A boil on the head in the hair is a fairly common occurrence. It is on this part of the head that there are many hair follicles, and any of them can become inflamed. You can discover a small boil by accident when scratching your head. If the inflammatory process is severe, then discomfort will be felt immediately in the first stages of the formation of an abscess. The causes and treatment of furunculosis on the head are closely interrelated. Some patients are recommended general restorative therapy, others – applications with antibacterial drugs. Treatment tactics are determined by the doctor after examining the pathological area and clarifying concomitant chronic diseases.
Causes of boils
The cause of boils is infection of the hair follicle with Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (most often) or other pathogenic microorganisms. An infection can get into the hair root when scratching the head with dirty hands. Any cracks, scratches, or burned surface are suitable conditions for the penetration of pathogenic flora into the dermis.
A boil appears on the head suddenly, without previous general symptoms. According to statistics, there is a surge in furunculosis in the head and neck area in the autumn and spring periods. This seasonality is explained by provoking external conditions - drafts, wind, increased humidity - and a decrease in one’s own defenses due to hypovitaminosis and deterioration of immunity.
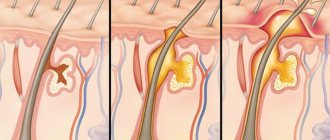
After infection of the hair follicle on the head, an inflammatory reaction begins in nearby tissues. In place of the hair, a purulent rod forms. This process is caused by a defense response when macrophages are released to fight infection. Dead leukocytes and bacteria form purulent masses. With significant suppuration of the boil, tissue at the site of inflammation may partially die. This process is called necrosis.
Prohibited Measures
The problem will remain uncured if the patient does not follow simple recommendations:
- you cannot open the abscess yourself - premature or inept opening of the abscess will lead to serious complications;
- a burst abscess must not be rubbed or tried to squeeze out the purulent core; the contents of the boil must leave the body on their own;
- Mechanical impact on the burst boil should be avoided - the patient should try not to put pressure on the boil;
- antibiotics should be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor;
- Do not swim or wet a burst boil.
Such actions can cause new development of bacteria in the lesion or provoke sepsis.
Signs
The first symptoms of a boil on the head in the hair are the appearance of local hyperemia and thickening.
In the case when a carbuncle develops, that is, inflammation of several nearby hair follicles occurs, the patient feels severe pain when palpating the affected area on the head. A single small boil, as a rule, almost does not provoke pain symptoms; discomfort is felt more.
With your fingers you can feel a small bump or infiltrate in the layers of the skin. If you examine the pathological area on the head in the mirror, redness will be visible.
Boils on the head quickly fester, and white or yellow contents begin to be visible in the center of the hyperemic area under the skin. The tissues of the head are better supplied with blood, and the scalp is no exception. Therefore, the process of formation of a purulent-necrotic core proceeds faster than in other parts of the body.
If extensive ulcers occur on the head, the following may appear:
- chills;
- significant increase in body temperature;
- general weakness up to loss of consciousness.
These are signs of the spread of infection, which leads to serious consequences.
Why is pathology dangerous?
Any purulent-inflammatory process can lead to the spread of infection throughout the body. Furunculosis on the head is more dangerous due to its close location to the brain. If the infection penetrates the blood-brain barrier, the sensitive membranes of the brain quickly become infected and meningitis and encephalitis are formed. With the development of these complications, the prognosis for the patient is unfavorable, even death.
A small boil on the head, if not aggravated, should quickly ripen, and after 4-5 days the tissue is completely regenerated, not even a trace remains at the site of the boil.
If the patient injures the affected area, the infection spreads to adjacent healthy tissue. Inflammation of the sebaceous glands begins, neighboring hair follicles become infected, and several abscesses form. This process will require long and careful treatment.
