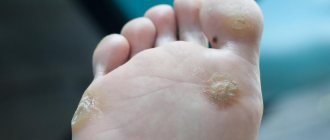
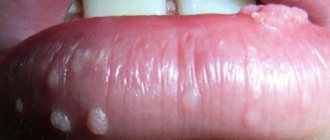
Types of anal papillomas
Anal papillomas are benign formations that affect the anus. They are both single and multiple. Often such growths merge, forming large lumpy islands or surrounding the anus with a ring.
Anal papillomas have their own classification based on appearance. There are pointed, papular, keratotic and tumor-like papillomas.
Pointed ones look like processes that have a thin base and resemble ridges in shape.
Papular papillomas usually have a dark pink color and a bumpy surface, very similar in appearance to ordinary warts. They are found in most cases on the skin of the genital organs. They are characterized by growth and association into small tubercles.
Keratotic neoplasms are growths on the skin that differ from other types by their characteristic hard and dry surface.
Tumor-like papillomas resemble growths in appearance with characteristic swelling, as with tumors. In the anal area, neoplasms of this type are practically not found.
Causes of anal papillomas
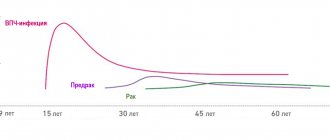
The main reason for the penetration of the human papillomavirus into the body is a sharp decrease in immunity. Moreover, a person infected with such a disease may simply be its carrier, without even knowing about its existence. According to statistics, almost sixty to eighty percent of the population are carriers of the human papillomavirus.
Weakening of the functions of the immune system, as a result of which HPV arises and is activated, can be caused by the following factors:
- childbirth, since according to statistics, the majority of patients who went to the doctor with this problem became infected with anal papillomas during delivery;
- infection through sexual contact, and even condoms cannot provide a 100% guarantee of protection against the penetration of this virus into the human body;
- constant stress, susceptibility to neuroses, disorders of the nervous system;
- physical or emotional fatigue, systematic lack of sleep, since it is during this period that a significant decrease in the body’s protective properties occurs, leading to the penetration of the human papillomavirus into the patient’s blood;
- poor-quality and irregular nutrition, excessive infatuation with fatty, salty and spicy foods, fast food, sweet carbonated drinks, which entails a lack of vitamins and beneficial nutrients, which is a beneficial environment for the development and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules, which can cause injuries and severe irritation of the skin in the anal area;
- the presence of inflammatory processes and various infectious diseases, which entail a significant weakening of the immune system, and the lack of proper treatment can lead to the activation of even those viruses that previously did not make themselves felt at all;
- bad habits, smoking, drinking alcohol.
Usually, the emergence and development of HPV is not promoted by any specific cause, but by the presence of a combination of negative factors simultaneously acting on the body. In this case, the immune system suffers significant disturbances and cannot resist the penetration of foreign viruses into the human body.
Provoking factors
The strength of immunity depends on many conditions. The decrease in the patient’s body’s defenses is facilitated by:
- prolonged exposure to low temperatures;
- injuries of various types;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- hard physical labor;
- bad habits (alcoholism, smoking);
- infections of viral, bacterial, fungal etiology;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- malignant tumor processes;
- endocrine diseases;
- use of certain medications (hormones, antibiotics, cytostatic drugs).
The likelihood of infection is additionally influenced by a number of provoking factors.
| Factor | Description |
| Young age | The appearance of papillomas on the anus is most often recorded in patients from 16 to 33-34 years old. The peak incidence occurs in the age period from 20 to 24-25 years. |
| Sexual debut at an early age | Early initiation of sexual relations negatively affects the possibility of infection. This is explained by the body’s vulnerability to HPV in conditions of unfinished hormonal changes. |
| Promiscuous sexual relations | The presence of several sexual partners and their frequent change increase the risk of anal papillomas in representatives of both sexes. |
| Neglect of barrier contraception | Barrier contraceptive - a condom is currently the only readily available and relatively inexpensive means of possible protection against papillomavirus. Why only possible and not guaranteed? Because a condom is not able to isolate all contacting areas of damaged skin. But unprotected sexual intercourse is a very high risk of infection. Anal sex without a condom further increases the likelihood of HPV infection, as it is often accompanied by microtrauma to the rectal mucosa and skin near the anus. |
There may be several predisposing factors that facilitate the penetration of HPV into epithelial cells.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
Small anal tumors usually occur without showing any symptoms. As papillomas grow, the first signs of physical discomfort appear, manifested in the following symptoms:
- blood discharge in stool;
- painful sensations during the act of defecation, since at this time multiple injuries to pathological formations occur;
- severe itching in the anus;
- constant feeling of wetness in the anus;
- a sharp and unpleasant odor caused by wet spots that form on underwear during the acute stage of condylomatosis;
- blood discharge on underwear, as a result of friction of growths on panties and subsequent injury to them;
- sensations of a foreign body in the anus;
- pain when walking or sitting.
