Papilloma is a benign tumor caused by a viral disease. This small piece, known for its ugly appearance, appears completely harmless.
However, you should not ignore your doctor's advice, since in some cases papilloma can cause cancerous tumors. Doctors warn that papilloma is especially dangerous for the fair sex for various reasons.
What does papilloma look like???
Signs of mild tingling, itching and slight redness in the infected area are common symptoms of papilloma. In most cases, papillomas form in the form of skin warts, similar to warts, but with a more complex structure.
Papilloma resembles cabbage, cones or mushroom caps. The size is usually limited to two centimeters. Typical areas of the body where papillomas occur are usually the shoulders, neck, face, arms (especially the arms).
However, papilloma can also occur in other parts of the body. Only the most popular papillary transmission sites are listed here.
Why does papilloma occur???
Unfortunately, the carrier of the papilloma virus is not always aware of his disease, since papilloma may not form immediately.
Typically, when entering the human body, the virus infects the basal epithelial layer. Infection in this area is caused by the transformation of squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium.
Cells infected by a virus can be benign or malignant. The benign form is characterized by the fact that it is located outside the chromosomes of cells. Moreover, a malignant tumor is inserted into the genome of the cell itself.
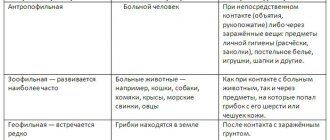
Doctors and cosmetologists know several causes of papilloma:
- One of the reasons for the appearance of papillomas is associated with two factors: microdamage to skin tissue and accidental contact with infected objects.
- The second cause of papilloma is sexual contact with an infected person, which has unintended consequences: anogenital warts, also called genital warts, occur in various parts of the body and in the genital area.
- Surprisingly, this virus can occur not only in adults, but also in small newborns. Some children may have signs of laryngeal papillomatosis at birth.
Main types of papillomas
Papilloma can take different forms. In some cases, the papilloma virus does not cause any characteristic symptoms. However, sometimes the papilloma virus can cause the development of acute condyloma. Fortunately, papilloma in women rarely causes cervical cancer.
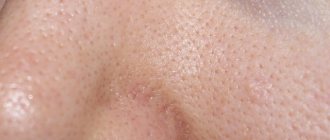
- Simple papilloma (or papilloma) Looks like small bumps with an uneven crust. Usually they do not exceed 1 mm. Simple growth occurs in all parts of the body, from the feet to the chin. However, the most common sites for this papilloma to spread are the hands, fingers and knees. A simple papilloma is an isolated structure that can exist for months or even years. They usually don't change over time. However, this does not exclude the situation of transformation and scaling.
- Plantar papilloma has a cone-shaped shape and rough growth.
A distinctive feature of this papilloma is that the sole has a protruding edge (hence the name “sole”). This growth is formed in singular or plural. Typically, the appearance of plantar papilloma can lead to infections in nearby areas of the body, which can lead to other growths. Pain when walking is another sign of plantar papilloma. Usually this growth interferes with walking. Sometimes the papilloma disappears when walking. However, its disappearance does not mean complete removal of the virus. In any case, consultation with a doctor is necessary. - Flat papilloma This is a small flat sprout, similar to ordinary yeast. However, flat papilloma has an unusual geometry and several angles. The color of flat papilloma matches the color of healthy skin. Therefore, flat papillomas cannot always be detected immediately. Distribution parts: hands, face. Flat papillomas cause not only unpleasant itching, but also severe pain.
- Filar papilloma Mostly suitable for people aged 40 to 50 years.
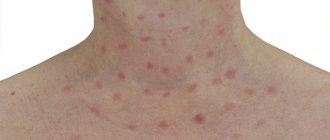
The place of distribution is the most unexpected: armpits, groin, eyes. However, filiform papillomas most often occur on the neck and shoulders. Filamentous papilloma looks like small yellow bumpy formations. They tend to change gradually. Over time, they will change shape and become thinner, like short wires (5-6 mm). An inflammatory process sometimes occurs at the site of filamentous papilloma. - Papilloma acuminata - Condyloma acuminata - These are papillary formations that usually appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. In some cases, genital papilloma does not cause serious health problems. However, sometimes these papillomas can lead to malignant neoplasms.
How to treat papilloma?
Firstly, do not take the medicine yourself as it will have negative effects. Under no circumstances should you remove the papilloma yourself, burn it, or use ointment or any medicinal gel. Your doctor will help you find your
a way to cure or eliminate growth.
The dermatologist conducts a special examination of papilloma, and then offers one of the treatment options:
- Use a laser device to remove papilloma and stop natural bleeding after removal. After this procedure, the growth disappeared without a trace, leaving no scars or scars. This method is commonly used to remove simple plantar acuminate papillomas.
- Cryotherapy is one of the most effective ways to remove papillomas. Use liquid nitrogen to remove sediment. This method is used in dermatology and cosmetology to remove all types of papillomas.
- Radiosurgery Resection-surgery of papilloma with a radioknife. Using this instrument, the specialist will remove the affected area of skin and conduct a thorough histological examination. This is a painless way to remove papilloma; the process takes very little time and does not require re-treatment.
- Electrocoagulation was additionally removed. This process is also called "diathermic curing". Apply high frequency current to it.
- Surgical intervention is the classic method of papilloma resection. Use a traditional surgical scalpel to remove the growth. This method is often used for simple papillomas.
Measures after resection of papilloma
Removing a papilloma does not mean completely removing the virus. Therefore, be sure to attend courses to strengthen your immune system after surgery. The goal of this course is to reduce the activity of the virus.
After some methods of removing papillomas, the skin will be noticeable: scars, scars, ulcers, etc.d. A month later the tissue was completely healed.
Causes of the disease and symptoms of papillomas
A virus is responsible for the formation of formations in the perianal area, which can be caught during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. Modern methods of contraception do not provide complete protection; in addition, the insidious virus can be transmitted through mucous membranes and skin.
Symptoms of papillomas in the anus are listed below:
- Excess moisture in the anal area.
- Burning, itching.
- Pain during bowel movements, sometimes accompanied by blood.
It is important to understand that many proctological problems have similar symptoms, and in order to understand what kind of disease you have been exposed to, you need to see a doctor. And the sooner, the more accurate the diagnosis will be made, and the easier it will be to go through the treatment phase.
Rectal papillomas are formed on the mucous membrane of the rectum and anus as a result of infection with the human papillomavirus. The incubation period varies and can last up to six months. As a rule, papillomas in the rectum form against the background of weakened immunity. Papillomas bring many problems to the patient, ranging from unpleasant sensations to the possibility of papillomas transforming into cancer.
Rectal papillomas are usually divided into three categories:
- Single, small size.
- Single, large.
- Multiple, forming united areas.
Visually, they look like a wart with a mottled surface on a thin stalk, but sometimes their size exceeds 2 cm in diameter. The color of papillomas can be different: light or dark.
Causes of the disease and symptoms of papillomas.
You can become infected with rectal papilloma during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. Modern methods of contraception do not provide complete protection; in addition, the insidious virus can be transmitted through mucous membranes and skin.
Symptoms of papillomas in the rectum:
- Sensation of moisture in the anal area.
- Burning, itching in the anus.
- Pain during defecation, blood in stool.
Almost all proctological diseases, such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, papillomas, cancer, have similar symptoms, so in no case should you self-medicate if you experience discomfort in the anus.
You need to contact a professional doctor - proctologist at the Only Clinic, undergo a proctological examination for an accurate diagnosis and strictly follow the treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of rectal papillomas.
At an appointment with a proctologist at the Only Clinic, to finalize the diagnosis, you will be prescribed blood and urine tests, as well as anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy procedures. These proctological examinations allow a thorough examination of the rectal mucosa, so that reliable information about the condition of the intestine can be obtained, and, accordingly, appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
It is impossible to cure papillomas forever. The virus is dangerous because of its relapses, and papillomas can develop into cancer. Therefore, most often, proctologists offer patients removal of papillomas.
