The term papilloma defines a benign tumor that forms from skin cells or mucous membranes. The reason for its development is a specific human papillomavirus, which can be transmitted sexually or through household contact. Replication (division) of viruses leads to an increase in the activity of division of infected cells with the formation of characteristic formations (they are also called warts). The main method of treating papillomas is their removal using various modern physical techniques, including cryodestruction, electrocoagulation or laser therapy.
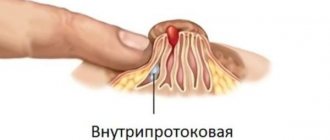
Intraductal papilloma (ductal papilloma).
Removal of papilloma on the nipple
Ductal papilloma (intraductal papilloma) occurs near the nipple; removal of papilloma on the nipple is possible using electrocoagulation under local anesthesia. Signs of intraductal papilloma (or nipple papilloma) are the appearance of blood-stained or transparent discharge from one nipple. Ductal papilloma is often a precancerous condition. Treatment of papillomas on the nipple and intraductal papilloma is carried out by a mammologist-oncologist.
On the picture:
papillomas on the face
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is widespread throughout the world. HPV causes warts, papillomas, and genital warts. Different types of human papillomavirus (there are more than 100 of them) cause different diseases.
Genital warts are small skin-colored formations, their size ranges from 1 mm to several centimeters. Genital warts can form on the genitals, near the anus, on the face, even in the mouth, on the body, abdomen, in the groin area, and in the armpits. This is a viral disease. The causative agent of genital warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
In men, the glans penis and frenulum of the foreskin are most often affected. In women, damage by the human papillomavirus appears on the labia, clitoris, vagina, and cervix.
Genital warts can be localized around the anus.
From single ones, genital warts can grow into rashes that can spread, taking on the appearance of cauliflower. “High-risk” HPV types (16, 18, 31, 33 and 35) cause cervical dysplasia and can become malignant.
Causes
The most common cause of pathology is traumatic damage to the papilloma - for example, it can be squeezing or rubbing with clothing.
Most often this happens if the tumor is located in areas of the body that are constantly in contact with items of clothing - on the neck, in the armpit or in the groin area.
Inflammation of a wart can appear as a result of the following factors:
- Accidental injuries, as a result of which the integrity of this neoplasm is disrupted.
- Frequent stress and nervous shocks that occur over a long period of time.
- Diseases of a genetic nature.
- Long-term use of hormonal medications, hormonal disorders in the human body that can occur during pregnancy or lactation.
- Side effects after taking certain medications .
- Redness or blackening of the papilloma located under the armpit may be due to improper depilation.
- Aggressive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
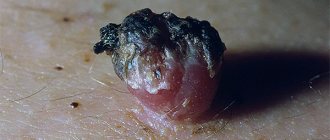
Any changes in papillomas should be treated with extreme caution, since there is always a risk of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one. That is why, at the first symptoms of a modification of papilloma, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Genital warts - routes of infection
The route of infection with HPV is contact. But household infection with the human papillomavirus is also possible. When a person comes into contact with infected skin or mucous membranes of a sick person, HPV infection occurs. Very often, this does not appear outwardly; the virus may not show itself for a long time. But under certain conditions (decreased immunity, concomitant diseases), HPV is released onto the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. In a latent (dormant) state, infection of other people with HPV is rare. From the moment of HPV infection to the appearance of genital warts, it can take from several weeks to several years.
Photo of condylomas on the genitals and in the perianal area
| In the photo: condylomas on the foreskin and on the frenulum of the penis | In the photo: genital warts in the perineum | In the photo: papillomas in the anus |
There are “low-risk” and “high-risk” types of HPV. Genital warts are caused by “low-risk” HPV types 6 and 11.
HPV in men: symptoms
Most often, HPV can be present in the human body for a long time without manifesting itself. However, the most important sign (symptom) of the possible presence of HPV in men and women is the appearance on the skin and mucous membranes, including in the groin or pubic area, of condylomas and papillomas - warts, lumps and irregularities of the skin, the color of which does not differ from the main one skin.
Condyloma is a genital type of papilloma, which looks like a small growth attached to the mucous membrane with a kind of “leg”. The size of condyloma can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters - in the latter case we are talking about an accumulation of condylomas.
Such papillomas can appear on the head of the penis, on the foreskin, and also around the anus (then there is a high probability that condylomas may also be in the rectum). Most often they are painless, but in some cases men may experience additional symptoms of the human papillomavirus if the disease manifests itself as:
- pain when urinating, defecating, or having sex;
- bleeding of condylomas: sometimes ulcers that do not heal for a long time may form in their place;
- also sometimes condylomas can itch.
The listed symptoms usually indicate damage to the condyloma.
