Why do papillomas appear?
The reasons for the appearance of papillomas on the body can be divided into main (main) and accompanying ones, which rather act as triggers for the formation of visual manifestations of the disease. The cause of skin papillomas, which is considered the leading and no alternative, is infection of the patient with the human papillomavirus (HPV), which in medical practice is classified as a group of Papillomaviruses.
Statistics demonstrate the highest level of HPV prevalence among the population of our planet, stating that 9 out of 10 people are carriers of one of the 100 strains of this virus known to official medicine. Moreover, each of the isolated types of viral agent has different characteristics, localization zones and the likelihood of developing complications and unpleasant consequences.
Despite its prevalence, the papilloma virus has relatively low resistance to aggressive environmental factors, which dictates the predominance of the contact route of its transmission from the carrier to a healthy person. The risk of infection is especially high during prolonged contact with the bare skin of a person suffering from the disease, which is observed, for example, during a massage. In medical practice, there are also cases of household spread of a viral agent that enters the patient’s body through common objects, however, this reason for the appearance of papillomas is significantly inferior to the contact mechanism of spread of the virus.
When HPV gets on the skin, it primarily affects the basal layer of the epidermis, remaining in a latent state for a long time, which is characterized by an asymptomatic course of the disease. This condition most often accompanies an incubation period, which lasts from 1 to 6 months, but can persist for years.
The following factors act as provoking agents for the appearance of papillomas on the skin:
temporary decrease in immunity or development of an immunodeficiency state (HIV, AIDS); the presence of microtraumas, cracks, scratches, open wounds on the surface of the patient’s skin; hormonal imbalance, which may be associated with pregnancy, lactation, menopause, etc.; promiscuous sexual intercourse, oral sex with a carrier of the papilloma virus; nervous-emotional tension, stress, physical or mental fatigue; bad habits, poor nutrition; endometriosis.
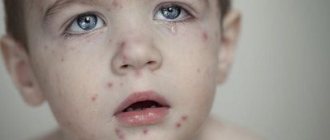
Attentive attitude to the health of the child is the most important task of responsible parents.
Moreover, often any pathological conditions, and especially neoplasms, cause fear and panic not so much in the smallest patient as in the caring mother. If you notice a papilloma on your child’s face or body, you should not perceive it as something terrible. Papillomas in children are a common phenomenon that is caused by one of the most common viral agents on the planet - the human papillomavirus (HPV). We will try to figure out how to rid the baby of an unpleasant tumor and whether it is possible to prevent infection.
Symptoms of papillomas
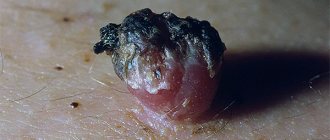
The penetration of the papilloma virus into human blood is not accompanied by a pronounced symptom complex, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease. The patient does not even suspect that he is not only a carrier of a viral agent, but can also infect other people. The main symptom of infection is the direct formation of a skin tumor on the body, which can be localized in almost any part of the human body.
Numerous photos on the Internet clearly demonstrate what papilloma looks like on the body. Typically, a skin growth is represented by an oval or dome-shaped compaction, or a papule, which is attached to the tissue through a thin stalk or thickened base. The color characteristics of papilloma on the skin can vary widely, from light pink to dirty brown.
Some HPV strains are characterized by multiple manifestations, which may be accompanied by the fusion of individual neoplasms. As a result, an epidermal structure is formed that looks like a lobed cauliflower.
Types and features of localization of papillomas in children
Parents are often frightened by the variety of shapes and colors of epidermal growths on the child’s skin. This is due to the fact that medicine has identified about 120 different strains of HPV, each of which is manifested by specific visual characteristics and localization on the body. Children most often encounter the following types of papillomavirus:
- Ordinary papillomas - appear in the form of small oval or spherical bumps on the skin (warts) that can have different colors. Ordinary papillomas are most often localized on the hands (back of the hand), on the scalp and buttocks, but can appear in almost any area of the epidermis.
- Flat papillomas - the second name for this type of neoplasm - juvenile warts, however, quite often small small papules the color of healthy skin appear in infants. Most often, such papillomas are localized in a child’s face, head and hands.
