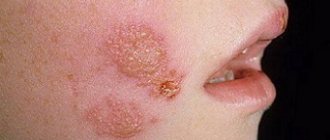
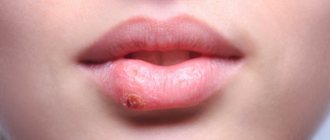
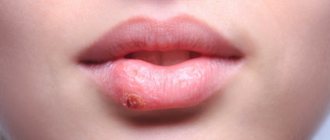
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that can cause small, raised papules to grow anywhere on the body, particularly on the genitals (lips, clitoral area, vaginal opening), as well as the perineum and anal area. There may be just one or a whole group, and although they are usually painless, they can become quite itchy.
Molluscum contagiosum papules on the labia are usually smooth and firm with a dimple in the center, but may be pink, white, or flesh-colored in appearance. The infection is spread through sexual or non-sexual skin-to-skin contact and is most common in children, sexually active adults, and immunocompromised people.
General information
Molluscum on the skin is often called "contagious molluscum."
This is a kind of special form of viral infection that affects the skin.
The virus quickly penetrates the basal layer of the epidermis and provokes excessively rapid division of cellular structures, as a result of which growths-nodules of a roundish shape and small size with an umbilical depression in the center are formed on the surface of the skin.
In this case, a certain number of epidermal cells are destroyed.
It is worth noting that this is a benign disease. This is due to the fact that the growth of nodules occurs in a small place. At the same time, no inflammatory process is observed in the layers of the epidermis.
This disease affects people of different age groups, regardless of gender. But this problem is especially relevant in childhood. Namely for preschool children and the elderly (after 60 years).
Babies under one year of age almost never become infected with this virus. Doctors explain this by saying that a large amount of maternal antibodies were transferred to them through the placenta.
This especially affects individuals with a weakened immune system, those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis and taking cytostatics or glucocorticoid hormones.
But those who come into contact with other people’s skin should also be careful. For example, massage therapists. In addition, the infection factor does not depend on the location and characteristics of the climate zone.
Each mollusk looks like a small tubercle. Pale pink or slightly transparent shade (sometimes with a pearlescent tint).
Causes
As mentioned earlier, the disease is caused by a virus, which, according to some experts, belongs to the smallpox virus.
Even in the era of active medical research, it was not possible to get rid of the pathogen. This is due to the fact that it remains in the DNA structure.
But with the help of systemic prevention and strengthening the immune system, relapses are successfully minimized.
Due to reduced immunity, various clinical manifestations are possible. In this case, the localization zone is different.
It all depends on how exactly the infection process occurred.
The main causes of molluscum contagiosum:
- Bad environmental situation. This significantly increases the risk of infectious diseases.
- The AIDS epidemic, unfortunately, is also increasing the number of people getting sick. Many patients diagnosed with HIV have contagious dermatosis.
- An active sex life, which may result in promiscuity regarding sexual partners.
- Densely populated areas are one of the factors for transmitting the virus through contact and household contact.
According to statistics, the virus is often found in children's institutions.
It is also detected in adults during a medical examination. Molluscum contagiosum in babies can affect any area of the skin.
When infected at home, it is difficult to determine the area where the rash occurs.
Infection can even occur due to the use of certain objects.
For example, children often do not even suspect that they are already carriers of viruses. Therefore, molluscum contagiosum is transmitted from one child to another during play.
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself only as skin symptoms, there are no disturbances in the general condition, there is no feeling of well-being, the temperature is normal. The main symptom of molluscum contagiosum in children and adults is a typical, round, pearl-colored rash, painless, against the background of healthy skin or during scratching.
The size of the nodules is from 2 mm to 5 mm, rarely reaching 1.5–2 cm. They can be single or multiple, do not merge, and do not cause itching. The consistency is soft and painless. The number of rash elements is most often up to 20 pieces, but there may be more of them against the background of ARVI, stress, or decreased immunity.
The virus itself does not cause inflammatory changes. If there is swelling or hyperemia around the elements, these are signs of a secondary infection - streptococci, staphylococci, fungi. Also in this case, purulent pustules, pain, and itching appear.
The main discomfort from a molluscum contagiosum rash in children is psychological due to a cosmetic defect. This is especially true for forms localized on the face and multiple papules. Also, the child is restricted from visiting the group, so adults are required to respond and cure the pathology.
