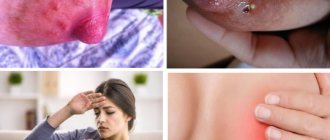
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is a benign papillary growth formed from the epithelium of the ducts of the female organ. It is otherwise called papillary cystadenoma or cystadenopapilloma. Pathology develops regardless of age. Teenage girls, young women, and elderly patients who have already stopped menstruating turn to doctors. Statistics show that cystadenomas account for about 10% of common cancer diseases in mammology. In appearance, cystadenopapilloma resembles a cystic formation. Her body is easily injured. The damage is accompanied by the release of bloody fluid into the excretory ducts and its release out of the nipple. Hemorrhages and tissue necrosis occur at the location of the tumor. Multiple papillomas formed in the mammary gland more often undergo a process of malignancy (degeneration).
Discharge from the mammary gland
When pressing on the nipple, a woman may have different discharge patterns. Sometimes they spontaneously leave stains on laundry.
If this discharge is the same on the right and left , it is never associated with a tumor or papilloma. Most likely, such discharge is associated with hormonal changes or incorrectly selected hormonal medications (which the woman is taking).
Discharge from nipples
These photos show light or slightly cloudy scanty whitish discharge - they are not a pathology . Moreover, their volume and color are the same on the right and left . Light transparent, or brown, yellow discharge is not a manifestation of papilloma.
If they are symmetrical on the right and left in volume and color but abundant , they are most often associated with hormonal changes (ovaries or thyroid gland).
With papilloma, the discharge is always asymmetrical: abundant and on one side.
Causes
Cystadenopapillomas most often form in dilated ducts against the background of diffuse or nodular fibrocystic disease. The main reason for their occurrence is mainly a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. It can be caused by:
- violation of the hormonal function of the ovaries;
- uterine fibroids, inflammatory processes in the endometrium and uterine appendages;
- surgical interventions on the internal genital organs, artificial termination of pregnancy;
- lack of childbirth and breastfeeding;
- stressful conditions;
- periods of puberty, pregnancy, menopause and the use of hormone replacement drugs;
- family predisposition;
- smoking and alcohol abuse in adolescence;
- disorders of fat metabolism (excess body weight);
- hormone-producing tumors and thyroid dysfunction.
Blood from the gland
Photo of bloody discharge from the nipple of the mammary gland and ultrasound marking of the dilated duct with papilloma (first photo). Such markings help during surgery to quickly and accurately detect the fragment of the mammary gland that needs to be removed.
Risk factors
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing neoplasia and aggravate its course include:
- hereditary predisposition – cases of diagnosed cancer in immediate family members;
- early sexual development - up to 10 years;
- age over 50 years;
- regular injuries of the nipple-areolar complex, cracks;
- frequent contacts with carcinogens;
- late menopause - after 55 years;
- primary infertility – inability to become pregnant for the first time;
- benign and malignant tumors in one of the glands.
Blood from nipple video
Video of bloody discharge from the nipple with pressure on the duct marked by ultrasound.
This is how this papilloma looks on an ultrasound and this is how the ultrasound doctor who performed the markings before the operation on the same patient describes it in detail:
| Focal changes in structure: LEFT GLAND At a distance of 50-75 mm from the center of the nipple in the lower-outer quadrant, at a depth of 15.6 to 20.1 mm, a duct dilated for up to 40 mm with a parietal tissue inclusion of 9.4x2.9x4.5 mm is determined - cannot be excluded intraductal papilloma 9.4x2.9x4.5mm v=0.064cm3 NB marks were made with a pencil “Edding 8020 haut-skin marker” in a supine position, lying down, arms raised behind the head. |
Treatment of papillomas, condylomas (HPV)
- performed on the body by a dermatologist-cosmetologist,
- on the male genitals - urologist,
- for women - a gynecologist,
- in the area of the anus and perineum - a proctologist.
There is now a treatment that is highly likely to eliminate HPV infection. Modern treatment for genital warts can not only remove or reduce the symptoms of the disease, it eliminates the HPV infection and prevents further transmission of the virus in many cases. However, after any treatment method, relapses are possible.
- Laser removal of genital warts is performed under local anesthesia.
- Electrocoagulation, removal of genital warts using high temperature, is carried out under local anesthesia.
- Interferon blockades (genital warts are injected with an interferon drug).
- Radio wave removal of condylomas. Today, the most effective method for removing genital warts. There is no trace left of condylomas.
Discharge from the nipples of the mammary glands
Pus from the nipple is not actually pus, but just a discharge. If it were pus, there would be fever, pain, redness of the skin - signs of inflammation. More often, such discharge occurs with ductectasia (dilation of the ducts, which can be detected by ultrasound) and with hormonal changes.
