The problem of allergic reactions is very acute in infants and slightly older children. And the point here is not only in the reaction to external stimuli, but in the body’s increased sensitivity to them. Therefore, to treat diathesis in children, it is not enough to simply exclude the allergenic factor. An integrated approach to therapy is important, which will help minimize the impact of all possible causes of the occurrence and exacerbation of diathesis.
Causes of diathesis in children
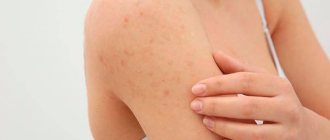
Diathesis in an infant on the cheeks or other parts of the body is not a specific disease, but a predisposition to the development of pathological reactions to irritants. This is considered a feature of the body that determines its reactivity. At the same time, against the background of diathesis, certain diseases may develop under the influence of unfavorable factors.
The causes of diathesis itself can be:
- unfavorable course of pregnancy;
- past infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- abuse of medications and bad habits during pregnancy;
- hypoxia or asphyxia of the fetus during childbirth;
- too little or too much birth weight;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- artificial feeding;
- dysbacteriosis;
- chronic diseases;
- insufficient or poor care;
- vaccination.
Rash in children. Let's look at the reasons.
Tretyakova Daria Alexandrovna
Pediatrician
April 25, 2021
In the life of every parent, sooner or later there comes a time when, suddenly, some acne appears on the body of their beloved child. It's a rash. A rash is any change on the skin. It occurs in many diseases and conditions, some of them are very dangerous.
Let's try to figure out what the rash is, in what cases it appears, what it is accompanied by, and how mom and dad should behave so that it goes away faster.
Let's start with the simplest thing - insect bites. Primarily mosquitoes. As a rule, this rash causes surprise in early spring and late autumn, when mosquitoes are not yet remembered or are already forgotten. In modern winter conditions, mosquitoes can live indoors (for example, in the basement) almost all year round. Of all family members, small children are the most “tasty” for mosquitoes.
Parents notice changes in the skin in the morning, after the child wakes up. Mosquito bites are characterized by the appearance of pink or reddish spots mainly on open areas of the body: hands, forearms, feet, legs, i.e. those parts of the body that are not covered by pajamas, and there must be elements on the face, or, sometimes, on one half of it (if the child slept on his side). Most often, this rash is accompanied by itching, but not very severe. The child's general condition does not suffer. He behaves as usual - plays, runs, throws things around, watches cartoons and eats with appetite. If the child is not allergic to mosquito bites, then they do not require special treatment. It is enough to turn on the fumigator in the children's room (now there are special ones for children), and the problem will be solved by itself. In case of a severe allergic reaction, accompanied by severe swelling, redness, severe itching, it is necessary to give the child an antiallergic drug (for example, suprastin). You can treat bites with drugs such as Psilobalm or Fenistil-gel, which relieve swelling and irritation.
The next fairly common situation in which a rash occurs is an allergic reaction. Typically this is a food allergy. There are children who have allergies from early childhood. Parents of such children know exactly what food can be given to their child and what not. And they know very well how to care for the skin in this situation. Now I would like to dwell in more detail on the problem of the sudden development of allergies in a previously healthy child. This situation can develop when eating previously unfamiliar foods, exotic fruits, vegetables, and seafood. Or if familiar dishes are prepared in a special way, using a large number of spices and aromatic additives. Or if your child, having lost control, ate a pack of chips, snacked on tangerines, chocolates and washed it all down with a carbonated drink.
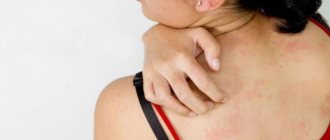
An allergic reaction appears quite quickly. Red spots of irregular shape, prone to merging and accompanied by severe itching, appear on the skin of the entire body or individual areas (cheeks, buttocks, behind the ears). The child's general condition may change: he may be lethargic or, conversely, too excited. Sometimes there is vomiting or loose stools. But more often the child feels well, but is very itchy. How can you help your child in this situation? First of all, it is necessary to exclude from his diet foods that cause an allergic reaction, even if they are very tasty and he loves them very much. Then you need to give the child sorbents - drugs that will remove the allergen from the child’s body. These include activated carbon, smecta, zosterin-ultra, filtrum. It is mandatory to take antiallergic drugs (the same suprastin or other drugs from this group). Fenistil-gel and moisturizer are applied to the skin. It would be a good idea to see a pediatrician or dermatologist.
