Allergies in children are as common as colds. While many parents may find it intuitive to distinguish between runny nose symptoms and allergies, in some cases it can be quite challenging, especially if symptoms appear when plants are in bloom.
If persistent symptoms of a runny nose, cough, sneezing and itchy eyes persist for more than a week while pollen is flying, then an allergy is most likely to blame for your runny nose. But with one important caveat - if your child is an infant or a toddler under the age of three, then he is much less likely to have seasonal allergies. While there are exceptions to every rule, most children don't begin to experience hay fever symptoms until they are 3 or 4 years old, after they have been seasonally exposed to large amounts of pollen and have developed a sensitivity to the allergen. Interestingly, pollen allergies and food allergies are linked: more than half of children who suffer from hay fever also have food allergies.
What is allergic arthritis
Allergic arthritis is an inflammation of the joints caused by an allergy to various particles entering the body. This disease develops especially often in children. Minor disruptions in the process of formation of the immune system lead, as a rule, to the development of an acute inflammatory process, which is easily treatable and ends without any consequences.
If the disease is based on complicated heredity, then sometimes the disease can become chronic with slow destruction of the joints.
The most common clinical form of this disease is infectious-allergic arthritis, which today is more often called reactive arthritis. According to statistics in our country, among rheumatic diseases, infectious-allergic arthritis in children under 14 years of age is more than 50%.
The code for allergic arthritis according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) is M13.8.
Allergic diseases can also include rheumatoid arthritis, which is based on an allergy to the patient’s own tissues. The ICD code for seropositive rheumatoid arthritis is M05.8; seronegative – M06.0.
Is this an allergy?
First of all, it is important to understand the nature of the rashes that appear on your baby’s body. At first glance, redness, irritation and rash clearly indicate problems in the body. However, there is a rash that is completely natural and is not something to be afraid of.
We are talking about the so-called “newborn acne,” which appears on the skin in the first month of your baby’s life. Its appearance is explained by the following: the baby’s hormonal levels begin to return to normal, and the mother’s hormones, which were obtained during pregnancy, leave the child’s body. During the process of this restructuring, a small reddish rash appears on the body - most often on the face, sometimes the rash is localized on the upper part of the body.
After a maximum of a month, such a rash goes away on its own. The only thing you shouldn’t do is squeeze out small pimples and try to “remove” them with a cotton swab.
If the redness does not go away for a long time and is accompanied by itching that bothers the baby, or the rashes become profuse, you should consult a pediatrician. Perhaps this is already a true allergy.
Causes of allergic arthritis
The cause of allergic arthritis is the body's increased sensitivity to various environmental factors - allergens. Allergens can be various particles that enter the body - food, particles of skin or animal hair, fish scales, medications, infectious agents, etc. The disease can also develop in response to the introduction of a vaccine or serum.
The introduction of an allergen into the body causes sensitization - increased sensitivity of the body to a certain substance - antigen. In response to the introduction of this substance, the body produces antibodies that neutralize it. When this allergen enters the body again, antigen (allergen)-antibody complexes are formed, deposited on the walls of target organs and causing an inflammatory process. In case of allergic inflammation of the joints, the target organ is the internal synovial membrane lining its cavity.
Allergic arthritis in children in most cases is of an infectious-allergic nature. Its onset is associated with a bacterial or viral infection. Most often it is a streptococcal, staphylococcal, intestinal or chlamydial infection. The disease is acute, benign in nature and with proper treatment of arthritis ends in complete recovery.
In some cases, in the presence of a hereditary burden (close relatives suffering from allergic diseases), an allergy to the infection first develops, and then an allergy to the patient’s own tissues joins it. In arthritis, it is an allergy to intra-articular tissue. As a result, a long-term, recurrent autoimmune inflammatory process develops that destroys the affected joint - rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to children, persons suffering from diabetes mellitus, cancer, AIDS, sexually transmitted infections, other allergic diseases and chronic arthritis of various etiologies are prone to the development of infectious-inflammatory arthritis.
How do allergies occur in children?
Allergy symptoms occur when a child's body overreacts with a protective immune response to normally harmless substances. Instead of not reacting to dandelion, an allergic child's body will quickly release a series of chemicals (including histamines) upon encountering the flower that cause itchy and red eyes, swollen mucous membranes, a runny nose and sometimes a cough. There is no clear, accurate way to tell at a glance whether your child has seasonal allergies when they start sneezing in the spring (or fall).