Usually, with frequent trauma to growths, an infection enters the affected area, which causes inflammatory processes and the formation of purulent discharge.
Neoplasms cause severe pain, swelling and redness of the skin. Often, the patient develops a high temperature and their general health deteriorates significantly.
Sometimes such growths appear directly in the rectum itself. In such cases, in addition to the above symptoms, there is a feeling of a foreign body appearing inside the intestine.
Removal of anal warts
Which doctor removes condylomas in the anus? Women and girls can go to our clinic to see a gynecologist, girls and teenagers under 16 years old should go to a pediatric gynecologist, and young people are sent to a dermatovenereologist or urologist (but this is a different medical center - we don’t accept such specialists). If you feel something “extra” near the anus, then consult a doctor promptly!
The therapeutic approach to this problem is well known and standardized. The choice of method and volume of exposure is determined by the totality of data from a specific woman or man, namely the following:
- localization of formations (external or internal),
- their number (single or multiple),
- episodicity (primary lesions or relapse),
- analysis data of instrumental tests.
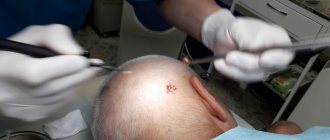
Removal of anal condylomas is mandatory, regardless of their location and number. Of course, removing papillomatous lesions inside the anal canal or on the walls of the rectum is much more difficult than cauterizing them around the anus. Based on the specifics and information on points No. 1-4, the optimal method is selected and the cost of the procedure is determined. As a rule, modern proctology and gynecology gives preference to the radio wave method, which allows you to get rid of these warts quickly and bloodlessly. And modern local anesthesia will make this process minimally uncomfortable. See “Prices for genital wart removal.”
The presence of formations of significant size, and especially condyloma in the rectum in the middle and upper third, may require surgical treatment in a hospital setting.
Trying to get rid of anal growths at home, inserting suppositories, applying ointments and creams, wanting the condylomas in the rectum to go away on their own, is a futile task, and in some cases, extremely harmful. Some substances from such traditional medicine can cause burns to the mucous membrane, provoke more active growth of papillomas and their degeneration.
Forecasts
Anal warts, if treated and removed, are not life-threatening and in most cases do not turn into cancer. However, HPV can linger in the body, causing repeated episodes of growth inside the rectum or around the anus. To monitor for a possible relapse and take the necessary measures in time, schedule your next appointments with your doctor in advance. This is especially true in the first three months after the end of treatment.
Prevention measures
While there is no surefire way to prevent contracting HPV and anal warts, as they say, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. There are some measures you can take on your own to help reduce the likelihood of infection developing and reoccurring:
- Using a condom can significantly reduce the risk factors for the appearance of condylomas on the anus.
- Abstain from polygamy or limit the number of partners with whom you have sexual contact.
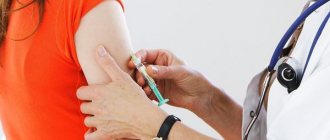
- Get vaccinated with Gardasil (relevant for girls, women under 35 years of age and men).
- If you already have a papilloma on your anus, do not touch or scratch it, as it may spread to other areas.
- When using a shared shower, pool or locker room, such as at a gym, always wear sandals or flip-flops to avoid contact with areas where people infected with human papillomaviruses may have been present.
- Individual items of clothing, towels, and sheets that come into contact with your or someone else's wart. Contact of these household items with genital papilloma and then use of them in different parts of the body, such as the anus or vulva, can lead to infection or household contact spread of the infection.
- If your boyfriend or girlfriend (for lesbian couples) has papillomas or condylomas in their intimate areas, anal play will most likely contribute to the transmission of the disease. Use barrier contraception and get rid of these formations quickly!
Diagnosis and treatment of the disease
To diagnose and treat a disease such as anal papillomas, you must consult a proctologist who uses the following methods of examining patients:
- Initial visual examination or anoscopy. With this type of diagnosis, the doctor examines the patient’s anus for the presence of papillomas, and also conducts a survey to obtain information about the symptoms and signs that bother the patient, his lifestyle and any chronic diseases he has ever suffered.
- Coloproctological instrumental examination is an examination of the anus using an optical device with very high resolution. A special microscope allows you to determine the presence of possible deformations of the rectal epithelium, as well as the severity of the lesion.
If any symptoms occur, you must urgently seek medical help, since such benign neoplasms very often turn into cancer.