How does infection appear? Main symptoms
Infection with the virus occurs in various ways.
Both the result of sexual intercourse and domestic infection are possible.
The incubation period of molluscum contagiosum lasts from two weeks to several months.
After this stage ends, the main symptoms begin to appear.
The clinical picture of the disease is quite pronounced. Localization of molluscum contagiosum:
- external genitalia,
- hip area,
- buttocks or lower abdomen.
Raised nodules appear on healthy skin. They have a hemispherical shape. The color matches the natural color of the skin or is slightly pinker, single or multiple.
In the middle of the hemisphere there is a depression, slightly reminiscent of a human navel.
The nodules are smooth to the touch and only slightly differ from the natural color of the skin. The skin around these formations usually does not change. But sometimes the rim around them becomes inflamed. The person does not experience any particular discomfort.
A significant increase in manifestations is observed after approximately 3 weeks. And with slight pressure a cheesy plug is released.
It is worth considering that in most cases, symptoms can go away on their own after six months. Clinical manifestations are dense nodules, sometimes with a light pearlescent hue.
Painful sensations may not be observed at all. Often these are small skin rashes that are localized in certain small areas.
Such nodules can have different sizes. This significantly complicates diagnosis. But a specialist will immediately understand what the problem is. Because the symptoms are quite specific. If you press on the manifestation, a slightly whitish liquid will appear.
In some situations, patients complain of itchy skin. However, the risk of bacterial infection should not be excluded. Few people know, but symptoms can appear for several years. The appearance of these bubbles is possible anywhere. But such formations are rare on the palms and soles. Most often, the “abode zone” of the mollusk is the face and neck.
The first sign that should alert you is a small lump on the skin. Then other nodules appear.
In the case of small sizes, they merge into a single seal. It can be 1 cm in size.
Therefore, it is quite difficult not to notice it. Already at this stage, it is important to immediately consult a doctor.
As for general malaise and fever, this is rare.
Interesting fact: apart from its appearance and slight itching, mollusk on the skin does not cause discomfort. Therefore, the child may not be aware of his illness. After the course of therapy there are no scars left on the skin. Only slight depigmentation occurs. In some situations, inflammation of the skin around the nodules occurs. In this regard, the use of antibiotics is relevant.
Folk remedies
Photo: kräutererleben.at
Traditional medicine has long been familiar with molluscum contagiosum and methods of its treatment. To get rid of rashes, use:
- Celandine juice. The juice from a freshly picked celandine stem is applied directly to the shellfish once a day until complete recovery. This remedy should be used with great caution, since celandine contains toxic components.
- A decoction of the string. Two tablespoons of dry string are brought to a boil in 250 ml of water, allowed to brew for an hour and filtered. The resulting decoction is used for a week, wiping the area of the rash three times a day.
- Garlic. The head of garlic, ground to a pulp, is mixed with butter in a 1:1 ratio. Before use, warm the oil to room temperature and lubricate the rashes three times a day. If the skin is not sensitive to garlic, only the juice of this plant can be used for rubbing.
- Alcohol tincture of calendula copes well with infection and prevents the development of bacterial complications.
- Various oils and ointments based on eucalyptus extract can also be used to lubricate rashes.
- After surgery, bird cherry juice will help greatly to restore the integrity of the skin and prevent the formation of scars. It has good regenerating properties and promotes rapid healing. Bird cherry juice is squeezed from the leaves of the plant. It is recommended to take fresh juice for each new use, but it is also acceptable to store it in the refrigerator for several days.
- If you have potassium permanganate powder somewhere in your supplies, then a strong solution made from it is suitable for fighting molluscum contagiosum. The rash should be lubricated 2 times a day for a week.
- Like celandine juice, nodules are treated with juice from freshly picked dandelion stems and leaves 2-3 times a day. You can also prepare an alcohol tincture from dandelion roots, which should be used to treat large areas of rashes.
- Herbal decoction. To prepare it, calendula, eucalyptus, juniper berries, pine shoots, birch buds, and yarrow herb are used. Everything is taken in equal proportions, crushed to a homogeneous mass and mixed thoroughly. A fresh decoction is prepared every day. For a glass of water you need a pinch of the mixture. Bring to a boil, let cool. Take half a glass orally at a time, twice a day, and also lubricate the rash with gauze soaked in the broth.