Symptoms
In most cases, allergic arthritis is acute. However, in the presence of constantly influencing internal or external predisposing factors, the process can become chronic.
First signs
The onset of the disease is acute or subacute, associated with the reintroduction of the allergen into the body. Inflammation can develop immediately or 1 to 2 weeks after repeated contact with the allergen. The joints swell, become inflamed, and moderate pain appears, intensifying with movement. Asymmetrical damage to joints involving small, medium and large (for example, knee) joints is also characteristic. Sometimes the patient’s general condition suffers: malaise, weakness, body temperature rises, and other manifestations of allergies appear in the form of a rash and Quincke’s edema. There is also a mild course of the disease with the absence of pronounced symptoms.
Obvious symptoms
Varying degrees of inflammation with swelling, redness of the periarticular tissues, and joint pain last for several weeks. All this time, general symptoms may persist: a slight increase in temperature, decreased performance, weakness, urticaria. Allergic arthritis lasts for 4 to 6 weeks, then complete recovery occurs. Infectious-allergic arthritis also has a similar outcome in most cases.
Swelling in allergic arthritis
When to Seek Medical Help
You should consult a general practitioner or rheumatologist if the following symptoms appear:
- painful sensations in the joints, intensifying after physical activity;
- swelling and redness in the area of one or more joints;
- general malaise, weakness, slight fever due to joint disorders and urticaria.
Persons prone to developing allergic reactions, suffering from other allergic diseases or chronic arthritis should pay special attention to such symptoms.
Symptoms of allergic arthritis in children
In childhood, the cause of the disease is most often infection. These may be untreated chronic ENT infections, intestinal infections, as well as chlamydia.
If the cause of infectious-allergic arthritis is a streptococcal or staphylococcal infection, the disease is acute or subacute, but almost always benign, ending in 1 - 1.5 months with complete recovery. Main symptoms: asymmetrical damage to the joints of both the upper (elbow) and lower (hip, knee) extremities, their inflammation, swelling, redness and pain in combination with general disorders: slight fever, weakness.
After intestinal infections caused by Yersinia, Salmonella, Shigella and some other pathogens, the disease also occurs initially acutely with asymmetric damage to the joints of the lower extremities. Often the hip joints are involved in the process. The process becomes subacute and lasts up to 3–5 months, after which complete recovery occurs.
Prolonged inflammation of the joints is typical when affected by chlamydia. This intracellular infection is difficult to detect and is prone to long-term recurrence, which maintains the inflammatory process in the joints.
Swelling in allergic arthritis in children
Food allergies
Hives and facial swelling are the most common symptoms of food allergies. Hives appear as raised pink bumps with pale centers, similar to insect bites. Other symptoms include itching and swelling in the mouth, runny nose and cough, vomiting and diarrhea. Life-threatening allergic reactions may also include difficulty breathing and/or swallowing. The medical name for this phenomenon is anaphylaxis. Most of these reactions occur suddenly within 10-20 minutes. All this happens within 2 hours after eating a certain food containing allergens.
How dangerous is the disease?
Allergic arthritis is dangerous because upon further contact with the allergen, acute allergic reactions such as Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock can occur. Sometimes the disease can take a chronic course with gradual destruction of the joints.
Stages of allergic arthritis
In the typical course of the disease, three stages are distinguished:
- Early
– with an acute course, asymmetrical damage to the joints, increased body temperature, and malaise. In adults, the ankle and foot joints are more often affected, which is often accompanied by damage to the ligamentous apparatus, pain in the foot and heel. In children, in most cases, the hip and knee joints, as well as the joints of the lumbosacral spine, are initially affected. Symptoms: pain in the buttock and sacrum, slight lameness, general malaise, weakness, fever, urticaria. - Expanded
– inflammation of other joints is associated, also asymmetrical. The pain intensifies, the process becomes protracted. Children often develop skin rashes and swollen lymph nodes. The temperature is slightly elevated or normal. There are no changes on the x-ray. - Final
– the disease ends with complete recovery after 4 – 6 weeks.
Possible complications
With infectious-allergic inflammation of the joints against the background of chlamydia, the process can become chronic. The disease occurs with relapses and remissions, and the development of destructive disorders and gradual loss of joint function is possible.
In children, infectious-allergic arthritis can develop into juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA) if there is a hereditary predisposition.
To prevent complications, it is very important to consult a doctor in time: the progression of the disease can be stopped at any stage.
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
Preventive actions
The occurrence of allergic reactions can be prevented. To do this, the child needs to strengthen the immune system in the following ways:
- hardening;
- physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- personal hygiene.
Only special children's products for a certain age should be used for bathing and body care. Clothes and shoes should preferably be made from natural materials. To avoid an allergic reaction to the cold, do not bundle up in winter, but dress in warm, natural clothes. Foot allergies are often caused by foods consumed. It is important that the child’s diet consists of natural products.
Classification
Allergic arthritis develops for various reasons and manifests itself in various clinical forms. The most common of them are infectious-allergic, toxic-allergic, and rheumatoid arthritis. Most of them can occur in the form of acute, subacute and chronic arthritis.
Infectious-allergic arthritis
Currently, infectious-allergic arthritis is more often called reactive arthritis, since it is based on an allergic reaction to a specific infection. In children, allergic arthritis of this form develops mainly after intestinal infections and upper respiratory tract infections. Women and children, including small ones, are more often affected; the disease progresses acutely or subacutely and lasts for 4–6 weeks and ends with complete recovery.
The main symptoms: the lesion is asymmetrical, pain appears in the joints, aggravated by movement, swelling and redness of the periarticular tissues. In adults, small (feet and hands) and medium-sized joints are affected, in children, most often large (hip, knee) and medium-sized (elbow) joints are affected.
With chlamydial infection, which is difficult to identify and treat, the disease can have a protracted and even chronic course with gradual destruction of the joints. In adults, the cause of such arthritis is genital infections, in children - chlamydial pneumonia.
Toxic-allergic arthritis
Toxic-allergic arthritis
This form of the disease occurs with prolonged repeated exposure to the body of toxins released by an infection or formed during a long-term metabolic disorder due to an infection. Examples of such damage can be toxic-allergic inflammatory processes in tuberculosis (Poncet tuberculous arthritis), gonorrhea and sepsis.
Ponce's tuberculous arthritis is quite rare and develops when tuberculosis occurs unnoticed. In contrast to infectious tuberculous arthritis with damage to the joints by the tuberculosis bacillus, the toxic-allergic process develops with prolonged intoxication of the body and exposure of the joints to toxins. The inflammatory process in the joints (often in the knee and elbow) is sometimes benign in nature and goes away during treatment and the development of remission of tuberculosis. But in some cases it has a course similar to rheumatoid arthritis: small joints of the hands are affected, followed by their destruction, change in shape and dysfunction.
Gonorrheal arthritis can also be purely infectious and toxic-allergic. In the latter case, 2-3 large joints are affected (almost always the knee), the disease is acute and, with properly prescribed treatment, ends in complete recovery. If left untreated, the process can become chronic with gradual loss of joint function.
With the generalization of an inflammatory nonspecific infectious process (sepsis), joint damage can be infectious (bacterial-metastatic) and toxic-allergic in nature. In the latter case, acute polyarthritis develops with migrating (moving) joint damage, which after treatment ends in complete recovery.
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
Rheumatoid allergic arthritis
This clinical form is classified as an autoimmune disease, however, allergies in this case play an important role. Predisposition to the disease (including allergic processes) is inherited. First, an allergy to a previous infection develops, and then an allergy to the patient’s own tissues develops (autoimmune inflammatory process).
Rheumatoid arthritis affects the small joints of the hands and feet with an initially chronic course of inflammation and its slow progression. Gradually, the destruction of the joints occurs, their deformation and complete loss of function.
Arthritis requires timely treatment, which is why it is so important to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease.
Treatment
After confirming the diagnosis with tests, the doctor chooses individual therapy for the child. Simply taking antihistamines will help eliminate the symptoms, but will not solve the problem as a whole. Medicines will relieve the itching. This will prevent the child from scratching the wound and subsequent infection.
Any manifestations of allergies will require comprehensive measures from parents:
- special diet for a nursing mother;
- eliminating contact with the immediate irritant;
- delaying the introduction of complementary foods with new products;
- hypoallergenic household environment - limiting contact with animals, flowering plants, synthetic and woolen items;
- bathing with hypoallergenic products (water temperature when swimming should be cool or warm).
