentiated from scabies due to similar clinical manifestations. After seven years, in almost all children, urticaria goes away without a trace.
Giant hives
Giant urticaria, or Quincke's edema, is characterized by the sudden appearance of swelling of the subcutaneous tissue, muscles and fascia; this form of urticaria that occurs in the larynx is especially dangerous, since if assistance is not provided in a timely manner, patients die from asphyxia. Giant urticaria is characterized by the presence of diffuse swelling that spreads along the muscles and fascia. Usually the swelling lasts from several hours to several days and goes away without leaving a trace. In case of Quincke's edema, patients are subject to emergency hospitalization for hyposensitization therapy.
Cold urticaria
Since urticaria can be triggered by various factors, cold urticaria is divided into cold urticaria, when blisters appear in people sensitive to cold, this is the so-called cold allergy. With hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation, solar urticaria appears; in people with sensitive skin in the spring and summer, blisters appear on exposed areas of the skin after sun exposure. Solar urticaria mainly affects women with fair skin and blond hair. In older people, urticaria occurs when there is a sudden change in temperature and can appear either immediately or within several days after the change in temperature.
Other forms of urticaria
In some women, symptoms of urticaria appear immediately before menstruation, and apart from external manifestations it does not cause discomfort; sometimes mild itching and slight swelling may be noted; most often, this form of urticaria occurs with the formation of 10-15 elements in the chest and face area. Toxic urticaria is caused by direct contact of certain plants, insects, fish and animals with the skin. It can occur through contact with jellyfish and poisonous plants. The presence of cats in the house can cause chronic, indolent urticaria.
How to treat urticaria using traditional methods
The question that concerns all patients who develop urticaria is what to do and how to treat it? Whatever the cause of urticaria, treatment must begin with eliminating the cause of its occurrence. A mild form of the disease can be cured using traditional methods.
Advantages of traditional methods:
- Treatment is carried out at home;
- Natural ingredients are used;
- There is no need for large financial expenses.
Disadvantages of traditional methods of treating urticaria :
- A lot of time is spent on preparing products;
- It is dangerous to treat a severe disease with such drugs.
Forecast and prevention of urticaria
Hives usually go away over time. However, it is impossible to predict how long this problem will persist. In many cases, the disease can be controlled by avoiding trigger substances and taking antihistamines.
Prevention methods include diet control and avoidance of contact with volatile and food allergens. You should wear loose clothing made from natural fabrics and not cause stress in your child. It is unacceptable to neglect chronic diseases.
Before treating hives in a child, you should consult your doctor. Contact a pediatrician or allergist at the RebenOK clinic in Moscow. We employ specialists with extensive practical experience. Thanks to modern equipment, it is possible to quickly diagnose and, based on the results obtained, prescribe effective therapy.
Methods of treatment with traditional methods
The following methods will help relieve itching, soothe the skin and speed up the healing of blisters.
Honey and horseradish:
- Mix honey and horseradish juice in a 1:1 ratio.
- Take the resulting mixture 1 tsp. 3 times a day.
Mint tincture:
- Pour 20 grams of boiling water over it. mint, leave for several hours.
- Strain and take 3 tbsp. l. in a day.
Mint decoction for lotions:
- Pour 30 gr. fresh nettle leaves 2 tbsp. water.
- Bring to a boil and simmer over low heat for 2 minutes.
- Leave for one hour, strain.
- Soak gauze in the infusion and apply to the sore spot several times a day.
hives in a child photo
The mechanism of occurrence of urticaria (pathogenesis)
The human body contains mast cells or mast cells, which are specific elements of connective tissue. They are the central element in the development of urticaria, activators of inflammation. When an allergen enters the body for the first time and in small doses, the child does not experience any external manifestations or reactions, but sensitization occurs, which can be represented as the first acquaintance with the allergen, resulting in the production of histamine. It is this substance that causes redness, swelling and other inflammatory factors. It gradually accumulates in mast cells, and when its amount reaches a critical threshold, the cell membrane is destroyed with the release of histamine into the bloodstream and a subsequent cascade of pathological changes in the body.
Treatment of urticaria by a doctor
Depending on the type of urticaria, treatment of the disease can be carried out either by a dermatologist or an allergist. If necessary, a thorough examination of the patient is carried out, including urine, blood and stool tests, and sometimes x-rays. After this, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment, which, as a rule, consists of taking antihistamines and drugs designed to relieve itching.
In severe cases, special treatment (plamapheresis) may be required, which is carried out in specialized medical centers.
