Causes of the disease
Children's skin has its own characteristics that predispose to the appearance of seborrhea. Seborrheic dermatitis in infants occurs due to the large size of the sebaceous glands and increased secretion of sebum. Also, the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis in infants is associated with high levels of maternal hormones in the child’s body.
Manifestations of the disease
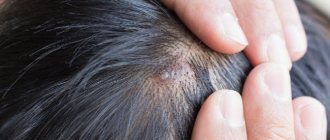
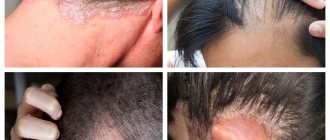
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face of a baby most often affects the forehead, and on the body it manifests itself as inflammation of the folds in the neck, armpits, and groin areas. But the most common manifestation of seborrheic dermatitis in infants is damage to the scalp with the formation of milky crusts - the so-called “baby cap”.
Course of the disease
Mostly, signs of the disease appear on the scalp about a couple of weeks after birth. Fatty-looking yellow crusts appear on the skin, most often on the scalp and forehead. Redness of the skin and flaking behind the ears and at the border of hair growth may also be noted. The rashes on the body are mainly located in the skin folds in the armpits and groin. A rash appears in these areas, skin irritation and maceration begin.
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants does not always lead to severe discomfort ; its manifestations may be minimal. With significant damage, the baby feels itching and becomes restless. In severe cases of the disease, complete redness and peeling of the entire skin is observed, the child may refuse food, and the body temperature rises. This condition requires emergency hospitalization and hospital treatment.
Complications of the disease
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants can be complicated by infection. This condition can lead to pyoderma. If treated incorrectly or untimely, the process can spread to healthy skin, in some cases affecting the entire body.
Forms of seborrhea
Taking into account the external manifestations of the disease and the specificity of the disorders, three forms of seborrhea of the scalp are distinguished:
- fat;
- dry;
- mixed.
Oily seborrheic dermatitis is observed with excessive production of fatty secretions and is characterized by high oiliness of the dermis and hair, yellowish or red spots on the skin, profuse oily dandruff, thinning and hair loss. Moderate manifestations of the fatty form of the disease are quite common in adolescents and, with proper care, after normalization of hormone levels, do not require special therapeutic effects.
With dry seborrhea, the fatty secretion is produced in insufficient quantities, resulting in a feeling of skin tightness, dryness, severe itching and burning, and dandruff in the form of small dry scales. The hair becomes very thin, becomes dull, brittle and begins to fall out profusely.
The most problematic in terms of treatment is the mixed form of seborrheic dermatitis, in which fatty secretion is secreted in excess in some areas of the dermis, and in deficiency in others.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated in children?
If seborrheic dermatitis appears in newborns, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected in an infant, treatment is carried out with external means. To loosen the crusts on the head and remove them painlessly, use products based on salicylic acid and oil compresses, which are applied about half an hour before water procedures. To treat seborrheic dermatitis in newborns , you can use drugs with a keratolytic effect. This will help remove excess gland secretion and cleanse the scalp. After softening and removing the crusts, anti-inflammatory agents may be prescribed.
For treatment to be more effective, it is necessary to ensure that the skin is well hydrated and supplied with nutrients in the right quantities. This helps restore and strengthen the water-lipid barrier and restore the proper functioning of the sebaceous glands. Suitable for care are dermatological creams created for children, which contain vegetable oils, sebum-regulating and wound-healing components. If treatment for seborrheic dermatitis in newborns turns out to be ineffective, the following may be included in the therapeutic regimen:
- topical corticosteroids;
- antibiotics and antiseptics;
- antihistamines for severe itching.
Factors influencing the development of pathology
The main factors that can increase the activity of the fungus include the following:
- the sebaceous glands secrete too much secretion, which is common in newborns;
- there is increased sweating;
- there are too many maternal hormones in the child’s body;
- the baby has a weak immune system;
- there are diseases of the digestive system that provoke malfunctions of certain organs;
- hereditary predisposition in the newborn.
Preparations with zinc pyrithione
For mild to moderate seborrheic dermatitis on the head in infants, preference may be given to non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs based on zinc pyrithione. For example, Skin-cap shampoo containing activated zinc pyrithione has anti-inflammatory, sebum-regulating, and antimycotic effects. Skin-cap shampoo is prescribed as the main method of treatment to soften crusts and eliminate inflammation; in the future it can be used to prevent relapses of the disease. The activated zinc pyrithione contained in Skin-cap shampoo helps:
- reduce the intensity of inflammation;
- reduce the activity of fungi and bacteria;
- effectively moisturize the skin;
- eliminate peeling, feeling of skin tightness;
- reduce itching.
