Since childhood, we know that there is a normal temperature, and there is a “bad” one. Normal means a temperature of 36.6 degrees. Everything higher and lower indicates that something wrong is happening in the body.
The reasons for the increase in temperature can be quite innocent: for example, in women approximately in the middle of the cycle, when ovulation occurs. The thermometer readings may increase even after intense physical activity - this is normal. But sometimes the reasons are much more serious.
The first thing to do is to listen carefully to yourself and try to understand what else is bothering you besides the fever. The effectiveness of the treatment prescribed by the doctor will depend on how correctly you determine this. With a very high temperature (above 39 degrees), the condition can be very serious, and the best thing to do is to immediately call an ambulance. Intense fever can be accompanied by convulsions, short-term loss of consciousness, even delirium - in short, this is not a condition when it is enough to just lie down at home.
Febrile fever
Temperatures above 38 degrees, as a rule, occur in acute situations - when an infectious or viral disease begins to develop in the body, since it is at this temperature that the causative agents of such diseases - bacteria and viruses - die.
The body can also react to poisoning by a sharp increase in temperature.
If you have wounds or unhealed injuries, a rise in temperature is a very dangerous signal and may mean that the injured area has become infected.
Among the diseases that are accompanied by fever, the most common are:
- Flu . It differs from ARVI, first of all, in the heat. As a rule, it is accompanied by pain in muscles and joints, but catarrhal symptoms (cough, runny nose) appear later. With ARVI, on the contrary, sneezing and coughing are the first to appear, and then the temperature gradually rises.
- Angina . This disease is also familiar to everyone from childhood, and it is difficult to confuse it with something else - a sharp rise in temperature, sore throat, swelling and pain in the throat: the picture, as a rule, is quite clear. If a sore throat is not treated on time, it is fraught with complications, and very serious ones.
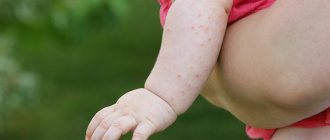
- Chickenpox and measles . These childhood diseases can easily attack an adult. In the event that he did not get sick with them in childhood. Adults suffer from these diseases more severely than children, and sometimes take longer to be treated. The tricky thing is that no other symptoms - except fever - are observed for the first two days. Characteristic blisters on the skin appear on the third day. Therefore, if the temperature has risen, you feel unwell, but nothing hurts, it is best to immediately call a doctor at home.
- Pneumonia . In this case, in addition to fever, the patient will be bothered by severe chest pain, shortness of breath, and a dry cough (sometimes, however, there is no cough). If the temperature is high and you find it difficult to breathe, you should call a doctor immediately - pneumonia can only be properly treated in a hospital.
- Pyelonephritis . The inflammatory process in the kidneys also has characteristic manifestations, except for fever. There may be discomfort or pain in the lower ribs or in the side. Blood pressure rises, swelling appears - because the kidneys cannot cope with the usual load. You should not treat yourself: the disease is serious, tends to take a chronic form and is fraught with complications.
- Hemorrhagic fever . A very dangerous infectious disease transmitted by rodents. A critically high temperature is accompanied by an almost complete absence of urination, muscle pain, and the skin acquires a reddish tint. What to do: Call an ambulance immediately.
- Gastroenterocolitis is a group of diseases that includes cholera, typhoid fever, dysentery and some others. Alas, they still occur in our time. As a rule, in addition to fever, there are characteristic symptoms - uncontrollable vomiting or incessant diarrhea. What to do: call an ambulance, which will most likely take you to the infectious diseases department, where they will take all your tests, determine the problem and prescribe treatment.
- Appendicitis . High temperature is accompanied by pain in the umbilical region, nausea, and vomiting. If your stomach hurts, and this pain intensifies with movement or changing body position, call an ambulance immediately. An inflamed appendix in itself is not so terrible - the operation to remove it is not particularly difficult and you will recover quickly after it, but possible complications (for example, peritonitis) are extremely dangerous.
- Meningitis and encephalitis . Infectious inflammation of the meninges. The condition is serious, severe fever is accompanied by headache, blurred vision, nausea, and spasms of the neck muscles are common. A hemorrhagic rash may appear on the abdomen and legs. The best thing you can do is call an ambulance and immediately begin treatment in a hospital.
- Hepatitis A . Of all the types of hepatitis, it is the most harmless, but it is still a serious disease. It is difficult to determine in the first days - the skin and whites of the eyes acquire a characteristic yellowish tint on days 4-5, and the intense fever stops by this time.
Scleroderma
You can tell that a person has scleroderma by the characteristic order in which the spots are found. This disease mainly affects the arms and legs of a person. What is scleroderma? Scleroderma is an inflammation of connective tissues in the body, which appears due to disorders in the human immune system. These disorders are in most cases congenital. They can appear mainly at a suitable period for them, for example, after suffering from viral diseases. As a result of strong pressure on the vessels, small vessels cannot withstand and fail. They become brittle, weak and lose their protection. Under fatal stress, they rupture and as a result, red spots form. In no case should you treat scleroderma on your own, but you should immediately visit a dermatologist.
Low-grade fever
Low-grade fever - between 37 and 38 degrees - would seem to be a less dangerous thing. However, it is often very difficult to bear, the person feels overwhelmed and exhausted. And the most unpleasant thing is that all this can continue for weeks.
Without a strong fever, in a “sluggish” mode, people with an impaired immune status, weakened people get sick - in this case, the body simply cannot adequately respond to the disease. Most often, a low temperature accompanies ARVI - after a cough and runny nose appear, the thermometer begins to show increasingly higher numbers, and the symptoms, of course, do not go away.
