- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
Pityriasis versicolor is a chronic fungal skin disease.
The fungus is present on the surface of the skin of most people and, when exposed to certain circumstances, can quickly multiply and cause a pathological process. Provoking circumstances include:
- immunodeficiency states;
- pathologies of internal organs;
- excessive sweating;
- living in conditions of high air humidity;
- disorders of the hormonal system.
The most typical lesion for this pathology is the upper part of the body: face, neck, chest and back. It mainly affects males.
Symptoms
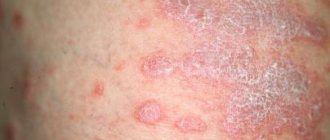
The main symptom of pityriasis versicolor is the appearance on the surface of the skin of asymmetrically located round spots with clear boundaries . They can vary in size and tend to grow larger as the disease progresses. At later stages of pathology, the lesions are characterized by fusion.
The color of such spots is very different and can vary from whitish to pink-red. Layers of small scales are visible on the surface. The skin in these places thickens and changes its structure. The lesions are not characterized by itching or other unpleasant sensations. They do not tan when exposed to ultraviolet radiation and can disappear on their own over time.
Pityriasis alba
Skin pigmentation is one of the most variable phenotypes in humans. There are hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation, the causes of which can be both genetic and acquired factors.
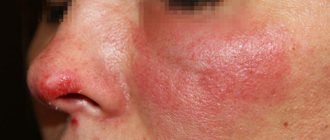
Lichen alba (pityriasis alba, pityriasis alba) is considered an eczematous dermatitis of mild severity and a minor sign of atopic dermatitis, which is characterized by patchy hypopigmentation. The term comes from the words pityriasis (scaly) and alba (white). The word "pythyriasis" was used by the physician Hippocrates in ancient Greece to describe sloppy skin that looked as if it were covered with fine grain bran called "pythyron". Alba (Latin for “white”) means the pallor of the spots that appear.
Description. Asymptomatic, hypopigmented, slightly raised, small scaly patches with ill-defined borders, typically located on the lateral surface of the cheeks. Lichen alba affects the lateral surface of the cheeks, the lateral surface of the shoulders and thighs. It is observed more often in children aged 6–16 years; among adults, it is observed in people who work outdoors.
The etiology and pathogenesis of pityriasis alba are not clear. Some sources indicate prolonged exposure to sunlight, frequent showering and warm baths.
Lichen alba is asymptomatic. When interviewing the patient, there is no indication of previous rash, trauma, or inflammation. Patients are often atopic.
Clinically, the disease is represented by white spots of round or oval shape of various sizes, about 2–4 cm in diameter. On the surface of the spots, fine superficial peeling can be discerned.
Differential diagnosis is carried out between eczematous dermatitis, pityriasis versicolor, vitiligo, chemical leukoderma, hypopigmentation after resolution of psoriasis plaques, tuberous sclerosis. For differential diagnosis with depigmented nevus, videodermatoscopy can be used.
In laboratory diagnostics, examination of thin scales with potassium hydroxide for the presence of fungi gives a negative result.
Treatment. It is usually recommended not to undergo any treatment as the disease is benign and may resolve on its own. You should avoid washing your face with soap; it is advisable to cleanse the skin with hydrophilic oils or a non-greasy emulsion ointment. Applying 1% hydrocortisone cream/ointment or 2% sulfur-salicylic ointment to the affected skin for several weeks may help those patients who are very bothered by uneven pigmentation.
If rashes appear, contact specialists from St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution KVD No. 4.
Makarov M. S.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of this pathology is carried out by a dermatovenerologist and is based on objective examination data and additional research methods. Most often, the Balser iodine test is used to clarify the diagnosis. The essence is to stain the spots with a 2% iodine solution, under the influence of which the foci of pityriasis versicolor become colored. The method with an ultraviolet Wood lamp is also used.
Additional examination for the presence of fungi in the layers of the skin is possible.
Solar lichen: causes and symptoms of the disease
29.01.2021
In summer, most people like to lie in the sun. Sometimes, after lying down like this, strange white spots appear on the body. They begin to peel off. What is this and what causes it?
This disease is called solar lichen . The causative agents of the disease are fungal microorganisms that live on the skin. In their normal state they are harmless.
After prolonged exposure to the sun, the fungus becomes active and affects areas of the body. The skin is affected mainly in the warm season.
This disease, which is classified as dermatological, is not considered contagious. A person can be a carrier of the fungus but not have symptoms of the disease.
The main causes of the disease:
- problems with the vegetative-vascular system;
- problems with the endocrine system and excess weight, diabetes ;
- frequent colds;
- problems with the liver and bile ducts;
- increased sweating;
- synthetic clothing;
- love for solariums;
- using sunscreen;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- use of drugs that weaken the immune system .
If you have sun lichen, you should not expose your body to tanning, as this can cause an exacerbation of the disease.
Symptoms of the disease are visible to the naked eye; it is indicated by the appearance of asymmetrical spots with uneven edges. Their color may vary. This is the first stage of the disease.
After some time, the spots may darken and merge into one whole. They will be conspicuous because the tan does not stick to them. This is already the second stage. The spots do not become inflamed, red, or swollen, but scales form on them, causing itching. If you scratch them, they begin to peel off.
Spots appear mainly on the chest , back , sides, stomach , and neck . In children and adolescents, the main places of localization are the head, lower and upper limbs, and armpits.
Solar lichen is considered a beach disease, so at the first symptoms you need to stop being in the sun. This disease has a fairly long incubation period, which can last from two weeks to three months. lichen appears in both autumn and winter.
To make a correct diagnosis for this disease, the doctor needs to conduct a thorough visual examination of the skin. In addition to the examination, it is necessary to undergo a general blood and urine , and blood biochemistry tests. And only after that the doctor will prescribe treatment.