Another dangerous complication if proper treatment is not followed is sepsis, that is, blood poisoning. In a healthy person, the blood is sterile and does not contain any bacteria. With extensive infection or mechanical damage to the boil, pathogenic bacteria enter the interstitial fluid and then into the bloodstream. Blood has a bactericidal effect, but with a large number of bacteria and a decrease in immune functions, the infectious agent does not die, but is spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. Staphylococcus or other microbes begin to infect new areas of the body, take root on the mucous membrane of the intestines and other organs, provoking endless foci of inflammation. This serious complication requires urgent hospitalization. Treatment with loading doses of antibiotics cannot always stop sepsis; the prognosis for the patient is rarely favorable.
Symptoms
It can be difficult to detect an inflammatory process on the back of the head. The initial sign will be discomfort when touching any part of the skin.
The patient can feel a slight swelling on his own.
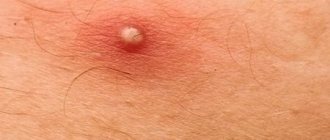
Externally, a boil on the scalp has the following symptoms:
- swelling between the hairs , which is painful during palpation;
- the skin in this area is enlarged and feels hot to the touch;
- in the middle there is a rod with purulent contents;
- when the abscess is opened, pus ;
- the hair in this area falls out , the roots can become covered with a purulent crust;
- the inflammatory process is associated with itching;
- the inflammation ends with the formation of a crust , which will fall off after 4-5 days and leave a slight scar.
Some patients experience general symptoms such as weakness and chills. Symptoms will become more pronounced during multiple furunculosis. This condition is characterized by the appearance of 2 or more ulcers in different parts of the head at once.
Without proper therapy, the abscess can increase in size, in which case a carbuncle will form. It represents a broader pathological process that does not disappear on its own.
The diagnosis is made based on typical symptoms. Inflammation in the blood is extremely insignificant or absent altogether.
From this we can conclude that if a lump appears on the surface of the head, you must immediately contact a specialist - regardless of the appearance of the growth. Even if the neoplasm is a simple lump, the doctor will recommend eliminating the pathology as soon as possible in order to avoid any consequences.
Treatment methods
What to do when a boil appears on your head? Surgical, local drug treatment, and restorative therapy will be required. Treatment methods should be determined by a specialist after assessing the external condition of the boil, collecting anamnesis, and clarifying concomitant chronic diagnoses.
The choice of treatment method is influenced by:
- localization (the closer to the temple, the more dangerous);
- area of inflammation;
- the presence of necrotic lesions;
- general health of the patient;
- the presence of endocrine pathologies, especially aggravating the course of furunculosis, diabetes mellitus;
- the presence of other infectious diseases delays recovery (sore throat, acute respiratory infections, intestinal infections);
- pathologies of the immune system (HIV, secondary immunodeficiency).
Having specified all concomitant diseases and characteristics of the body, the doctor will prescribe general and local treatment. In case of severe, advanced suppuration or in the presence of complications, the doctor may resort to surgical intervention.
Conservative
An abscess on the head under the hair, if it has a small affected area, can be treated using conservative methods.
To quickly rid the patient of a boil on the scalp and prevent the spread of infection, the doctor prescribes vitamins and microelements. Complex multivitamins activate immune reactions and accelerate the process of tissue epithelization.
Local therapy consists of several stages:
- It is necessary to treat the surface of the boil and the skin around it. To do this, the hair is parted, the localization of the pathological process is wiped with a swab moistened with alcohol, furatsilin or another antiseptic.
- Lubricating the scalp where the boil is located with an antibacterial drug. This may be an ointment containing streptomycin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, etc. Ichthyol ointment or Vishnevsky liniment is often used.
- After the boil has opened on its own, its surface is smeared with antiseptics, which have a drying effect. These include a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green, a weak solution of salicylic acid.
- The use of healing ointments to accelerate regeneration. You can use Methyluracil, Solcoseryl.
To quickly rid the patient of a boil on the scalp and prevent the spread of infection, the doctor prescribes vitamins and microelements. Complex multivitamins activate immune reactions and accelerate the process of tissue epithelization. Tablets and powders based on brewer's yeast are often used to combat boils.
Operational
If the boil on the head continues to fester for more than five days, the doctor suspects complications, then surgical intervention will be required. Incision of the skin slightly below the center of the chirp will allow the purulent exudate to be quickly eliminated.