An allergic reaction can also occur when the skin comes into contact with some substances, such as washing powder, fabric softener, etc. In this case, the rash appears only in those areas that were in direct contact with the allergen. The tactics of parental behavior in this case are similar to those for food allergies. Additionally, the substance that caused the reaction should be removed from the skin - rinse off under running water.
Now it is necessary to dwell on a large group of infectious diseases accompanied by a rash.
Varicella (chickenpox).
The appearance of a rash is usually preceded by a slight malaise, and symptoms of a mild acute respiratory infection may be observed. Then a rash appears. At first there is not much of it - a few red spots. Every day more and more new spots appear, and the old ones turn first into a papule - a “bump” that protrudes slightly above the skin, then into a blister with transparent contents, and finally, the blister dries out and a crust forms, which after a while disappears. From the moment the first spot appears until the last crust falls off, about 10-15 days pass, during which the sick child is contagious. The chickenpox rash is spread throughout the body, including the scalp and mucous membranes (mouth, eyes, genitals). The appearance of a rash with chickenpox is accompanied by itching, sometimes quite severe. Therefore, you can use suprastin, fenistil gel or psilobalm that you already know.
Rubella.
With rubella, the rash appears almost simultaneously throughout the body, but is more pronounced on the face, chest and back. It looks like small pale pink spots, almost the same size. The rash is profuse. Disappears without a trace within 4 days. A characteristic sign of rubella is enlargement of the occipital lymph nodes. All this is accompanied by mild symptoms of acute respiratory infections. There is usually no special treatment for rubella. But all children aged 1 year are recommended to be vaccinated against rubella.
Scarlet fever.
The disease begins acutely with high fever, sore throat when swallowing, and sore throat. At the beginning of the disease, the tongue is thickly covered with a white coating, then becomes bright red and shiny. The rash appears a few hours after the onset of the disease on the torso, limbs, with thickening in the natural folds of the skin (armpits, groin area). The rash is pink, pinpointed. In this case, the area around the mouth remains pale. After the rash disappears at the end of the first - at the beginning of the second week of the disease, peeling appears on the palms and soles. The disease is quite serious, because... leaves behind complications in the form of damage to the heart and kidneys. Requires mandatory prescription of antibiotics and a period of clinical observation with mandatory monitoring of blood and urine tests.
Measles.
A measles rash appears on the 4-5th day of illness against the background of severe signs of acute respiratory infections (cough, runny nose, conjunctivitis, high fever) and rashes within 3-4 days. The first elements of the rash appear on the face and upper chest. On the second day they spread to the torso, and on the third day to the upper and lower extremities. It looks like small red spots that tend to merge. Nowadays it is rare due to immunization of children at the age of 1 year.
“Sudden exanthema”, “roseola” or “sixth disease”.
It manifests itself as a high temperature, up to 39C, for 4-5 days with relatively good health. Then the temperature returns to normal, and a soft pink rash appears all over the body. Once the rash appears, the child is not contagious. Very often this rash is mistaken for an allergic reaction to antipyretic drugs.
Meningococcal infection and meningococcal sepsis are a deadly disease.
It is manifested by a very high temperature, a severe general condition of the child, which worsens every hour, vomiting, and impaired consciousness. Against the background of a high temperature, the child develops a rash (there may be only a few elements), which does not disappear with pressure. If you see such a picture in a child, you should immediately call an ambulance.
In addition to these diseases, a rash on the body occurs with a herpetic infection - in the form of blisters, with infectious mononucleosis - with the prescription of antibiotics from the amoxicillin group, with pseudotuberculosis and yersiniosis - in the form of “socks” and “gloves” and many others.
As a rule, the rash associated with various infections is quite typical and additional laboratory examination is not required to make a diagnosis.
In almost all infectious diseases, in addition to the rash, there is a high (or not so high) temperature, general malaise, loss of appetite, and chills. Your head, throat, or stomach may hurt. Have a runny nose, or cough, or diarrhea.
In addition to infections, the rash occurs with diseases of the blood or blood vessels. In these cases, the appearance of a rash is provoked by injuries, sometimes very minor. The rash looks like large or small hemorrhages (bruises) and requires additional examination to make an accurate diagnosis.
In conclusion, I would like to once again draw the attention of parents to the fact that they should not try to understand on their own what kind of rash the child has developed. Call a doctor. And most importantly, do not paint on this rash with fucorcin, iodine or brilliant green. Once you have satisfied your drawing needs, no doctor will ever guess what was really there.