A stool test may be required . Also, if necessary, special studies are carried out in the form of the Balzer iodine test, when a little iodine is applied to the lichen . If it really is ringworm , it will change color to brown. Another examination is carried out using fluorescent lighting. The light stream is directed onto the formed spot. If it changes its color and turns green or red, then the diagnosis is confirmed. The test for the presence of Beignet's symptom involves scraping off the top layer of the epidermis. The results are compared with the symptoms of leukodermatitis, leprosy, Gibert's disease, syphilitic roseola, and a diagnosis of solar lichen .
To avoid becoming the owner of solar lichen , prevention is needed. To avoid getting burns, take sunbathing in the morning and evening, use a protective cream, wear clothes made from natural fabrics, do not visit the solarium, and eat fresh fruits and vegetables. Do not use antibacterial soap or gel constantly, watch your heart and blood vessels .
Solar lichen does not stain, although it is not dangerous, so treatment should be timely.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic
Types of lichen
Depending on the cause of development and characteristics of manifestation, several variants of lichen are distinguished:
- Pityriasis rosea (Giber's disease). The disease is characterized by a viral nature - the cause of pityriasis rosea is considered to be herpes viruses types 6 and 7.
- Shingles (herpes zoster). Origin - the herpes virus (Herpes Zoster), which causes chickenpox in childhood. Often appears after hypothermia, the rash is usually localized in the direction of the nerves.
- Pityriasis versicolor (variegated, solar) lichen. Occurs due to the action of a fungus of the Malassezia species. The peak of the disease is the summer season; infection often occurs on the beach, in shared showers. Without proper treatment, it can become chronic.
- Ringworm. Most often diagnosed in children. The cause of the disease is fungi of the Microsporum and Trichophyton species, which can be transmitted from sick people or animals.
- Lichen planus. It occurs quite rarely, its appearance is not associated with infection. The cause is considered to be autoimmune reactions of the body.
- Scaly lichen (psoriasis). It also does not apply to infectious and “contagious” lichen; the reasons for its development are still unknown. One of the theories discussed is an autoimmune variant of the disease - systemic damage to connective tissue. Characterized by seasonality, deterioration after stress. Increases the risk of developing arthritis and other systemic manifestations of autoimmune disease.
Lichens of infectious origin with contact transmission also differ in the degree of “infectiousness” (Table 1).
Table 1. The degree of infectivity of various types of lichen.
| Type of lichen | Contagiousness degree |
| Shearer | The tallest |
| Pink | Low (there is an opinion that lichen is not contagious) |
| girdling | High, especially in the phase of active rashes |
| Pityriasis | Low (there is an opinion that lichen is not contagious) |
Treatment of lichen in adults and children
Glucocorticosteroid creams are effective against shingles caused by herpesvirus infection.
Photo: AGLPhotoproduction/Depositphotos Therapy for each of the variants of this group of diseases depends primarily on the cause of the lichen, as well as on the severity of the changes. In adults and children, treatment regimens are almost the same, only in childhood the dosages of drugs may change, and some “adult” drugs are prohibited for use at an early age.
Treatment of the main variants of the disease:
- Therapy for pathologies caused by the herpes virus (pink and herpes zoster) is reduced to the prescription of antiherpetic drugs (acyclovir), anti-inflammatory and antiallergic drugs (antihistamine tablets), as well as the use of local steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments.
- Fungal types of pathology (pityriasis versicolor) are treated with antifungal, antimycotic ointments.
- To quickly treat ringworm, you need to get rid of the hair and then use antifungal ointments. Between applications of medicinal compositions, it is necessary to lubricate the stains with iodine.
For types of disease with unknown causes, specific treatment regimens have not been developed; therapy is selected individually. There is information about the incurability of scaly lichen - only an asymptomatic course of the disease is possible.
Causes of lichen
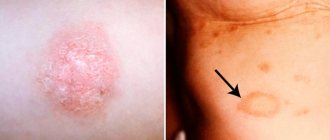
The diagnosis of “lichen” is made on the basis of the clinical picture - small rashes that rise slightly above the skin level and look like a localized area of rash with clear contours (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Plaques of pityriasis rosea usually have a clear outline. Source: PHIL CDC
Since we are talking about various diseases, the causes of lichen may be different. Most variants of pathology occur due to exposure to harmful microorganisms (viruses, fungi, bacteria), which are especially active against the background of weakened immunity. In some cases, contact with sick animals plays a decisive role. For certain types of deprivation, the question of the reasons for development still remains open - there are hypotheses that require further study.
Predisposing factors for the development or exacerbation of the disease are:
- stressful influences,
- hypothermia,
- previous infections,
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
The risk group includes both children and adults who have a decrease in immune defense, hormonal imbalances, and neurological disorders. The hereditary factor is considered only for some types of lichen with an unknown infectious cause of development.
All types of lichen that occur due to exposure to microorganisms on the body are transmitted by contact and are therefore considered quite contagious. For other variants of the disease, there is no convincing data on the danger to others.
Self-medication: consequences and dangers
Scratching the rash can cause scars to form on the skin.
Photo: LaCameraChiara / Depositphotos Treatment of lichen without the help of doctors most often turns out to be ineffective - it is almost impossible to independently determine the exact cause of the disease. Self-medication can also be dangerous - for example, erroneous use of antibiotics for herpes zoster not only affects the manifestation of a viral disease, but also causes a toxic effect on the body and the development of antibiotic resistance in the future. A common complication of herpes zoster is postherpetic neuralgia. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, any of the variants of the disease can progress, become more difficult to treat, become a chronic pathology and cause the formation of irreversible changes on the skin - scars.