This is not a global problem and does not lead to cancer, but it is recommended that such discharge be applied to a glass slide and examined under a microscope (cytological analysis of discharge).
Nipple discharge during
Nipple discharge may occur during orgasm. This is due to muscle contraction and squeezing out contents from the ducts. Another thing is why there is so much of this content that it does not remain in the ducts, but is squeezed out. More often this is due to hormonal changes (gynecology, thyroid gland or excess intake of hormones from food - broiler poultry, fish, semi-finished broiler meat products).
Are breast papillomas dangerous during pregnancy?
Regardless of location, papillomas during pregnancy can cause significant discomfort to a woman and cause concern for the health of the child. It should be understood that the papillomavirus cannot influence the development of the baby in any way, however, with a high degree of probability, the child will be a carrier of the viral agent at birth, which will enter the body through the perinatal route of infection. This most often manifests itself in the formation of epidermal neoplasms in childhood.
As for the risks to a woman’s health, there are several potential dangers, the most significant of which can be considered the possibility of malignant transformation of a harmless neoplasm, which leads to an oncological process. This is especially true for intraductal papillomas, which can exist for a long time in a latent, undiagnosed form. In addition, such papillomas after childbirth during the process of active growth can clog the duct, preventing the outflow of breast milk, which can cause stagnation.
There is also a risk of mechanical damage to the tumor when wearing too tight underwear and clothes. This outcome may be accompanied by severe bleeding and infection of the wound, which is unacceptable during pregnancy.
Discharge from the nipple of the breast
light serous or white discharge with ductal papilloma , but then it is abundant and more pronounced only on one side (not symmetrically).
Then it is necessary to analyze these secretions under a microscope for papilloma cells, ultrasound for detection of ductal papilloma and/or ductography for the same purpose. Please note that it makes sense to do these studies only with those who already have experience working with this problem, and not with the first doctor you come across.
How to recognize papillomas?
Many of these growths look like elongated papillae, but the shape and size of papillomas can be different.
The color of the neoplasms also differs.
Most HPV products are flesh-colored. Pale or dark growths are less common.
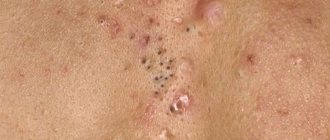
The number of papillomas depends on the state of the immune system - handfuls of tumors often accumulate on a weakened body.
All papillomas are contagious. So due to frequent touching, they quickly colonize the skin all over the body.
At home, it is almost impossible to find out the origin of certain neoplasms. Many of their varieties have similar signs.
Therefore, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Later we will talk in more detail about diagnosing breast papillomas in other places, but for now let’s talk about the consequences of HPV infection.
Nipple discharge
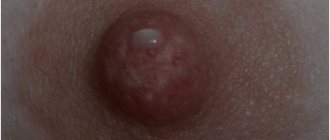
A clear sign of breast duct papilloma is bloody discharge from the nipple when pressed or spontaneous - like stains on linen.
Data allocation is also not a problem. Most likely, they are also associated with hormonal changes, and the dark drop from one duct is due to ductectasia (dilation of the duct after feeding). An examination of the secretions under a microscope is shown. If red blood cells or papilloma cells are found - ultrasound and ductography, with the prospect of surgery.
Brown discharge from the nipple
Brown or rusty discharge from the breast ducts - may appear as stains on laundry. The rusty color is due to destroyed red blood cells. This is also a sign of bleeding.
Diagnosis of papillomas
The doctor first examines skin tumors. In many patients, tumors have characteristic signs, so the doctor quickly determines their type.
Of course, there are difficult cases.
Some growths are similar to others and therefore additional research is carried out. Often the doctor will order a biopsy. He cuts off a piece of the tumor and examines it under a microscope.
What if papilloma grows in the breast?
To detect intraductal tumors, the following is carried out:
- Mammography
This is what a breast x-ray is called.
- Ultrasound diagnostics
The doctor sends sound waves into the chest, and after they are reflected, he receives an image of the mammary glands.
- Ductography
The doctor identifies the tumor by abnormal filling of the milk ducts. The procedure determines the location of the papilloma. The doctor also sees the size of the growth.
Sometimes the doctor takes a sample of the growth using a hollow needle. Usually after this he receives enough information to make a diagnosis.
And then it’s up to the patient.
He must decide the fate of the tumor - leave it or eliminate it.
Blood from the nipple
Blood discharge from the nipple ducts must be distinguished from nipple cancer. With nipple cancer, there may also be blood discharge, but then a wound with crusts appears on the skin of the nipple. Signs of nipple cancer SEE HERE .
