Dermatitis is the general name for a group of inflammatory skin diseases that have different origins. The disease can affect any part of the body, but most often appears on the skin of the hands, feet and face. The main symptoms are itching, burning, and damage to the skin, which causes a lot of inconvenience and significantly impairs the quality of life. Most often, these manifestations are short-lived, but sometimes the pathology becomes chronic. In any case, dermatitis needs to be treated with medications, including ointments and creams, recommended by a doctor.
Causes and types of dermatitis
The disease occurs when the protective function of the skin is weakened due to prolonged exposure to aggressive substances or decreased immunity. The cause of the pathology can be the following factors:
- mechanical irritation, friction, compression of the skin;
- thermal burn or frostbite, ionizing, UV and other radiation, electric current;
- contact with chemicals contained in skin care products, household chemicals, decorative cosmetics, as well as salts of heavy metals, acids or alkalis, medications for external use;
- allergic reaction to plant pollen, animal hair, food, medications;
- infection with viruses, bacteria or fungi;
- taking antibiotics, sulfonamides, novocaine-containing drugs;
- systemic diseases, hormonal disorders, hypovitaminosis, pathology of the digestive organs, liver, disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism, helminthic infestation, influenza and ARVI.
According to etiological factors, there are:
- Perioral dermatitis. It occurs due to the abuse of cosmetics, improper local use of hormonal drugs, the use of medicated fluoride-containing toothpastes, hypovitaminosis A and E. In childhood, it appears with increased salivation and during teething.
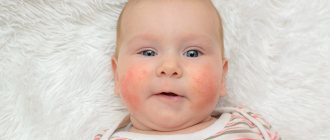
- Atopic dermatitis. Occurs mainly in children prone to allergic reactions and has a hereditary predisposition. Irritants may include foods, allergens of plant or animal origin, dust mites, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, and mold fungi. Rashes in a child of the first years of life are localized mainly on the face and extensor surfaces of the limbs, and at an older age and in adults, dermatitis appears on the elbows and popliteal folds.
- Contact allergic dermatitis. Appears when the skin comes into contact with substances to which the immune system is sensitized. May develop at lightning speed and be accompanied by anaphylactic shock.
- Actinic dermatitis. An allergic reaction to ultraviolet radiation, also known as sun allergy.
- Drug dermatitis. Occurs as a reaction to the use of medications (iodine, brilliant green).
- Seborrheic dermatitis. The cause of the disease is fungi of the genus Malassezia. Exacerbation occurs in hot and humid weather, with stress, hormonal, immune and neuroendocrine disorders, when the activity of the sebaceous glands increases. In places where they accumulate, the symptoms are more pronounced. Most often, seborrheic dermatitis affects the scalp, face, and upper third of the body.
- Infectious dermatitis. It develops when the skin is damaged by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Dry dermatitis. Occurs in people with sensitive skin during the cold season.
- Lichen planus. It is characterized by the appearance of red or pink plaques and intense itching. May affect nail plates.
- Toxidermy. A disease of an allergic nature, in which an irritant enters the body through the blood, respiratory system or oral cavity. There are medicinal, food and professional forms.
Prevention of neurodermatitis
Preventive measures reduce the risk of developing the disease and help with treatment. The basic rules that must be followed include:
- Balanced diet and vitamin intake;
- Treatment of diseases of the digestive and endocrine system;
- Timely fight against infectious diseases;
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- Regular wet cleaning of the room where the patient is located;
- A daily routine that involves rest from physical and mental stress;
- Choosing clothing that does not interfere with blood circulation and does not chafe the skin;
- Avoid contact with allergens;
- Strengthening the immune system (sports, walks in the fresh air);
Neurodermatitis can appear at any age, contact us at the first sign!
Symptoms of dermatitis
The main manifestations of the disease are redness and increased pigmentation of the skin, the formation of focal rashes, thickening, swelling, itching of varying intensity in the affected areas, burning, pain and other symptoms of tissue irritation. In acute form, the inflammation process occurs in stages:
- In the erythematous stage, redness, itching and burning are moderate, and there is slight swelling.