Symptoms of diathesis in children
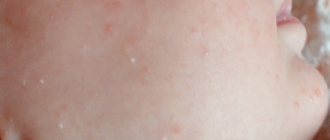
If we look at the symptoms of diathesis in children in the photo, the most typical signs are crusts on the scalp and redness of the skin on the face, most often on the cheeks. For children, the exudative form of the disease is most typical. It appears at the age of 1-2 months. Characteristic symptoms of diathesis in children:
- flatulence and abdominal cramps;
- persistent diaper rash in the folds of the skin and on the buttocks;
- frequent rhinitis, otitis, bronchitis, atopic dermatitis;
- unstable weight gain;
- swelling and weeping of the affected skin.
How diathesis manifests itself in a child directly depends on the form of the disease. If with exudative skin manifestations are more often observed, then with uric acid (nervous-arthritic) the symptoms will be:
- anxiety;
- excessive excitability;
- sleep disorders;
- arthralgia;
- constipation and colitis;
- asthmatic bronchitis;
- eczema, urticaria, neurodermatitis, Quincke's edema.
Hemorrhagic diathesis in children is rare. They can be recognized by small hemorrhages and large hematomas on the body, which are accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting with blood and stool disorders.
Why do pimples occur?
White pimples
Newborn acne
Their cause is too much maternal hormones in the baby’s body. After birth, the baby’s body is saturated with mother’s hormones, which have a direct effect on the condition of the skin. In turn, this entails so-called hormonal acne. From a scientific point of view, they are called neonatal acne. Typically, such pimples are localized on the face, but they do not need to be treated. You just need to keep your skin dry and clean. Acne is not contagious and does not occur because you do not keep your baby clean enough. If pimples are noticed in the area of the face, neck and hair, then this is acne.
Overactive sebaceous glands: acne
When a child is born, his glands are active and therefore acne appears. These pimples look like blackheads that cover large areas of the skin. Typically, the rash appears a week after birth and does not go away for about a month. There is no need to worry if it does not interfere with the child in any way. This type of pimples is characterized by the accumulation of pus under the skin of a white-yellow hue, they have a red base and a white tip.
Milia
Small white pimples on a baby's face that look like dots the size of a pin's head are called milia. This is an accumulation of sebaceous gland secretion in the ducts. They cannot be eliminated in any way, but they will go away on their own. If you try to squeeze them out or cauterize them, you can cause problems in the form of inflammation.
Red pimples
Allergic reaction
It often occurs due to a product that the mother ate, since not only beneficial substances, but also allergens are transmitted to the baby through breast milk. A similar reaction can occur with feeding formulas. To prevent allergies, it is better to write down all the foods you eat and monitor your baby’s condition. If you notice red pimples in a child 18 hours after eating food, then the product that caused them should be removed from the diet. Allergies can also be caused by washing powder; you should use only special types. Finally, animal fur, plant pollen, and so on become allergens. A typical sign of an allergy is peeling, crusting and a small rash on red spots. A child with an allergic reaction should definitely be shown to a doctor.
Prickly heat
If a child is dressed too warmly or is not wrapped up enough, then he sweats very actively. His skin remains damp all the time and is covered with pimples. They first appear in the neck area, and then move to the face. To avoid prickly heat, monitor the temperature in the room; it should not exceed 18-22 degrees Celsius. Choose clothes for your baby exclusively from natural fabrics, selected according to the weather.
Dysbacteriosis
In this case, pimples are only a symptom of an intestinal illness, so you should not self-medicate, but consult a doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment of diathesis
The doctor determines how to treat diathesis on the cheeks of a child depending on the diagnosis performed. It includes a general urine test, general and biochemical blood tests, an immunological examination, and a stool test for dysbacteriosis. In case of lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis, additional examinations are required: radiography of the respiratory organs, ultrasound of the liver, lymph nodes, spleen and adrenal glands.
How to treat diathesis in children under one year of age and older:
- Follow the diet and feeding schedule prescribed by your doctor.
- Introduce complementary foods no earlier than 6 months.
- Limit consumption of cow's milk.
- Enrich your diet with vitamins.
- Use prescribed medications: antihistamines, absorbents, vitamins, antipruritics.
As a local treatment, an ointment made according to the original recipe “PsorMak” is used. It does not contain hormones or other harmful components, and contains only natural ingredients that are gentle on the skin.
