A child’s immature immune system often causes allergic rashes. Externally, this is manifested by the appearance of redness on the skin accompanied by itching, blisters and other skin rashes. Obviously, the mother in this situation is concerned about many questions: “How to get rid of an allergic rash?”, “What to do to prevent the rash from appearing?”, “What is first aid in case of an acute reaction of the body to an allergen?”, “How long does it take to pass?” allergic rash?
What are allergies in children
Allergy is the body's hypersensitivity to any foreign substance (antigen) followed by an immune response. According to scientific data, this feature itself is not inherited, but the predisposition to it is. Children whose parents have allergies (especially if both of them or just the mother are allergic) may be more likely to develop it.
When we come into contact with an allergen, the body reacts in such a way as to block the access of “dangerous” substances, according to its data, into the blood. This is expressed in inflammatory phenomena that occur due to the release of immunoglobulin E and histamine, a hormone that regulates various functions of the body.
Histamine causes swelling of tissues, stagnation of blood in capillaries, a decrease in pressure, makes the heart beat faster - all these changes should help the body quickly deliver as many leukocytes - protective blood cells - to those areas where their presence is needed.
Excessive sensitivity of the body to a particular allergen leads to the release of excessive amounts of histamine, which is why doctors prescribe antihistamines for allergies.
It is believed that in Russia from 15 to 35% of people suffer from allergies.
What are the symptoms of allergies in children? Common manifestations of this condition include the following:
- runny nose;
- sneezing;
- cough;
- itching;
- watery eyes or dry eyes;
- labored breathing;
- chills;
- rash or redness of the skin, eczema;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes;
- Digestive problems - with food allergies.
In the case of acute allergies, life-threatening anaphylactic shock can develop, when pulmonary edema occurs, breathing is impaired and blood pressure decreases.
Caring for a child with allergies
Cool air is preferable for allergy sufferers. Children with skin lesions, allergic rhinitis, and asthma live easier at a temperature of 18-22 °C and a humidity of at least 50%.
Children with allergies need to be bathed daily. In this case, the water temperature should be 32-36 °C, and the duration of swimming should not be more than 10 minutes.
With atopic dermatitis, children's skin needs intensive hydration after bathing. For this purpose, special creams and ointments are used. Without sufficient hydration, the skin quickly becomes dry and easily injured.
In children with allergies, it is important to regularly determine the level of vitamin D in the blood. A sufficient content of this substance in the body reduces skin permeability and serves as a barrier to the penetration of allergens.
Vaccinations are not contraindicated for allergy sufferers, but they should be carried out during remission.
Online consultation with a pediatrician
consultation cost: 500 rubles
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
What types of allergies are there?
The list of main allergens includes:
- dust - it contains several allergens at once, from plant pollen and dust mites to epithelial scales of pets;
- pollen - allergies can also develop to pollen from domestic plants;
- pet hair and particles of their skin, as well as down and feathers;
- fungal or mold spores;
- Food. Food allergies in children are common. It is very important to take care of its prevention during the mother’s pregnancy;
- Insect bites - usually from wasps, hornets, bees, bumblebees and ants. This allergy occurs in 0.4–0.8% of the population. These and other insects produce a variety of poisons that can cause reactions ranging from hives or swelling to seizures, diarrhea, suffocation and shock. If an allergic reaction occurs, it is important to get to the hospital very quickly or give the child the necessary medications within the first hour, which should be discussed with a pediatrician in advance;
- some medications. It is usually difficult to check in advance which medications cause an allergic reaction. In addition, an allergy to a specific drug can appear at any time in life, even if a person has not previously had one;
- latex - this allergy can manifest itself in very different ways and, as a rule, develops in people who are forced to frequently wear latex gloves, for example, doctors.
Other risk factors include smoking, using a gas stove, dry pet food, household chemicals and industrial pollution. It is believed that a child living in an area where the air is polluted due to proximity to the road can cause allergies.
Course of allergy
- Allergies in children can develop instantly - for example, in the case of an ant bite - or over several months, as happens when it is caused by cat fur or pollen. It all depends on how often the child comes into contact with the allergen.
- Seasonal allergies occur every year in the spring, summer and fall, and mold allergies can develop if there is prolonged rain outside and humidity levels in the home have increased, leading to the growth of microorganisms.
- It is important to understand that allergies in children can come and go, and there is no exact explanation for this.
Features of taking an allergen test
Allergen analysis in children is necessary to identify specific immunoglobulins (causal allergens) responsible for the development of food or other allergies.
The main indications for laboratory diagnostics include:
- the need to confirm food allergies;
- the need to assess the effectiveness of diet and treatment;
- hereditary predisposition to the development of allergies;
- a history of any immediate allergic reaction (Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock);
- confirmation of allergy to the vaccine.
How to distinguish a cold from an allergy in a child
A cold goes away within 10 days at the latest, but allergies appear constantly.
Here are the obvious signs of an allergy:
- the child constantly sniffles, especially if the nasal discharge is clear and liquid, and not yellow or green and thick;
- the baby constantly sneezes, his eyes are red, wet and itchy;
- the child has dark circles under his eyes, his nose is constantly stuffy, and he breathes through his mouth;
- dry cough;
- the skin is inflamed, red and itchy.
Allergy prevention
It has been proven that hypersensitivity to a particular allergen can occur in a baby when he is still in the mother’s belly, in the second trimester of pregnancy. This means that even before its birth, the expectant mother must take precautions.
Precautionary measures:
- if she is allergic to a particular substance, she must avoid contact with it during pregnancy;
- you need to stop smoking, take medications not approved by a doctor, carefully ensure that there is no contact with allergens at work - these may include platinum salts, formaldehyde, nickel or chromium compounds, pigments, pesticides, epoxy and other phenol-formaldehyde resins, organic compounds, which include chlorine, fluorine and phosphorus;
- unbalanced diet, the presence of allergenic foods in the diet, products with chemical additives. It is best to formulate a preventive diet that does not contain potential allergens;
- minimize the number of stressful situations.
After the birth of the child you must:
1. Try to establish breastfeeding (we write about how important this is for immunity in a separate article;
2. Follow a diet (which foods can be included in it and which cannot, we tell you here;
3. Temper the baby, monitor his health, give him a strengthening massage and do gymnastics with him;
4. If the child’s parents had bronchial asthma or atopic dermatitis, as well as other allergic reactions, the baby should be examined by an allergist: the sooner the problem is identified, the more effective the treatment will be.
However, it is important to understand that the best way to treat and prevent allergies is to eliminate the factors that trigger them.
If a child is allergic to dust and feathers, in addition to treatment, hygiene rules must be followed:
- mattresses and pillows must be in special plastic covers;
- special bedding should be used;
- if the laundry is ordinary, it needs to be washed and boiled 1 – 2 times a week;
- it is important to choose pillows and blankets with synthetic filling;
- the apartment should have a minimum of upholstered furniture;
- Carpets or rugs with a strong odor should not be used;
- clean using special vacuum cleaners and carry out wet cleaning.
If your baby is sensitive to mold and mildew, you need to:
- wipe surfaces in the bathroom dry after bathing;
- wash the bathroom with special solutions once a month;
- remove steam in the kitchen using a hood;
- dry clothes in a special room, not in the room.
If your child is allergic to wool, you should:
- exclude clothing made from wool and fur;
- do not go to the zoo, circus or houses where there are animals;
- If a cat or dog previously lived in your apartment, the room must be thoroughly cleaned.
If you need to protect your baby from pollen:
- when plants bloom, windows should be closed;
- do not walk in windy weather;
- You need to be careful with soaps and shampoos containing herbal preparations.
It is also important to avoid:
- stress;
- hypothermia or overheating of the baby;
- too high humidity;
- intense physical activity;
- infectious diseases - they provoke an exacerbation of allergies.
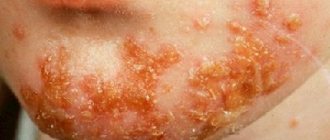
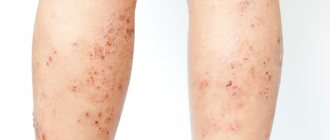
Allergic rash
In any case, parents are recommended to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the rash on the baby’s body. If a specialist discovers an allergy, then it is necessary to identify its form and irritant. Typically, the causative agent may be the following:
- the body's reaction to the weather (sun or cold);
- food allergies (in which the allergen product can be consumed by both the baby and the mother, if the former is breastfed);
- heredity (a child is at risk if at least one of his parents is predisposed to allergies);
- cosmetical tools;
- animal hair, dust, pollen;
- vaccination vaccines.
Once the cause of the rash is known, the next important step is to completely eliminate the irritant. It will be easier to do this in cases where the reason lies in external factors that they simply stop using (if they are creams, powders, detergents and other hygiene products). In the case where skin manifestations are the result of consuming certain products, it is important to exclude the product itself. The first signs may appear as early as an hour and a half after eating the allergen. Breastfeeding mothers must follow a diet and avoid spicy, fatty, chocolate, brightly colored fruits and vegetables, and alcohol. In such cases, it will be more difficult to get rid of the rash, since the product must be digested by the intestines, leave the baby’s body, and only after that the spots on the body will begin to disappear. You should know that when the pathogen reaches the baby through mother's milk, the process is delayed and recovery occurs after two weeks. Parents who themselves suffer from allergies should be extremely attentive to what their child is surrounded by and what he eats. Unfortunately, such babies are more prone to skin diseases than others. In this case, the irritant of an adult and an infant can be completely different. At the genetic level, only the predisposition itself is transmitted.
Almost always, allergies as a disease can be prevented. To do this, you will need to fulfill simple requirements:
- maintaining ideal cleanliness in the room, frequent wet cleaning and ventilation;
- introduction of complementary foods no earlier than four months from birth, and in some cases no earlier than six months. At the same time, it is important not to overdo it: if the introduced product is not suitable, then it should be offered to the baby again after one or two weeks;
- Diet compliance by a nursing mother. Drinking large amounts of liquid, broths and soups. Complete exclusion of harmful products;
- You should not self-medicate and try to prevent this or that reaction with the help of medications without appropriate doctor’s recommendations;
- maintaining hygiene and sharing a healthy lifestyle between mother and baby.