After promptly opening the abscess, the wound is washed with antiseptic solutions, then antibacterial ointments are applied, which will lead to the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms. The faster the inflammatory pathogens die, the sooner the healing process will begin.
In severe advanced cases of diffuse furunculosis, when pus spreads towards the brain, more serious surgery is required. The surgeon cleans the damaged surface as much as possible and leaves drainage for the outflow of pus. At the same time, he prescribes tableted antibiotics in large quantities.
Traditional medicine recipes
Treatment at home can be carried out for small, local processes when the root of one hair on the head is inflamed.
Boils on the head are treated with natural antiseptics: onions, garlic. Mumiyo quickly heals and kills bacteria. It is applied to the center of the boil and secured on top with a gauze cloth. If this procedure is done at night, then by morning the inflammation will be significantly reduced.
How does a boil on the head manifest itself?
Not everyone knows what a regular boil looks like and how the symptoms associated with its occurrence manifest themselves. It is difficult to recognize a boil in an adult, especially if it is located in the occipital region under the hair, and even more so in a child. Children are so restless that they can easily get a bump anywhere, including on the back of their heads.
A boil appears, first as redness, then as a tumor, which begins to grow in size, and later as an abscess with a purulent head, which increases as it matures. If the boil is not treated, then it will break through, well, if it comes out, and if an internal breakthrough occurs, then one of the above complications for the poor fellow who has it is guaranteed, therefore, if there is a suspicion of a boil, then you should not tempt fate, but you should rush headlong to the clinic for medical help.
Features of child treatment
In children, boils appear on the head under the hair quite often due to poor hygiene and hypothermia. Small ulcers on the head are not dangerous; they go away with minimal treatment. However, the child needs to be explained that he should not touch the inflamed area. If boils appear in several places on the scalp, you should immediately consult a specialist for treatment.
A feature of the course of furunculosis in children is frequent relapses. The children's immune system is not able to maintain the production of protective immunoglobulins for a long time. When pathogenic microbes enter the skin layers again, the skin’s own defense does not work and inflammation develops again. Another feature is that children's skin is thin and easily vulnerable.
What not to do
In order not to provoke aggravation of the process, you should not perform manipulations that lead to the spread of infection and inflammation.
In case of furunculosis on the scalp, it is prohibited:
- squeeze out the abscess yourself;
- comb the affected area;
- make lotions, compresses;
- cut hair at the root around the boil;
- walk without a hat appropriate to the season and weather.
When the abscess is forcibly squeezed out, the inflammation spreads to the adjacent healthy tissue, and microbes begin to multiply there. This leads to the development of complications.
Possible complications and when to see a doctor
The main danger of the disease is that it provokes a number of additional disorders. Additional rashes are localized in the nasolabial triangle and in the area of the nasal mucosa. The effectiveness of recovery depends on the approved therapeutic regimen. Depending on the location of the disease, the following classifications are distinguished:
- local level, accompanied by an abscess, the formation of a carbuncle, phlegmon and erysipelas;
- long-term complications are represented by lymphadenitis and phlebitis;
- general ailments are represented by brain damage and pathologies of internal organs; sepsis should not be ruled out.
Staphylococcus can lead to the formation of phlegmon of soft tissue structures.
Transformation of the disease into blood vessels and veins provokes abscesses of a metastatic nature. The rashes are localized on the person’s face, developing into large colonies. You should seek help from a doctor at the first signs of distress. The article has been verified by the editors
What measures can stop the further appearance of boils?
To avoid relapses of furunculosis, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. Hardening, taking vitamins, and proper nutrition with sufficient intake of proteins and microelements helps develop resistance to skin infections.
Autohemotherapy helps increase resistance to infections to which the body is susceptible. The principle of treatment is that several cubes of blood are taken from a vein and immediately injected intramuscularly.
If you follow hygiene standards, maintain the elasticity of the skin, eat only healthy foods, and do not overcool, then the risk of boils appearing is minimal.