If in childhood a child undergoes a course of effective treatment for diathesis, then he has every chance of not encountering complications and being absolutely healthy in adulthood. Here it is important to contact a specialist in time. The PsorMak clinic practices an individual approach to the treatment of each patient, developing not only a treatment regimen, but also a diet, as well as a prevention program.
Contact us through the form on the website or by calling +7 (495) 150-15-14. We will help you form a correct understanding of the disease itself and its treatment at all stages.
Prevention of diathesis in children
To achieve a sustainable result in the treatment of diathesis in children, doctors recommend reducing the exposure of the child’s body to allergens of all groups (not only food ones) as preventive measures.
For this it is proposed:
- refuse to keep pets;
- regularly carry out wet cleaning of the apartment;
- when choosing clothes for a baby, give preference to natural fabrics;
- reduce the number of soft toys as much as possible;
- use hypoallergenic skin and hair care products.
To prevent diathesis, other factors that provoke an allergic reaction and causes of pathology are also minimized.
Do pimples need to be treated?
As you can see from this material, the majority of small white pimples in children go away on their own. You just need to wait, usually by the age of two months, children have completely smooth skin without rashes. You should not squeeze pimples, otherwise there is a risk of damage to the upper layers of the skin, infection and scarring later.
If you doubt the causes of acne, be sure to visit a specialist to make a correct diagnosis. To alleviate the child’s condition, the following options can be recommended:
- washing with boiled water three times a day;
- bathing the baby in a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
- bathing a child in a line;
- rubbing the baby’s face with a decoction of string or chamomile;
- competent care for baby's delicate skin.
Under no circumstances use fucorcin, a strong solution of potassium permanganate or brilliant green for treatment, avoid lotions with alcohol, as all these compounds will negatively affect the baby. You should also forget about fatty oils, ointments, powder, calendula tincture, hormonal ointments, lactic acid bacteria, adsorbents (for example, smecta), antibiotics and antihistamines. And, as already mentioned, you should not squeeze out pimples of any kind in children.
Diet
Diathesis in children responds well to treatment if the recommended diet is followed.
During breastfeeding, the baby's mother should adhere to it. Allergenic foods are excluded (sweets, citrus fruits, eggs, honey, etc.). During the introduction of complementary foods, in order to avoid the development of diathesis, the baby’s skin reactions to the new product should be monitored, and if signs of illness appear, exclude it for three to five months, until the next attempt. After the introduction of complementary foods, the basis of the menu should be cereals, lean meat and fish, vegetables and fruits. The consumption of sweets and foods high in food additives should be limited as much as possible. Contact us!
Specialists at the PsorMak Skin Diseases Center have been successfully treating diathesis in children for many years. Contact us for an initial consultation, our doctors will help you develop a complete understanding of how to properly treat the disease in the acute stage (with skin rashes). In addition, we will help you create a dietary diet and suggest what other measures to correct the child’s lifestyle should be taken to improve his health and effectively combat the disease. Make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 150-15-14,
HOW TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT at the PsorMak Institute for Healthy Skin
1. Click the button you see below -
Make an appointment
2. Fill in the fields in the form that appears. Be sure to check the correct phone number so that our specialist can reach you. After filling out, click on the “Submit” button.
3. Wait for our specialist to call. He will answer any of your questions and agree on the date and time of your visit to PsorMak.
The initial appointment includes:
- Visual examination , which will allow the specialist to get a general understanding of the condition of your skin and the pathology itself.
- Collecting anamnesis - finding out information about the development of the disease, living conditions, previous diseases, operations, injuries, chronic pathologies, allergic reactions, heredity, etc. Together with a general examination, this allows you to make a fairly accurate diagnosis and choose a method of treatment and/or prevention.
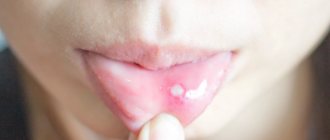
Milia on the face
Milia, which are colloquially called “milia,” appear as a result of the sebaceous glands producing too much secretion .
Such formations can be primary or secondary. Primary ones form for no apparent reason, and secondary ones are a direct consequence of skin damage (traumatic or as a result of inflammation).
The size of such formations can range from two to three millimeters .
Reference! Milia are white, dense blackheads containing sebum.
Considering that their contents do not come into contact with air, which may contain bacteria and microbes, they do not become inflamed. Although sometimes microorganisms enter through the skin, and then inflammatory processes begin .