- The bullous stage is more severe. Blistering rashes appear on the affected areas, and the itching becomes intense. When scratching, first weeping wounds are formed, which are subsequently covered with a dense crust.
- The last necrotic stage is characterized by the formation of scabs and ulcers at the site of scratching. The rash covers increasingly larger areas. Old injuries gradually heal without consequences or with the formation of scars.
With chronic dermatitis, the symptoms are less pronounced, the disease remains in the first stage for a long time.
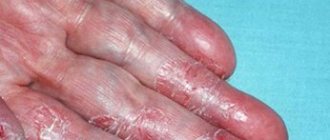
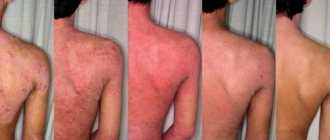
As a result of prolonged inflammation, the skin becomes rough, dense scales and a white coating resembling a dry callus appear on it. In severe cases, the affected areas atrophy and turn pale. The clinical picture depends on the form of the disease. In the case of its allergic nature, the itching and burning are more intense, the redness is more pronounced than with contact dermatitis. Affected skin areas can spread throughout the body, regardless of where the irritant is applied.
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by intense itching. As it progresses, blisters filled with cloudy liquid form in hyperemic areas of the body. In the last stages of the disease, severe dryness and pallor of the skin predominate.
In the oral form of dermatitis, the first rashes are localized on the face - in the area of the cheeks, bridge of the nose, chin, and near the mouth. This is characterized by the presence of a rim of healthy skin around the red border of the lips. Itching, flaking, dryness and a feeling of tightness are noted.
Contact dermatitis is characterized by local redness of the skin in places of contact with the irritant, swelling, a rash in the form of blisters, the appearance of cracks, dryness and weeping. There is itching of varying severity, burning and pain in the inflamed areas.
Eczema is manifested by a variety of rashes, severe itching, dryness and flaking of the skin, cracks, redness, swelling or weeping.
Toxidermia is characterized by urticaria, the appearance of red and pigmented spots on the skin, oozing, swelling of the face and limbs, peeling of large scales, and acne.
The generalized form can occur as lichen planus, allergic vasculitis, lupus erythematosus.
Complications of dermatitis
Any form of dermatitis accompanied by skin damage can be complicated by infection.
In the chronic course of the disease, thinning of the skin and the appearance of small dilated vessels - telangiectasia - are possible. With prolonged atopic dermatitis, a child may develop asthma and allergic rhinitis. Among the adverse consequences of the seborrheic form of the disease are acne with the formation of visible skin defects, abscess, and baldness. The most serious are considered generalized complications such as Quincke's edema, Lyell's syndrome or Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
General preventive recommendations
- Minimize the child’s contact with external irritants that can cause relapse.
- Use products with a moisturizing effect for hygiene.
- Do not use alcohol-containing products for hygiene.
- To soften and moisturize the skin, use emollients (preferably odorless). These products do not contain acids or hormones, perfectly moisturize and nourish the skin, reducing dryness and itching. Apply 2 times a day, even during the period of remission, when there are no allergic manifestations or itching.
- The duration of water procedures to cleanse the skin should not exceed 15 minutes. The water should be warm or cool, dechlorinated (filtered or settled for 1–1.5 hours). If the child has good tolerance to herbs, you can add infusions or decoctions of one of the plant components to the water - birch leaves, string grass, burdock root, oak bark.
- Do not use washcloths or rub the skin during water procedures. Shampoos for washing hair should be neutral acidic. After water procedures, the body is not wiped. It is necessary to carefully blot the skin with a soft sheet and apply emollients.
- To prevent scratching, your child's nails should be trimmed short.
- During periods of relapse, children should sleep in gloves and socks made of cotton fabric or yarn. Pajamas should be spacious and made of natural cotton.