Photo of a nipple with bloody discharge due to ductal papilloma of the mammary gland (cystadenopapilloma).
This kind of bloody discharge from the nipple should alert you! With them, it is necessary to analyze them under a microscope for papilloma or cancer cells. Detection of red blood cells in the analysis is a potential indication for surgery - removal of all ducts or a duct for its examination.
Papillomas during pregnancy: treatment
It is advisable to remove any neoplasms located on the skin and mucous membranes before pregnancy. If for any reason this rule was not followed, or primary papillomas appeared during pregnancy, the woman should immediately contact a specialist. Depending on the location of the defect, medical advice and assistance can be provided by a dermatologist, mammologist, gynecologist or oncologist.
It is strictly forbidden to resort to self-medication with the help of pharmaceutical ointments and plasters, folk recipes, as well as mechanical cutting of the body of the wart during pregnancy.
Intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland on ultrasound
In practice, we often have to console frightened patients whose ultrasound revealed “ductal papilloma”, but presented completely unclear and dubious ultrasound images, did not confirm it with an analysis of nipple discharge, did not do mammography (for a girl over 35 years old) or ductography, but offered it immediate VAB removal. Obviously, this approach is justified only for making money on the patient’s fear.
In the photo, a 37-year-old patient has abundant light transparent discharge from the nipple of the right mammary gland (taken for analysis under a microscope), ultrasound revealed a papilloma in the duct, mammography with ductography in 2 projections contrasted the ductal system with a filling defect - due to for papillomas located in this place. After ductography, the amount of discharge temporarily decreased (the contrast has a cauterizing effect). Planning to give birth. Therefore, we proposed removal of only the duct with papilloma, and not all ducts (Babcock's operation - selective ductectomy).
Why do papillomas grow?
Neoplasms do not appear on their own - they are formed due to the human papillomavirus or HPV. Over 100 types of it are now known.
The virus spreads in different ways. Most often, people become infected through direct contact - sexual intercourse and even ordinary touching allows HPV to penetrate the skin.
Indirect infection is also possible. Sometimes the virus first gets on a towel and other personal hygiene items, and only then gets to another person.
HPV takes quite a long time to settle in a new place. The incubation period lasts up to three months, so it is not possible to quickly detect infection.
In addition to the main reason for the appearance of papillomas on the chest, it is important to consider the conditions under which this occurs.
The virus does not grow tumors in every person. Some remain healthy. Even with multiple infections.
Our body monitors foreign organisms and fights them. Yes, not always effective. But with strong immunity, growths on the skin form much less frequently.
Another point is that the integrity of the skin affects infection. It is difficult for the virus to get through intact skin, but scratches and other wounds allow it to sneak inside. This is confirmed by research by doctors. In many patients, colonies of papillomas often appear next to injured skin.
So, we talked about HPV.
Let's move on to the appearance of the neoplasms.
Breast papilloma surgery
Treatment of cystadenopapilloma is surgical. The operation consists of removing all the ducts of the mammary gland (Koenig operation or ductectomy). The patient will not be able to breastfeed after this operation. Such an operation is possible under a compulsory medical insurance or voluntary medical insurance policy.
For nulliparous women, or in cases where our patient plans to give birth and breastfeeding in the future, we offer Babcock surgery - this is when we find, isolate and remove only the duct with papilloma . In this way, it is possible to preserve the possibility of lactation in a woman through other (unremoved) ducts of this mammary gland.
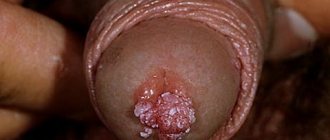
Photo of the discharge of a duct with papilloma during Babcock's operation: the duct filled with bloody contents is different from all the others, which remain intact and will allow the girl to breastfeed in the future.
Video of the isolation of a blood-filled duct with papilloma during Babcock's operation: the remaining ducts - the light ones - remain intact, and the girl will be able to breastfeed.
And what danger can neoplasms on the breast pose?
The female body is an amazing biological system, which during pregnancy faces enormous stress and not only successfully overcomes all challenges, but also transforms and transforms, adapting to any needs of the baby. It’s great when the period of bearing a child passes easily, without such unpleasant surprises as papillomas during pregnancy.
But if epidermal tumors do appear, the expectant mother faces an acute question regarding the removal of the growth and its effect on the development of the baby. Indeed, is it possible for pregnant women to remove papillomas and why, while expecting a baby, do warts choose the breasts of the expectant mother?
