Molluscum contagiosum or contagious molluscum is a viral infection of the skin or mucous membranes. It is often called "water warts". It belongs to the group of sexually transmitted diseases. And although this is not a classic STD disease, sexual transmission is one of the most common.
The causative agent is a DNA poxvirus called molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). It can only infect people. There are four types of MCV:
- MCV-1;
- MCV-2;
- MCV-3;
- MCV-4.
MCV-1 is the most common, while MCV-2 is more common in adults.
What is molluscum contagiosum
This is a viral skin pathology that mainly occurs in children under 10 years of age.
The disease also occurs in young people aged 20-30 years, during the period of their most active sexual life. This disease is characterized by the appearance of hemispherical nodules with a diameter of 2-5 millimeters on the skin or mucous membranes. Regarding the prevalence of this infection, rates in different countries vary from 1 to 22%. It is difficult to determine the exact incidence rate because the virus is easy to spread. To do this, you just need to come into contact with a patient or a virus carrier. The virus remains active for some time on the surface of objects, so infection is also possible when using things and objects shared with the patient.
Molluscum contagiosum is not considered a dangerous disease. It does not threaten the life and health of a child or adult. The presence of the disease, as a rule, indicates a reduced immune status. This is why the infection most often affects children whose immunity is just developing. The risk group also includes people with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency.
Important! You can become infected with molluscum contagiosum again. After illness, patients do not develop stable immunity, which makes reinfection possible. Minimizing the risk of infection is mainly associated with strengthening the immune system and compliance with preventive measures.
Overview of topical products
Molluscum contagiosum is contagious in men and women and is transmitted through contact. Infectious dermatosis is detected after visiting public baths, spas, and swimming pools. Often appears after using rented sun loungers or mattresses on the beach. The symptoms disappear on their own within six months to two years. It is not necessary to treat symptoms. To eliminate the disease, mechanical and laser therapy are used, and topical medications are used.
| Product name | Description | Price |
| Alcohol tincture of iodine 5% | Cauterizes external nodules, stopping the spread of the disease. | From 10 rub. |
| Silver nitrate tincture | Cauterizes tumors, does not affect lesions. | From 90 rub. |
| Levomekol | Has an antimicrobial effect. Improves the healing of aging nodules. | From 50 rub. |
| Retin A | An effective cream with anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects. | From RUR 1,362 |
| Feresol | Stops the development of the disease, affects the source. Can be used for no longer than two weeks. | From 175 rub. |
| Phenol | Disinfects the surface of the skin, cauterizes nodules. | From 370 rub. |
Ointments and gels are part of conservative therapy. Most often used for adults. For children it is used when the disease has already passed and only external manifestations remain. Doctors recommend removing nodules with liquid nitrogen, laser, scraping with a curette, or tweezers. Proper removal leaves no consequences in the form of scars or stains.
Causes of molluscum contagiosum
The causative agent of the disease is viruses of the orthopoxvirus family, which belong to the smallpox virus family. Molluscum contagiosum virus is abbreviated as MCV (Molluscum contagiosum virus). Today, 4 varieties of such viruses have been identified, but the most common viruses in the human population are MCV-1 and MCV-2. Moreover, if the first occurs in adults and children, the second occurs mainly in adults, since it is transmitted through sexual contact. Characteristic skin manifestations of infection appear in those areas where the virus has penetrated. Most often these are the limbs, face or genitals.
Molluscum contagiosum virus. Photo: PHIL CDC
All smallpox viruses, including orthopoxviruses, are large DNA viruses. This means that the mutation rate of such viruses is much lower than that of RNA viruses (for example, influenza viruses). This is due to the fact that when copying genetic material, DNA viruses use DNA polymerase, which also performs editing functions, clearing the genome of mutations.
The incubation period for this pathology ranges from one week to several months. Most often it is 2-8 months. In most adults and children, characteristic symptoms develop within a specified period of time after infection.
Important! A patient with molluscum contagiosum remains contagious until all skin manifestations disappear.
Review of pharmaceutical drugs
Nitrogen is used for treatment, which allows you to remove nodules on the skin painlessly. Drug therapy works less effectively, but helps in the initial stages and in minimal areas of damage. The main quality of the products is that the active substance affects the root cause of the appearance of molluscum contagiosum.
| Name | Active substance | Manufacturer | Price |
| Acyclovir 5% | acyclovir | Russia OZON LLC | From 46 rub. |
| Oksolin | Dioxotetrahydroxytetrahydro - naphthalene | Russia JSC "SINTEZ" | From 47 rub. |
| Viferon-ointment | Interferon alpha-2b | Russia FERON LLC | From 201 rub. |
| Tebrofen ointment 5% | Tebrofen | Russia "TsKhLS-VNIHFI" | From 200 rub. |
| Betadine ointment | Povidone-iodine | Hungary EGIS Pharmaceuticals PLC | From 246 rub. |
Ointments penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis, restore infected tissues, and increase local immunity. Gels and creams are rubbed into the affected areas up to four times a day. They also prevent infection from spreading to healthy areas. Tablets FOR children and adults act on the source of infection and help improve regenerative processes.