Herbal tincture. Walnut leaves, calendula and celandine are mixed in equal proportions. After grinding, the mixture is poured with vodka in a ratio of 1:3. Infuse in a dark, cool place for 3-4 weeks, after which the prepared tincture is applied to the rashes 4 times a day.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Main transmission options
The virus that causes the disease is transmitted from one person to another. Representatives of the animal world are not carriers of orthopoxvirus. There are 3 main infection options:
- Due to sexual intercourse with an already infected person;
- through water;
- contact-household method.
The last case occurs most often. You can become infected through tactile touch (hugs, travel on public transport, massage of a sick subject). This explains why children are often treated for this disease.
The indirect contact route is dangerous because a person cannot be sure that infection will not occur even in the absence of obvious signs (an incubation stage is possible).
You can simply walk into an unfamiliar room, sit on the sofa and become a carrier of the virus. After all, it is wonderfully preserved in various materials. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out thorough disinfection in residential premises and public places.
Another situation is frequent change of sexual partners. In this case, the person takes responsibility for his health. You need to understand that contraception cannot protect against all diseases.
In this case, even a hug will be enough to cause health problems. Although the virus foci are predominantly located in the genitals, so a condom can still protect against infection.
The waterway is often not classified as a separate group. In fact, infection occurs through water, but viral particles enter it from an infected subject. Therefore, many experts are inclined to believe that this is also a household contact route.
A similar outcome of events is possible when visiting swimming pools, saunas and public beaches.
In addition, a person who has previously suffered from molluscum contagiosum may become self-infected again. This happens when the skin rubs. But regardless of the method of infection, the clinical symptoms are very similar.
Some people are immune to this infection.
Symptoms
Molluscum contagiosum infection is determined by the following symptoms:
- the patient develops nodules no more than 2 mm in diameter;
- papules are easily removed from the skin with a fingernail;
- over time, condyloma may form due to molluscum contagiosum;
- formations can gradually increase in size, merging into large areas;
- the seals are painless and soft to the touch;
- When pressed, a curdled mass containing epithelial cells and a virus is released from the seal.
Many patients at the initial stage of infection do not feel any discomfort; over time, itching and redness appear.
How does the disease progress?
From the onset of infection to the onset of early clinical symptoms, it takes from 2 weeks to 6 months. Then small nodules appear, which subsequently increase in diameter.
These nodules often disappear on their own within 12 weeks. But medicine knows cases of symptoms persisting for several years. Of course, in the absence of proper treatment.
In addition, the difficulty is that until all these rashes have disappeared, repeated self-infection occurs, so the disease can drag on for a long time.
Often people decide to remove nodules cosmetically without undergoing treatment. This is wrong, since the virus is in the body, and new formations will appear.
The disease is caused by an orthopoxvirus, which belongs to the family Poxviridae, subfamily Chordopoxviridae and genus Molluscipoxvirus. This virus is related to the variola, varicella and vaccinia viruses.
Scientists identify 4 types of orthopoxvirus (MCV-1, MCV-2, MCV-3, MCV-4), but molluscum contagiosum in most cases is caused by viruses of types 1 and 2.
In the case of abundant accumulation of molluscum on the skin or when they occur in different areas of the skin, we can talk about immunodeficiency. In this case, it is better to seek help from an immunologist.
You also need to be vigilant when blisters appear on the eyelid. This is often fraught with deterioration of vision and loss of eyelash hair follicles.
Features of the disease
It’s worth mentioning right away that the subcutaneous mollusk has nothing in common with living mollusks or any other living creatures. Although officially this disease is called molluscum contagiosum. In fact, the virus got its name because of the contents that are inside this pimple. This is a kind of white opaque mass interspersed with keratinized skin epithelial cells. Under a microscope, a subcutaneous mollusk vaguely resembles mollusk shells, hence the name.
The good news for many is the fact that this disease does not spread over the entire surface of the skin. However, the patient is quite capable of becoming a carrier of this disease and beginning to actively transmit it to others. It is important in this case to get rid of subcutaneous molluscum contagiosum as quickly as possible. This should be done not only for the aesthetic effect, but also because of a number of possible unpleasant symptoms that constantly accompany this disease.
