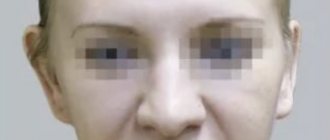
- Failed otoplasty.
- Bleeding and hematomas. Since during the operation the surgeon breaks and excises the cartilage tissue in your ears, bleeding and bruising in the postoperative period cannot be avoided. The problem is that hematomas do not go away for a long time, and most likely, within six months you will not be able to sleep on your side, and touching your ears will cause pain. For example, the excessive pressure that a hematoma exerts on the cartilage can lead to its necrosis.
- Wound infection. May develop around the operated area 3 or 4 days after ear otoplasty . It may seem insignificant (manifests itself as slight redness and slight soreness) - and this is its insidiousness. Advanced infection may require surgery.
- During rehabilitation after otoplasty Suture cutting and overcorrection may occur. Basically, both are associated with insufficient competence of the surgeon, incorrect selection of suture material, as well as insufficient preoperative diagnostics. The ears after such otoplasty do not look aesthetically pleasing, and such sutures require surgical removal.
- Warping of the ear cartilage.
The most unpleasant thing is if the ears become uneven after otoplasty. This is mainly noticeable at the site of the formed antihelix and occurs due to the fact that the surgeon did not apply the sutures close enough, and the ear cartilage sought to return to its original position.
Your ears may return to their original position.
Moreover, they can do this asymmetrically, which will make your appearance even more unattractive than if your ears were simply protruding. Another option may be a repeat operation, because... the ears may begin to return to their original position. This can happen for several reasons - the surgeon was not experienced enough, he used self-absorbing suture material, which did not hold the auricle in the desired position for a long enough time. Perhaps the patient himself removed the fixing bandage too early, which led to this result.
Of course, in this case, you will most likely have to have a second operation. And again, no one will give you a guarantee that this operation will be the last.
Unsuccessful otoplasty, the consequences of which were described in this article, is not common, but not such a rare occurrence. Those who decide to undergo otoplasty should remember all these consequences, and also that in many cases, even after removing the compression bandage and sutures, the surgeon will still advise you to wear ear correctors. They are recommended to be worn for about a year after ear otoplasty. They will serve as a good guarantee that your ears will fit snugly to your head, become symmetrical, and you will be happy with your new appearance.
What happens after surgery
After the surgeon has finished working with the ears, suture threads will first be applied to these places, holding the edges of the wound together. Then the patient is put on a special bandage that has a fixing effect. Its main task is to hold the ears in place and protect them from displacement, loss of shape, or infection.
The bandage can be either a regular compression bandage or a mask bandage. The first product looks like a regular decorative headband, is comfortable to wear, has good throughput, i.e. "breathes". The mask bandage covers the entire neck of the patient and passes under the chin, along the ears and through the back of the head. This option is no less reliable and functional, but wearing a mask can be a little difficult in the summer, when the air temperature rises high.
Wearing a bandage after otoplasty is mandatory.
Basics of proper care
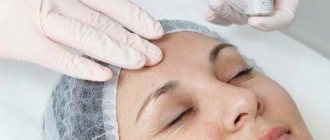
During the entire period while the suture threads are not yet removed, the patient must carry out mandatory antiseptic treatment of the incision sites. As a rule, a standard solution of chlorhexidine or another agent with a disinfecting effect is used for this. This procedure is required in order to prevent infection from entering the injured areas, which are currently very vulnerable.
Also, in the first days, it is forbidden to wash your hair and wet the incision sites. Any contact with water requires antiseptic treatment of the incisions. You cannot remove the suture material yourself! Even if it seems that it can be done easily and quickly. Only a surgeon can remove the threads. If the threads dissolve, then the patient does not have to worry about it at all.
How to prepare for a consultation
First of all, look in the mirror. Press your ears to your head lightly at first, then harder and harder until they completely hide on your cheekbones. Which of the intermediate options did you like best? Remember this and come for an otoplasty consultation.
During the consultation, we will ask you to tell us about the presence of certain health problems, about taking medications, and about allergic reactions to medications.
If you have had any diseases of the ENT organs, please take all related papers for consultation (extracts, results of examination by specialists, research results, etc.)
Sources
- Zanin EM., Maximiliano J., Oliveira ACP., Arpini NE., Duarte DW., Portinho CP., Collares MVM. Otoplasty: Rasps or Puncture Needles? A Clinical Trial. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol45 - N2 - p.521-527; PMID:33123781
- Li Z., Filobbos G. What is the UK Public Searching for? A Correlation Analysis of Google Trends Search Terms and Cosmetic Surgery in the UK. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol44 - N6 - p.2312-2318; PMID:32986171
- Kalmar CL., Patel VA., Humphries LS., Zimmerman CE., Vu GH., Swanson JW., Taylor JA. Pediatric Otoplasty: Does Surgical Specialty Training Affect Safety and Rates of Adverse Perioperative Events? // J Craniofac Surg - 2022 - Vol31 - N6 - p.1739-1742; PMID:32433130
- Ors S. Prominent Ear Correction With Anterior Rasping. // J Craniofac Surg - 2022 - Vol31 - N5 - p.1408-1411; PMID:32310890
- Siegert R., Magritz R. Otoplasty and Auricular Reconstruction. // Facial Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol35 - N4 - p.377-386; PMID:31470466
- Ordon A., Wolfswinkel E., Shauly O., Gould DJ. Aesthetic Otoplasty: Principles, Techniques and an Integrated Approach to Patient-Centric Outcomes. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2022 - Vol43 - N5 - p.1214-1225; PMID:31289880
- Kang N.V., Sabbagh W., O'Toole G., Silberberg M. Earfold: A New Technique for Correction of the Shape of the Antihelix. // Laryngoscope - 2022 - Vol128 - N10 - p.2282-2290; PMID:29658102
- Gantous A., Tasman AJ., Neves JC. Management of the Prominent Ear. // Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am - 2022 - Vol26 - N2 - p.181-192; PMID:29636149
- Smittenberg MN., Marsman M., Veeger NJGM., Moues CM. Comparison of Cartilage-Scoring and Cartilage-Sparing Otoplasty: A Retrospective Analysis of Complications and Aesthetic Outcome of 1060 Ears. // Plast Reconstr Surg - 2022 - Vol141 - N4 - p.500e-506e; PMID:29595722
- Brian T., Cheng PT., Loo SS. Audit of 117 otoplasties for prominent ear by one surgeon using a cartilage-cutting procedure. // ANZ J Surg - 2022 - Vol89 - N3 - p.E66-E70; PMID:29415346
How to prepare for surgery
The patient must first undergo a comprehensive examination, including a blood test. The scope of examinations depends on the type of anesthesia; for otoplasty under anesthesia, the list of examinations is longer.
Two weeks before surgery, you should stop smoking if you smoke. On the eve of the operation, you must wash your hair thoroughly. At home, please prepare a soft elastic fabric strip that will gently press your ears after surgery.
Possible complications
After otoplasty, as after any other plastic surgery, complications cannot be ruled out. Most complications are the result of the patient's negligence in caring for the operated areas during the rehabilitation period. Complications include:
- asymmetry,
- severe pain,
- high body temperature,
- suppuration and more.
In these situations, you cannot treat yourself. You should definitely consult your surgeon first.
If unusual symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
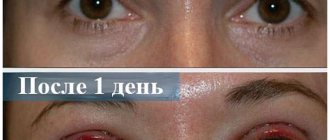
It is important to understand that bruising, swelling and minor pain are not considered complications. These are natural companions to almost any surgical intervention. You can worry if the severity of these effects either does not decrease over a long period of time or increases.
When to see a doctor
A visit to the surgeon is required if the suture material does not have absorbable properties. In this case, the doctor must remove the threads himself. The patient is strictly prohibited from doing this.
A visit to the surgeon is necessary to re-bandage. In addition, you will have to consult a doctor if any unusual sensations or effects occur - for example, one or more of those mentioned in the previous paragraph.
The result of plastic ear correction is usually visible immediately. But for final tissue engraftment and shrinkage, about 3-6 months should pass. After this period has expired, the final outcome of the operation can be summed up. The patient will have to be patient and listen to his surgeon in everything. However, the result is definitely worth the effort.
General Tips
How the suture heals after otoplasty and what kind of scar remains after it is also influenced by the patient’s general attitude towards the recommendations for recovery. Firstly, this concerns sports and physical activity. These things need to be excluded from life during the recovery period. After rehabilitation is completed, you will be able to return to your normal lifestyle.
Cigarettes, salty and spicy foods, and any thermal procedures such as a hot bath, sauna, steam room or steam room also negatively affect the healing rate. At first, it is not advisable to sleep in a position other than on your back. It is advisable to limit exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the operated areas.
It is worth noting that all restrictions are temporary and not lifelong. Therefore, there is no need to worry that the operation will somehow affect your usual everyday comfort. The main thing is to carefully follow all recommendations and observe prohibitions.
When is it filmed?
The exact period after which the stitches are removed is 10-14 days. At the same time as the threads, the fixing bandage is also removed and the dressing is done again. From now on, the patient can wear the bandage during nighttime sleep, rather than wearing it on an ongoing basis.
But the withdrawal period may vary, since the recovery rate is different for all patients. If threads that can dissolve on their own were used, there is no need to worry about removal. In this case, a visit to the surgeon will only be necessary for a second examination.
After otoplasty, the seams, or more precisely, the scars at the incision sites, are almost invisible. At first, traces of the intervention will be visible, but in the process of tissue restoration, the visibility will gradually disappear.