Therapeutic procedures should be started immediately after the onset of an allergic reaction . Antihistamines are intended for systemic use and can only be prescribed by a doctor. The principle of their action is to block the reaction of receptors to an irritant. Such drugs include hormonal drugs, as well as Zyrtec, Claritin, Telfast. In case of individual allergic reactions, Suprastin and Tavegil can help. Complications of severe reactions of the body to an allergen require the use of corticosteroid hormones - Kenalog, Prednisone, immunomodulators. Complex preparations will not only help with allergies, but also strengthen the overall immune system. Individual indications for their use will be, for example, allergic dermatitis.
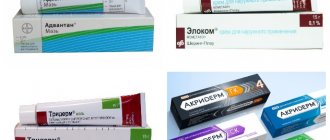
Cool salt compresses and contrast showers will help reduce itching and relieve acute irritation. For infants, the latter method is contraindicated. This will give temporary relief. External products such as creams and ointments have a long-term effect. Hormonal medications are recommended during periods of exacerbations; their use has a number of contraindications. Corticosteroid ointments (advantan, elocom, fluorocort) reduce the manifestations of allergies on the legs. Most allergists prescribe them. Corticosteroids undergo rigorous medical testing for effectiveness and safety for use in children.
The mild effect of non-hormonal drugs allows them to be taken for a long time. Ointments are used to treat allergies:
- Skin-cap is a zinc-based ointment that copes with inflammation, itching, and moisturizes the skin;
- Elidel – effective for inflammation, atopic dermatitis;
- Bepanten – treats microcracks, softens, moisturizes;
- Lanolin – reduces irritation and pain;
- Desitin, Dropalen - antiseptics, relieve inflammation.
Drug treatment of allergies is mandatory in the acute phase . Medicines quickly remove toxins from the body, relieve irritation and swelling, and prevent the development of anaphylactic shock. Pharmaceutical groups of drugs allowed in the treatment of children:
- Antihistamines - reduce the production of antibodies and the permeability of vascular walls. The period of admission is several days. Drugs are divided into several generations. In pediatrics, first generation medications that reduce symptoms are avoided. Second-generation sedatives can be used for a long time and do not cause drowsiness. Third generation drugs that have a cumulative effect are used to treat children of different ages.
- Antibacterial, antibiotics - prevent the occurrence of intoxication, sepsis, treat secondary infection - inflammation with fever, pyoderma.
- Ointments for external use. When first used, the ointment can be diluted with baby cream, this will prevent a reaction to the drug.
The choice of medication, dosage, and duration of therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the child’s age and general health.
Localization
The inflammatory process most often develops in large joints - the hip and knee.
Allergic arthritis of the hip joint
Allergic arthritis of the hip joint in children and adults appears after severe hypothermia and as a reaction to certain medications. It can occur in a purulent or reactive aseptic form with severe symptoms: high fever, sharp and acute pain, hyperemia.
To exclude the development of sepsis, you should consult a doctor after the first symptoms appear. Inflammation is eliminated with a comprehensive course of medications; in difficult cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
Allergic arthritis of the knee joint
The main symptoms of allergic knee arthritis are swelling, redness and pain in the knee area. Consult a doctor immediately; in the early stages, inflammation responds well to treatment without causing complications or becoming chronic.
Clinical researches
Clinical studies have proven the effectiveness, safety and tolerability of the products. The products are suitable for daily care of children's skin with mild to moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients.
The properties of the products are confirmed by clinical studies, during which it was found that La-Cri cream for sensitive skin:
- reduces itching and irritation;
- relieves skin redness;
- moisturizes and gently cares for the skin.
Based on the results of clinical studies, the product packaging contains information that the creams are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
Sources:
- Kamasheva G.R., Khakimova R.F. Valiullina S.A., Methods for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis in young children, Dermatology journal, 2010
- Kovyazina N.A., Fedosimova N.A., Illek Ya. Yu. Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in young children, Vyatka Medical Bulletin, 2007
- Smirnova G.I. Managing the course of the disease: atopic dermatitis in children, Russian pediatric journal, 2014
Photos of allergies in children
Photo album on the disease
Diagnostics
In order to prescribe adequate treatment, it is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and, if possible, find out the cause of the allergy. For this purpose, the following studies are prescribed:
- Laboratory:
- general clinical
- a general blood test reveals signs of inflammation; - biochemical
– metabolic disorders and signs of inflammation are detected (high levels of C-reactive protein); - immunological
– detection of antibodies to certain allergens, including those of infectious origin; They also determine the presence of rheumatoid factor – autoantibodies to the body’s own tissues; - microbiological
– inoculation of biological media (blood, joint fluid) on nutrient media in order to detect infection and its sensitivity to antibiotics. - Instrumental studies of joints:
- Ultrasound
– reveals signs of inflammation; - radiography
- possible changes in bone structures; - arthroscopy
– performed according to indications; this is an examination of the inner surface of the joint with the possible collection of synovial fluid for examination; helps to distinguish an infectious process from a toxic-allergic one.
It is impossible to diagnose and properly treat allergic arthritis at home. This can only be done in a clinic equipped with modern equipment.
Folk remedies
Before using your grandmother’s recipe, you should definitely consult an allergist or pediatrician. Allergic rashes, discomfort and itching can be relieved by a decoction of calendula, chamomile, string, and oak bark. These are natural antiseptics. It is recommended to bathe your baby with this decoction added to the water from the first days. Preparing a decoction for a bath is simple. You need to take 1 tablespoon of the herb, pour boiling water, leave for at least half an hour, strain. Add the resulting tincture to the baby’s bathing water.
Nettle has antihistamine properties. An infusion of it is used to wipe the affected areas of the skin. Older children can be given a nettle decoction to drink. The preparation method is the same as for chamomile and string.
It is important to remember that self-medication and uncontrolled use of medications and folk remedies to treat a child is unacceptable. This may cause more allergens in the future. To avoid scratching and infection of skin areas with rashes, you need to treat them with special ointments as quickly as possible. Treatment is most effective when provoking factors are identified and eliminated.
Treatment of allergic arthritis
After identifying the causes of the disease, treatment is prescribed, including:
- eliminating the entry of the allergen into the body that caused the disease;
- if an infectious-inflammatory process is suspected, identification of the infectious agent and its complete removal from the body;
- suppression of an allergic reaction;
- elimination of the inflammatory process;
- prevention of chronic disease.
Treatment of allergic arthritis is comprehensive and individually selected
Drug therapy
The following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- prescribed orally or intramuscularly, as well as externally (Voltaren, Fastum-gel). Popular 1st generation NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen) perfectly relieve inflammation, but have a negative effect on the stomach. The latest generation NSAIDs (Nise, Movalis) act more mildly and have almost no side effects. Children are more often prescribed Paracetamol, which does not give side effects. - Glucocorticoid hormones
are prescribed for severe joint swelling and severe pain. They quickly relieve these symptoms, but have many side effects, so they are prescribed in short courses orally, intramuscularly or as intra-articular injections. - Antihistamines
are prescribed to suppress the secretion of histamine, which supports inflammation. Drugs in this group include Suprastin, Tavegil - they also promote sleep, so they are prescribed at night. The latest generation drugs (Claritin, Erius) do not cause drowsiness and can be taken during the day. - Antibiotics
are prescribed based on the results of laboratory tests to determine the sensitivity of the identified infection to them. - A course of antirheumatic basic drugs
- when there is a risk of chronic arthritis (Metatrexate, Sulfasalazine) or combines their administration with a group of biological agents (MabThera, Enbrel, etc.). This contributes to long-term suppression of inflammation and prevention of relapses.
If toxic-allergic inflammation of the joints is detected, treatment is prescribed for the underlying disease that caused the complication. Sanitation (improvement) of identified foci of infection is also carried out - carious teeth, chronic diseases of the ENT organs, etc.
Drugs for the treatment of allergic arthritis
Non-drug treatments
At different stages of the disease, the following therapeutic measures are prescribed:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures - electrophoresis with hydrocortisone, UHF, paraffin or ozokerite, magnetic or laser therapy.
- Therapeutic massage is prescribed after eliminating severe symptoms of inflammation to improve blood circulation and metabolism, prevent chronicity of the process and muscle atrophy.
- Therapeutic exercises – prescribed depending on the activity of the inflammatory process to accelerate recovery processes in the joints and muscle strength.
- Reflexology (RT) is an effect on active points on the surface of the body, reflexively associated with joint tissues. Inflammation and pain are eliminated, tissue restoration is stimulated.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Traditional methods
Experts resort to traditional methods quite often in order to reduce the drug burden on the patient. But it is not recommended to use these remedies on your own: without a doctor’s prescription, this can aggravate the course of the disease. Popular folk remedies include:
- saline applications
- carried out with a hypertonic salt solution (a heaped teaspoon of salt per 100 ml of water - approximately a 9% solution is obtained); moisten a napkin with saline solution, wring it out lightly and bandage it to the affected joint; the application can be left for 1 – 3 hours; perfectly eliminate swelling and pain; - ointment from poplar buds
– grind dried poplar buds, grind into powder and combine with an equal volume of butter; store in the refrigerator and use as a rub overnight; relieves unpleasant symptoms well.
How to treat seasonal allergies in children?
Over-the-counter antihistamines are most often used for allergy symptoms. Typical antihistamine active ingredients found in over-the-counter medications include diphenhydramine, loratadine, cetirizine, or chlorpheniramine. Most often, antihistamines that do not have a sedative effect are used for children - loratadine or cetirizine.
Over-the-counter allergy medications should only be used in children over 6 years of age. If your child is under 6 years of age and has allergy symptoms, talk to your pediatrician about prescribing the best medications available at the lowest appropriate dose.
How allergic arthritis is treated at the Paramita clinic
Our specialists treat each patient with allergic arthritis very carefully. He is carefully examined to exclude other clinical forms of the disease and to establish the presence or absence of degenerative changes in the joint. Only after this is treatment prescribed, including:
- methods based on the achievements of modern medicine, developed in leading clinics around the world; the latest medications and non-drug treatment methods are used;
- traditional oriental techniques that came to us from China and Tibet; they have been successfully used for centuries to treat various types of allergies; These techniques are based on restoring the patient’s energy potential, which leads to stimulation of the patient’s vitality, normalization of the function of the immune system and elimination of foci of inflammation.
This approach to treating the disease allows us to completely eliminate the threat of chronic inflammation and joint destruction. But even in advanced stages of the disease, we can stop the progression of the disease. Contact us!
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Signs of an allergic rash in a baby
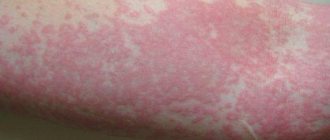
In children under one year of age, allergic rashes are localized on the cheeks, neck, arms (forearms) and buttocks. At first - usually short-term, just a few hours - the allergy looks like red spots, gradually merging into one spot. The skin in these places swells slightly and swells.
True allergies are not limited to rashes. Symptoms include redness of the skin, roughness and dryness. The appearance of the rash is accompanied by itching, which worries the child. The baby becomes irritable, sleeps poorly, and may refuse to eat. In some cases, allergies are accompanied by changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
When emergency help is required
If an allergic rash in a newborn is accompanied by lacrimation, nasal congestion, and swelling on the face, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Symptoms may indicate angioedema, the development of which causes swelling of the larynx and tongue, leading to suffocation.
Recommendations for those who have been ill
Allergic and infectious-allergic arthritis usually ends in complete recovery. But there is always a risk of relapse upon repeated contact with the allergen that caused the disease. Therefore, it is recommended for a recovering person to:
- avoid contact with allergens;
- follow a hypoallergenic diet, excluding from the diet foods that have an allergenic effect: honey, nuts, chocolate, eggs, as well as sweets and baked goods;
- do therapeutic exercises, swimming and feasible sports, move more;
- eliminate heavy physical activity, monitor your weight, avoiding its excessive increase;
- promptly treat all acute diseases and sanitize foci of infection.
Prevention of allergic arthritis
This should be especially taken care of by persons suffering from allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma) or a tendency to develop allergic reactions (urticaria, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock). Prevention should include: a hypoallergenic diet, elimination of exposure to allergens and timely treatment of all acute and chronic diseases.
Allergy treatment
If a child develops an allergic condition associated with increased symptoms of the disease, first aid should be provided immediately. Firstly, you need to immediately remove or stop contact of the allergen with the baby’s body. If you are outside, where there is a variety of pollen from flowering plants, you should immediately go indoors. If an allergy is caused by contact with a pet, you need to remove it from the child. In cases of allergies and certain types of food, you must stop eating it.
If you switched to artificial feeding and the child developed an excessive rash on the body, which is also a manifestation of an allergy, you need to change the type of complementary food for the child. In other words, in the first stages of the fight, contact of the child’s body with the source of allergens should be stopped.
Allergic reactions manifest themselves in different ways
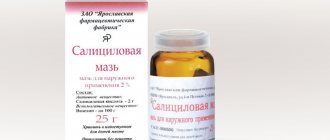
When the attending physician has accurately determined the type of allergen that causes excessive allergic symptoms in the child’s body, the child must be given an antihistamine antiallergic drug prescribed by the doctor. Next, you need to alleviate the symptoms of an allergic disease appearing on the body. Areas of skin where the baby experiences itchy skin can be anointed with salicylic alcohol. Any other alcohol tincture is also good for such cases.