It is thanks to this combination of effects that Skin-cap shampoo can be used during an exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis in an infant, then the treatment will be more effective. You can combine the use of Skin-cap shampoo with accompanying medications, including it as part of complex therapy.
Treatment with medications is supplemented by general recommendations for changing diet and caring for the baby. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected on the face of a baby , it is recommended to exclude foods with potential allergens from the diet. You should not put synthetic clothing on your baby so that the skin is not subject to friction and irritation. Parents should pay special attention to the selection of laundry detergents, choosing products without aggressive substances in their composition.
The likelihood of stress for a child needs to be reduced as much as possible, so it is important to maintain a favorable psychological environment in the family.
How to remove crusts from a baby's head?
When my son was a month old, his head suddenly became covered with some yellow scales. I didn’t know anything about seborrhea at that time, so I was very worried: what kind of skin disease is this? Isn't it dangerous? But the pediatrician said that this is a common occurrence and not worth worrying about. You need to carefully remove the crusts and soon there will be no trace left of them. What did I do?
- 2-3 hours before bathing, I smeared my son’s head with baby oil (you can use olive oil) so that the crusts softened. Oil is very difficult to remove from fabrics. Therefore, the baby must wear a cap (which you don’t mind ruining) or a scarf. Otherwise, sheets, pillowcases, and clothes will be covered with greasy stains.
- Then - swimming. While fighting the scabs, I washed my child’s hair as usual once a week. More often it is not necessary. Changed shampoo. Our old one, it seemed to me, dried out the skin. Bathing proceeded as usual, except that I paid a little more attention to massaging my head. Some of the scales were washed off at this stage - along with the foam. All that remained was to blot the child's head with a towel.
- Now - direct removal of crusts. First, I went through my hair with a regular comb—a child’s comb with sparse teeth rounded at the ends. Thus, she removed the crusts that had already separated, but were stuck in the hair. Next, I took a baby brush with soft bristles (sold complete with a comb) and combed out the remaining crusts.
- The first time I couldn't get rid of all the scales. This is fine. Under no circumstances should you tear them off with force: scrape them off, use tweezers. This can injure the child’s skin, which can lead to infection in the wounds. Therefore, I acted on the principle “if you drive more quietly, you will keep going,” that is, I repeated the procedure for several days in a row. In the following days, I washed my son’s hair without shampoo, so as not to dry out the skin.
- After 3-4 procedures, every single scale disappeared from the baby’s head.
Possible complications
This disease can cause serious complications:
- Crusts can begin to spread not only on the head, but also far beyond it. The child becomes very capricious, constantly cries because the crusts are itchy, there is also redness, burning and rash. In this case, seborrheic dermatitis can develop into atopic form.
- Infection can occur in the affected areas of the skin. This process is very dangerous, because the inflammatory process begins to develop quickly. Soon a secondary infection may join the dermatitis. The affected areas of the skin begin to become covered with pus. In most cases, this is observed exclusively in the groin, axillary or buttock areas. In this situation, it is impossible to get rid of the disease without the use of various medications.
Although seborrheic dermatitis in most cases is considered a non-serious disease, you should not delay visiting a doctor after the first signs of pathology appear. The sooner the use of special means to eliminate crusts is started, the higher the chances that the disease will disappear sooner, complications will not arise and the child will feel normal.
Folk remedies
Seborrheic dermatitis can be treated with decoctions of medicinal plants after consulting a doctor.
Recipes:
- Take 15 g of dry roots of burdock, elecampane, and St. John's wort flowers. Place a tablespoon of the mixture in a thermos and add a glass of boiling water. After 8 hours, strain. After each shampoo, rub the infusion into the affected areas.
- Place 20 g of dry sage herb in a container, add 200 ml of hot water, boil for 15 minutes. After cooling and straining, moisten the skin daily in areas where crusts have accumulated.
- Pour 25 g of crushed oak bark into a saucepan, add 200 ml of boiling water, keep in a water bath for 5 minutes. Leave for 3 hours. Strain and rub the broth into sore spots.
- Make a mixture of equal parts of plantain leaves, calendula and chamomile flowers. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a thermos with 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 3 hours. Use a gauze swab dipped in liquid to wipe the affected areas.
Traditional methods are effective when used regularly. Before using herbal infusions in a child, you should make sure that there is no allergy to a particular remedy . To do this, attach a cotton pad soaked in a herbal infusion to the inner surface of the baby’s arm near the wrist with an adhesive plaster. If the skin does not turn red after 24 hours, you can use the test product for treatment.
Diagnostics
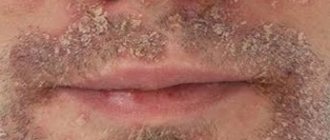
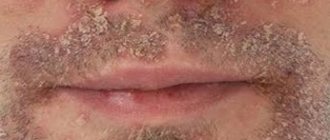
The diagnosis is made on the basis of characteristic clinical symptoms: localization of pathology in the scalp in the form of scaly formations. Peeling on the face is finely lamellar, with whitish scales.
In unclear cases, diagnosis is carried out by a dermatologist. Using a dermatoscope under multiple magnification, pathological lesions on the skin are studied and microscopy of scales is performed.
If seborrheic dermatitis does not go away in the first year of life, but continues to progress, differential diagnosis with atopic, allergic dermatitis and psoriasis is necessary.
How to properly care for your baby's skin
You need to take care of your baby's skin very carefully and carefully. There are some rules that must be followed every day, especially if the child suffers from seborrheic dermatitis.
- You should choose clothes for a newborn only from natural fabric. Synthetics should be avoided.
- If diapers are used, then it is imperative to maintain a certain distance between the body and the surface of the diaper. It is important to ensure that there are no leaks.
- To prevent the development of seborrheic dermatitis, it is necessary to regularly give your baby air baths.
- Carefully monitor the temperature in the room where the child is. The maximum temperature should not exceed 23 degrees.
Treatment
Treatment consists of eliminating factors that contribute to the chronicity of the process: vegetative-vascular dystonia, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, foci of chronic infection. It is carried out jointly by several doctors of various specialties depending on the etiology: always a dermatologist, if necessary a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, urologist and neurologist - and only under their supervision.
After a diagnosis of seborrhea is established, it is recommended to follow a dietary diet that is limited in carbohydrates, fats and salt, rich in fiber, vitamins and dairy products.
The baby requires careful care. When the first symptoms appear, contact of synthetic fabrics with the baby’s skin should be avoided, opting for natural things without seams.
- In women, combined oral contraceptives are used in cycles with an interval of 7 days to normalize hormonal levels.
- Vitamins A, C, E and group B are prescribed immediately after diagnosis.
- The trace element zinc is used in tablet form, 1 tablet three times after meals for 1-2 months.
- For dermatitis of the scalp, antifungal drugs are recommended, especially if fungi of the genus Pityrosporum have been found to influence the process. They are applied topically as a cream, shampoo or ointment. Additionally, local antiseptics are prescribed - tar soap, zinc paste. If the above is ineffective, you need to switch to taking glucocorticosteroids.
- If the skin of the face or behind the ears is affected, “Zinerit” ointment or “Dalacin-T” gel is used for a long time.
- When washing your hair, use special medicated shampoos (Nizoral, Sulsen, Danex), sulsen paste and soap.
Traditional methods of treatment and prevention
The most popular and effective method is treatment with sea salt. First, dirt is removed from the head and hair with any shampoo, and then salt is rubbed into wet hair for a couple of minutes. This helps stop hair loss and increases the volume of blood flowing to the hair follicles. For prevention, this technique is indicated once every 1-2 weeks.
Apple cider vinegar is also used, as it contains vitamins, pectin, and enhances regeneration. You can use it as a hair rinse: dissolve 4 tablespoons of a 6% vinegar solution in a glass of clean distilled water. Rinse your hair several times, then rinse off the residue with water. There are also several options for masks:
- Vinegar applied to a cloth is applied to the scalp for 20 minutes and then washed off.
- Add two tablespoons of vinegar and chamomile decoction or castor oil to water at room temperature. Then they apply it to the head and cover it with a bag. After an hour, wash off with water.
Both masks are used for a month, twice a week.
Another home treatment option is to use a beaten egg mixed with 1 spoon of mayonnaise, sunflower oil and honey, rubbed into the scalp for half an hour.