Burn injury is one of the most common traumatic injuries in the world. Patients are often faced with a choice of which bandage to apply to the burn site. In this case, the method of treatment depends on the area of the lesion, the depth of the burn, and the general health of the victims. It is important to remember that superficial minor burns can be treated at home . If a more serious injury occurs, consult a doctor.
Classification of injury
To determine what treatment is necessary, you need to briefly describe what degrees of damage are distinguished:
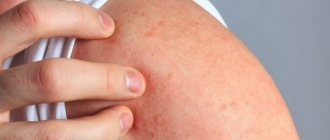
- First degree burn . Redness, slight pain and swelling appear in the superficial layers of the epidermis.
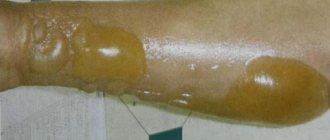
- Thermal wound II degree . Severe redness, swelling, detachment of the damaged layer, formation of blisters filled with yellow liquid. The affected area heals in 11-15 days, skin pigmentation can persist for 2.5-3 weeks.
Wounds of the first two degrees are considered superficial. Their treatment is possible on an outpatient basis. They are able to heal with conservative treatment.
- IIIA degree burns are accompanied by damage to the epidermis and dermis. A light-colored scab forms. Beneath it there are noticeable pink areas - the papillae of the dermis. As the scab moves away or changes, areas covered with epithelium appear in patches. Recovery occurs after 3-6 weeks. The result is a rough scar.
- IIIB degree : skin damage, muscles are often injured. The wound is cleared of dead tissue after 4-6 weeks.
- IV degree is the most prognostically unfavorable and severe. These injuries affect the fascia, muscles, tendons and bones. The scab is thick and charring may occur. Possibly accompanied by purulent complications such as arthritis, abscesses and phlegmon.
Lesions of IIIB and IV degrees are deep wounds that require hospital stay and surgical treatment, as well as the issue of skin restoration using skin grafting. It is necessary to seek specialized help and rational treatment from appropriate specialists without delay.
Lesions of IIIB and IV degrees require hospital stay and surgical treatment.
Basic Rules
The burn dressing is treated with solutions that achieve the following results:
- surface disinfection;
- moisturizing the skin;
- accelerated recovery;
- anesthesia;
- the antibacterial properties of the antiseptic are manifested.
Before using burn remedies, read the list of recommendations. The application rules for burns are as follows:
- Complete sterility is maintained. A bandage is usually used to secure the patch. It must be clean, preferably from a new package that has not yet been opened. This will eliminate the risk of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms;
- You can only apply a bandage to a burn wound of mild or moderate severity. It is forbidden to apply any pressure to a severe burn. In this case, the fabric may stick and be difficult to remove;
- It is permissible to apply wet antiseptic dressings only after treating the surface of the affected area with disinfectants. A healing ointment is also applied before use.
Complications
A more serious condition in the case of deep burns occurs if they occupy more than 5-11% of the body or the total burn area is more than 20%, then in this case burn disease occurs. This disease is associated with loss of skin and profound impairment of their functions (protection against infection, loss of pain and tactile sensitivity, maintaining water balance, thermoregulation). A serious condition requires a systematic approach and comprehensive treatment aimed at preserving the life of the victim, being in intensive care conditions and a multidisciplinary approach of specialists. It is important to note that for children under one year old, 3-5% of the burn area is sufficient for this complication to appear.
Treatment in hospital
The decision about what kind of dressing to apply to the site of a severe burn in a hospital setting is made only by medical specialists. Thus, for the treatment of dermal superficial and dermal deep (2nd and 3rd degree) burns under the supervision of a physician, it is recommended to apply a sterile bandage.
It is most preferable to use the sterile wound covering Aquacel Bern (in the form of a rectangular plate), made using the special Hydrofiber technology. Despite the fact that the coating is very thin, it is capable of absorbing a large amount of wound discharge and providing a moist environment for faster and better healing.
Thanks to the stitching, the coating remains intact while on the wound surface, even during physical activity. The use of Aquacel Bern eliminates the need for frequent dressings, since it can remain on the wound for up to 21 days, that is, until the wound is completely healed. More detailed information can be obtained by watching the video in the “Webinars” section.