- Papilloma of the throat - especially often manifests itself as a consequence of infection of the baby during childbirth and can be accompanied by a change in voice and difficulty breathing. Papilloma on the tonsil in a child can manifest itself for a long time as unexplained discomfort in the neck area.
- Plantar papillomas - form as single warts on the foot and can cause pain when walking and especially running. Such structures can result from damage to the skin of the foot and prolonged wearing of compressive or, on the contrary, too large shoes.
- Thread-like papillomas are round or oblong formations that usually form in the area of skin folds: (on the neck, in the armpits, in the groin area, on the face in the area of the nasolabial triangle).
- Epithelial hyperplasia is visually diagnosed as excessive growth of mucous membrane tissue, which, like classic neoplasms, is of a viral nature. Hyperplasia can appear as small papillomas on the child’s lip, as well as on the surface of the tongue or palate.
Most types of papillomas that affect children do not exhibit pronounced oncogenicity, that is, they are not inclined to cause an oncological process, however, to clarify the diagnosis, you should still consult a specialist.
Common types of papillomas
As mentioned above, medicine knows more than 100 types of virus, which indicates the diversity of manifestations of the disease. However, about 10 types of HPV are considered the most common:
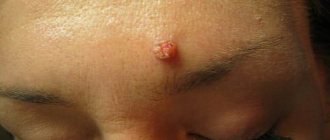
- Vulgar papillomas. They are oval seals that may have a keratinized yellowish surface. Vulgar papillomas on the hands of adult patients are the most common localization option, while children are more often characterized by a knee location of the growths;
- Plantar papillomas. The causative agents of papilloma on the leg are HPV types 1, 2 and 4, which are manifested by the formation of single or multiple growths on the sole of the foot, which, as they grow, make walking difficult. Moreover, such structures are often confused with calluses, which complicates the identification and timely treatment of papillomas;
- Flat papillomas. They are provoked by HPV types 3 and 10 and appear as multiple flat lumps, constant color, with a smooth surface;
- Filiform papillomas. They are most typical for the older age group of patients whose age exceeds 50 years. Yellowish bumps or growths are localized in the eyelids, groin, armpits and neck. If the filamentous neoplasm is subjected to trauma or constant friction with clothing, treatment of the inflamed papilloma should be carried out as quickly as possible;
- Lewandowski-Lutz papillomas. This type of skin manifestation is often called epidermodysplasia verruciformis, which manifests itself as multiple macular warts localized on the arms and legs, having different color characteristics;
- Genital warts. The most dangerous type of symptomatic manifestation of the human papillomavirus. The growths are pinkish or gray pointed growths located on the external and internal genital organs, as well as in the pubic area and tongue;
- Juvenile papillomas. Caused by HPV types 6 and 11. They affect the larynx area, complicating the breathing process and complicating the patient’s normal speech. Infection usually occurs during childbirth, by transmitting the virus from the mother's vagina to the child;
- Local epithelial hyperplasia. This manifestation is a consequence of infection with HPV types 13 and 32, which is expressed by the formation of multiple papillary rashes, prone to fusion, on the tongue and red border of the lips.
What is papilloma and how it is dangerous, we will try to figure it out below.
Etiology of childhood papillomas
You can become infected with the papilloma virus through several mechanisms, but for children, spread most often occurs during personal tactile contact with a carrier, for example during play, or when using common objects, which is especially typical for places where children gather in large numbers (kindergarten, playground), where Toddlers often exchange toys or have common objects. Another route of infection is transmission of the virus from mother to child perinatally and during childbirth. Passing through the birth canal, the baby can come into contact with papillomas or condylomas of the mother’s internal organs, which is considered a key factor in infection.
As already mentioned, any papilloma is a visual manifestation of the presence of a virus in the body. However, not all HPV carriers experience pathological proliferation of epidermal tissue or mucous membranes. If a person's immune system is sufficiently stable, skin growths may not appear for a long time. The following factors and conditions of the child’s body can provoke tissue proliferation:
- Weakening of the immune system due to vitamin deficiency or illness;
- Traumatic violations of the integrity of the skin: abrasions, scratches, wounds, etc.;
- Poor nutrition;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Hormonal changes during puberty.
It should be remembered that, according to statistics, nine out of ten people on the planet are carriers of the papilloma virus, which means you should not panic if you notice a small skin growth on a child, which is popularly called a wart.
Are papillomas on the body dangerous?
In fact, papillomas cannot be considered completely harmless neoplasms, since in the absence of timely treatment, they can spread to healthy tissue, which is called autoinoculation, and cause multiple warts. However, this is also not the key factor why papillomas on the body are dangerous. Hidden here is also the answer to the pressing question of many patients about how a mole differs from a papilloma. A mole, being a simple accumulation of pigment, does not pose a danger to human health.
The main risks associated with the presence of papillomas on the body include the possibility of melanization of the neoplasm, which consists of malignant degeneration of the tumor. As a result, the patient may experience an oncological process or be diagnosed with a precancerous condition. The likelihood of such an outcome depends on the type of HPV and the area of localization of papillomas. For example, genital warts located on the surface of the cervix in 50% of cases provoke cancer of this organ.
Another danger is the high risk of mechanical damage to the papilloma, which can lead to severe bleeding, infection of the wound and the formation of scars or scars on the skin. Based on this, to the question of whether it is necessary to remove papillomas on the body, the answer should only be positive.
Papilloma in children, causes, treatment and removal.
Papilloma in children. Basic principles of treatment.
Neoplasms on the skin or mucous membrane of the mouth, nose, pharynx, etc., which are viral in nature, are one of the most common skin diseases. They can appear in the form of moles, warts, papillomas. People of different ages suffer from this disease, among them, of course, children. With their appearance on the body, we can say that papillomavirus infection in children has been activated. The causative agents of the infection are human papillomaviruses, of which about 100 species are known today.
The main factors leading to the spread of the virus are decreased immunity and hormonal imbalances in the body. There are many ways of infection:
- Papilloma in children (especially the larynx) can occur after birth due to infection during childbirth if the mother had vaginal condylomas.
- Upon contact with a carrier of the virus, especially if there are microtraumas, cracks, or abrasions on the body.
- Autoinfection. If a child bites nails, hangnails, or tears off existing warts, more and more surfaces of the skin become infected.
In adults, infection also occurs through sexual contact.
So what does papilloma look like in children? How to treat them? Where are they most likely to be located? And, in general, how does papillomavirus infection occur in children?
Manifestation of papilloma in children.
Papilloma is a growth or tumor on the skin or mucous membrane, most often mushroom-shaped, on a thin stalk. Color varies from white to dark brown. The incubation period is on average 2-3 months, the virus is most active after 6 months of infection.
The forms of manifestation of papilloma are very diverse:
- warts (skin papillomas), most often observed on the hands;
- simple or vulgar papillomas. Most often they appear on the backs of the hands and knees in children. They look like hard bumps with a keratinized surface (from 1 to 10 mm);
- plantar papillomas. Quite painful formations that make walking difficult. Not to be confused with calluses, which have a smooth surface;
- flat papillomas. Smooth lumps of natural color can cause a lot of trouble for the child, in the form of redness, itching, inflammation and pain;
- A rare disease is epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Red-brown papillomas on the hands and feet, high risk of degeneration into malignant tumors (30%);
- juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis. Babies born from an infected mother are at risk. The growth of papillomas on the vocal cords can lead to speech impairment and even create breathing problems. It should be especially noted that the disease is quite rare.
Treatment of papillomas
Based on the fact that there is no single standard for the treatment of papillomas, parents must figure out for themselves what to do if papilloma is discovered in children. Of course, you need to watch her carefully. Is it growing, is there inflammation? How many tumors appeared? An appointment and consultation with a doctor will help dispel many doubts and fears.
Doctors, examining the tissue of papillomas, will be able to establish the correct diagnosis. Treatment of papillomas is complex. In the first place, of course, is the correction of immunity. As soon as the body’s natural defenses begin to work, it will become easier to fight the virus. There are many cases, especially in children, when papillomas disappeared spontaneously.
When fighting the human papillomavirus, a variety of antiviral drugs are used, and surgical removal of formations is also proposed.
Nowadays, there are a wide variety of surgical methods, where the removal of papillomas occurs quickly and painlessly. This can be cryodestruction (exposure to low temperatures), laser and/or diathermocoagulation (cauterization with electric