Cystadenopapilloma
Cystadenopapilloma is a papilloma of the mammary gland duct, but when it is located far from the nipple and discharge accumulates in the thickness of the mammary gland, without exiting through the nipple. This papilloma forms a breast cyst with growths.
| Ultrasound signs of peripheral cystadenopapilloma. The papilloma was located in the duct far from the nipple. Discharge (having no outlet) accumulated around her. Read more about such cysts HERE |
Bloody discharge from the nipple
Blood discharge from the nipple of the mammary gland also occurs with cancer. Therefore, it is imperative to perform their microscopic examination.
If the papilloma is inside the cyst, but there is no discharge from the nipple, a puncture (puncture) of the cyst is performed to examine its contents.
The specialists of our Center can take nipple discharge for analysis and perform a biopsy of cystadenopapilloma on the same day of your consultation.
How to treat papillomas and warts?
So far, doctors have not learned how to treat viral tumors.
But don't despair.
Although tumors cannot be cured, they can be removed.
What is the difference?
It’s simple - papillomas appear due to HPV, which means you need to fight the virus, not the symptoms. Modern medicine will not help here, so rely on your immunity. Over time, he dealt with the virus.
The growths themselves are sometimes best left alone. Just don't touch them.
But if the papillomas become damaged and hurt, then they need to be shown to a doctor. He will check the tumors and determine the best way to eliminate them.
Nowadays, dermatologists remove warts using different methods. They have almost no restrictions. Therefore, you can easily say goodbye to annoying tumors. Sometimes even in one session.
Ductography
Ductography is used to detect papilloma in the mammary duct. To do this, a thin tube (blunt needle) is inserted into the duct (from which discharge is detected), through which a contrast agent is injected into the duct. This drug fills the ducts and “flows around” the papilloma - it becomes noticeable. For small papillomas, the introduction of contrast has a cauterizing effect on them and the discharge may stop. If they appear again, surgery is indicated.
Ductography is a mammography with contrast filling of the breast ducts.
Methods for removing warts and papillomas
To eliminate the tumor, doctors perform operations:
- Electrocoagulation
The doctor cuts off the top of the tumor with high-frequency current, and then scrapes off the remains with curettage.
- Surgical excision
The dermatologist uses a scalpel or other sharp instrument. He cuts out the growth. The doctor removes not only the papilloma, but also the thin layer of skin around it. This reduces the risk of relapse.
- Cryotherapy
The doctor freezes the upper part of the tumor. Usually liquid nitrogen. The growth tissue slowly dies, and then the tumor falls off.
- Laser surgery
The doctor cuts off the top of the papilloma with a powerful beam of light. Then he burns the roots. A small inflamed wound remains at this site, which is covered with a protective crust. It lasts about three weeks, and new skin grows underneath.
Is it possible to remove papilloma in the breast?
New growths inside the body are a little more difficult to eliminate - low-traumatic methods are not suitable for this. Therefore, the tumor is removed surgically.
The breast is cut near the areola. In this case, traces of the procedure are almost invisible, and the shape and size of the mammary glands do not change.
Let us remind you that operations remove only the external manifestations of HPV. So doctors do not guarantee the final elimination of papillomas. There is always a risk of relapse.
But we do not recommend removing tumors in dubious beauty salons, even at a low price. The quality of therapy affects the speed of skin healing. Yes, and for traces of treatment.
Choose the right medical center carefully.
Leaf-shaped tumor
Leaf tumor is a polycyclic, well-demarcated tumor of the nipple, usually occurring unilaterally in mature women (mean age 45 years).
The skin and nipple in patients with a tumor may become distorted as a result of the pressure of the tumor, but their infiltration is never observed. These tumors are often indistinguishable from fibroadenomas on imaging and biopsy. Only a microscopic examination of a completely excised tumor gives an answer to the question of whether there is cancer.
There are 3 forms of tumor: benign, borderline and malignant, so therapeutic management and prognosis vary. Treatment of the tumor occurs surgically and consists of excision of the tumor with a narrow margin of healthy tissue in the case of a benign form or amputation of the nipple in a malignant form.
In women diagnosed with a malignant tumor, local relapses and distant metastases (to the lungs and bones) are most often observed in the first 3 years.
Fibroadenoma
Fibroadenoma is more common in girls and young women and in postmenopausal women.
A typical adenoma is a painless tumor, well demarcated from the surrounding parenchyma and skin. The most frequently performed examination in this case is ultrasound (due to the harmfulness of mammography in young women and good differentiation from nipple cysts).
The presence of a palpable tumor is an indication for its removal. Inconspicuous tumors can be left, but only after cancerous lesions have been excluded using imaging tests and biopsies and provided that the patient undergoes regular radiological monitoring.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of breast cancer in women diagnosed with fibroadenoma.