Causes of development of ringworm
Since this is a mycosis, the etiology of its development is fungi.
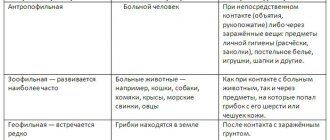
In nature, there are two genera of fungi known to cause ringworm: the genus Trichophyton (translated from Greek as “growing in hair”) and the genus Microsporum. Hence two other scientifically based names for the disease: trichophytosis and microsporia. Children become infected by contact with a sick person, or by using his personal belongings (headdress, comb, bed linen, scissors). But most often, children become infected from pets - cats or dogs, which serve as carriers of the disease. You can also get the fungus and become infected by visiting hairdressers, kindergartens, schools, gyms, swimming pools and other public places where sanitary and hygienic standards are not observed.
From the moment of infection to the onset of the disease, it can take from 3 to 7 days. This period, when the child is already sick, but there are no manifestations yet, is called the incubation (hidden) period.
For infection, the general condition of the body is of great importance. Children who have a weakened immune system get sick much more often.
Types of ringworm
By type of pathogen:
- Ringworm caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton, or trichophytosis.
- Ringworm caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum, or microsporia.
According to the manifestations of the disease:
- Surface form.
- A chronic form, which also includes nail damage.
- Infiltrative-suppurative form.
By location of the lesion:
- Ringworm affecting smooth skin.
- Ringworm affecting the scalp.
Chronic trichophytosis.
This is the result of untreated trichophytosis. Among adults, only women who were not treated for the superficial form in childhood suffer from the chronic form. Since the hair of healthy adults contains organic acids that protect against fungal damage, the chronic form develops in people with endocrine diseases and weakened immunity. Women with the chronic form serve as a source of infection and spread of the disease among children.
The deep, or infiltrative-suppurative form is observed mainly among residents of rural areas. People become infected when working with sick animals, most often cattle. But other animals, such as cats, can also become a source of infection. This form occurs with equal frequency in both children and adults.
Which doctor should I see for ringworm?
It is important to understand that the treatment of ringworm will be long, averaging 4-6 weeks , which depends on the type of the disease, the depth of the lesion and prevalence, and the age of the baby. It is important to strictly follow all medical recommendations and refrain from attempting self-medication so that this does not lead to the infection becoming chronic. Infectious disease doctors or dermatologists are involved in the treatment of ringworm in children; they will carry out measures aimed at ensuring that the infection does not become chronic and does not affect more and more areas.
note
Self-cure from lichen is rare, typical for boys in adolescence, which is associated with changes in the composition of skin secretions (especially the sebaceous glands). Special acids appear there that have a detrimental effect on the fungus. But you shouldn’t hope for this; treatment is important in all cases.
Before starting therapy, the doctor must clarify the diagnosis, since different types of skin infections, including fungal ones, are treated differently. First of all, the doctor will conduct a visual examination of the skin and the elements formed on it, and to determine the fungal infection, he will use a special device - a Wood's Lamp, in the rays of which the fungal affected elements give off emerald green shades of light. To clarify the type of fungus and confirm the diagnosis, a scraping is taken from the affected area and cultured on nutrient media, and microscopy of the specimen is performed. This helps to identify colonies of fungi and confirm the diagnosis of microsporia or trichophytosis. Only after all this can you begin treatment when there is an accurate diagnosis!
Main manifestations of ringworm
Signs of superficial form of lichen on the head
- The superficial form of ringworm, which occurs in the area of the scalp, is manifested by foci of different sizes, oval, round or having clear boundaries.
- The hair in the outbreak is broken off and falls out. Hair affected by the fungus is dull and thickened, and hair broken off at skin level appears as black dots (they are also called “stumps”). Some “stumps” of broken hair protrude above the skin, and it seems as if the hair in this area was trimmed at the same level.
- The skin of the affected area is covered with gray and white scales, similar in appearance to dandruff, and flakes off without causing any sensation to the patient.
- If left untreated, the lesions grow and can become quite large. Redness of the affected area of the skin is observed, along the edges of which a rim of small bubbles appears; the bubbles, bursting, dry out and become covered with yellow crusts.
- Although the patient does not have any unpleasant sensations, due to the unkempt appearance of the hair on the head, many people experience discomfort, especially children. After all, the appearance of lichen and bald spots on the head can become a reason for jokes and ridicule from peers.
Signs of ringworm on smooth skin
- The superficial form is characterized by the appearance of round or oval lesions, spots that have clear boundaries and are surrounded by a red ridge. The roller is formed by bubbles and crusts, it is thickened and rises slightly above the surface of healthy skin.
- Inside the roller, the skin is light and covered with gray small scales.
- When lesions appear on smooth skin, they are usually larger than on the head, and when they merge, they form extensive pink, slightly flaky lesions, with uneven, blurred edges.
- Lesions can appear throughout the body, affecting any area of the skin, but the most favorite places for ringworm to localize are the skin of the face and neck.
- Skin affected by ringworm itches, causing discomfort.
Signs of chronic ringworm
- Lesions can be located on the head, in different areas of smooth skin, and fingernails and toenails are often affected.
- The disease manifests itself in the presence of small atrophic bald patches with scars on the scalp, as well as hair broken off at the very root, reminiscent of black dots.
- Round bald spots are usually located on the temples and back of the head. The scalp may become flaky, but the flaking is usually minor. As a rule, the manifestations of the disease do not cause any discomfort; only a small number of patients may experience mild itching.
For this reason, the disease often goes undetected and untreated, lasting for many years, spreading among healthy people. Children are most often infected.
- On smooth skin, the chronic form manifests itself in characteristic lesions with uneven, unclear boundaries. The lesions are located mainly on the skin of the buttocks, in the area of the knee joints, the inner surface of the thighs and forearms, but it is possible that lesions may appear in other areas. The lesions are red or pinkish-bluish in color, with slight peeling on the surface.
- Most patients with chronic trichophytosis experience nail damage. First of all, fungi affect the fingernails, and then the toenails. When affected by fungi, the nails gradually become dirty gray, thicken or thin, crumble, look dull and uneven.
In patients with significant disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, common forms of trichophytosis may occur, when fungi affect internal organs. Fortunately, this phenomenon is extremely rare.
Signs of infiltrative-suppurative form of ringworm
- Dark red round formations appear on the affected skin, protruding above the skin. They are located under the hair, most often on the head; in men, formations can appear on the beard and mustache. At first, the elements are dense and painful when you touch the affected area, then they soften and become covered with crusts on top. When the scabs fall off, there is a discharge of pus from the areas where the hair grows.
- The patient's general well-being may be impaired, which is accompanied by a rise in temperature. The patient experiences headaches and malaise, and an allergic rash appears on the skin. There is also an increase in lymph nodes located close to the lesion.
- Oddly enough, the disease can go away on its own, without treatment. But then scars will remain at the site of the lesion.
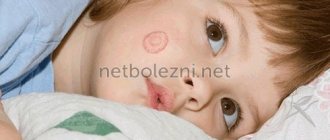
Description and photo of ringworm on the child’s body
Fungus infection of children's smooth skin forms typical manifestations. At the site where the spores enter, a swollen pink spot forms with peeling skin, which has a clear boundary. On the surface of the spot you can see small pimples, inside of which there is yellowish ichor. As the pimples open, crusts remain in their place. As inflammation develops and swelling decreases, the skin turns pink and begins to peel off finely. The lichen zone is surrounded by an inflammatory halo, rising above the surface of the skin, which consists of vesicular grouped elements, under which the skin is inflamed, irritated and swollen, the spot has a round, oval or slightly uneven shape.
note
Often, a new ring formation of lichen appears in the center of this formation, for which this typical phenomenon is called a ring within a ring. This is one of the typical signs of ringworm in children, based on which a diagnosis can be made.
The skin around the lichen plaques usually does not change, although options for screening out smaller plaques from the main large one are also possible. Ringworm in children can be found on open areas of the body and those covered by clothing. It especially often affects the face and neck, forearms and shoulders, chest, and back in children. When scratching the elements, ringworm is complicated by the addition of a secondary microbial infection, which leads to suppuration of the elements. This is typical for young children and those kids who have problems with immunity.
Treatment of ringworm in children
The basis of treatment for ringworm is to destroy the fungus that causes the disease.
Treatment is prescribed by a dermatologist. When smooth skin is affected by fungi, local, external antifungal drugs are prescribed.
When there are many lesions on the skin and vellus hair is affected, as well as the skin and hair on the head, a complex treatment is prescribed, which, in addition to the local antifungal drug, also includes systemic agents.
Local treatment of ringworm
- To speed up the removal of fungi and their spores, it is necessary to shave off the affected hair once a week.
- Creams, ointments, gels, lotions, and shampoos containing antifungal agents, such as Exoderil cream, are prescribed. To treat nail plates, a special varnish with an antifungal agent in its composition can be used.
- In the morning, the lesions are treated with a 5% iodine solution, and in the evening, sulfur-salicylic or sulfur-tar ointment is applied.
