Free consultation with a doctor by phone
Surgeon appointments are available daily by appointment!!!
LLC "Your Doctor"
Chat with the doctor
Addresses of medical centers in Moscow (unified reference) +7 (495) 255-45-59
Make an appointment at the clinic Discount on services Promotions
- +7 (495) 255-45-59
- Surgical centers in Moscow
- Every day from 9.00 to 20.00
- call me back
You can make an appointment with our operators by calling +7 (495) 255-45-59
Prices for services Clinic address Make an appointment Call a surgeon to your home Pediatric surgeon Ligation
Inflammation of atheroma is a complication of a disease such as a sebaceous cyst. A sebaceous cyst or atheroma is a tumor that appears when the ducts of the sebaceous gland close. It is formed in various parts of the human body where hair is present. If this tumor is not removed in time, inflammation of the neoplasm develops. This tumor itself is not dangerous. But when the tumor becomes inflamed, a purulent process occurs, which can cause a complication such as sepsis.
If the sebaceous gland cyst is inflamed, you should not try to get rid of it yourself and squeeze it out, this can lead to serious consequences and complications. You can use ointments for external inflammation, such as levomikol or ichthyol ointment. It must be remembered that with inflammation, atheroma is difficult to treat. Atheroma can be treated with surgical, laser or combined methods.
Useful information on the topic:
- Treatment of atheroma
- Ear atheroma
- Atheroma on the head
- Atheroma on the face
- Atheroma on the back
- Atheroma on the penis
- Atheroma of the eyelids
- Purulent atheroma
- Breast atheroma
- Laser removal of atheroma
- Removal of atheroma at home
- Atheroma on the neck
- Atheroma on the lips
- Atheroma on the leg
- Atheroma in the groin
- Atheroma on the labia
Causes
The development of atheromas is noted in every tenth adult, mainly at a young age (up to 35 years), equally often in both sexes. Epithelial cysts develop when difficulties form for the release of secretions - narrowing or blockage of the excretory duct of the gland. Their reasons are as follows:
- congenital structural features of the glands, in which case the formations are detected immediately after birth;
- violation of the desquamation of keratinized skin cells, with the mouth of the gland being blocked completely or partially;
- excessive sebum production due to hormonal imbalances or psychosomatic disorders;
- mechanical damage to the skin: it has been noticed that atheromas often form in areas of scars after burns or frostbite;
- insufficient hygiene.
Characteristic differences of atheroma.
Atheroma has a number of characteristic features by which it is quite easy to distinguish it from other skin formations:
- atheroma always has a clear round shape;
- upon palpation, the atheroma always moves inextricably along with the thickness of the skin; it is not possible to move it separately;
- atheroma is pliable, soft to the touch;
- in the absence of inflammation in the atheroma, touch does not cause discomfort or pain.
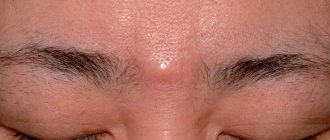
Rice. 2. Atheroma during removal.
Classification
In practical dermatology, two classifications are used: according to the type of structure of capsule cells (histological) and according to the type of formation. Practitioners mainly use the second one. There are:
- Congenital (or primary) atheromas, the formation of which is caused by congenital changes in the ducts. The size of such formations is up to 0.5 cm, they are multiple and are detected soon after the birth of the child.
- Acquired (or secondary) atheromas develop in initially unchanged gland ducts in people with skin damage or impaired sebum production. The size of cysts can reach several centimeters. As a rule, they are single.
Removal of inflamed atheroma
If pus appears in the atheroma, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will diagnose it and prescribe the correct treatment. Basically, the inflamed cyst is removed surgically. During this surgical procedure, the fatty content of the atheroma and its capsule are removed. It is also necessary to remember that if the atheroma becomes inflamed, it cannot be removed immediately in order to reduce the risk of pus breaking through the skin.
Treatment of atheroma with inflammation is quite complex. First, the surgeon opens the tumor and removes its contents. Then he rinses the cavity, cleared of pus, with antiseptic drugs. Afterwards, drainage is installed, with the help of which the rotting products will be removed, and the cavity will be washed with antiseptics. A special sterile bandage with medicinal ointment is applied to the affected area. If the suppuration of the cyst is severe, the attending physician may prescribe antibiotics.
The most important task for the surgical treatment method is to remove the atheroma shell itself in order to avoid the development of relapse. That is why, after a certain amount of time, it will be necessary to repeat the procedure to completely remove the capsule.