Walking in the fresh air, swimming, and hardening will have a positive effect on the health of all family members.
Urticaria and dermatitis are also types of allergic reactions. In the first case, there is a sudden appearance of itchy blisters on any part of the body. Such symptoms can occur from insect bites, from interactions with chemicals, and from eating strong allergens such as cow's milk, nuts, and honey. It is important to consider that prolonged exposure to the pathogen can worsen the baby’s condition, develop into edema and, at the same time, complicate breathing. Therefore, it is necessary to get rid of the presence of the irritant as quickly as possible and consult a doctor. Treatment occurs with the help of antihistamines and sedatives.
Dermatitis , like other types of allergies, is provoked by prolonged exposure to an irritant, increased sensitivity and predisposition to similar manifestations. Symptoms include inflammation of certain areas of the child’s skin (most often the hands, groin, cheeks), possibly burning and discomfort. Dermatitis is divided into several types:
- diaper (long-term interaction of delicate skin with irritants, such as wet diapers, diapers. Here you should change the diaper more often and wash the baby with running warm water before each change.
- Use wet wipes only when necessary, and apply a special protective cream under the diaper.);
- atopic (an outbreak occurs at the immune level, as the body’s response to respiratory and contact irritants. Localized on the cheeks, thighs, arms. Characterized by peeling lesions.);
- allergic (lack of vitamins in the body, consumption of allergic pathogens in food, lack of fresh air, moodiness, hyperactivity).
As in other cases, it is very important to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin treatment in order to prevent transition to a chronic form. All allergenic foods should be excluded from the baby's diet; to reduce itching, the doctor will prescribe the use of a cream or ointment, and also prescribe the necessary medications to eliminate the causes. It is worth understanding that the problem always lies inside, and it is important not only to eliminate external symptoms, but also to completely destroy the original cause of the disease. When an allergy manifests itself against the background of vaccinations for a child, it is important to take into account the child’s predisposition in advance, notify the doctor about this and follow a number of measures prior to vaccination. Such events include the following:
- taking tests;
- use of antihistamines two to three days before vaccination;
- close observation on the day of vaccination and refusal of new products.
Parents need to know that any vaccine contains a potential pathogen. It can be chicken egg white, gelatin and other components that make up the drug. Therefore, after the vaccination has already been done, you need to stay with the child in a medical facility for about half an hour, in order to observe and take measures, if necessary. Most often, doctors do not recommend going for walks on the day of vaccination, especially if the baby is still very small and fragile. It will be necessary to monitor the general condition and possible changes for two weeks.
Rash caused by infections and viruses
Only a specialist can recognize the etiology of the formation of a rash on the baby’s skin and prescribe the need for treatment. But in cases where skin manifestations are accompanied by fever, stool disturbances, vomiting, and difficulty breathing, then most likely the nature of the disease is directly related to infection. Infectious rashes are caused by diseases such as:
- chickenpox (caused by the appearance of blisters containing liquid inside. The areas of spread itch and itch, and the temperature rises to critical levels. Throughout the maturation of the blisters, the child is a carrier of the infection. The affected areas are treated with brilliant green. If all the doctor’s instructions are followed, recovery occurs after 21 days.);
- rubella (this type of infection is characterized by cough, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, intestinal dysfunction, and, as a result, diarrhea and vomiting. The rash is usually not palpable, but appears in the form of redness of the skin. Most often, this disease occurs in children older than two years, but infants can also be infected, especially those who do not have the appropriate vaccination. The disease proceeds without complications and does not require special measures. It is only important to maintain bed rest and reduce the risk of rubella infection for other small family members, since five to seven days, an infected infant can infect unvaccinated children.);
- measles (the main reason for its appearance is the lack of vaccination. Infection occurs by airborne droplets, and symptoms begin to appear no earlier than a week later. As a result, it is not possible to notice the disease in time. Only after a few days do the symptoms of the disease make themselves felt : the temperature rises, a small rash appears first on the inside of the cheeks, head, and then throughout the body.The child’s immunity weakens, so it is necessary to feed it with vitamins during this period, and allow the body to cope with the disease on its own.
It is recommended to help the baby during this period, based on the symptoms that appear: antipyretics, throat sprays, nasal drops, as well as bed rest and frequent fluid intake. Treatment can take place both at home and in a hospital, under the supervision of a doctor, in order to eliminate the possibility of complications). A dermatologist or allergist will help you make the correct diagnosis. To do this, you need to undergo tests and, if necessary, skin scraping. An important role is played by external factors, the nature of the rashes, their localization, as well as the accompanying deterioration of the baby’s condition. In any case, it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions regarding treatment and compliance with certain rules. The duration of allergies is also particularly influenced by the child’s immunity: the stronger it is, the sooner it will cope with the disease. Parents are required not to panic, but to notice the slightest manifestation of symptoms in time and contact a doctor as soon as possible.