Other diseases that may be accompanied by low-grade fever and their symptoms:
- Exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (in this case, you will cough more than usual)
- Chronic sinusitis and sinusitis (headache, difficulty breathing through the nose)
- Asthma (cough, shortness of breath, shortness of breath)
- Pulmonary tuberculosis (unstoppable cough, possibly with blood in the sputum)
- Myocarditis (pain in the heart area)
- Chronic pyelonephritis (pain in the side, slight swelling)
- Inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary area - for example, cystitis (frequent and painful urination)
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers (abdominal pain after eating, blood in the stool)
Psoriasis
If red spots appear on the body
With psoriasis, white formations can be found on previously appeared red spots. The spots first begin to affect the arms and legs, and over time can move throughout the body; severe itching is felt. It should be remembered that you cannot scratch these spots, as you can further aggravate the situation by spreading the infection throughout the body. Unfortunately, psoriasis cannot be treated; you can only stop its spread.
What to do if the temperature does not go away?
Contact the clinic. If you cannot determine which specialist you need, you should start with a therapist - he will assess your general condition and recommend that you take tests that will give a more objective picture (usually a general blood and urine test).
Our clinic provides a full range of medical services in all areas - our allergists, surgeons, gynecologists, urologists, gastroenterologists, and dozens of doctors of other specialties will provide you with qualified assistance. Here, in the clinic, you can undergo all the necessary tests. A serious plus is that all examinations and treatment measures will be carried out at a time convenient for you.
If you have previously been diagnosed with diseases that have become chronic, be sure to inform the doctor about them during your appointment - this will make it easier for him to navigate the list of examinations that you need to undergo.
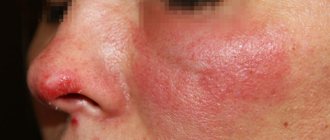
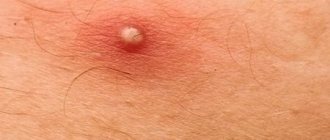
Causes of redness on the skin
The main causes of erythema on the skin are: Redness of the skin
- irritation: mechanical, high and low temperatures, chemicals;
- allergic reactions (urticaria);
- trauma (redness around the scratch);
- insect and other animal bites;
- autoimmune diseases, for example, eczema, psoriasis;
- infections: viral, bacterial, fungal;
- venereal diseases;
- dermatitis of various origins;
- In young children, a common cause of redness is diaper rash.
Typically, redness is accompanied by swelling, pain (more typical for infections), itching (more typical for allergic conditions).
As you can see from the list above, redness is a symptom of many skin conditions. It is often combined with other skin elements: blisters, ulcers, pustules, nodules, etc. The combination of signs makes it possible to suggest one or another diagnosis.
Temperature with vegetative-vascular dystonia
What to do if you feel a “temperature condition”, but without signs of a cold? You should take your temperature to see if there is any cause for concern.
What temperature is considered low-grade?
If it exceeds 37, then action should be taken, and if not, then it can be ignored. Most people's idea of elevated and normal temperature differs from the medical norm. A temperature several tenths higher than 37 degrees is considered low-grade and is a common symptom of VSD.
Should I be concerned if my temperature is slightly elevated?
The presence of elevated temperature cannot be left without attempts to find out the cause. If it does not exceed 37C, then this is considered normal, but if it is slightly higher than this figure, then it is considered low-grade. In “dystonics” it is a frequent occurrence and varies from 37.1 to 37.5C. Higher numbers indicate that this symptom is no longer related to the above disease.
Causes of elevated temperature during VSD
With VSD, temperature instability occurs, and the figure can change quite often during the day. The cause of this disorder is a deviation from the normal functioning of the thermoregulatory zone in the brain. Ensuring the same body temperature depends on it, that is, independent of external conditions. The failure occurs due to increased production of the hormone adrenaline, and there are frequent surges of its off-scale level, occurring due to little things that cause ordinary people to not have such amounts of this hormone. This is just one aspect of the pathologies of the autonomic system in VSD.
However, to more accurately identify the cause of this disease, you should undergo an examination and take tests that a specialist will prescribe. Based on their results, he will make a diagnosis, which will clarify the situation by confirming or denying the presence of other diseases that cause an increase in body temperature. If no such diseases were identified, then most likely the cause is vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Features of temperature during VSD
It should be borne in mind that this phenomenon in vegetative-vascular dystonia has its own distinctive features. One of them is her promotion, as some would say, because of all sorts of nonsense. For example, this could be physical activity, or even a state of rest. It is curious that it can return to normal if you just lie down or fall asleep, with a short rest being enough. Most likely, this is because in sleep it decreases a little for everyone.
Abnormal temperature with vegetative-vascular dystonia may not disappear for years. It usually appears in the morning and decreases at night. If it increases after any type of physical activity, then this indicates the presence of VSD. You should not overuse antipyretic drugs, as this does not eliminate the underlying cause, but it is quite possible to “earn” gastritis. At times it may fall below normal, but this is not a cause for concern as it will later rise to normal.
Is low-grade fever dangerous during VSD?
In general, no, but all these fluctuations are by no means healthy. This instability leads to two more violations. One of them is hyperhidrosis, that is, excessive sweating that occurs in a calm state, for no reason. The second consequence is that a person feels cold all the time, even in the warm season, not to mention the cold season. This is especially true for limbs, which get cold even with gloves and insulated shoes.
Is it possible to get rid of this trouble, which is one of the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia?
In principle, there is no particular cause for concern. If this really bothers you, then you can take medications from time to time, but not antipyretics, but sedatives. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr