Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
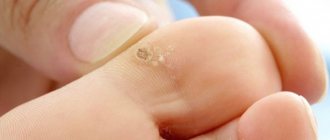
A plantar wart is a nodule or plaque with an uneven surface located in the place where the foot takes the greatest load. Most often, a wart forms on the heel or at the base of the big toe. Treatment of a plantar wart in a child involves removing the altered cells using one method or another.
The causes of a benign formation are usually infection with the papilloma virus. The issue of intervention is decided in each case individually.
General information
Warts are hypertrophied areas of the epithelium, usually resulting from infection with papillomavirus.
They are benign formations on the skin or mucous membrane. They appear more often in children and adolescents who have a weak immune system. Warts can be single or multiple, oval or round, lighter or darker than the surrounding tissue. If left untreated, they can increase in size and cause discomfort.
Neoplasms are localized in different parts of the body:
- face;
- fingers, especially around nails;
- articular surfaces (knees, elbows);
- soles.
Sometimes found on the mucous membrane of the larynx and nose. Such warts often degenerate into cancerous tumors, and therefore require immediate medical attention.
Who is contraindicated for
It is possible to remove a plantar wart from a child in almost every case; the procedure has almost no strict contraindications. However, it is important to accept some limitations. Thus, in children under 4 years of age, in the absence of high risks of complications and severe discomfort, surgery may be postponed.
If you have recently undergone routine vaccination or suffered from an acute respiratory viral infection, your doctor will recommend waiting 10 to 14 days to avoid complications.
General contraindications for all intervention methods include the following:
- purulent diseases of the skin, subcutaneous tissue;
- bleeding disorders;
- taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (temporary contraindication);
- high risks of keloid scar formation;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus.
If the patient has time restrictions, the doctor will tell you when the surgery can be scheduled.
Symptoms of warts
Signs of warts in children depend on the type of tumor:
- Ordinary, or vulgar. These are the most common growths that have a stalk. The formations are round, ball-like, rising above the skin. Common warts are characterized by uniform pigmentation, and hair growth is possible in the central part. The formations do not bother the child, do not hurt or itch. Vulgar warts form on the legs, arms, and back.
- Youthful, or flat. This type appears in children over 5 years of age. The formations are clear, irregular in shape, do not rise above the skin and do not have a stalk. They are slightly pigmented, the surface is even and smooth. A distinctive feature of this type of wart is the formation of several growths in one area of the body. They are localized on the face, neck, lower legs, hands and never appear in the armpits or skin folds.
- Pointed, or condylomas. Pink growths consisting of multiple neoplasms of the papillary structure. This type of wart appears on areas with thin skin, genitals, and mucous membranes.
- Acrochords, or filamentous. Long, elongated neoplasms that appear on the face and in the armpits. They do not differ in color from the surrounding tissues and grow quickly. Warts are clearly visible, easily injured and cause discomfort.
- Plantars, or spinules. The growths are located on the foot under the big toe, have a deep root, round shape and resemble calluses. Pathologically changed areas of the dermis hurt when walking. To detect warts in time, parents should regularly examine the child's body while bathing or changing clothes.
Where do warts come from?
The cause of warts is the papilloma virus. This virus can be transmitted through direct contact with a sick person or in public places through various objects. From the moment the skin is infected with the virus until the wart appears, a period of 2 to 6 months can pass. Fertile ground for infection with the papilloma virus is water and heat, so people who sweat a lot are especially susceptible to this disease. In addition, flat warts can appear in places where the skin is damaged.
Causes of warts
The main cause of warts in children is the papilloma virus.
Children and adolescents become infected with this pathogen through contact through household items, personal hygiene items, clothing and underwear. Infection occurs in public places, in transport, on playgrounds. It is possible to transmit microorganisms from mother to child during pregnancy. Once on the skin, the virus enters the body through microcracks and wounds. The disease may not manifest itself in any way for a long time. The activation of microorganisms and the appearance of growths occurs under the influence of a number of factors:
- weakened immunity;
- hormonal changes during adolescence;
- unbalanced diet;
- avitaminosis;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- stress, chronic fatigue;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes (relevant for plantar warts).
Important! Neoplasms appear mainly in weakened children with weak immune systems.
Why do warts appear?
The appearance of warts is caused by the activity of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which enters the child’s blood through scratches or wounds. It may not manifest itself for a long time, but if the immune system malfunctions, it begins to change the structure of epidermal cells and leads to the formation of growths on the skin. Many factors can provoke a decrease in immunity:
- stress;
- overweight;
- lack of minerals and vitamins;
- hypothermia of the body;
- frequent colds;
- hormonal changes during adolescence.
Treatment of warts
The decision on how to get rid of a wart in a child should be made by a doctor.
Independent removal of pathologically overgrown areas is dangerous due to the spread of infection to uninfected areas of the skin. Currently, wart removal is possible in various ways:
- Surgical. The wart is excised with a scalpel under local anesthesia. The resulting wound heals in 1-2 weeks, but after removal a scar often remains. This method is not recommended for small children.
- Electrocoagulation. Neoplasm cells are destroyed under the influence of electric current. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia. After cauterization, the wound is treated with an antiseptic. After 2-3 days, a crust forms at the site of the wart. It disappears after 5-7 days, a scar is formed in rare cases. Electrocoagulation is not suitable for spine removal.
- Cryodestruction. The method involves cauterization with liquid nitrogen. To remove the tumor, 2-4 procedures will be required. After treatment with nitrogen, a blister forms, then a crust, which falls off over time. The method is suitable for older children.
- Laser. This method of wart removal is painless, does not cause complications and does not leave scars. The laser has an antiseptic effect, eliminating infection of the wound. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia and takes a few minutes.
Before removing a wart from a child, the doctor prescribes medications to strengthen the immune system and reduce viral activity. The virus cannot be completely destroyed: it remains in the body for life.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say?
According to Dr. Komarovsky, it is better not to touch warts at all if they do not cause inconvenience or painful symptoms.
He believes that over time, the child’s immunity will cope with this on its own .
That is, all efforts should be directed specifically at strengthening the immune system, which means it is necessary to provide the child with proper nutrition with a sufficient amount of vitamins, minerals and other substances. You should also monitor the hygiene of your child’s feet and instill in him the habit of taking care of it himself.
Prevention of warts
Preventive measures are aimed at strengthening the immune system:
- taking vitamin complexes;
- good nutrition;
- physical activity;
- walks in the open air;
- limited stay in public places (if possible).
The answer to the question of how to remove warts from children in the least traumatic and effective way will be answered by the doctors of the SM-Doctor clinic. A dermatologist will quickly and objectively make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Remember that removing tumors on your own is dangerous for the child’s health.
Concept and origin
Plantar warts in children - photo:
This is a benign formation on the soles of the feet, which is of viral origin . After a child’s body is infected with a virus that causes warts, a mutation occurs in the tissue cells of the affected area.
As a result, abnormal growth of the mutated areas of the sole begins. However, this does not always happen, meaning the virus does not necessarily activate immediately after infection.
For this to happen, there must be favorable conditions in the form of weakened immunity . Therefore, it is often difficult to determine the source and time of infection.
Methods for removing warts
Our mothers and grandmothers fought warts with cauterization and various tinctures: Kalanchoe and dandelion juice, garlic, calendula, etc. Such methods are ineffective and also require a lot of time and effort.
In medicine, there are the following methods for removing warts:
- Freezing warts with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction).
- Electrocoagulation is the cutting of warts using a thin metal loop under high-frequency current.
- Laser coagulation is the removal of warts using a laser.
- Surgical intervention . It is prescribed only if there are too large warts or their accumulation.
- Chemical exposure . The use of chemicals to remove warts can cause damage to surrounding tissue, so this method is rarely used.
How to treat warts
Warts certainly look very unsightly and disgusting. If the warts are in inconvenient places or simply bring you psychological discomfort, it makes sense to consult a surgeon and remove the warts with a laser.
There are cases when it is necessary to seek help from a dermatologist:
- change in the shape and color of the wart;
- uneven color of the wart;
- blurred borders of the wart;
- wart injury or pain;
- increase in the number of warts;
- bleeding of the wart;
- the appearance of warts in the genital area.
Important! The main danger of warts is that with the progression of the papilloma virus in the human body, these formations can turn into polyps, and then into low-quality tumors. Therefore, the first priority is to fight the virus itself and increase the human body’s immunity.
Warts in children
To date, there is no method of treating this pathology with absolute effectiveness. Not every wart requires treatment. Elements that cause pain, itching, interfere with walking, or represent a gross cosmetic defect are subject to treatment. Also, an absolute indication for therapy is concomitant immunodeficiency pathology.
Conservative treatment
Etiological therapy is the fight against the virus. There are no specific drugs directed exclusively against HPV. A course of antiviral drugs based on interferon or its inducers is prescribed. To increase effectiveness, probiotics, prebiotics, and vitamin-mineral complexes are added to therapy. According to indications, after agreement with an immunologist, it is possible to prescribe immunocorrective agents.
Chemical destruction
The drug of choice for local treatment of flat warts is the topical retinoid tretinoin. The cream is applied over a long course - up to 3 months. Acids with a keratolytic effect are also used. Salicylic acid 15-40% in the form of ointment and patch is approved for use in pediatrics. The combined drug Solcoderm, which contains 4 types of concentrated acids, has a good effect. The regimen for using any of the above remedies is prescribed by the doctor, based on the clinical picture.
Methods of physical destruction
The choice of method for removing warts in children depends on the location, size, and depth of germination. In dermatological practice the following are successfully used:
- Laser coagulation.
Treatment is carried out simultaneously; a single session is usually sufficient. If necessary, the procedure can be repeated after 3-4 weeks. First, the skin and mucous membranes are anesthetized by treating with an anesthetic spray or cream. Direct laser exposure lasts 2-3 minutes. The laser beam provides minimal trauma with maximum precision. - Cryodestruction.
It involves treating the affected area with liquid nitrogen. The technique is considered effective and safe in pediatric practice. The substance in liquid form is applied to the lesion twice per session, with an exposure of 15-30 seconds. The course consists of several sessions. After cryodestruction, tissue regeneration is long-lasting, without scars; relapse is possible. The number of procedures depends on the course of the disease. - Electrocoagulation
. The essence of the method is to cauterize a child’s wart with a low-power electric current, causing thermal damage to the tissue. Advantages: precisely targeted impact with the ability to regulate the depth of penetration, no bleeding or scarring. - Radiocoagulation.
A minimally invasive method for treating warts in children. It is used for different sizes and localization of formations. It is a targeted effect of radio waves on the affected skin area. The technique is highly effective without the need for rehabilitation.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated for cases of risk of malignancy, suspected oncology, and large formations. There are several methods of surgical treatment of warts:
- Curettage.
Curettage of the wart is carried out with a curette. A relatively low-traumatic technique, quick to use, used for small warts. Curettage is more effective in combination with cryodestruction. - Excision.
The surgeon performs extensive removal of damaged tissue with a scalpel. The most traumatic technique, requiring sutures and a longer healing period. Used for deep invasion of formations. - Blunt excision.
Removal is carried out without the use of sharp instruments, for example, specially designed scissors. Of the surgical techniques, this is the most acceptable in pediatrics: it does not leave scars and the probability of recovery is 90%.