Systemic treatment of ringworm includes the appointment of Griseofulvin, for oral administration, at the rate of 18 mg per kg of child’s body weight per day. The daily dosage is divided into three doses. It is recommended to take the drug every day with a teaspoon of regular vegetable oil. The course of treatment continues until the first negative test taken from the site of the lesion. Then the drug is taken in the same dosage, but every other day for another two weeks, and then twice a week until the end of treatment.
An alternative drug for the treatment of ringworm in children is Terbinafine. It is prescribed in tablets for children who weigh more than 40 kg - 250 mg, those weighing from 20 to 40 kg - 125 mg, and those weighing less than 20 kg - 62.5 mg. It is recommended to take the drug daily, after meals, once a day, for 5 - 6 weeks.
For the treatment of chronic forms, along with antifungal drugs, a complex of vitamins, immunomodulators and drugs that improve microcirculation are prescribed.
Treatment is stopped after three negative tests taken in case of damage to the scalp, once, for 7 - 10 days, and in case of damage to smooth skin - once a week.
Due to the possibility of developing relapses (repeated episodes of the disease), after completion of treatment, children are under the supervision of a dermatologist for three months if the hair on the head was affected; and one month if smooth skin was affected.
A control examination for children under observation is carried out once a month if the lichen was on the head; and once every 10 days if on smooth skin.
In some cases, hospital treatment may be required.
Indications for hospitalization are:
- lack of positive effect from treatment carried out at home;
- infiltrative-suppurative form;
- presence of severe concomitant diseases;
- the possibility of isolating sick children from healthy ones in boarding schools, hostels and large families.
Features in children at different ages
After 3-4 years and during adolescence, ringworm usually occurs in the same way as in adults. The general well-being of children with ringworm usually does not suffer; only local skin reactions without significant discomfort predominate. If we talk about babies and children prone to allergic reactions, they may develop an erythematous-edematous form of the pathology . Against this background, children become restless and capricious, which is associated with severe itching in the affected area, a burning sensation and sleep disturbances. Children may feel severe weakness and malaise, inflammation develops in the area of the lymph nodes, which sharply enlarge and are sharply painful when palpated. The lesions are bright red in color, the edges of the lesions are swollen with pronounced blisters along the edges. The surface of the affected skin is prone to weeping, which occurs due to plasma leakage through the thin walls of the capillaries. Due to injury and scratching, the affected areas are prone to suppuration; their treatment is often difficult, and sometimes hospitalization may be required.
Prevention of ringworm
- Isolation of the patient to prevent the spread of the disease.
Considering the fact that ringworm is very contagious, patients are subject to isolation until complete recovery and are allowed into the children's group only after three negative tests for fungi.
- Maintaining hygiene.
This implies the separate use of personal hygiene items: combs, elastic bands and hair clips, washcloths, towels, as well as hats and bed and underwear (T-shirts, pajamas, socks, slippers). Thorough hand washing is necessary after the child interacts with animals, especially those living on the street;
- Carrying out disinfection in places of detection, treatment of the patient (at home, in children's institutions, as well as in hospitals).
- Control over disinfection in public places (baths and saunas, swimming pools, sports complexes, hotels and hostels).
- A sick child is prohibited from visiting child care institutions (kindergarten, school, camp, club), as well as swimming pools, baths and saunas, until complete recovery.
- All persons in contact with the patient are examined daily by a medical professional for the first three days. Further examination is carried out 1 or 2 times a week, for 21 days. At the same time, the skin and hair on the head are examined.
- After the patient recovers, all objects with which he came into contact are disinfected.
Who gets sick more often?
Ringworm is most often reported in childhood, from toddlers to teenagers. This is due to the fact that children are more likely to come into contact with animals, including street and stray animals, which may be infected with the fungus. Plus, the skin of children is much more delicate than adults, the hair on the head and body is thinner and more delicate, they are less protected from the negative influences of the external environment by natural secretions of the glands (sebum, organic acids). Usually, with plaques similar to ringworm, the maximum time to see a doctor is in mid-summer and autumn, when there are school holidays and children spend a lot of time on the street or in villages, where they come into contact with animals and closely communicate with each other.
Familial cases of lichen are often observed, since this is a contagious disease transmitted from a sick child to adults. This fungal infection is the second most common after mycotic infection of the feet and nails. However, adults are less susceptible to ringworm due to the fact that cosmetics, organic acids and sebum secretion inhibit the proliferation and growth of the fungus on the body of adults. More often, young women get sick along with their children.
note
People with red hair and freckles are naturally protected from ringworm.