- New clothes should be washed before wearing (only with liquid detergents).
- When washing bed linen and clothes, do not use industrial conditioners and fabric softeners. Linen is rinsed with clean water and ironed thoroughly after drying.
- You should not buy heavy and rough clothes for sick children.
- Tanning should be avoided. On sunny days use sunscreen.
- It is important to exclude children with atopic dermatitis from participating in sports competitions. Intense sweating, skin friction and close contact with clothing can trigger a relapse of the disease.
- The entire apartment and the child’s room should be cleaned regularly (preferably in his absence).
- Avoid smoking in the presence of a child. Even passive contact with nicotine can trigger the production of antibodies.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
The diagnosis is made based on the existing symptoms, the results of an external examination of the patient’s skin and mucous membranes, visual assessment and localization of pathological changes.
An anamnesis of the disease must be studied in order to establish the possible cause of dermatitis and its genetic cause. Laboratory diagnosis of dermatitis includes the following studies:
- General clinical blood test. During an allergic reaction, an increase in the number of eosinophils is observed, and an accelerated ESR indicates inflammation.
- Blood chemistry. Includes determination of the concentration of AST, ALT, total bilirubin, triglycerides, cholesterol, total protein.
- Determination of the level of immunoglobulins in blood serum, antibodies to food, household antigens, antigens of plant, animal and chemical origin.
If necessary, it is possible to conduct a histological examination of the biomaterial obtained through skin biopsy. Genetic blood testing helps determine hereditary predisposition to the development of atopic disease. In the presence of a purulent process or severe inflammation, a microscopic and bacteriological examination of the smear is prescribed in order to clarify the causative agent. Additionally, for dermatitis, tests are carried out for giardiasis and other forms of intestinal parasites, and the organs of the digestive tract are examined.
Treatment of dermatitis
Treatment tactics for dermatitis depend on the cause and form of the disease. General recommendations for the patient include:
- establishing a work and rest schedule, sleeping at least 8 hours a day;
- a diet based on limiting fried, spicy and canned foods, possible food allergens;
- carrying out hygiene procedures in warm water (not higher than 34°C);
- eliminating stress and nervous overload.
In case of severe itching, accompanied by sleep disturbances and neurological disorders, the prescription of sedatives, mainly of herbal origin, is indicated.
It is important to stop contact of irritants with the skin or internal environment of the body as soon as possible. To achieve this, cleansing and general detoxification measures are carried out:
- in case of chemical exposure to the skin, it is thoroughly washed and a bandage is applied with a neutralizing substance - alkali for an acid burn or an acid for an alkali burn;
- for perioral, drug-induced and allergic dermatitis, after washing the skin, enterosorbents, a hypoallergenic diet, and in severe cases, intravenous infusions of special solutions are prescribed;
- Treatment of parasitic infestation is carried out using anthelmintic drugs.
Also in the treatment of dermatitis, antihistamines, antibiotics and antifungals are used both locally, on the skin, and systemically.
Wet areas of the skin can be treated with antiseptic solutions and herbal infusions that have a drying effect. Hormonal ointments for dermatitis have an anti-inflammatory effect. Severe itching and pain, as well as a large area of damage and the appearance of areas of tissue necrosis, are indications for urgent hospitalization of the patient. In case of severe disease with damage to more than 20% of the skin, a course of prednisolone tablets is recommended. In such situations, treatment may be supplemented with immunosuppressive drugs.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist
Stages of neurodermatitis
According to the degree of development of the disease, several stages are distinguished:
- initial;
- the stage of pronounced changes, occurring in both acute and chronic forms;
- remission, which can be complete or partial, including without the use of special treatment;
- clinical recovery of the patient.
There is a division into three groups according to the severity of cutaneous neurodermatitis: mild, moderate and severe. In children, a mild form is more common. With it, redness is noticeable in a small area, but there is no severe itching.