When atheroma becomes inflamed, the main thing is to begin treatment immediately. To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor. The clinic provides the services of highly qualified surgical specialists who will help get rid of such problems as inflammation of atheroma.
Diagnostic methods in surgery:
- Doppler in surgery
- Colonoscopy
- Angiography
- CT scan
- Gastroscopy
- MRI
- Abdominal ultrasound
- X-ray
- Endoscopy
Prices:
| Code | Name of service | Prices |
| 1 | Initial appointment | 1200 |
| 2 | Repeated appointment | 900 |
| 3 | Calling a surgeon to your home | 3500 |
| 4 | Abdominal ultrasound | 2200 |
| 5 | Ultrasound of veins and vessels | 2400 |
| 6 | Doppler 2-3 trimester | 1200 |
| 7 | Rectoscopy | 1500 |
Symptoms
Atheroma looks like a round or oval formation that rises above the skin level. When palpated, it has an elastic consistency. If the atheroma grows to a large size, fluctuation appears - a feeling of vibration of the liquid contents. The skin over the cyst is not changed; at the top you can see a crater-like depression - this is the mouth of the sebaceous gland duct.
The structure of atheroma
Most often they develop on those parts of the body where there is a high density of sebaceous glands. This is the face, upper chest and back, scalp and neck. Congenital cysts are typically located in the perineal area.
Atheroma slowly increases in size. Often the reason for visiting a doctor is only suppuration, since the growth of the formation is not accompanied by any symptoms or pain. The cyst is easily displaced relative to the deeper layers of the skin, since it is surrounded by a dense capsule of connective tissue and is not fused with the surrounding tissues. On the surface of the atheroma located on the scalp, hair often falls out.
With the development of a complicated form of atheroma - inflammation - the skin turns red, becomes swollen, and pain occurs when touched. Thick, cheesy contents or pus with an unpleasant odor may be released from the mouth of the gland. Since the formation is delimited by a sheath of connective tissue, general manifestations of the inflammatory process (fever, intoxication, etc.) do not occur.
Photo of atheroma of the sebaceous gland
Symptoms of inflammation
It is quite difficult to independently identify this tumor, since in appearance it is very similar to a lipoma. It is a capsule containing sebum and exfoliated epithelium. The inflammatory process in atheroma can occur due to the entry of pathogenic bacteria into its capsule, which damage the capsule and cause the appearance of pus. Symptoms indicating that the atheroma is inflamed:
- The skin at the site of atheroma formation has swelling and redness;
- Painful sensations;
- The temperature at the site of inflammation is increased (if the problem is not removed in time, an increase in the temperature of the whole body may occur);
- General discomfort of the body;
- Bad feeling.
The pus formed in the capsule can break out or under the skin. With an external breakthrough of pus, the consequences are minimal and combined treatment is suitable. Opening the atheroma under the skin can lead to more serious consequences. If this happens, the person’s condition will worsen, a headache and symptoms of intoxication will appear. In order to minimize the consequences of inflammation, it is necessary to remove the inflamed atheroma in a timely manner.
Useful information about visiting a surgeon at the clinic:
- How to prepare for a surgeon's appointment
- What diseases does the surgeon treat?
- Calling a surgeon to your home
- Surgical care in the clinic
- Surgical care at home
- What symptoms should you contact a surgeon for?
- Treatment of surgical diseases
- Treatment of intestinal pathologies
- Treatment of skin surgical pathologies
- Treatment of bedsores and necrosis
- Treatment of parasitic diseases
- Treatment of inflammatory processes of soft tissues
- Treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- Diagnosis of surgical diseases
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist, surgeon or general practitioner. Most often, a general examination is sufficient for diagnosis, since the appearance of the formation has characteristic features.
In rare cases, for differential diagnosis with other benign formations - fibroma, lipoma, hygroma - ultrasound is recommended. This reveals a dense capsule and liquid contents of the cyst.
Since the risk of atheroma degenerating into a malignant tumor is extremely low, a biopsy is usually not recommended. After its removal, a histological examination of the capsule can be performed. The result takes 10-14 days to prepare.
Diagnosis and risk factors
To correctly diagnose a tumor, it is necessary for a doctor to examine and palpate it. If the development of a malignant tumor is possible, the doctor at the clinic will prescribe additional diagnostics (a sample of the contents of the atheroma capsule is taken during surgery).