Diagnostics
The symptoms are quite specific, so once symptoms appear, diagnosis is not difficult. For example, a rash with an umbilical depression and crust-like contents is typical of molluscum contagiosum.
After examining the nodules, a dermatologist can immediately make the correct diagnosis.
Additional examinations are extremely rarely required. To do this, a small amount of skin is taken from the neoplasm. Next, it is studied under a microscope.
Such a biopsy of the biopsy thoroughly shows all the features of the disease. Molluscum contagiosum nodules are often confused with similar formations, which happens with certain diseases.
Among them are the following formations:
- Flat warts. They usually appear on the face or the back of the hands. They are small in diameter and smooth.
- Keratoacanthomas are convex-shaped formations. They are usually hemispherical in shape and slightly reddish in color.
- Milia are small white dots located in the sebaceous glands of the skin. They occur when excessive amounts of dense sebum are produced. It is not completely released from the layers of the skin and the pores begin to clog.
- With scabies, small pink papules appear on the skin.
- Basal cell carcinoma actually resembles a clam on the skin. They are also lightly pearlescent in color and protrude above the surface of the skin. The main difference is the single location. But the “contagious mollusk” appears in plural quantities. Moreover, these rashes are nearby.
But the risk of confusing this disease with warts or lichen ruber is minimal.
Diagnostic measures
A variety of clinical research methods are used to make a diagnosis.
Papular lesions are predisposed to the development of bacterial infection, for this reason the symptoms of the disease can often change. If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, you can take material from the formations and conduct a microscopy of the contents. This study usually reveals inclusions of the eosinophilic type in the cytoplasmic inclusions of keratinocytes.
Such a diagnosis is necessary to exclude other diseases with similar external signs.
Skin lesions that must be excluded during examination:
- papilloma virus;
- keratoacanthomas;
- syphilitic manifestations in the form of papules;
- pyodermism;
- warts
HIV is often accompanied by molluscum contagiosum, which is why during medical examinations it is necessary to take tests for a virus that affects the human immune system.
Molluscum contagiosum: specific features in adult men and women
Molluscum on the skin of women shows some specific symptoms. It is worth remembering that in the case of pregnancy, this problem does not pose a serious health threat. Does not affect the child's development.
As for the male sex, the only peculiarity is the localization of formations in the penis area (see photo below).
This complicates the process of sexual intercourse. But in women, damage to the mucous membranes of the vagina does not occur. But it happens on the skin near the genitals. This also causes discomfort, but is much easier to tolerate than in men.
What are the features depending on the location?
Molluscum contagiosum on the eyelid should be removed without waiting for natural disappearance. This is necessary to avoid damage to the mucous membrane of the eye. Conjunctivitis or more serious eye diseases may develop.
But on the face it is better to wait until it completely disappears. Certain cosmetic procedures may leave marks on the skin. But after the natural disappearance, no skin defects will remain.
These formations on the genitals must be removed immediately. This will not only make sexual intercourse easier, but also minimize infection of the partner.
Getting to know the disease
Molluscum contagiosum is a contagious disease that is viral in nature and manifests itself as a specific rash on the skin. Typically for the disease, the rashes are “pea-shaped” with a whitish filling of varying sizes. The following photos will show you exactly what molluscum contagiosum looks like.
Molluscum contagiosum in children
Molluscs on the body of a child are more common than in other age groups. The symptoms are not particularly different from how the disease progresses in adults.
Cases of group infection have been recorded.
This happens because children come into contact with a large number of people every day. They love to play games with tactile contact.
Children are often taken to various sections. As a result, infection occurs through contact and household contact.
The difficulty is that children cannot control all their actions. Scratching causes the number of bubbles to increase. In addition, repeated self-infection occurs.
A secondary infection may occur. In this case, long-term use of antibiotics is required.
Mollusks on a child’s body are located in different places. But often it is the stomach, face and neck. It can occur on the genitals of children if the bacteria were already on the fingers, and then the child touched the genitals.
Diagnostics are not very different from those carried out for adults. The signs are clearly expressed. A dermatologist makes a diagnosis based on a simple examination. Sometimes scrapings are taken from the nodules.
Who is at risk
Most often, unfortunately, subcutaneous molluscum appears in children. First of all, they are the ones at risk. It manifests itself in minors mainly between the ages of one and ten years. The easiest way to become infected is through contact with another carrier. Subcutaneous molluscum also appears in adults, although much less frequently.