The appearance of papillomas, in addition to the presence of HPV in the human body, also indicates a depleted immune system and the possible presence of other sexually transmitted diseases. In addition, some types of papillomas, in particular condylomas on the head of the penis, have a high oncological potential, so when signs of the disease are first detected, you should consult a specialist. The sooner you start treating the human papillomavirus, the more chances a man has to avoid serious health consequences of condylomas. (All of the above applies to women as well.)
Initial appointment
An initial appointment with a specialist involves a thorough visual examination of the patient’s mucous membranes and skin, as well as questioning him and prescribing tests.
Although most often papillomas have a characteristic appearance, additional tests and diagnostics make it possible to absolutely accurately determine the presence of HPV in the patient’s body.
If HPV infection is suspected in men, the following tests are usually prescribed:
- blood test (for condylomas, also analysis of urethral discharge): modern diagnostic methods make it possible to isolate the DNA of the virus from the available material and thereby confirm its presence in the patient’s body;
- biopsy of papillomas (condylomas): done in order to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells in neoplasms.
Treatment of papillomas, condylomas (HPV)
- performed on the body by a dermatologist-cosmetologist,
- on the male genitals - urologist,
- for women - a gynecologist,
- in the area of the anus and perineum - a proctologist.
There is now a treatment that is highly likely to eliminate HPV infection. Modern treatment for genital warts can not only remove or reduce the symptoms of the disease, it eliminates the HPV infection and prevents further transmission of the virus in many cases. However, after any treatment method, relapses are possible.
- Laser removal of genital warts is performed under local anesthesia.
- Electrocoagulation, removal of genital warts using high temperature, is carried out under local anesthesia.
- Interferon blockades (genital warts are injected with an interferon drug).
- Radio wave removal of condylomas. Today, the most effective method for removing genital warts. There is no trace left of condylomas.
What is genital papilloma?
This is a type of STI caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Appear in the form of a small tubercle or group of pimples in the area of the external genitalia. Some genital warts are so small that they are practically invisible to the naked eye.
Causes of papilloma on the genitals
Almost all cases of genital warts are caused by HPV. Most often, these formations spread through direct skin-to-skin contact during vaginal or anal sex. The virus that causes genital warts can spread and be transmitted to another person even if one of them does not even have visible signs of papilloma infection on the skin or mucous membranes.
Less commonly, they are distributed in the following ways:
- Performing oral sex on someone who has HPV or genital warts;
- Receiving oral sex from someone who has HPV or genital warts on their mouth, lips or tongue;
- During childbirth, from a woman to her child;
- Masturbation with HPV-contaminated hands or objects;
- By household means (shared towel, underwear, hygiene items, etc.).
How long does it take for them to appear?
Papillomas usually appear within a few months after a person has sexual contact with the types of HPV that cause the genital lesions. Sometimes they appear in just a few days or weeks, while for other people, genital papilloma does not appear until years later. Some people can get HPV, but never genital warts.
Find out in more detail what genital warts look like and how to remove them quickly and painlessly, how much it can cost and where is the best place to go with this problem in Moscow!
Clinical manifestations
Genital papilloma viruses usually appear in the form of various types of rashes on intimate areas. They are flesh-colored and may be flat or look lumpy like cauliflower. Some genital warts are so small that they are not visible.
In women, papillomatous lesions can be:
- Inside and on the walls of the vagina;
- On the vulva, cervix or groin;
- In or around the anus;
- In the lower parts of the rectum;
- On the lips, mouth, tongue or throat (this is very rare).
In men, genital papillomas can grow:
- On the penis (around the head);
- On the scrotum, thigh or groin;
- On or around the anus;
- Inside the anal canal;
- On the lips, mouth, tongue or larynx (very rare).
Genital papilloma viruses can cause itching, burning and discomfort. Talk to your doctor if you think you may have these growths or if there are risk factors or possible causes for them.
Treatment methods
There is no cure for HPV, but genital papillomas can and should be removed. If you decide to remove warts, do not use special medications at home on your own. Most of them are intended for professional use and can cause harm if applied incorrectly.
Methods for removing papillomas on the genitals in women:
- Electricity
- Laser ray
- Low temperatures (cryotherapy)
- Surgical excision
- Radio wave removal
Questions and answers about genital papillomas
1. Do genital warts need to be treated? Some people choose not to treat genital warts. If left untreated, genital papillomas may disappear, remain the same, or significantly increase in size and number. The prospects for the process depend on immunity, the amount and type of virus, sexual activity and the presence of concomitant STIs.
Even if you treat genital papillomas, you can still spread papillomatosis and the virus that causes it to other people. Doctors do not yet know how long you will be contagious after all the papillomas appear and are removed.
2. Will I still have HPV if I have my genital warts removed?
Yes. Even if you undergo treatment, you may still have HPV in your body. This is why these growths may return to the genitals after treatment ends. You can still pass HPV to other people after your skin tags are removed.
3. How does the disease affect pregnancy?
If you've had warts that go away on their own or after treatment, you probably won't have any problems during pregnancy. Papillomas on the genital organs in women during pregnancy often:
- Bleed and grow (in size and quantity) due to hormonal changes in the body;
- The birth canal is blocked - if this happens, a caesarean section will be required.
- Expose children to types of HPV that cause papillomas in the respiratory tract, a very rare condition called recurrent respiratory papillomatosis.
4. Can women who have sex with women get skin tags?
Yes. It is possible to get genital papillomavirus or any other STI if you are a woman who only has sex with women. Talk to your partner about her sexual history before intimacy, or better yet, visit a good gynecologist in Moscow and get tested for infections!
Prevention measures
The best way to prevent skin tags on your external genitalia or any other infections is to not have vaginal, oral, or anal sex. If you are sexually active or otherwise sexually active, reduce your risk of getting viruses by taking the following steps:
- Get the HPV vaccine. It is approved for people ages 9 to 45 and protects against the types of virus that cause most genital papillomas and most cervical cancers. Contact our clinic where you can receive this vaccine.
- Use a condom—be sure to put it on before your penis touches your vagina, mouth, or anus. The virus that causes genital papillomas can affect areas not covered by the condom. Other birth control methods, such as birth control pills, shots, implants, or the IUD, will not protect you from disease.
- Get tested - Make sure you and your partner get tested and tested for HPV.
- Be monogamous—having sex with only one partner can reduce your risk of developing the disease. Be faithful to each other - this means that you only have sex with each other and no one else.
- Your risk of getting the disease increases with the number of partners you have.
- Watch how much alcohol you drink and keep your own drink under control. Some people use alcohol or drugs to make a person drunk or high. Someone who is drunk, drugged, or under the influence of drugs may not be in control of the situation or fully understand what is happening. There is a real threat of sexual violence and possible infection with sexually transmitted diseases.
The steps listed above work best when used together. Be reasonable and careful, avoid unambiguous situations and unforeseen troubles!
home
Advantages of treating human papillomavirus at Deltaclinic
- Our clinic has all the necessary specialists (dermatologist, dermatologist-oncologist, proctologist, urologist, gynecologist) who remove condylomas and papillomas of any location.
- The most modern equipment (lasers, electrocoagulation, radio wave), which allows you to get rid of condylomas on the day of the visit.
- Condylomas are removed without leaving a trace. Excellent cosmetic effect - no trace remains on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Fast healing time.
- An accurate diagnosis of the type of papillomavirus is carried out. General immunostimulating and antiviral therapy is prescribed.
- Removal of candylomas is carried out on an outpatient basis; hospitalization is not required.
Photo:
Surgitron device for non-surgical (radio wave) removal of condylomas.
Do not delay your visit to the doctor, genital warts must be removed! If papillomas are not removed, they can spread throughout the body. The virus can be transmitted to other people with whom an HPV-infected person comes into contact. A woman can infect her fetus during childbirth. Cases of familial infection with the human papillomavirus are common.
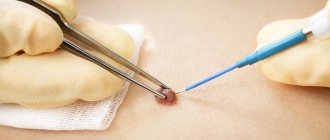
How is papilloma removed?
Removal of papillomas is carried out in a beauty salon or medical institution equipped with special equipment, as well as meeting the conditions of asepsis (measures to prevent infection of the skin or mucous membranes during medical procedures). In most cases, the medical clinic performs papillomas removal on an outpatient basis, which does not require hospitalization of the patient. Regardless of the technique, the papilloma removal procedure does not last long (on average 15-20 minutes) and does not cause significant pain or discomfort.
Is itchy papillomas dangerous?
To understand whether danger exists in each specific case, you should understand what factors provoked this sensation.
In the presence of external provoking factors, after they are eliminated, the feeling of discomfort disappears, and the condition of the growth returns to normal.
Papilloma can begin to itch if there are serious problems with the body or cause their formation.
When scratching, there is a risk of damaging the growth, and this can happen accidentally.
Then, in addition to itching, other symptoms will appear:
- the appearance of redness around the tumor.
- painful sensations.
- growth tear.
- discoloration, including black.
- increase in the size of papilloma, intensive growth.
- loss of shape.
- bleeding of the growth.
- the appearance of cracks on the surface of the neoplasm.
If the cause of the itching is not identified in time, the risk of developing negative consequences increases.
There is a risk of the following complications:
- infection by pathogenic microorganisms;
- development of papillomatosis;
- suppuration of the affected area;
- development of sepsis;
- tissue necrosis.
One of the most dangerous complications is the possibility of papilloma degenerating into melanoma.
Melanoma takes about two months to form, after which the person is diagnosed with cancer.
Melanoma is one of the most terrible complications, since the development of this form of cancer cannot be stopped.
She is not amenable to chemotherapy and other procedures.
Therefore, if discomfort appears in the area where skin tumors are localized, you should immediately seek advice from the appropriate medical institution.
Timely measures taken will save health, and in some cases, life.