The most common inflammation of the cyst is in the following cases:
- After the onset of puberty;
- In men, inflammation of the sebaceous gland cyst can occur on any part of the body except the head;
- In women, the head is most often affected;
- In cases where acne appeared during puberty;
- After a heavy tan;
- If there were microtraumas of the skin on the body.
If atheroma appears, its formation cannot be prevented. People who have already had similar neoplasms are also at risk of developing cyst inflammation.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
Treatment of atheroma
Extruding the contents yourself is not recommended. The capsule delimits the contents from the surrounding tissues; under mechanical pressure it ruptures, which can lead to an inflammatory reaction up to the development of sepsis - blood poisoning.
The only effective treatment method is the complete removal of the contents of the cyst along with the capsule - the so-called enucleation - since the remaining membrane often serves as the basis for the regrowth of the formation. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia.
Cysts on the face or other areas of the skin where it is necessary to maintain an aesthetically beautiful appearance can be drained by performing a cystotomy - dissecting the capsule with evacuation of the internal contents. Healing occurs without suturing; an atrophic scar forms at the site of the cyst.
An alternative removal option is the use of laser techniques:
- laser coagulation of formation;
- laser excision of a cyst with a membrane;
- laser evaporation of the capsule from the inside.
For inflammation, local anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs in the form of ointments are prescribed. Taking antibiotics in tablet form can only be indicated for severe inflammatory processes - phlegmon.
Surgical removal of atheroma
Methods for treating and getting rid of atheromas on the head
You should not try to get rid of atheroma at home. Neither “grandmother’s methods” nor opening a tumor on your own will lead to anything good. Unfortunately, it is impossible to do without surgical intervention, but it should be carried out in the office of an experienced doctor. This is the only way to get rid of not only the ugly growth, but also the occurrence of possible complications. After undergoing medical manipulations on the head for atheroma, the patient may be prescribed a number of medications for oral administration, including anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and so on.
Modern medicine allows you to get rid of scalp atheromas using the following methods:
- Laser removal of atheroma. To get rid of atheroma on the head, this method is the most preferable, since it allows you not to shave off the hair around the formation before surgery. The procedure is painless and leaves no scars. It lasts from 30 minutes. It involves treating the atheroma cavity with a laser, which evaporates its contents. After the operation, the skin is treated with antiseptic and regenerating substances.
- Mechanical exfoliation of the contents of the capsular bag of atheroma. It is carried out by making longitudinal or 2 bordering incisions. The scalp atheroma is removed through incisions using pressure and special instruments. After the operation is completed, the edges of the wound are sutured.
- Radio wave surgery of atheromas. It differs from the laser technique in the nature of the waves affecting the atheroma - here they are radio-high frequency.
Rice. 3. Atheromas on the head should not be squeezed out.
Rice. 4. Atheroma on the head needs to be removed.
The appearance of atheroma, why does this happen?
Among the causes of atheroma, there are several main ones:
- insufficient skin care - with prolonged accumulation of dirt particles mixed with sweat in the thickness of the skin, blockage of the glandular duct is possible, which leads to the formation of atheroma;
- systematic injury to the skin - causes detachment of skin cells that prevent the outflow of glandular secretions;
- hormonal imbalance – this especially applies to sex hormones;
- excessive sweating;
- poor environmental situation.
Rice. 3. Squeezing out atheroma is not recommended.
What is atheroma
Simply put, atheroma is a soft bump on the head, usually yellow in color. Both isolated cases of atheroma development and atheromatosis, in which frequent relapses occur, are possible.
In Buddhism, the bulge on the top of the head is a symbol of enlightenment, which is always present in images of Buddha. In real life, things are a little different. If the atheroma is not removed in time, sooner or later it will become inflamed and suppurate. Its symptoms are as follows: when the atheroma is inflamed, it begins to change color to light brown, a “bump” breaks through, and pus is released from it. All this is accompanied by an indescribable aroma, faintly similar to the blooming of a spring meadow.
Naturally, like any purulent process, when atheroma suppurates, immediate surgical intervention is required. But it is better to go to the doctor without waiting for such developments.
Expert comment:
“Bringing atheroma to inflammation is not worth it for many reasons.
Firstly, to treat purulent wounds, the surgeon is forced to make a large incision in order to properly clean them.
Secondly, as a result of excess inflammation, an unsightly keloid scar can form.
So the operation to remove atheroma, when the atheroma is calm, is much easier and requires almost no time for rehabilitation.”
Maxim Vasiliev, plastic surgeon.