Treatment, that is, removal of papillomas, can be carried out in several ways:
- Laser.
- A surgical scalpel.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Electric shock.
Difference between condylomas and papillomas.
Condylomas and papillomas have different forms, but the nature of their origin is the same: the cause of their appearance on the human body is the HPV virus.
In addition, the symptoms of papillomas and condylomas are also similar.
The differences between these diseases are as follows:
Condylomas have a hanging appearance, protrude forward, have the shape of papillae, and the method of infection is through sexual contact. Condylomas must be removed.
Papillomas are similar in appearance to warts and can be transmitted through household contact. If they do not cause pain, papillomas do not need to be removed.
Prevention of papillomas.
It is very difficult to get rid of a virus that causes formation in the rectum. It is easier and simpler to take precautions to avoid becoming infected with this virus:
- You need to lead a healthy lifestyle and constantly improve your immunity, then go in for sports, exercise, moderately combine work and rest, get enough sleep, eat right, and give up bad habits.
- You can take immunostimulating drugs after coordinating the use of medications with your doctor.
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- You can get vaccinated against strains of the virus. You can do it either under the direction of a specialist, or at your own request.
- Avoid casual sex
- Do not use other people's personal hygiene products
- Be careful in crowded places: swimming pools, baths, saunas, gyms.
- Regularly, at least once a year, undergo examination by a proctologist at the Only Clinic.
Watch your health! Don't start the disease!
If you suspect the appearance of anal diseases, consult a doctor - proctologist!
Self-medication of proctological diseases is not only ineffective, but also dangerous!
Call us, we will help!
Diagnosis and choice of treatment method for papillomas
In addition to the obligatory visit to the proctologist, for the final confirmation of the diagnosis it is necessary to take control blood and urine tests, consult with related specialists and undergo a sigmoidoscopy procedure. This study allows you to carefully examine the rectal mucosa, obtain reliable information about the condition of the intestines, and, accordingly, prescribe appropriate treatment.
No method of combating papillomas provides an absolute guarantee of complete recovery. Such viral diseases are dangerous due to their relapses; in addition, growths can develop into malignant formations. Therefore, it is most often suggested to remove them.
Excision of papillomas can be done in several ways:
- Laser.
- A surgical scalpel.
- Radio wave therapy.
- Electric shock.
To achieve the best result, it is necessary to cut out all formations present on the patient’s body. The method of excision should be agreed upon with the attending physician after all tests have been completed.
Attentive attitude to the health of the child is the most important task of responsible parents.
Moreover, often any pathological conditions, and especially neoplasms, cause fear and panic not so much in the smallest patient as in the caring mother. If you notice a papilloma on your child’s face or body, you should not perceive it as something terrible. Papillomas in children are a common phenomenon that is caused by one of the most common viral agents on the planet - the human papillomavirus (HPV). We will try to figure out how to rid the baby of an unpleasant tumor and whether it is possible to prevent infection.
Difference between condylomas and papillomas
Condylomas and papillomas that occur on the human body have a common nature - a viral type pathogen. In addition, the signs of the presence of these pathologies in the rectum are also similar. But there are also differences between them:
| Appearance | Infection method | Treatment | |
| Condylomas | “hang”, protrude forward, are formations of the papillary type. | appear as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner. | must be excised. |
| Papillomas | similar to warts - pathologies that have grown into the mucous membrane or skin. | may occur even after contact with the patient’s personal belongings. | sometimes it is not necessary to remove them, since they do not always cause pain, discomfort and are not so dangerous. |
4.Treatment
An anal papilloma, even a single, small, completely asymptomatic and generally discovered by chance, is not recommended to be left “as is”. Simply put, you can't. The risk of further growth, inflammation, and malignancy is too great. Therefore, not only a thorough clarifying and differential diagnostic examination is indicated, but also surgical removal. Today, various high-tech methods are successfully used - for example, radio wave, cryodestructive, electrocoagulation, laser - to minimize trauma, pain, the risk of complications and the duration of the rehabilitation period. However, there is always a possibility of relapse, since it is extremely difficult to completely destroy the HPV virus in the body (in practice, this should be understood as “impossible”), and surgical removal of the papilloma does not mean eliminating its etiopathogenetic causes. Therefore, immunostimulating and restorative therapy is mandatory with the categorical exclusion of those risk factors listed above that can be excluded. To relieve postoperative discomfort, analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, as indicated, as well as bed or home rehabilitation.