Levomekol for treatment
The drug rarely helps if chosen independently. Typically, patients take an inexpensive ointment that fights infections. It relieves symptoms, but the disease itself is not eliminated. The doctor relies on the overall clinical picture and prescribes a suitable remedy. Levomekol is often chosen for home treatment.
Can be used after liquid nitrogen therapy.
The ointment is used when a mollusk appears on the inner thighs, pubis, genitals, and lower abdomen. Helps in finding rashes on the face. Not used for eyelid lesions. Levomekol can be used both after standard therapy with a curette, and as an independent antiviral agent. Alternates with other drugs:
- Feresol;
- Salicylic acid;
- Iodine;
- Phenol;
- Silver nitrate.
Under the supervision of a dermatologist, you can build an effective treatment regimen at home. Levomekol is inferior in effectiveness to more modern means, but is used in cases where the patient has an acute allergic reaction to other creams and gels. Prescribed in short courses of up to ten days.
Acyclovir against illness
An antiviral agent that has an etiotropic effect. Directly affects the source of infection and stops the development of the disease. Prevents the spread of molluscum contagiosum to healthy areas. Relieves irritation and itching, dries out nodules in the first day and reduces the intensity of symptoms.
It is used both after removal by laser, nitrogen, and as an independent product.
Acyclovir is a quick-acting ointment. It stops any number of lesions and is used on any surface of the skin. Effective in the treatment of molluscum on the lips, eyelids, and face. It is noteworthy that the mollusk is similar to smallpox. If the nodules are removed incorrectly, scars remain. Acyclovir has a complex effect:
- increases local immunity;
- destroys foci of infection;
- prevents spread.
Antiviral cream has a number of side effects. Apply up to four times a day. If redness, itching or burning occurs, the drug should be discontinued. Prohibited for a number of diseases and conditions. It is not recommended to combine with antiviral agents, as it may cause an adverse reaction due to an overdose of the active ingredient. Prescribed by a doctor for isolated manifestations of the disease, especially on the face or genitals.
Isoprinosine: drug review
Getting rid of the mollusk is not easy; it is transmitted by touch, through objects or toys. May appear after visiting the pool or massage parlor. Patients who are not affected by the disease for the first time often use Oxolinic ointment, but it is less effective than modern remedies. Isoprinosine has a number of advantages:
- stimulates local immunity;
- suppresses the spread of the disease;
- restores the body's protective functions;
- activates the regenerating properties of the epidermis.
It acts specifically on lesions, even if there are several of them. Proven to be highly effective when used in the early stages. The active substance Isoprinosine destroys the root cause, interfering with the reproduction of new lesions. Can be used as an independent remedy or as part of complex therapy.
Often combined with broad-spectrum tablet medications.
Used for primary lesions, for recurring episodes. It has similar qualities to Acyclovir, but is more aggressive. The effect is noticeable in the first day. Use strictly in the indicated dosage. Excessive amounts of the active substance may cause adverse reactions.
Sinaflan product
A topical product that was created in the laboratory. Its high efficiency is due to the synthesized hormone fluocinolone acetonide. Highly effective against molluscum contagiosum. A wide spectrum of action allows:
- influence the foci of the affected areas;
- stop further development of the virus;
- relieve itching and irritation;
- remove nodules without a trace.
Helps cure molluscum contagiosum at any stage. Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect. It should not be used by pregnant women without a doctor’s recommendation, as the hormone and excipients can adversely affect the development of the fetus. Oily liniment has antihistamine and decongestant effects. It is unacceptable to apply to a child without a specialist’s prescription; there is a risk of a dose-dependent reaction.
The average cost of a tube is from 60 rubles. A small tube is enough for full therapy. The doctor regulates the duration of use. The average course is from ten to fifteen days. continue to use after the disappearance or weakening of symptoms. Helps with molluscum on the pubis, groin, face and other areas.
Doxycycline for molluscum contagiosum
A potent, effective drug with a maximum duration of use of up to five days. The tablets act on the source of the disease, stop the disease on the first day and prevent it from spreading. From the first day of treatment, new lesions do not form. Active against chlamydia, staphylococci, salmonella and other pathogenic microbes.
The antibiotic cannot be combined with other drugs of similar action.
Contains the active ingredient of the same name. It has a reduced risk of negative reactions. If you exceed the daily dose, the patient may feel dizzy and nauseated. Often in such cases allergic reactions occur. Prohibited when:
- leukopenia;
- liver failure;
- porphyria;
- myasthenia gravis;
- in the second and third trimester of pregnancy;
- children under eight years old.
Tablets can be used at home, but the infusion solution is administered strictly under the supervision of a doctor. Treats molluscum on the face, penis, lower abdomen and other areas. Can be combined with hormonal creams to enhance effectiveness. Does not apply to children's treatments.
Biseptol for systemic therapy
An antimicrobial drug that is used only as an exception. It is effective against viruses, bacteria, fungi, but has a less pronounced effect than similar modern products. Slowly rids the body of pathogenic microflora and restores local protective functions. Has the following effect:
- stops the growth of bacteria;
- prevents the appearance of new lesions;
- destroys pathogenic microflora.
Biseptol helps get rid of molluscum on the eye, face, and genitals. It is used in cases where the patient has an acute allergic reaction to other drugs. It has a small list of contraindications. Negative reactions occur extremely rarely. The side effect is dose dependent.
The bacteriostatic property persists for 24 hours after discontinuation of the medication. If nausea, dizziness, or vomiting appear during this period, it is recommended to visit a medical specialist. A wide spectrum of action allows you to fight various ailments from pneumonia and laryngitis to molluscum contagiosum. Therefore, the dosage is determined by the doctor. Biseptol can be used as maintenance therapy after removal of nodules with laser or liquid nitrogen.
Methods of infection and provoking factors
Infection with the virus occurs through contact with a patient or carrier of the virus. Using things and objects shared with the patient also poses a danger, since orthopoxviruses remain active for some time on various surfaces. For this reason, children often become infected when visiting sports sections, where the likelihood of infection spreading is especially high due to the large crowd of people who use the same sports equipment. Contact sports (such as combat sports) also pose a risk because close contact increases the likelihood of transmitting the virus.
Children's judo section. Photo: nomadsoul1 / freepik.com
In young people who are sexually active, infection most often occurs through sexual contact. As in young children, in older people the provoking factor for infection is weakened immunity. HIV-infected people, as well as people suffering from atopic dermatitis, are at risk. One of the factors in the development of the disease is long-term use of glucocorticoid drugs and cytostatic agents that reduce the activity of the human immune system.
Important! If molluscum contagiosum is sexually transmitted, many people mistakenly believe that they can protect themselves from the virus by using a condom. This is a big misconception, since a condom is only effective in protecting against infections concentrated directly in the urethra, penis, semen or vagina. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from sexually transmitted infections such as molluscum contagiosum, syphilis or genital herpes using a condom.
Reasons for appearance
Being a virus, molluscum contagiosum may also have immunological causes of infection.
Weakened immunity allows the virus to actively develop in the body of an adult or child, reaching the peak amount of the pathogen. Not all international organizations consider this disease to be a venereal disease, since the cause of infection is not sexual contact itself, but the contact and friction of the skin of two partners against each other, during which a papule with infectious fluid is opened.
Among the risk groups you can answer:
- People weakened by chemotherapy after cancer.
- HIV-infected people.
- Patients with an acute form of almost any somatic disease.
Quite often, infection occurs in the pool, when the rashes are especially “prepared” for opening in the aquatic environment.
As already noted, the causative agent of the disease is the molluscum contagiosum virus. Today, medicine does not know how to completely cure the disease.
This is explained by the presence of DNA molecules in the structure of the virus. The main method of increasing the intervals of relapses or avoiding them is to strengthen the body's immune system.
Important! The disease molluscum contagiosum is transmitted through household items and directly from person to person. The incubation period can last from ten days to several months.
Weakening of the immune system and, at the same time, exposure to various unfavorable factors activate the development of molluscum contagiosum, which in turn causes the manifestation of symptoms.
The virus often manifests activity against the background of HIV infection. Most often, the disease occurs in underdeveloped countries with hot climates.
There is also a predisposition to CM in people with atopic dermatitis or eczema.
As you have already learned, the disease is viral in nature. In total, doctors identify 4 types of virus that provoke the appearance of molluscum contagiosum:
Molluscum contagiosum is a disease caused by a virus that belongs to the smallpox group. Most often it affects the skin, and in rare cases, mucous membranes. The virus is active only against humans; not a single case of infection of animals has been identified.
The molluscum contagiosum virus causes formations on the skin.
Due to the fact that the protective reaction of the immune system decreases, the molluscum contagiosum virus begins to activate, and therefore the disease progresses.
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease that is transmitted from person to person through direct contact, and only people are susceptible to this disease: animals have one hundred percent immunity to this virus and cannot be its carriers.
Very often, this disease affects children in groups, for example, in kindergartens. In such communities, a large number of children are constantly in contact with each other: they share toys and household items, and since young children do not take hygiene seriously enough, outbreaks of molluscum contagiosum can cover an entire kindergarten.
In adults, this virus is mainly transmitted through sexual contact, but the disease is often spread through household contact: sharing utensils, towels or shaving equipment with a patient are the most common methods of transmission.
Due to the fact that molluscum contagiosum is very resistant to various medications, it can exist outside the human body, so experts know of many cases where molluscum contagiosum was transmitted to people in the pool.
Since in adult men the main route of transmission of the virus is sexual, the virus is localized mainly in intimate areas: the lower abdomen, perineum and genitals themselves.
Moreover, the lower the immunity of a sick man, the larger the size of the rashes will be and they will occupy a larger area.
Symptoms
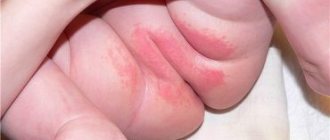
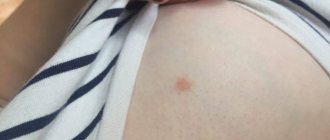
The main symptom of a skin infection is painless nodules 2-5 mm in diameter with a small dimple in the center. Let's take a closer look at the main characteristics of rashes and other symptoms.
- The rashes have the appearance of dome-shaped papules. The surface of the papules may be smooth or waxy. The consistency of the papules is dense, and as the tumor grows it softens. In patients with HIV infection, as well as in people with weakened immune systems, the diameter of the rash reaches 10-15 mm.
- Papules are flesh-colored, pink, or darker in color. When pressed, curdled contents come out of the papule. Sometimes pearlescent stains, like a pearl, are clearly visible on the papules.
- Papules form at the sites of viral infection penetration - in various parts of the body. They are often grouped into one or two areas, but diffuse distribution of papules over a specific area of the skin is also possible. Often in people with weakened immune systems, the rash affects large areas of the skin.
- The rash is painless, but the area of the rash may become inflamed, which is accompanied by itching.
- In approximately 10% of cases, patients develop eczema in the affected area - an inflammatory skin lesion (dermatitis).
- Papules never appear on the palms or soles. Very rarely, rashes form on the mucous tissues of the oral cavity.
- Skin tumors with molluscum contagiosum grow slowly. The papule increases in size and is filled with a light, cheesy mass consisting of skin cells, sebaceous gland secretions, as well as dead leukocytes and the viral particles themselves.
- Around the 12th week, papules reach their peak size, after which their growth stops. Then the tumors gradually die off.
Figure 1. Molluscum contagiosum rash on the face. Source: Ben Naafs/Community Eye Health/Flickr
Symptoms in women
In adults, rashes most often affect the genital area. This is due to the predominance of transmission of infection through sexual contact. For infection, genital contact itself is not at all necessary; just contact with the infected area of the partner’s skin is sufficient.
Most often in women, papules form in the lower abdomen, on the thighs, pubic area or external genitalia.
It is noteworthy that pregnant women are especially susceptible to infection due to a natural decrease in immunity. The manifestations are indistinguishable from the classic clinical picture of the disease. The virus does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus. However, if the baby comes into contact with the mother's infected skin, the child runs the risk of becoming infected.
Symptoms in men
In men, as in women, the rashes are predominantly located in the genital area. This is the groin area, penis, inner thighs. Men are more likely than women to rub papules on clothes, which leads to the release of viral particles and re-infection. Therefore, the rash affects not only the area of contact with the infected partner, but also nearby areas.
How does the infection manifest in children?
Skin manifestations in children mainly affect the face, limbs and chest area. The rashes do not cause any inconvenience to children other than aesthetic ones, especially if they are located on the face. Papules in children do not hurt and very rarely cause itching. It is important to ensure that the child does not scratch or rub the affected areas. Otherwise, secondary infection with the virus will occur.
Important! In children, rashes are extremely rarely observed in the genital area. If a child has papules on the genitals, pubis, buttocks or inner thighs, the circumstances of possible infection should be especially carefully examined, since sexual abuse cannot be ruled out.
Clinical picture of the disease
Molluscum contagiosum is characterized by the appearance of a characteristic rash on the skin and mucous membranes, in most cases without any subjective sensations. Sometimes patients are bothered by itching and burning. Atypical forms of the disease are very rarely recorded.
Localization. The rash in children is localized on the skin of the face (often in the forehead and eyelids), neck, upper chest (including the armpits), upper and lower extremities. Most often, the rash appears on the face, torso, armpits and diaper area. If a rash appears in the genital area, the assumption of sexual abuse should be excluded.
Prevalence. Nodules in the disease are usually single - from 5 to 20 pieces, grouped in one area. In immunodeficiency and in persons with atopic dermatitis, they appear in large numbers, scattered throughout the body.
When scratched, the lesions spread in a linear direction.
Characteristics of the rash. At the beginning of the disease, small (1 - 2 mm in diameter) papules appear on the skin. Gradually they increase in size (up to 5 - 7 mm) and take on the appearance of a dome-shaped nodule. The nodules are hard, flesh-colored or whitish with a pearly sheen. Most of them have a depression in the center, which is clearly visible when magnified. When pressed from the sides, a dense, mushy mass emerges from the nodule, containing keratin and “mollusc bodies” filled with a huge number of virions. In atypical or advanced cases, this sign is absent.
Course of the disease. Molluscum contagiosum is characterized in most cases by self-healing within several months. With constant scratching and the spread of infection to other areas of the skin, nodules appear again and again, and healing is delayed up to 6 - 9 months or more. Sick children are subject to isolation from the children's group until complete recovery.
Complications. Complications of the disease include cases of secondary infection and spread of infection to the eye tissue.
Rice. 5. Scheme of the structure of a nodule in molluscum contagiosum.
Rice. 6. Molluscum contagiosum. Type of rash on the skin.
Types of molluscum contagiosum
There is no generally accepted classification for molluscum contagiosum. At the same time, in addition to the “classical” papules, atypical forms of rashes are distinguished. These include:
- giant clams, the size of which is 3 cm or more;
- cystic molluscs - the appearance of cysts (cavities, with a wall and contents) instead of papules of the same size;
- ulcerated mollusks - instead of nodules, small areas of erosion appear, which subsequently turn into bleeding ulcers;
- molluscs in the form of eels or warts;
- pendicular mollusks - neoplasms are located on a thin stalk above the skin.
Depending on the prevalence of lesions, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Localized - affects only a specific area of the body, such as the face, genital area, upper or lower extremities.
- Generalized - rashes are observed over a large surface of the body. In some cases, neoplasms are noted throughout the body.
Molluscum contagiosum: specific features in adult men and women
Molluscum on the skin of women shows some specific symptoms. It is worth remembering that in the case of pregnancy, this problem does not pose a serious health threat. Does not affect the child's development.
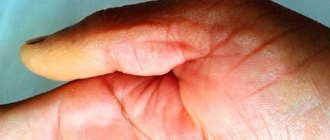
As for the male sex, the only peculiarity is the localization of formations in the penis area (see photo below).
This complicates the process of sexual intercourse. But in women, damage to the mucous membranes of the vagina does not occur. But it happens on the skin near the genitals. This also causes discomfort, but is much easier to tolerate than in men.
What are the features depending on the location?
Molluscum contagiosum on the eyelid should be removed without waiting for natural disappearance. This is necessary to avoid damage to the mucous membrane of the eye. Conjunctivitis or more serious eye diseases may develop.
But on the face it is better to wait until it completely disappears. Certain cosmetic procedures may leave marks on the skin. But after the natural disappearance, no skin defects will remain.
These formations on the genitals must be removed immediately. This will not only make sexual intercourse easier, but also minimize infection of the partner.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Source: Fantasy Children's Clinic
Before starting treatment, a diagnosis is carried out, which is not difficult for molluscum contagiosum. The diagnosis is made based on the external manifestations of the disease. For atypical forms, specific laboratory tests are used to identify viral particles. This is staining of the contents of nodules according to Romanovsky-Giemsa, Papanicolaou or Wright. Instrumental diagnostics for molluscum contagiosum are not used.
There is no specific treatment for molluscum contagiosum. Treatment is aimed at eliminating skin lesions as quickly as possible. The disease is treated on an outpatient basis by a dermatologist.
Treatment for molluscum contagiosum is not always carried out, since within 6-18 months the papules “go away” on their own. Treatment measures are resorted to based on aesthetic considerations, as well as in severe cases of the disease (when a significant part of the body is affected by rashes) and when patients at risk are infected (people with HIV and a weakened immune system).
Drug treatment
Drug therapy is ineffective. However, to eliminate papules, salicylic acid is used as an external agent. The healing of rashes in this disease is also facilitated by topical preparations with retinoids (in particular, tretinoin).
To eliminate rashes, cantharidin is used, a poison contained in the hemolymph of some types of beetles. Currently, cantharidin is used as a blister agent. In particular, one drop of cantharidin is applied to the papule of molluscum contagiosum. In this case, blisters may appear at the application site. Cantharidin has not yet been registered in the Russian Federation and cannot be used.
Cytostatic drugs (podophyllotoxin) and potassium hydroxide are also used for medicinal purposes. However, the effectiveness of these drugs, as well as the above, for molluscum contagiosum is extremely low.
Antiviral drugs
Since molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease, it is logical to assume that antiviral drugs can help in treatment. Unfortunately, here too the existing arsenal of antiviral drugs turned out to be powerless against the molluscum contagiosum virus. Some doctors prescribe acyclovir and oxolinic ointment to such patients, but these drugs are ineffective against the molluscum contagiosum virus. Currently, antiviral drugs acting directly against the molluscum contagiosum virus have not yet been developed.
Immunomodulators
Some doctors may prescribe immunomodulatory and immunostimulating drugs to patients. For example, this is imiquimod, a drug that enhances local immunity; Local drugs with inducers of interferons, proteins that have antiviral activity, are also prescribed. However, there are no studies confirming the effectiveness of such drugs for molluscum contagiosum.
Thus, in the treatment of molluscum contagiosum, medications and folk remedies are either ineffective or useless. An effective way to eliminate rashes are methods of direct papule removal.
Surgery
The following surgical techniques are used to remove molluscum contagiosum papules:
- Cryosurgery is treatment using liquid nitrogen. The papule is exposed to liquid nitrogen for a few seconds, which leads to its deep freezing and destruction. Since new papules may form over time, the patient will have to undergo several cryotherapy sessions. Among the disadvantages of this treatment is the painfulness of the procedure. Therefore, it is not used to treat young children. In addition, after exposure to liquid nitrogen, blisters may form, and then barely noticeable scars.
- Evisceration is the removal of a papule using thin tweezers. The advantage of the method is that the removed papule is not destroyed, which means it can be sent for laboratory testing.
- Curettage is the removal of lesions using a curette. This is a tool that resembles a long metal fork with a loop instead of teeth. This technique is painful, and after removal scars may form. As a rule, curettage is used for a small number of papules. If there are a lot of rashes, then curettage is ineffective, since after the procedure there is a high risk of new rashes appearing.
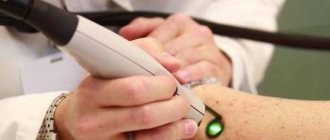
- Laser therapy - laser exposure to molluscum contagiosum papules. As a rule, one session is enough for laser removal of papules, but in some patients the rash may persist, which requires re-treatment after 2-3 weeks.
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of skin lesions using electrical cauterization. For this purpose, an electrocoagulator is used - a device that supplies high-frequency current. Under the influence of current, the proteins of the papules are destroyed, which leads to its destruction.
Treatment of the disease in children
In many cases, molluscum contagiosum will disappear without a trace on its own, without treatment, usually this process lasts about 2-3 months.
However, sometimes new growths reappear after the old growths disappear, so molluscum contagiosum can completely leave the human body after a long 6-18 months (in some cases, this process can take up to 4 years).
Sometimes doctors use special procedures that help patients get rid of growths faster, in particular:
- removal of the infectious center by opening the growth with a scalpel or squeezing with tweezers;
- removal of processes by freezing (cryotherapy) or scraping them with a sharp instrument (curettage);
- using a chemical or ointment such as salicylic acid, tretinoin, cantharidin, benzoyl peroxide, or other wart treatments
- prescribes the use of a special drug called cimetidine
Although these treatments provide quick relief from symptoms, most doctors do not use them for childhood rashes because they are very painful and can burn, scar, or discolor the skin.
Treatment sometimes depends on the location and number of growths. Many people ask for treatment if the rash causes them discomfort or other problems, such as pain or itching.
Treatment is most effective in the early stages, when only a few growths have formed on the skin. Your doctor will tell you about the advantages and disadvantages of certain treatment methods, and will also help you make decisions regarding the need for medical procedures.
Be sure to consult with your doctor before you begin to remove (squeeze) the mollusks yourself, as this can provoke further spread of the disease through the skin and will only worsen the symptoms and increase the recovery time.
Prevention of molluscum contagiosum
Source: Jesselton Medical Center
There is no specific prevention against molluscum contagiosum (a vaccine against the pathogen has not yet been developed). Basic preventive measures involve isolating patients to avoid infecting other people. To minimize the spread of infection, doctors recommend:
- isolate the sick person until complete recovery;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- conduct preventive examinations for children of preschool and school age;
- be more attentive to your sexual partners - a quick examination of the person can help you avoid infection, and motivate your partner to undergo examination.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis when a person is infected with molluscum contagiosum is usually not difficult. In this case, the clinical picture is mainly taken into account, and if the doctor observes a questionable situation, then a histological examination will be informative, during which molluscan bodies are found in the cytoplasm of epidermal cells. It is important to differentiate this disease from certain types of lichen, warts, and epithelioma.
A microscopic examination of the contents of the nodules is also carried out, which reveals special ovoid (mollusc) bodies characteristic of this disease, as well as keratinized cells of the epidermis.
If molluscum contagiosum recurs too often, a specialist may advise the patient to be tested for HIV, since this disease is very common in patients who suffer from immunodeficiency.
However, in most cases, the diagnosis can be made based on a thorough visual examination. If the nodules affect the genital area, then patients are also recommended to undergo additional tests to identify other diseases that are sexually transmitted, in particular genital herpes.
In the classic form, the diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is easy to make. The following factors are taken into account: childhood age, the presence of children with molluscum in the team, multiple spherical formations on the skin with an umbilical depression.
Three types of disease development can be distinguished:
1. Typical development, due to which a small number of neoplasms appear, they occupy some areas on the skin.
2. Generalized development, neoplasms begin to rapidly increase, they affect skin areas that are located in different places.
3. Complicated development occurs when the disease is accompanied by pathogens. At the same time, the skin around the neoplasm becomes much redder, pus begins to ooze out of it, the lesions begin to greatly disturb the patient, and the disease also becomes more complicated for HIV-infected people.
A dermatologist can make an accurate diagnosis; he takes the contents of the fluid in the tumor for analysis. Under a microscope, epidermal cells are visible; there are very few of them due to the mollusk bodies. With the help of research, you can find out that viral cells multiply in the epithelium.
In children, tumors appear in the facial area, in adults most often on the genitals, lower abdomen, and anus.
It is very important to differentiate molluscum contagiosum from syphilis and chickenpox, which is why it is so important to consult a specialist in a timely manner.
Molluscum contagiosum is diagnosed quite easily due to its striking clinical manifestations. In case of difficulties, a microscopic examination of the contents of the nodules is performed.
In addition, differential diagnosis is necessary. Elements of molluscum contagiosum must be distinguished from warts, lichen planus, benign and malignant formations on the skin.
As mentioned earlier, treatment for molluscum contagiosum is not always necessary. A healthy body copes with the disease itself, and the symptoms disappear after a few weeks or months. The decision about the need for treatment is made by the doctor, so going to the hospital is mandatory.
There are various ways to get rid of rashes, including traditional ones, which can be used in combination. The main method of treating the disease is to remove the molluscum contagiosum with surgical tweezers or a sharp spoon.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis by a dermatologist. In this case, each element is carefully scraped out to ensure complete removal of the contents of the nodule.
After this, treat the affected surface with iodine or brilliant green. Antiviral drugs may be prescribed, as well as immunostimulating agents, such as Isoprinosine.
This method is indicated for multiple rashes.
Removal of molluscum contagiosum is carried out not only with tweezers. There are also more gentle methods, for example using a laser.
In this case, the surrounding tissues are not damaged, and healing occurs faster. Typically this method is used to treat children.
Laser is used to remove rashes on the face, neck and other open areas. In addition, mechanical squeezing out the contents of nodules with a sharp spoon or tweezers is now being replaced by electrocoagulation.
Surgery to remove molluscum contagiosum in men, women and children can be performed with liquid nitrogen. In this case, the affected area freezes and tissue dies without scarring.
Healthy tissue is not damaged during treatment with liquid nitrogen. The disadvantage of this method is the duration of treatment.
Several liquid nitrogen freezing procedures are required to obtain results.
All of the above operations (electrocoagulation, laser method, curettage, nitrogen removal) are painful, so they are performed under local anesthesia.
In some cases, conservative treatment of molluscum contagiosum with local drugs is indicated. This is an antiviral ointment or cream.
Painless methods are good for children. The ointment is applied to the affected area with gentle movements once a day or every other day.
It is recommended to do this at night. In the morning, wash off the ointment with warm water.
The course can last up to 16 weeks.
In generalized forms of the disease in children and adults, when there are multiple rashes on different parts of the body, antibiotics of the tetracycline group are prescribed.
Drug therapy for molluscum contagiosum includes taking antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. This could be the medicine Isoprinosine - a synthetic drug that blocks the action of viruses and increases the body's resistance.
Isoprinosine is used to treat persistent viral infections. Available in the form of oblong white tablets.
Isoprinosine is well tolerated by children and has been widely used in pediatrics for many years. Like all medications, it has side effects and is not recommended for self-administration.
Isoprinosine can be replaced with analogues, for example the drug "Groprinosin", but only on the recommendation of a doctor.
During treatment of children, it is necessary to treat toys, washcloths, linen, towels and other personal items. You should especially carefully observe hygiene standards in the apartment.
If molluscum contagiosum is detected in adults, it is necessary to examine family members and sexual partners. Sexual activity of men and women infected with this virus can only be resumed after the symptoms have completely disappeared.
Folk recipes
Treatment with folk remedies is always successful, but in any case you should consult a doctor. It is not recommended to treat molluscum contagiosum on your own in either adults or children.
How to remove a rash with folk remedies? Healers advise using celandine. To do this, apply fresh plant juice to the rash elements every day for several weeks.
If you don’t have fresh celandine, you can buy an alcohol tincture at the pharmacy.
Traditional healers suggest treating molluscum contagiosum with garlic. To do this, lubricate the sore spots with garlic pulp with the addition of butter three times a day.
Traditional healers advise pouring two tablespoons of chopped string into a glass of water, bringing to a boil and letting it brew. Wipe areas with rashes three times a day.
Folk remedies cannot fully treat molluscum contagiosum. These are just additional measures to avoid recurrence of rashes after surgical removal of nodules, nitrogen freezing or electrocoagulation.
The disease can be diagnosed exclusively visually, and the tests taken for the most part serve only to make sure that it is molluscum contagiosum and not a more serious illness.
During the examination, first of all, a histological examination is carried out using an electron microscope, which makes it possible to verify the presence of mollusc-shaped bodies in the rash.
That is, one of the methods for diagnosing molluscum contagiosum is under a microscope.
In some cases, a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test is performed, which is very often performed to diagnose viral diseases. The only type of analysis that is not performed when diagnosing molluscum contagiosum is culture, since scientists cannot isolate a colony of this virus under natural conditions.
Prognosis, possible complications, prevention
Molluscum contagiosum has a favorable prognosis. However, some complications cannot be excluded. A bacterial infection may occur and dermatitis may develop, leaving scars on the skin.
You should know that it is impossible to completely get rid of molluscum contagiosum. The disease is chronic, and the main task is to avoid recurrent rashes.
Prevention is important, which consists of observing hygiene standards: using only personal belongings, taking a shower after the pool and swimming in open water.
Of great importance is the early detection of molluscum contagiosum and timely treatment, which consists of a combination of traditional methods (mechanical curettage, laser removal, nitrogen freezing, drug therapy) with folk remedies.
Despite the visually unpleasant and even frightening manifestations, molluscum contagiosum often goes away on its own after some time, but this is not a reason to ignore the disease and neglect treatment.
This disease poses a serious danger to a person with a weakened immune system: in such people, the rash can spread throughout the body, and it is much more difficult to cure it.
Another possible and unpleasant consequence of molluscum contagiosum is scars, since in some cases surgery is required to remove the largest nodes.
Prevention and treatment
Is it possible to cure a viral disease? Of course, the pathology is treatable. The disease is usually treated with ointments and other topical medications.
In addition to cauterization with an alcohol solution of iodine, you can use ready-made ointments.
Among them are Acyclovir, Oxolinic or Fluorouracil ointments, Retin-A cream and calendula ointment. The course of treatment is about two weeks. Additionally, potassium permanganate, Fukortsin, Salicylic ointment, brilliant green and even homeopathy can be used.
To get rid of the disease, it is necessary to use broad-spectrum antibiotics and antiviral agents. Additionally, medications with an immunomodulatory effect and multivitamin complexes are used.
Before using any medications, you should read the instructions and consult with your doctor.
In addition, as an addition to drug treatment, you can use ointments and creams that you can make yourself at home:
- Peel the head of garlic, finely grate and add a teaspoon of unsalted butter. Stir well and apply to affected areas 2-3 times a day. A folk recipe will reduce the severity of clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Beat the juice of bird cherry leaves with butter 1:1 and lubricate the location of the mollusk overnight and apply a bandage. Instead of bird cherry, you can use celandine.
All of the above ointments, both pharmaceutical and folk, have an antiviral effect, their use is quite effective even in the initial stages of the development of the disease.
Let us remind you that all treatment examples are not ready-made schemes and require mandatory adjustment by a doctor. Self-medication is very dangerous because it worsens the course of the disease.
Removal can also be carried out through the use of liquid nitrogen and laser therapy. Minimally invasive procedures are used solely at the discretion of the doctor.
TO THE DOCTOR
There are often cases when a patient, after removal of molluscum contagiosum, after some time, increases the number of neoplasms several times (sometimes their number can reach hundreds).
This is a signal that deletion is not suitable in this particular case. It is best to find a good homeopath and try to treat the mollusk with medications.
This is especially true for children who endure the procedure of removing tumors very painfully, given that their number can vary from a couple of pieces to several dozen.
Diagnosis includes a detailed examination of the patient’s rashes and microscopic and histological examination of the contents of the nodules. An experienced dermatologist will only need to carefully study the clinical picture to recognize the disease.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum begins with complete isolation of the patient - if it is a child, then until complete recovery he should not attend school or kindergarten, if an adult - refusal to go to bathhouses, swimming pools and other public places.
Further, much attention is paid to observing the rules of personal hygiene both before recovery and after.
The most popular method of treating molluscum contagiosum is cryotherapy, which is carried out every 2-3 weeks until all rashes are completely removed.
Squeezing out the nodules using tweezers followed by scraping off the remaining lesions can also be used. The resulting wounds are treated with phenol, 10% iodine solution or silver nitrogen.
Don’t be surprised if your doctor suggests treating the lesions with garlic juice, which has proven itself in the fight against CM.
The main course of treatment for molluscum contagiosum consists of removal of tumors and a subsequent course of immunostimulants and antiviral drugs.
Removal is carried out by a qualified dermatologist on an outpatient basis using tweezers or a sharp Volkmann spoon. Then the wound is lubricated with an alcohol solution of iodine and a saturated solution of potassium permanganate.
Today, the laser method of removing molluscum contagiosum is also common, which is more convenient, and healing occurs faster and without subsequent scars.
It is possible to use diathermocoagulation and cryotherapy.
After removal, the affected skin is lubricated with iodine once a day for 4 days. The rashes may appear again, and therefore they need to be removed until they disappear completely.
Antiviral external medications help prevent relapses. Viferon ointment, Cycloferon liniment, and acyclovir ointment have proven themselves well in this aspect.
Imiquimod in the form of a cream, interferon alpha-2a in the form of an ointment, and meglumine acridone acetate in the form of liniment can be used as immunomodulators.
Since transmission of molluscum contagiosum is possible in a domestic environment, you should not only strictly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, but also thoroughly boil all underwear and bedding, and also clean your home using disinfectants.
How to treat molluscum contagiosum with folk remedies?
To date, there is no effective medicine that can cope with the disease. The action of medicinal substances, including various ointments, is aimed at eliminating the molluscum contagiosum nodes themselves, but not at fighting the virus.
It is impossible to completely kill the pathogen. All methods are aimed at combating the manifestations of molluscum contagiosum and preventing its further spread throughout the skin.
This is a kind of opportunistic virus: it will constantly be on a man’s skin and wait for the right time to activate.
Oxolinic ointment can be used as a medication. True, such treatment would be justified to combat cutaneous molluscum in children and adolescents.
Adult men have rougher skin and, accordingly, a more durable membrane of the nodes. Therefore, the use of oxolinic ointment and other medications will not be effective.
To cope with the problem, manipulations are carried out to remove the formed nodes. The level of development of modern medicine allows this to be done with minimal consequences for the patient.
- Surgical removal. It is carried out under the influence of local anesthetics, therefore it does not cause pain to men. The doctor carefully plucks out the formations using tweezers. After a while, a repeat operation will be required: new nodules may appear, albeit somewhat smaller in size.
- Cryodestruction. The doctor applies cold to the affected areas of the patient's skin. The advantages over surgical removal of molluscum contagiosum are absolute painlessness and short duration of the session - the nodes are removed in just a couple of minutes.
- Electrolysis. The mollusk is exposed to high-frequency electric current, due to which the formation is destroyed. A special feature of this method is the rapid restoration of damaged skin cells.
- Exposure to a laser beam – the treated area of skin is heated at a depth of up to 5 mm. An increase in temperature leads to the death of the virus, while the affected cells are literally evaporated. The effect of laser removal of cutaneous molluscum is noticeable after the first procedure.
In some cases, the problem can be dealt with by cauterizing the nodes with iodine or hydrogen peroxide. However, this method of therapy is associated with an increased risk of injury to healthy areas of the skin from the chemical. Therefore, such treatment is used very rarely.
Molluscum contagiosum - Molluscum contagiosum affects only humans, since its causative agent is Molluscipoxvirus, a pathogenic virus from the smallpox group. Due to the fact that infection occurs very easily, entire epidemic outbreaks of the disease are sometimes observed in certain regions.
The virus contains DNA, so it is quite difficult to fight it. The disease is chronic, therefore, it is impossible to get rid of it completely. However, it is quite possible to avoid relapses of the disease by strengthening the immune system.
For people whose immune system functions normally, there is no need to treat this disease at all: it goes away on its own in about 2-6 months. But still, many patients do not want to wait such a long time, considering, first of all, aesthetic reasons.