In most cases, people become infected with this disease in the sandbox, on the beach, when using someone else's clothes, or in the pool. From the photo of subcutaneous molluscum in adults, we can conclude that in them it usually appears on the stomach or inner thighs, and sometimes affects the genitals.
In children, peculiar pimple-nodules appear on the arms, face, chest, shoulders and abdomen. You need to understand that it is usually very difficult to accurately determine the source of infection due to the fact that the disease does not appear immediately, but within a period of two weeks to three months.
In fact, subcutaneous molluscum is a benign viral lesion of the skin, and in some cases, mucous membranes. The provocateurs of this disease are DNA cells, which in their structure are similar to the causative agents of smallpox. In childhood, subcutaneous molluscum often appears due to the fact that the children’s immunity is too weak and vulnerable.
Treatment
If the eyelid area and genitals are not affected, it is recommended not to resort to therapy. Literally after a few months the signs disappear on their own. The human body develops immunity to the virus that causes the disease. But this takes time. But after removing the nodules, traces may remain.
However, in some cases, doctors still advise removing the nodules. Children tend to scratch them, which leads to a protracted form of the disease. In addition, concomitant diseases are possible.
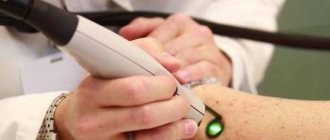
Removal is carried out using liquid nitrogen or products designed to remove various warts.
Often one of the active ingredients is salicylic acid. But still, experts are in no hurry to remove such formations, so as not to leave traces, and it is better to ensure immunity to this disease. The body itself must resist viruses of this kind. Complications are rare.
There are 4 ways to remove molluscum on the skin:
- freezing;
- mechanical;
- taking antibiotics;
- immune therapy.
The mechanical method uses a scalpel or a special device. This method has a significant drawback: there is no anesthesia, so it is a rather painful process.
Afterwards the rash is cauterized with iodine. This removal option is not recommended for children.
Laser removal is a modern and popular method. Despite the high cost, this is what most experts recommend.
The skin is minimally injured and it does not take much time. No discomfort. Relapse is minimized. But we must not forget that we need to disinfect clothes and household items.
Immune therapy is preferred for skin lesions in children. It is based on antiviral ointments. After the course of treatment, formations disappear and the immune system is strengthened.
Treatment with antibiotics is undesirable. It is necessary in advanced stages with a large number of rashes and severe redness of the skin.
The most gentle treatment option is immunotherapy. There is no serious burden on the body and no pain.
other methods
If there are very few rashes, then chemotherapy drugs are effective. But they are not recommended to be used for a long time, as this can lead to irritation to the skin.
For minor dissemination, UV therapy is also used. Healing ultraviolet rays have a desensitizing, restorative, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effect. The main thing is, before starting phototherapy with ultraviolet rays, to establish the presence of individual sensitivity to this method, as well as the optimal biodose, which is individual for each patient. It is determined by test irradiation of the skin of the forearm or buttock. Remember that UV therapy is contraindicated for precancerous skin lesions, albinism, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis, severe sensitivity to light therapy, and xeroderma pigmentosum.
When treating minors, the tuberculin application method is often used. In pediatric dermatology it is used as one of the most painless and safe. This is a new and modern technique, but there is no more or less accurate data on its effectiveness yet. The main thing is that minors have been previously vaccinated with isoprinosine or BCG.
Prevention
Special complications usually do not arise. Prevention lies in following the rules of skin care. It is necessary that each family member has their own means of cleansing the body.
Most often, molluscum contagiosum affects children. Parents must take care of the child's hygiene. Swimming pools are especially dangerous. Often the virus is contained in the water in which a large number of people bathe.
Most modern pools are thoroughly disinfected, but there are exceptions.
It is important to wash your hands after using public transport. It is advisable to use an antiseptic.
Recommendations for caring for a child during illness
To avoid spreading the infection to other parts of the body, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Cover the lesions with tiny bandages.
- Wash your hands often.
- Wash clothes in hot water and iron with a hot iron.
- Clean your child's skin with a hydrogen peroxide solution.
Rice. 15. If you have molluscum contagiosum, you should constantly clean and lubricate the skin with antiseptics.