Conservative treatment of anal papillomas is ineffective, self-medication with “folk remedies” is dangerous.
Prevention of papillomas
It is not easy to get rid of a virus that causes formations on the human body. But there is a small set of measures to help protect yourself from infection or eliminate the possibility of relapse:
- Work to improve your immunity: sports, hardening, good sleep, healthy eating, giving up bad habits.
- The use of immunostimulating drugs is allowed, as agreed with the attending physician.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- Vaccination against several strains of the virus is possible. However, in our country this vaccination has not yet been fully studied, and therefore it is not included in the preventive vaccination calendar. You can do it either under the direction of a specialist, or at your own request.
- Be attentive to your sexual partners, and also, if possible, avoid being in large crowds of people in saunas, baths, swimming pools - in places with a warm and humid environment that is favorable for the spread of the virus. You also need to be careful with other people's personal hygiene products.
- Regularly see a proctologist to monitor the condition of the rectum.
2. Reasons
The growth of papillomas is caused by the activity of the virus of the same name - HPV, or HPV, or, in its full name, human papillomavirus. The frequency of its carriage on the globe is very high, since HPV can be transmitted through sexual contact, household contact, tactile contact, and from mother to fetus during childbirth. To date, 27 species and several hundred constantly mutating and successfully adapting strains of this virus are known. Some of them are relatively harmless, others are “responsible” for the appearance of warts, condylomas and papillomas, and some subtypes have proven aggressive oncogenicity.
Considering the above, it is not difficult to identify the main risk factors for the appearance of anal and genital papillomas:
- decreased immunity (including those caused by alcohol, smoking, drug addiction, chronic diseases, hypovitaminosis, abdominal surgery, chemical and environmental hazards, frequent hypothermia, etc.);
- promiscuous sex life with frequent changes of partners and anal sex;
- visiting public baths, swimming pools, etc.;
- neglect of personal, especially intimate hygiene and basic precautionary principles.
Visit our Proctology page
Types and features of localization of papillomas in children
Parents are often frightened by the variety of shapes and colors of epidermal growths on the child’s skin. This is due to the fact that medicine has identified about 120 different strains of HPV, each of which is manifested by specific visual characteristics and localization on the body. Children most often encounter the following types of papillomavirus:
- Ordinary papillomas - appear in the form of small oval or spherical bumps on the skin (warts) that can have different colors. Ordinary papillomas are most often localized on the hands (back of the hand), on the scalp and buttocks, but can appear in almost any area of the epidermis.
- Flat papillomas - the second name for this type of neoplasm - juvenile warts, however, quite often small small papules the color of healthy skin appear in infants. Most often, such papillomas are localized in a child’s face, head and hands.
- Papilloma of the throat - especially often manifests itself as a consequence of infection of the baby during childbirth and can be accompanied by a change in voice and difficulty breathing. Papilloma on the tonsil in a child can manifest itself for a long time as unexplained discomfort in the neck area.
- Plantar papillomas - form as single warts on the foot and can cause pain when walking and especially running. Such structures can result from damage to the skin of the foot and prolonged wearing of compressive or, on the contrary, too large shoes.
- Thread-like papillomas are round or oblong formations that usually form in the area of skin folds: (on the neck, in the armpits, in the groin area, on the face in the area of the nasolabial triangle).
- Epithelial hyperplasia is visually diagnosed as excessive growth of mucous membrane tissue, which, like classic neoplasms, is of a viral nature. Hyperplasia can appear as small papillomas on the child’s lip, as well as on the surface of the tongue or palate.
Most types of papillomas that affect children do not exhibit pronounced oncogenicity, that is, they are not inclined to cause an oncological process, however, to clarify the diagnosis, you should still consult a specialist.