It should be remembered that self-medication of even such a seemingly harmless disease as urticaria can become dangerous. Urticaria at its maximum development can provoke the development of a complication such as Quincke's edema. This is dangerous due to swelling not only of the face, arms and legs, but also of internal organs. Therefore, in this case, the patient should be provided with emergency medical care.
Diagnosis of urticaria
Diagnosis begins with an examination by a medical specialist and most often ends at the stage of collecting an anamnesis. Typical urticaria is associated with the presence of a specific allergen. Most patients had atopic reactions in childhood. Visual assessment of the skin helps to make a final diagnosis - urticaria can be easily distinguished from other skin diseases.
If there are symptoms, but the patient finds it difficult to name the reason for the development of the pathological reaction, a number of specific tests are performed. Laboratory tests include determination of general and specific immunoglobulin E, as well as a general blood test. Special provocative tests allow you to identify a fairly specific allergy provocateur. If the cause is not established, further diagnosis involves testing for parasitic infestations.
Allergy to micellar water
Women love to use micellar water for skin care before applying cosmetics and even for medicinal purposes when the skin on their face becomes too dry. Micellar water in its pure form usually does not cause allergies, since its composition is balanced and safe. However, some manufacturing companies sometimes add extracts of various plants and even oils to it. They are precisely the powerful “provocateurs” of allergies, especially when it comes to sensitive and delicate skin.
Before purchasing micellar water, you should more carefully familiarize yourself with the substances included in its composition. Persistent skin itching after applying it to the face may occur due to the influence of bromides and glycerin.
Allergy to hot water
As with any tap water, an allergy to hot water occurs due to some substance in its chemical composition. The skin may turn sharply red, itching and burning appear, and after two to three hours the symptoms disappear without a trace.
It is known that a whole range of different means are used to treat water entering the water supply. In this regard, it is impossible to predict how the body of a particular person will react to them. The way out of the situation is to conduct a laboratory test and take action after you find out the exact cause of the allergic reaction.
Allergy to tap water
An allergy to tap water can occur due to the content of certain chemical compounds in it. It happens that a person, for example, changed his place of residence or went on vacation, and after contact with “new” water he developed symptoms of allergic skin irritation. In most cases, the body gradually gets used to the changes and the symptoms disappear. However, in some cases the condition deteriorates, then care should be taken to have employees of a special laboratory examine the water and determine what substances it contains.
1.What is idiopathic urticaria?
Hives
is a skin reaction that most people have experienced at least once in their lives.
Most often, itching and skin rashes have specific causes (which can range from foods eaten and plant odors to liver disease, parasites or exposure to cold). Atypical diseases of unclear, purely individual origin are considered idiopathic. Thus, idiopathic urticaria
is itchy skin that has no specific cause.
Idiopathic urticaria can develop in a person of any age and social status, in any climate zone, and is one of the most common diseases. 25% of cases of causeless skin allergies become chronic.
There is no consensus on the causes of idiopathic urticaria, but most doctors are inclined to the hypothesis that antibodies are not working correctly, which for some reason begin to attack their own body and thereby disrupt its immune status.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Important
Urticaria may be accompanied by Quincke's edema (angioedema, old name - angioedema). Angioedema is swelling that involves the deep layers of the skin in the pathological process. According to statistics, in 50% of cases, urticaria occurs in isolation, 40% of patients with urticaria develop Quincke's edema, and 10% of patients develop angioedema without urticaria. Some patients are sincerely mistaken in believing that Quincke's edema is only swelling of the face or throat.
Angioedema does often occur in the face, but this does not mean that it cannot appear on the hands, feet and other parts of the body. Prevalence of urticaria. Urticaria is a very common condition, affecting 15-25% of people worldwide (occurring at least 1 episode during their lifetime), with acute urticaria accounting for more than 60% of all cases.
Recommended drugs that are used to treat urticaria
- Antihistamines. The Gorbakov Clinic uses new drugs that do not have side effects.
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists.
- Histamine H2 receptor blockers.
- Immunosuppressants.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Slow calcium channel blockers.
- Androgens.
- Combination drugs that include M-anticholinergic drugs.
- Antidepressants.
- Medicines that are used in rheumatology.
- Plasmapheresis.
- Intravenous immunoglobulins.
Specialists at the Gorbakov Clinic individually determine the patient’s treatment tactics in each individual case. A systematic approach to treatment will help the patient get rid of the problem for a long time or forever.