If a child begins to experience attacks of anaphylactic shock, you should immediately call the hospital for an ambulance. Before the ambulance arrives, the child should be provided with an unimpeded flow of air into the lungs. To do this, in a stuffy room, you need to open the window and unbutton the clothes on the child’s chest. You should not use drugs that have an excessive odor, as this can lead to an increase in the symptoms of bronchospasm in the child’s body.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
Allergic arthritis is dangerous because it can be complicated by severe allergic reactions or give rise to the development of an autoimmune progressive disease with loss of ability to work. This is why timely treatment of allergic arthritis is so important. All this can be treated, specialists in Moscow are waiting for their patients!
Is it possible to get disability?
Allergic arthritis rarely leads to disability. The exception is rheumatoid arthritis, which is often a cause of disability.
Who should I contact with this disease?
See a rheumatologist. You will also need to consult an allergist.
What is the prognosis of the disease?
Favorable. Most patients make a complete recovery. If left untreated, the process sometimes becomes chronic, in which case joint dysfunction may occur. But even with rheumatoid arthritis, it is possible to stop the progression of the disease.
Bibliography:
- Alieva D.M., Akbarov S.V. Clinical variants of reactive arthritis in children. Scientific and practical rheumatology, 2001, No. 4, p. 74-79.
- Rheumatology. Clinical recommendations, ed. E.L. Nasonova, M., 2005, p. 86-90.
- JT, Petty RE Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology. Noronto, W. B. Saunders Company 2001; 819.
- Kingsly G., Sieper J. Third International Workshop on Reactive Arthritis: an overview. Ann Rheum Dis 1996; 55: 564-570.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 02/25/2021 Date of update: 04/03/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)
Why does a baby develop an allergic rash: looking for reasons
The long-established belief is that an allergic rash in a newborn occurs solely due to its diet, i.e. due to mother's milk, erroneously. This is certainly one of the reasons. However, other possible allergens should also be excluded.
Factors that indicate that a child is prone to allergies are:
- Having relatives who suffer from allergies, especially if it is the father or mother of the baby.
- Taking antibiotics by a child or mother.
- Artificial formula feeding.
- Complications of pregnancy due to maternal illnesses during this period.
In all these cases, the newborn is most likely predisposed to allergies. Following simple preventive measures will help prevent its occurrence.
- Clothes for a newborn should be of high quality, made from natural materials. The exception is woolen items, which can cause skin irritation.
- You need to wash your clothes thoroughly, using a special powder. An allergic rash in a baby can be a banal reaction to household chemicals. The same applies to parents’ clothing and other fabrics with which the child comes into contact.
- Check the baby cosmetics you use. It may contain components that can cause irritation. It’s better to choose reliable means. The La Cree line includes cosmetics for the care of newborns: foam shampoo for children from birth, cleansing gel and emulsion. All products have a natural composition and do not contain hormones.
- Nursing mothers should adhere to a special diet.
- An allergic rash in a formula-fed baby is no less common. In this case, the irritant is the proteins contained in infant formula. There is nothing more natural in nature than breastfeeding a baby. Mother's milk is in itself the best prevention against allergies.
What to do when an allergic rash appears in an infant?
If you cannot find the allergen on your own, consult a doctor. The pediatrician will be able to determine the cause of the rash.
Under no circumstances should you self-administer medications. If necessary, drug treatment will be prescribed.
During the treatment period, pay attention to any little things:
- Carefully monitor your baby’s hygiene and skin condition. If improperly cared for, diaper dermatitis may appear in the diaper area.
- Try not to dry out your baby's skin.
- Change wet clothes in a timely manner, do not wrap the child too tightly if it is hot indoors or outdoors - otherwise, the child may develop heat rash.
- Use special household chemicals for washing your clothes and children’s clothes, cleaning the children’s room - it is best to choose products marked “hypoallergenic”.
- It is best if there are no pets in the house that can cause allergies.
- Monitor your diet and your baby's nutrition. A nursing mother should not eat peas, beans, beets, peaches, apricots, bananas, eggs, fish, seafood, carrots, tomatoes, strawberries, citrus fruits, pineapples, melon, coffee, chocolate, mushrooms, nuts, honey, and possibly products containing cow's milk protein.