First aid for a thermal wound
First of all, when you receive a wound, you should not panic. If you are at home, to alleviate the condition, it is enough to immerse the affected areas in cold water until the pain stops . In case of a burn, your first aid kit should have the following items:
- Panthenol 5% in the form of cream or aerosol. Among the agents that can improve microcirculatory disorders and wound cooling, 5% water-soluble anilocaine ointment “Anikol” is also used. The use of antioxidants, for example Soderm ointment, vitamin E promotes faster recovery of the affected skin area.
- Sterile bandage to cover the wound.
- Hydrogen peroxide 3% or another antiseptic if the burn also causes contamination of the wound. Important! If the wound comes into contact with the ground, vaccination against tetanus is necessary.
General actions for burns
Most often, people suffer from burns caused by open fire, hot objects, or boiling water (thermal). However, there are also types of burns such as electrical (from electric shock), chemical (from acid, alkali), and radiation (from the sun). To begin with, we will list the general procedure that must be followed for any burn.
- Stop the effect of the negative factor: extinguish burning clothes, turn off the power supply, etc.
- Specify the type of burn, and, if possible, determine its area and degree. To determine the area, use the “rule of nines”:
- palm, genitals - 1% each,
- arm, chest on both sides - 9% each,
- leg - 18%.
Degrees: I - redness and swelling, II - blisters with transparent contents, III - necrosis of layers with the formation of a dense scab, IV - charring of tissues. - In severe cases, immediately take the victim to a medical facility or call "emergency".
- In case of minor injury, the burn area can be watered with cool water for 10-15 minutes. In case of extensive burns, this should not be done.
- Cut the clothing around the injured area; if any remains are stuck to the wound, leave them alone. Apply an aseptic gauze bandage around the burn. Do not use cotton wool for this.
- If your fingers are affected, cover them with gauze or a bandage. It is better to immediately remove rings and other jewelry from your hand before swelling occurs.
- Fix the burned part of the body, make sure that it is on top, preferably above the level of the heart.
- Give the victim a pain reliever and antihistamine. If there is no vomiting, provide him with plenty of fluids. Mineral water without gas or plain water with 1 tsp will do. salt and ½ tsp. soda per 1 liter.
Position the patient so that the burned areas are stretched as much as possible.
Modern headbands
There are a huge number of new dressings that can be used at home to promote rapid healing. The main difference from a regular bandage is that they create a favorable microclimate in the wound. After all, if the affected area of the skin dries completely, it will not speed up healing.
Branolind N with Peruvian balsam
The patch has a specific odor; it is used for wounds of 1-2 degrees; it cannot be used for necrotic damage. You can change the bandage once every two days. A contraindication is an allergic reaction to the patch, manifested by redness and swelling.
Hydrocoll
Gel dressing, which is used for 1-2 degree burns. The package contains a 15x15 cm bandage that can be adjusted to the size of the wound. The bandage should cover the damaged area by 1-2 cm.
Silkoplast Comfort IT-Burn
Used for grade 1-2 wounds, relieves pain and promotes rapid healing.
How to avoid complications and improve wound healing?
The main complication may be burn disease. It develops when more than 5–10% of the total skin area is affected. The complication arises due to a complex malfunction of organs and systems. We are talking about tachycardia, poor circulation, intoxication and other pathological conditions. It is important to contact the burn department in time, where specialists will eliminate pain, normalize breathing, and prevent kidney and cardiovascular failure.
Another complication of burn injuries is sepsis. To avoid infection, you need to use only specialized plasters on burns and only as prescribed by a doctor when it comes to serious injuries. Regular treatment, monitoring the condition of the wound and the healing process is what is required during treatment to avoid complications.
Burn: concept, degrees and types
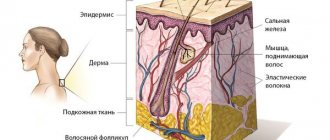
It is a type of physical injury. Occurs due to exposure to high temperature, a special chemical, ultraviolet or ionizing radiation, or electric current. The receiving process is accompanied by severe pain and noticeable damage to the skin, mucous membrane or cornea of the eyes.
The severity of the condition depends on the size of the burned surface and the depth of tissue damage. The larger they are, the more severe the injury.
There are four degrees of damage based on depth:
- The first degree is characterized by redness of the injured area, only the upper layer of the epidermis is affected.
- The second degree is characterized by the appearance of blisters filled with yellowish liquid.
- In the third degree, the skin is deeply affected, and the processes of death and scab formation begin.
- In the fourth degree, necrosis of the skin occurs, accompanied by charring; bones and muscles may be involved in the process.