There is no conservative treatment for this pathology. To completely get rid of anal papillomas, they must be completely removed. There are quite a lot of methods by which excision or destruction of condylomas in the anus occurs. Which one is suitable for a particular patient is determined by several qualified specialists - an immunologist, a surgeon, a proctologist and a dermatologist, based on the clinical picture of the disease obtained as a result of diagnosis, the degree of its severity, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
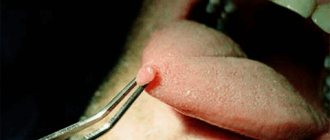
Anal papillomas can be removed using the following methods:
- Cryotherapy. This technique is characterized by exposing papillomas to extremely low temperatures until they freeze completely. The recovery period after such an operation is quite long, because the method is not particularly accurate in the area of localization. After the intervention, the affected area is covered with a cotton plaster.
- Electrocoagulation. In contrast to the first method, new growths are cauterized with electric current to third-degree burns, forming a white scab on the papillomas. This operation is performed under anesthesia and is not used on the mucous membranes of the anal canal.
- Chemical method. In this case, papillomas are removed using a medicinal solution of podophyllin, which affects formations at the cellular level. This medicine is applied to the papillomas using a special medical spatula, and then sprinkled with talcum powder. However, this technique also has a strong effect on healthy tissues located in close proximity to benign tumors.
- Laser removal of condylomas. The most progressive and most painless method of getting rid of anal papillomas. It has virtually no contraindications and does not cause possible relapses of the disease.
Regardless of which treatment method was chosen, after the operation it will be necessary to carry out a mandatory morphological examination of the tissue, for which it is necessary to send it for a biopsy. With any type of surgical intervention, the surgeon performing the operation tries to minimally injure healthy areas of the anus.
Very often, the removal of condylomas is accompanied by bleeding, so many experts insist on mandatory cauterization of each base of the papilloma.
Possible consequences and preventive measures
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Since this disease occurs due to the activation of the virus, simply removing papillomas will not help completely get rid of the disease. The feeling of internal physical and aesthetic discomfort may go away after surgery, but the virus lives in the body for a very long time and most often does not manifest itself at all.
That is why the lack of proper therapy or failure to follow the recommendations of the attending physician very often lead to relapse of the disease. The presence of HPV requires constant and regular examinations by a doctor to exclude the return of the virus.
For the purpose of prevention and to avoid relapse of this disease, the patient is prescribed courses of antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs that help restore immunity and the body’s natural defenses.
In addition, it is also necessary to normalize sleep and nutrition. Often, patients with HPV are prescribed a dietary program that includes all the necessary vitamins and nutrients in their diet. You should also give up alcohol and smoking and lead a healthy lifestyle. When preventing anal papillomas, personal hygiene in the anal area is mandatory, which means daily thorough cleaning of the skin around the anus.
Representatives of the fair sex are recommended to undergo regular examinations by a gynecologist in order to exclude and prevent the occurrence and development of condylomas on the mucous membranes of the cervix and vagina. And men should regularly undergo urethral swabs for testing.
How does the virus enter the body?
HPV is an anthroponotic pathogen, which means that its transmission occurs only from person to person. Papillomas of the perianal area and anal canal in adults are caused by certain strains of HPV that enter the body in several ways.
| Method of infection | Characteristic |
| Sexual | Main route of infection: The vast majority of cases of HPV infection and subsequent growth of genital warts are associated with sexual contact, including anal and oral-genital. With one sexual intercourse with a partner who has papillomavirus, infection occurs in 60% of cases. |
| Contact and household | The probability of infection is insignificant, but this route of infection is possible, since the virus can remain viable for a very short time in exfoliating skin cells and be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through towels, underwear, and care items. For this, microdamages to the skin and mucous membranes are sufficient. |
| Autoinfection | The virus can be spread from affected areas to new areas of skin, usually nearby, by the person himself when combing or removing hair during shaving and epilation. |
But papillomas in the genital and perineal area are found not only in adults; newborns can receive the virus from their mother during childbirth. The risk of infection is directly proportional to the severity of the infection in the woman in labor and the time of the anhydrous interval. Caesarean section does not reduce the risk of fetal infection, which indicates the possibility of intrauterine infection - transplacental transmission of the virus.
Manifestations of HPV infection in a newborn are not limited to the genital area; damage to the larynx is possible with the development of juvenile recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Manifestations of the disease in most cases are recorded during the anal period - from one to three years.
Summing up
Anal papillomas are benign neoplasms located in the anus, caused by the human papillomavirus. This disease can be completely asymptomatic, without causing any discomfort to the patient, but in advanced stages such formations can develop into malignant ones. Therefore, it is extremely important that if there are even the slightest primary signs indicating the appearance of such a virus, it is necessary to urgently seek advice from a proctologist.
To get rid of papillomas, it is necessary to completely remove them, but this will not rid a person of HPV. This disease must be treated with various antiviral and immune-restorative drugs, as well as undergo regular preventive examinations by a specialist.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons: