Symptoms of papillomas of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
If papillomas are located inside the nasal passages, the disease may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
Stuffy nose
Papillomas can grow, and at some point a person begins to feel nasal congestion.
More about the symptom
Postnasal drip syndrome
Papillomas can cause postnasal drip syndrome. The nasal cavities contain glands that produce mucus. If a person does not have a runny nose, little mucus is produced. It serves to moisturize the nasal passages and binds dust and bacteria that have entered there. Sometimes a person sneezes or blows his nose, thereby removing mucus from the nose. Papillomas can reach significant sizes, blocking the mucus path. In this case, mucus begins to accumulate and then flow down the nasopharynx (this is postnasal drip syndrome). As a rule, an accumulation of mucus in the throat is felt in the morning, after a night's sleep.
Nosebleeds
When mechanically damaged, papillomas can cause nosebleeds.
Red, brown, white papilloma. What color does it say?
Papilloma is a benign tumor, the appearance of which is caused by damage to the human papilloma virus. Infection can occur through unprotected sexual intercourse and through direct contact with a virus carrier. For many people, the virus is inactive, so they are not even aware of its existence.
Reader's recommendation. Our readers actively use this therapy to treat papilloma. More information
The color and shape of the growths may vary, but they are not dangerous until they begin to change. Their increase, change in color and shape may mean that the tumor has degenerated into a malignant tumor. In this case, treatment should be started immediately.
Red papilloma: causes and appearance
Sometimes a red papilloma initially appears on the body. This is due to the many design features of the building. This phenomenon should not be shocking. Red papillomas often appear on the skin of babies. They occurred due to the fact that the mother had an infectious disease during pregnancy.
In the same situation, if the original pink or fleshy growth suddenly turns red, this phenomenon cannot be ignored.
There are many factors that can cause this process:
- It grows and hurts;
- The patient is taking medications containing hormones;
- Alkaline products are used to remove sediment;
- Under pressure.
If the papilloma suddenly turns red and causes unpleasant pain, there is a high probability of injury. This led to bacterial infections in addition to viral infections.
Treatment methods for papillomas of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
It is advisable to remove papillomas found in the nasal cavity and nasopharynx. Papillomas that have caused at least some concern must be removed.
Removal of papillomas
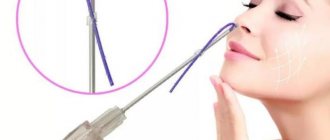
Removal of papillomas is best done using modern high-tech methods. This is radio wave removal or laser removal. This removal is easily tolerated by the patient. The technology ensures rapid healing, the risk of re-formation of papilloma is minimal.
Removal of papillomas of the nasal cavity with a laser or radio wave scalpel with Surgitr is carried out at JSC “Family Doctor”.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Inverted papilloma
Inverted papilloma (IP) of the nasal cavity is a benign tumor—histologically characterized by invagination of the surface epithelium into the underlying stroma. The etiology of IP remains unknown at present. Among the causes of IP, preference is given to allergies, chronic sinusitis and viral infections (Table 1). Inverted papilloma is a benign tumor and, according to the literature, accounts for up to 0.5% of all tumors of the nasal cavity.
Inverted papilloma occurs mainly in men aged 50–60 years. The ratio of men to women is on average 5: 1. The tumor has local aggressiveness, which is manifested by locally destructive growth. As it spreads, it can destroy soft tissues and bone walls, and grow into the paranasal sinuses and beyond. Inverted papilloma is localized on the lateral wall of the nasal cavity in the area of the middle turbinate and adjacent sinuses (maxillary and ethmoidal labyrinth cells). More often, a combined lesion of the nasal cavity and these sinuses is observed; the sphenoid and frontal sinuses are less often affected. Isolated sinus lesions are rare. Inverted papilloma is characterized by a high tendency to relapse (in 3 - 19% of cases) and malignancy (up to 5%). Diagnosis of inverted papillomas is carried out on the basis of clinical data, anterior rhinoscopy, radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, and histological examination. One of the most common and early signs of inverted papilloma is difficulty in nasal breathing, up to its complete absence on one side. Other signs of a neoplasm are: the presence of discharge from the nasal cavity, periodic nosebleeds from one half of the nasal cavity, impaired sense of smell, pain in the face on the affected side, the sensation of a foreign body in the nasal cavity, lacrimation, nasal sound, change in the shape of the external nose as a result tumor growth.
During rhinoscopy in this case, the papilloma on the vestibule of the nose is a small, bumpy, mushroom-shaped formation of a reddish-pink color, the surface of which resembles cauliflower (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Rhinoscopic picture of histologically confirmed IP papilloma: a red soft tissue mass (IP) fills the upper parts of the left PN.
The clinical features of IP, as well as the relationship of the affected anatomical structures with the anterior skull base (ASB), in particular the lamina cribrosa (LC) (Fig. 2), are of significant importance in the pathogenesis and treatment of this pathology. Assessing the extent of damage to a particularly anatomically vulnerable LC (even in the absence of signs of its destruction), including the olfactory tract (the area of possible development of a “tumor field”), can serve as one of the pathognomonic signs in choosing the optimal method of treatment for patients with advanced IP.
Of the diagnostic research methods, the most informative are CT and MRI (Fig. 3, 4).
The main method of treatment is surgery.
Despite the use of various surgical methods, in particular endoscopic operations and some operations using an external approach (lateral rhinotomy, Denker or Caldwell-Luc surgery), the rate of recurrence of IP is high and remains almost the same regardless of treatment methods.
The frequency of IP relapses depending on the surgical technique
- Primary transnasal removal - 50-80%.
- Endoscopic removal, laser evaporation – 3 – 18%.
- Surgery using external approaches (lateral rhinotomy with medial maxillectomy and/or “en-bloc” resection of the lateral wall of the PN, Caldwell-Luc and Denker surgery) – 12-19%.
flattery).
Reasons for development
Papillomavirus enters the body in two ways:
- contact;
- airborne.
Most often, infection occurs through the first route. Airborne transmission of the virus is more common in medical institutions.
Doctors become infected when removing papilloma from the patient's body using electrocoagulation or laser radiation. These methods involve burning out the tumor, as a result of which particles of the latter containing the virus penetrate into the air.
Papillomas in the nose are more common in the practice of an otolaryngologist.
As a rule, doctors of this specialization remove papillomas. The radio wave method is used more often.
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist
Zhikhoreva Inna Viktorovna
6 years experience
HSV penetrates into the immature basal layer of the mucosa. It provokes active cell growth, which leads to the formation of papillomas.
These tumors contain a virus that easily spreads through the sinuses, causing the appearance of new warts.
People at risk for contracting human papillomavirus include:
- have promiscuous sexual intercourse;
- come into contact with carriers of the virus;
- visit public institutions such as baths and swimming pools;
- do not follow hygiene rules.
HSV is present in the human body almost throughout life. It is often inherited. In a healthy person, the immune system suppresses the activity of the virus. He becomes agitated due to the weakening of natural defenses.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
The virus is activated under the influence of the following factors:
- addiction to smoking and alcohol;
- infectious infection of the body;
- long-term use of medications ;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies and others.
Nasal papillomas disappear without outside intervention within the first three years, provided that the immune system works without failures.
Mycetoma
non-invasive fungal sinusitis of the left maxillary sinus
The hypointense MR signal of a mycetoma may be mistaken for air in the paranasal sinus; Non-invasive fungal sinusitis does not look the same in different sequences.
If they are large, they cause headaches due to the pressure of the cyst shell on the walls of the sinus.
Often combined with allergic rhinitis, hypertrophy of the nasal turbinates and deviated nasal septum
Large cysts located in the lower parts of the maxillary sinus may be asymptomatic, while a small cyst located on the upper wall, in the area of the 2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve, can cause headaches.
Mucocele of the ethmoid labyrinth and frontal sinus on the right
This is a large formation of the paranasal sinus, lined with epithelium and filled with mucus, which is formed as a result of obstruction of the main sinus canal.
The most typical symptom: expansion of the paranasal sinus with smooth, clear contours with thinning and remodeling of the adjacent bone plate.
Chronic rhinosinusitis
characterized by parietal thickenings caused by hyperplasia of the mucosa and partial fibrous changes in it. The thickness of the mucous membrane ranges from 4-5 mm.
Sinonasal polyposis, hypertrophic sinonasal rhinosinusitis. Non-tumor inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane.
Recently, there has been an increase in the number of fungal sinusitis. Chronic forms occur under the guise of polypous recurrent sinusitis, the MRI picture is nonspecific, and laboratory diagnosis is difficult. There may be a change in the bony walls of the sinuses due to hyperostosis or destruction of the sinus wall as a result of prolonged pressure from the fungal body.
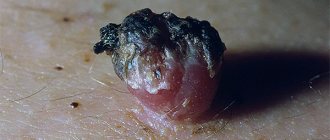
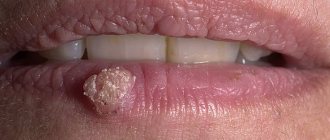
Vulgar warts
They form on the face and hands in both children and adults.
They are also called common or simple warts.
Morphological elements have the appearance of papules.
They can have different sizes.
Sometimes these are small warts on the face, the diameter of which does not exceed 1-2 mm.
There are also larger sizes – up to 1 cm.
In immunodeficiency states, they can grow to impressive sizes.
Upon inspection, it is noticeable that the surface layer of the element is covered with cracks.
Hyperkeratosis is observed on it.
That is, a layer of dead cells.
As a result, simple warts have a hard surface.
As a rule, they do not differ in color from the surrounding skin.
Although in some cases these may be red warts on the face.
At their location, the skin pattern is lost.
However, when the formation disappears, the relief of the epidermis is restored.
If a doctor examines a formation on the face under a magnifying glass, the warts are covered with black or brown dots.
They are capillaries (small blood vessels) that are blocked by blood clots.
This symptom is pathognomonic.
That is, it occurs only in warts.
Detection of this symptom makes it possible to differentiate them from other skin formations.
For example, from keratomas or skin tumors.
As a rule, small warts on the face are round in shape.
If they reach large sizes, they can acquire a polycyclic form.
More often, warts are single.
Less often they are located in groups of several pieces.
At the same time, no systematicity is observed.
The arrangement of the morphological elements of the skin is chaotic and asymmetrical.
If a wart on the face is removed poorly, new formations may appear in the same area.
They are located around the therapeutic area.