Depending on the type of injury, burns can be:
- Thermal. The reason is exposure to boiling liquid, steam, a hot object or open fire.
- Electrical. Occurs under the influence of electric current. Characteristic are small wounds at the discharge entry/exit points. They are characterized by great depth and electrical trauma to internal organs.
- Chemical. Occur under the influence of alkaline or dangerous acidic compounds, salts of heavy metals. Not only the skin, but also the oropharynx and esophagus can be affected.
- Radiation. Occur during atomic explosions and as a result of radiation leakage, they are rare. This category includes damage to the skin from exposure to the rays of the sun.
What to do in case of a burn?
Table of contents:
- Classification of burns
- Severity
- First aid for burns
- What is not recommended to do if you have a burn?
- Which doctor should I contact?
- Treatment of burns
- "EversLife-SP" and "EversLife - Gel" for healing burns
Everyone has received a burn at least once in their life: handling a hot frying pan, burning on the beach, touching a dangerous plant or jellyfish, etc. As a rule, such household injuries are the result of carelessness, ignorance or inattention. You can deal with minor injuries on your own, but in some cases you cannot do without the help of a doctor. In this article we will talk about what kind of burns there are, how to understand whether you need to urgently consult a doctor or just use a reliable remedy from your home medicine cabinet, as well as about proper treatment and skin care after a burn.
Classification of burns
A burn is damage to the skin that occurs due to contact with hot objects and liquids, hot steam, chemicals, electricity, and other reasons. Depending on whether the burn is superficial or deep, and what caused the injury, the scheme of competent first aid and subsequent treatment depends.
Therefore, you need to have an understanding of the types of burns.
Taking into account the causes of occurrence, the following types of burns are distinguished:
- Thermal - a person receives them due to high temperature. Such situations often occur in domestic conditions - for example, as a result of contact with fire, hot liquid, a hot object or steam. The damage they cause can be either mild and superficial or very severe, threatening health and life.
- Chemical - they appear due to various substances. At home, burns of this type are usually caused by compounds containing acid or alkali. This could be “chemicals” for cleaning or maintenance.
- car, laundry detergent, or acetic acid used in cooking.
- Electrical - occurs when current is applied to the skin, soft tissues and organs due to improper handling of household appliances or if the equipment is short-circuited, when touching wires or exposed contacts. A mild burn of this type is accompanied by minor damage to the surface layer of the skin. But more serious cases can result in widespread and deep injuries that affect internal organs and impair their function.
- Radiation - most often occur due to prolonged and intense exposure to ultraviolet rays. For example, working in the countryside under the scorching sun or relaxing on a sun lounger at times when the UV index is high can cause sunburn. However, such burns are usually superficial and relatively easy to treat. Another, much more dangerous source of radiation burns is radiation injuries from ionizing radiation.
- Combined - formed under the influence of several damaging factors.
Burns also differ in the location of the damage:
- on the skin;
- on the mucous membrane;
- in the respiratory tract;
- on internal organs.
Severity
The severity of the burn is directly related to the depth of the lesions. There are 4 degrees, and each of them is characterized by certain symptoms.
Grade I
The burn affects the superficial layers of the skin. The damage is accompanied by redness, slight swelling, severe or moderate pain, and a local increase in temperature. There may also be discomfort when moving. For example, if your hand or fingers are injured, the pain intensifies when you try to move them or when you touch the burned area. With simple treatment, first-degree burns disappear without traces within 2–3 days in adults and 3–5 days in children.
Grade II
The deeper layers of the skin are affected and blisters filled with fluid form. Inflammation occurs around them, and when the bubble is removed, weeping wounds of varying sizes may appear in its place. Grade II injuries are accompanied by swelling and redness. With such a burn, a person experiences burning pain, which for some time can interfere with sleep and leading a normal lifestyle. As the blister heals, it falls off and a crust forms at the site of the wound.
To provide first medical and sanitary aid for thermal and sunburns of 1st and 2nd degree, “EversLife - SP” should be used.
Grade III A
The skin is damaged very deeply; a so-called scab forms at the burn site - a dense gray-brown crust. The painful sensation before its formation is acute, since the damage affects the layers of skin with nerve endings. Sensitivity is reduced, regeneration is very slow, and skin grafting is often required. The risk of developing burn disease increases.
Grade III B
Irreversible damage affects not only the skin, but also the subcutaneous tissue.
For local treatment of 2nd and 3a degree burns and temporary closure after surgical treatment of 3b degree burn wounds, use the EverLife-Gel hydrogel dressing.
Grade IV
An extremely severe burn with charring of the skin and underlying tissues, muscles and bones are damaged.
The degree of burn cannot be the only guideline when providing first aid and planning further actions. For example, with grade I injuries that seem mild at first glance, but with a large area of damage, a burn disease may develop, which cannot be treated independently. This condition is characterized by disruption of the activity of internal organs and all body systems. For severe and extensive burns, treatment and care should be carried out only under medical supervision.
First aid for burns
Let's look at the rules of first aid for minor household burns.
First degree thermal burn of a small area - burn of a finger, hand, etc.
- Immediately stop exposure to high temperature;
- If you are burned by boiling water, steam or a hot object, wash the affected area of the skin with cool boiled water to reduce the pain;
- We apply the combined hydrogel product “EversLife-SP” (disinfectant and wound healing).
Thermal burn II degree
- Stop exposure to high temperatures;
- We apply the combined hydrogel product “EversLife-SP” (disinfectant and wound healing);
- Apply a sterile bandage. It should be changed daily to prevent infection.
Skin burn with vinegar essence
- We wash the wound with clean running water;
- To neutralize the effect of vinegar essence, apply a solution of soda, soap or ash. They are all alkalis, an antidote to acid;
- We use a product with a healing and analgesic effect “EversLife-Gel” openly or under a sterile bandage.
If the vinegar burn affects the eyes, call an ambulance; In this case, you cannot use “neutralizers” yourself.
Iodine burn
- We wash the area of skin that received iodine with running cool water;
- We use toothpaste, crushed chalk, tooth powder, sugar or soap solution as a “neutralizer”;
- If necessary, apply a healing hydrogel agent.
Treatment of burns with iodine can be carried out at home, since the damage is most often first degree. But if signs of allergy appear or the damage has spread over a large area, you need to consult a doctor.
Minor electric burn (1st degree)
- Stopping exposure to electricity. The person providing assistance to the victim must be safe.
- We treat the skin with an antiseptic;
- We apply the anti-burn hydrogel agent “EversLIFE-SP”.
- Even if the burn caused a small mark on the skin, you should definitely see a doctor. If the injury occurred due to high voltage current, and the resulting damage is extensive and deep, it is necessary to call emergency medical assistance.
Hogweed burn 5
- We blot the area where the plant juice has come into contact with a cloth, without smearing the juice on the skin;
- We protect the affected area from the sun and, if possible, go indoors;
- Wash with a solution of soap and soda;
- Treat with an antiseptic;
- We apply the anti-burn wound-healing hydrogel agent “EversLife-SP”.
In the future, a hogweed burn may require treatment with special means and observation by an allergist.
Jellyfish Burn 6
- We immediately leave the sea water;
- If the jellyfish or its fragments remain on the body, remove them from the skin, protecting your hands with gloves or at least a towel;
- We wash the burn site with an antiseptic; You can use alcohol-containing solutions or Evers Life alcohol wipes;
- If possible, make a lotion with a cotton swab dipped in soda solution;
- If blisters appear, apply a clean, damp bandage and go to a medical facility.
Ointment for jellyfish burns should only be prescribed by a doctor. Even if the injury is mild, special treatment for a jellyfish sting may be needed to avoid complications.
If a burn of any kind affects a large area of skin, mucous membranes, eyes and respiratory tract, as well as if the injury is severe or a child is injured, urgent medical attention is needed.
What is not recommended to do in case of a burn?
- When treating a burn with a blister, for example on a finger or hand, it is not advisable to open the blister at home - it is better to see a doctor to make a puncture and remove the membrane. A weeping wound may open under it, into which pathogenic bacteria can easily enter, causing inflammation and other complications.
- Do not touch damaged skin with dirty hands, even if the burn is first degree. Before applying a wound healing agent or when changing a bandage, your hands should be washed and treated with an antiseptic.
- Do not apply ice, cold metal or use ice water to the injury site, so as not to cause additional frostbite to the affected area. Such actions may provide temporary and short-term relief, but then the pain will only intensify. To relieve discomfort, you can wash the burned skin with clean, cool, but not too cold water.
- You cannot provide first aid without taking care of your own safety. This rule is especially important if a person needs help with an electrical or chemical burn.
- Contrary to the widespread “folk” tradition, you should not lubricate the damaged area with oil or fat-containing preparations - they can increase the severity of the damage due to the fact that they create a “film” on the damaged area.
- It is not recommended to use substances containing alcohol for antiseptic treatment - they can cause additional burns, increase pain, dry out already damaged skin, impairing regeneration.
Which doctor should I contact if I get a burn?
If you have a mild first-degree skin burn, you can contact a physician at the clinic. If the injuries are grade II, help can be provided by a surgeon or emergency room doctor.
Doctors who treat third- and fourth-degree burns are combustiologists. “Severe” victims, patients with burn disease and other complications are referred to them. It is extremely difficult to find a combustiologist in a district clinic; as a rule, doctors of this profile work in large or specialized medical institutions.
Treatment of burns
General treatment of household burns is aimed at:
- Protection against infection;
- Maintaining normal regeneration;
- Eliminate discomfort.
Local treatment of minor burns (1st degree) can be carried out at home using good over-the-counter preparations for external use, including EversLife-Gel and EversLife-SP
When treating second degree thermal burns when blisters appear, the following methods are used:
- Open With the open method, thanks to the constant flow of fresh air, the burned skin dries naturally and heals easily. The disadvantage of this method is a higher risk of infection. Additionally, touching, rubbing, or any other mechanical force on the damaged area can slow down recovery and cause discomfort. Therefore, in case of a burn, it is worth using EversLife-SP, which will prevent infections and help
- Closed With the closed method, moisture-absorbing sterile dressings with a healing agent or EversLife-SP are applied to the burn site, for example, when treating blisters. They absorb fluid discharged from wounds and protect against secondary injury and infections. The bandage must be changed regularly. The closed method of treating burns is often used when the skin on a moving part of the body or in contact with clothing is damaged. The disadvantages of the closed method are possible painful dressings and relatively high consumption of materials7.
- Mixed Open and closed methods can be used simultaneously, alternating throughout the entire treatment period. The open method is chosen when the victim can be at rest and the burn wound will not be subject to mechanical stress (touching, friction of clothing, stretching). Applying the EverLife-SP bandage will protect the wound from infection and unnecessary irritation, for example, if a person needs to move actively.
To treat inflammation during a burn, which can occur as a complication, antibacterial drugs and additional treatment of the burned area of skin are sometimes prescribed. At the healing stage, you need to reduce the mechanical impact on the affected area - this way recovery will take less time, and the wound will heal without leaving any traces. During this period, it is advisable to use special products that support regeneration and have an antiseptic effect, for example, EversLife-Gel gel or EversLife-SP bandage.
"EversLife-SP" and "EversLife-Gel" for healing skin burns
Domestic burns can be treated at home using anti-burn products. These include anti-burn hydrogel products “EversLife-SP” and “EversLife-Gel”, intended for minor skin damage8. The anti-burn wound healing effect of the product is based on the synergistic effect of stimulating skin regeneration processes with composite mixtures of chitosan-gelatin polyelectrolyte complex and dexpanthenol.
In addition, an important feature of EversLife-SP and EversLife-Gel is its analgesic and antimicrobial effect, due to which the pain subsides and the person feels better. Thanks to this, “EversLife-SP” and “EversLife-Gel” will become indispensable assistants for the mother of a baby or teenager.
The gel in the EversLife-SP and EversLife-Gel dressings with a light texture is easily absorbed and does not stain hands and clothes. This product is indispensable for a home, travel or children's first aid kit. Also, for skin restoration, protection and a speedy recovery from a mild household burn, “EversLife-SP” and “EversLife-Gel” can be used by both adults and children.
Conclusion
It is important to remember that most often in our lives we encounter minor burns, the main cause of which is carelessness and failure to follow safety rules when cooking, cleaning using cleaning products and operating household appliances. That is why the best way to prevent such injuries is caution and attentiveness.
Maybe you'll like it
Hemostatic agent "EversLife-Hemo"
Anti-burn agent "EversLife-SP"
Wound healing agent "EversLife-Gel"
Wound dressing Vilovond POVI Pad
Anti-burn wipes
An anti-burn napkin is a small non-woven fabric impregnated with a gel composition and intended for first aid for minor burn wounds. It acts in a similar way to bandages - it reduces skin temperature, disinfects, anesthetizes, and relieves itching.
In our catalog you can buy anti-burn wipes from the Water-Jel brand in sizes 40×10 cm , 45×20 cm , and 49×28 cm , as well as EVERS LIFE . The assortment also includes a wound-healing coating, Kollakhit-FA , which is a porous napkin with multi-component impregnation.