This article uses excerpts from the chapter of the same name in the Face Anatomy atlas. It is of particular importance for specialists involved in the correction of age-related changes and contouring using fillers. The title “Dangerous triangle of the face” was not chosen by chance; it is in this zone that there are prerequisites of an anatomical and functional nature that can interfere with medical manipulation and cause side effects, including severe ones. Let's look at the topography of this triangle and the reasons for its danger.
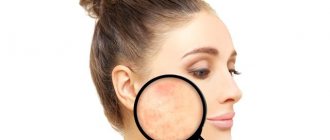
Red nasolabial triangle
Sometimes the color of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle changes to the red side, which can also be a rather serious symptom and indicate:
- Development of various allergic reactions. Unexpected symptoms of individual intolerance may appear when the skin is directly affected by allergens (cosmetics, drugs, herbs, etc.), as well as with systemic allergies (to wool, food, medications, etc.). Hyperemia in this case is often accompanied by unpleasant itching and flaking; reddish skin may become covered with rashes. It is also possible to experience an allergic runny nose, watery eyes, sneezing, etc.
- Demodecosis. This disease occurs due to the aggression of a microscopic parasite – the Demodex mite. It can live quietly on the skin for many years, but under the influence of provoking factors (decreased immunity, hormonal fluctuations, etc.) it begins to actively multiply and provokes inflammation, acne and other problems. Most often, demodicosis begins with redness of the nose and nasolabial triangle, after which it progresses and spreads to the cheeks.
- Other dermatological diseases. In particular, the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle may turn red and become covered with rashes due to streptoderma (in this case, a weeping rash or crater spots are visible to the naked eye), fungal diseases, etc.
Perioral dermatitis. In principle, this condition is a type of allergic reaction, but it is typically precisely located in the area of the nasolabial triangle (and near the mouth, in particular). With the development of perioral dermatitis, the skin first turns red, irritation occurs on it, and then it is covered with a small and frequent pustular rash. Most often, this problem occurs in adults - young girls and mature women. Some doctors suggest that the occurrence of perioral dermatitis may be associated with certain components of cosmetic products. A new toothpaste can also contribute to its appearance.
As a rule, the nasolabial triangle in children turns red in response to various allergic reactions. Subsequently, the redness may be accompanied by a rash and peeling.
Triangle and arteries
One of the main arteries in this area is the facial artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The facial artery, immediately after its origin, goes upward and passes to the face in front of the masticatory muscle, where its pulsation can be determined by palpation. Next, it is directed medially and towards the lips, giving off branches - the superior and inferior labial arteries, then passes under the muscle that lifts the upper lip, and reaches the wing of the nose, where its course becomes superficial and ends with two terminal branches - the arteries of the wing of the nose and the angular . Up to this point, everything is clear and clear, but in reality this is not always the case [Fig. 2].
Rice. 2. Facial artery - angular artery.
I will explain more clearly: there are many works with cadavers that emphasize the fact of the existence of frequently encountered anatomical variations and the place of origin of the facial artery, the course of this vessel and its branches. Often such variations are more the norm than the exception. Therefore, it can be argued that even with in-depth knowledge of anatomy, there is a possibility of complications due to the abnormal arrangement of blood vessels. Therefore, it is necessary to use techniques that help to avoid possible side effects as much as possible.
Numbness of the nasolabial triangle
The unpleasant feeling of numbness is not just uncomfortable. Its occurrence in the area of the lips and nose can warn of:
- Cervical osteochondrosis. This pathology can also manifest itself as frequent headaches, excessive fatigue, and pain when moving the neck.
- Lack of B vitamins. Also, such a disorder often leads to excessive fatigue, memory impairment, lack of concentration, sleep problems, etc.
- Bell's palsy or facial neuritis. This pathology is difficult to ignore, as it causes pain behind the ears, prevents the eyelids from closing fully and causes visually noticeable asymmetry of the face.
- Neurosis, depression or vegetative-vascular dystonia.
One-time numbness is not a reason to immediately run to the doctor. But if such a symptom bothers you from time to time, and even more so is complemented by other health problems, it is better to play it safe and undergo a full examination.
What to do if there are pimples on your lips?
Unlike other areas, white pimples on the lips are usually smaller, about 2 mm in diameter, and less prominent. In some cases, they may itch, but you should scratch them as they can become infected. You cannot squeeze them out, as this can cause microtraumas and scars.
It is necessary to consult a doctor who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. It may turn out that the rash on the lips is a completely different disease, for example, herpes or acne.
pale nasolabial triangle.
I have been noticing for a long time that my nasolabial triangle (between the nose and upper lip) is noticeably paler than the rest of my facial skin, that is, this place is clearly distinguished by such a white triangle (((and the places where nasolabial wrinkles occur (well, I don’t have them yet, I have I mean, just this area) - on the contrary, the skin there is redder than the whole face. So, near the mouth, it’s not the most pleasant picture: a pale nasolabial triangle, limited on the sides by such “redness”. I came across a mention that this could indicate problems with the heart, I checked the heart, except for prolapse (which “everyone has” and which has never bothered me since childhood) nothing else was found. Has anyone encountered this?
I'll wait and listen, the same bullshit
In this section, only neutral information is published in topics and comments. Topics and comments containing advice, recommendations, promotion of alternative methods of treatment or other actions will be closed.
1, oh, well, it turns out I’m not like her(
heart problems (
New features and design have appeared for the version of the Woman.ru Forum on computers. Tell us, what are your impressions of the changes?
Author, this also happens with internal bleeding. I hope this is not your case.
Author, this also happens with internal bleeding. I hope this is not your case.
I think it’s unlikely, I’ve had this for a long time, and I think the internal bleeding should have manifested itself somehow.
heart problems (
When the triangle heart is blue and pale and white indicates anemia.
Have you donated BLOOD recently?
I’m sure they will tell you so - there is a very lack of B vitamins and iron!
good health and good luck to you. )))
When the triangle heart is blue and pale and white indicates anemia.
no, I don’t have blue, but rather pale, white. and by the way, at one time (in my teens, now I’m 24) my hemoglobin level was low. ((maybe it is((
ZAZIKI, please share, how do you know about the connection between this area on the face and anemia?
you know, I have the same thing. I thought I was the only one so “beautiful” =)
no, I don’t have blue, but rather pale, white. and by the way, at one time (in my teens, now I’m 24) my hemoglobin level was low. ((maybe it is((
ZAZIKI, please share, how do you know about the connection between this area on the face and anemia?
my friend had this, a good friend had it too, (my uncle is a doctor) I’m studying medicine myself.
my friend had this, a good friend had it too, (my uncle is a doctor) I’m studying medicine myself.
wow, that’s clear then) can you tell me which blood tests are best? just “general”? I know that there is something special specifically for determining iron. or can anemia be not only “iron deficiency”?
and it looks like you need to stock up on Fenuls. (
my friend had this, a good friend had it too, (my uncle is a doctor) I’m studying medicine myself.
wow, that’s clear then) can you tell me which blood tests are best? just “general”? I know that there is something special specifically for determining iron. or can anemia be not only “iron deficiency”?
To begin with, take a general blood test, and the results will tell you :) GOOD HEALTH TO YOU.
When my child had pneumonia, this very pale nasolabial triangle was the first sign of this disease
A pale (white) nasolabial triangle clearly indicates low blood pressure. But the cause of this anomaly needs to be clarified, and first of all you should contact a therapist or neurologist.
Do not self-diagnose and wish you good health.
My daughter is 5 years old, when she exercises, running for example, her face turns red and her nasolabial triangle turns pale, why is this?
My daughter is 5 years old, when she exercises, running for example, her face turns red and her nasolabial triangle turns pale, why is this?
I have been noticing for a long time that my nasolabial triangle (between the nose and upper lip) is noticeably paler than the rest of my facial skin, that is, this place is clearly distinguished by such a white triangle (((and the places where nasolabial wrinkles occur (well, I don’t have them yet, I have I mean, just this area) - on the contrary, the skin there is redder than the whole face. So, near the mouth, it’s not the most pleasant picture: a pale nasolabial triangle, limited on the sides by such “redness”. I came across a mention that this could indicate problems with the heart, I checked the heart, except for prolapse (which “everyone has” and which has never bothered me since childhood) nothing else was found. Has anyone encountered this?
A pale, as well as blue, nasolabial triangle indicates circulatory disorders, but the doctor must look for the cause of circulatory disorders. In children it may be physiological, it will go away over time, but it is better to see a specialist.
My daughter is 5 years old, when she exercises, running for example, her face turns red and her nasolabial triangle turns pale, why is this?
My daughter (she is 10 years old) has the same thing when doing fitness! the teacher told me to see a doctor, which may have something to do with the heart, but the heart is fine.
It was said here that a pale nasolabial triangle clearly indicates low blood pressure, nothing like that, I have stage 1 hypertension, and the triangle is pale.
I live on insurance in Europe, I have a full check once a year, and due to the start of a course of serious medication (isotretinoin), I now have tests every two months. no abnormalities, all biochemistry, hemogram, immunogram, hormones are normal, ultrasound, emri, ecg too. During physical activity, a triangle appears. the pressure is 110 over 70 (this is the absolute norm for me), but often drops to 100/60, in the heat 90/5o, then the ears become blocked and water flows from the nose. here you can only contact a neurologist.
My daughter is 5 years old, when she exercises, running for example, her face turns red and her nasolabial triangle turns pale, why is this?
I've been noticing this with my son for a long time too. We didn’t go to the doctor, but we should. For some reason it seems to me that this is a heart problem. I don't approve.
When my child had pneumonia, this very pale nasolabial triangle was the first sign of this disease
I now have a child suffering from pneumonia, and it also manifested itself in her.
My daughter is 5 years old, when she exercises, running for example, her face turns red and her nasolabial triangle turns pale, why is this?
My son also develops a nasolabial triangle after physical activity. My mother-in-law scared me that this happens with asthma. They checked for asthma and it was not confirmed. Today I asked our children’s doctor, he said to measure the pressure after physical exercise. load, it should not weigh 160. We will measure.
My daughter (she is 10 years old) has the same thing when doing fitness! the teacher told me to see a doctor, which may have something to do with the heart, but the heart is fine.
I've been noticing this with my son for a long time too. We didn’t go to the doctor, but we should. For some reason, it seems to me that this is with If after physical activity (fitness, running, etc.) a white nasolabial triangle appears, this indicates excessive physical activity, you need to firstly reduce the intensity of the workout and secondly check the cardiovascular system. I speak from the perspective of a fitness instructor.
I’ll turn 50 in April, I’ve been doing regular fitness and dancing for more than 20 years, dancing in my childhood and adolescence. I myself had not paid attention before, but about 10 years ago one attentive instructor at a fitness club noticed my white nasolabial triangle, asked if I always have this, and said that it was vascular. Once I did an ECG, everything was great. The blood pressure is also almost always normal. I feel great, except for lately the numbness of my limbs from sitting for a long time. I know that problems with the spine have been going on since childhood, which is why I have been friends with sports for so many years so as not to fall apart. I heard the opinion of experts that the problem with blood vessels comes from the spine.
The trainer said either low blood glucose or heart problems
problems with the spine. or simply pinched and because of this, blood circulation is impaired. to a chiropractor.
It could also be a problem with the brain, my daughter has enlarged anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, we identified it with the help of an NSG, in adults probably through an MRI or ultrasound
When the triangle heart is blue and pale and white indicates anemia.
Recently, after cardio exercises, my nasolabial triangle has become white, my trainer advised me to do a cardiogram. Tell me, please, what can it be?
A light nasolabial triangle may be a sign of giardiasis. After treatment, my face became more uniform in color.
I read the comments, it turns out that with white triangles the brain, blood pressure, blood vessels, lack of iron, an abundance of lamblia, and a little of the heart are not in order. Thank you!
Good afternoon. And I have the same problem, but I have asthma (I think that’s because of this. This didn’t happen before.
Apparently due to a lack of zinc. I bought zinc ointment for acne, but it helped with white flaky and irritated skin after a bath and face wash, soap and some natural masks. That is, the skin becomes very soft after zinc ointment and everything disappears. Only the clay mask is an exception. She's aggressive.
Do you like guys kissing - is that not normal?
Who is hurting and feeling bad right now?
How to stop humiliating yourself in front of your ex?
Many lives in one life
Write delicious snack recipes. On holiday.
I read the comments, it turns out that with white triangles the brain, blood pressure, blood vessels, lack of iron, an abundance of lamblia, and a little of the heart are not in order. Thank you!
Apparently due to a lack of zinc. I bought zinc ointment for acne, but it helped with white flaky and irritated skin after a bath and face wash, soap and some natural masks. That is, the skin becomes very soft after zinc ointment and everything disappears. Only the clay mask is an exception. She's aggressive.
+1 but☝ I have it after a bath, after a steam room.. apparently I need to be more careful with the bath. I’m 33, but I noticed it since I was 25
and it looks like you need to stock up on Fenuls. (
You need to drink folic acid - it increases hemoglobin, i.e. iron, and restores immunity.
I had the same problem, I was looking for an answer for 5 years, until I took the following blood tests: gases, pH, oximetry, hemoglobin fractions, homocysteine. Then everything became clear. Good luck to you
+1 but☝ I have it after a bath, after a steam room.. apparently I need to be more careful with the bath. I’m 33, but I noticed it since I was 25
My son has been white since birth after a bath.
It could also be a problem with the brain, my daughter has enlarged anterior horns of the lateral ventricles, we identified it with the help of an NSG, in adults probably through an MRI or ultrasound
Nonsense. This is not connected in any way; moreover, a slight increase in the lateral horns (most likely this is what your child has) is a variant of the norm. At most, she is threatened with a good memory and musical abilities!)
I had the same problem, I was looking for an answer for 5 years, until I took the following blood tests: gases, pH, oximetry, hemoglobin fractions, homocysteine. Then everything became clear. Good luck to you
What exactly did you find out, please tell me? Were you treated somehow? And as a result?
A friend of mine (she’s a doctor) noticed it. I somehow didn’t pay attention. She said it was a vascular reaction. Perhaps because I recently started taking a drug against arrhythmia and for hypertension. By the way, hemoglobin and all blood parameters are normal (I recently tested everything because I saw a cardiologist, and there are no changes in the heart muscle or blood vessels either.
My daughter is nine years old, a pale nasolabial triangle appears from time to time, and we are registered with a cardiologist. We are prohibited from physical activity.
The user of the Woman.ru website understands and accepts that he is fully responsible for all materials partially or fully published using the Woman.ru service. The user of the Woman.ru website guarantees that the placement of materials submitted by him does not violate the rights of third parties (including, but not limited to copyrights), and does not damage their honor and dignity.
The user of the Woman.ru site, by sending materials, is thereby interested in their publication on the site and expresses his consent to their further use by the owners of the Woman.ru site. All materials on the Woman.ru website, regardless of the form and date of publication on the site, can only be used with the consent of the site owners.
Use and reprinting of printed materials from the woman.ru website is possible only with an active link to the resource. The use of photographic materials is permitted only with the written consent of the site administration.
Posting intellectual property objects (photos, videos, literary works, trademarks, etc.) on the woman.ru website is permitted only to persons who have all the necessary rights for such posting.
Copyright (c) 2016-2020 Hirst Shkulev Publishing LLC
Online publication “WOMAN.RU” (Zhenshchina.RU)
Certificate of registration of mass media EL No. FS77-65950, issued by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications (Roskomnadzor) on June 10, 2016. 16+
Founder: Limited Liability Company "Hirst Shkulev Publishing"
Editor-in-Chief: Voronova Yu. V.
Editorial contact information for government agencies (including Roskomnadzor):
Triangle of Death
The “triangle of death” is a zone on the face in the form of an imaginary isosceles triangle, the base of which is located along the edge of the upper lip, and the angle between equal sides is slightly above the glabella. In practice, clinicians should include the medial portions of the eyebrows in this area.
This zone is rich in lymphatic and blood vessels, but there is little connective tissue and virtually no fascial layers. The absence of these two components leads to the fact that the inflammatory process in this area is severely limited.
Read more about blood vessels. The main collecting vein in this area is the facial vein, which collects blood from the forehead, nose, eyelids, upper and lower lips, soft palate, parotid gland, muscles of the floor of the mouth and submandibular gland.
In the area of the corner of the eye, through the angular (angular) vein, it anastomoses with the ophthalmic veins. The superior ophthalmic vein is the main tributary of the cavernous sinus. This sinus and the veins listed above do not have valves and, accordingly, direct control of blood circulation.
And here we come to the essence of the name and the danger of this area of the face for life (in English this triangle is called a danger triangle). But, of course, not this zone itself, but the purulent inflammatory processes in it. The muscles in this area are attached to the skin, where purulent diseases can begin. The constant movement of facial muscles when displaying emotions, talking, chewing leads to the dissemination of purulent contents.
The accompanying swelling will cause blood to flow through the ophthalmic veins and then into the cavernous sinus. Only the pathogen is also carried through the bloodstream. Normally, blood flows slowly in the cavernous sinus, but in this case this leads to the development of thrombophlebitis.
Thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus, fortunately, is now rare. In the pre-antibiotic era, it not only occurred more frequently, but also had a 100% fatality rate. Now the prognosis of patients with this disease is much better, but it is still life-threatening. Despite its rarity, it is always important to exclude this disease in patients with cavernous sinus syndrome.
Cases of thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus of odontogenic origin have been described. Two such cases will be discussed below.
Case 1
A 64-year-old woman complained of headache for 2 days after a dentist removed a left canine tooth. NSAIDs and antibiotics (cefcapen, a third generation cephalosporin) were ineffective. 8 days after removal, the patient developed diplopia and ptosis on the left. After consulting a neurologist, she was diagnosed with left oculomotor nerve palsy and given a referral for hospitalization.
Upon admission, the patient showed anxiety, but was well oriented in space, time and self. A neurological examination revealed almost complete ophthalmoplegia, ptosis and mydriasis on the left. Proptosis, chemosis, and other cranial nerve abnormalities were not detected. There was no swelling on the face or in the oral cavity; a dental examination did not reveal the presence of abscesses or local inflammatory reactions in the area of the extracted tooth socket. Body temperature was 38°C, laboratory tests showed leukocytosis of 12.7 × 109/L and C-reactive protein of 6.6 mg/L. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid showed the presence of leukocytes 30 cells/μl, 66% neutrophils with normal values of cerebrospinal fluid pressure, protein and glucose levels. Blood and CSF cultures were negative.
CT with contrast and MRI with gadolinium revealed nonfilling and thrombosis of the left venous sinus and dilatation of the superior ophthalmic veins on both sides. Cerebral angiography showed nonfilling of the cavernous sinus and narrowing of the left internal carotid artery. Doctors suggested a connection between the development of thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus and tooth extraction.
Treatment began on the first day of admission, prescribing intravenous infusions of ampicillin + sulbactam. The headache decreased on the second day of hospitalization, and the body temperature decreased. Ptosis and eye movement disorders disappeared on the 7th day. Laboratory tests showed improvement. Antibacterial therapy continued for 2 weeks until body temperature and blood tests were completely normalized. Paralysis practically disappeared on the 14th day of hospitalization.
Figure 1 | Axial (A) and coronal (B) images obtained with contrast-enhanced CT. Filling defect of the left cavernous sinus (arrows)
Figure 2 | Axial (A, B) and coronal (C) images obtained with 1T gadolinium MRI. Filling defect of the left cavernous sinus (arrows A, C) and dilatation of the superior ophthalmic veins on both sides (arrows B)
Figure 3 | Angiogram of the left internal carotid artery showing dilation of the ophthalmic vein in the venous phase (A, arrow) and narrowing of the left internal carotid artery in the arterial phase (B, arrow)
Case 2
A 54-year-old man complained of pain in the left upper jaw for 2 weeks. Then he saw a dentist, who treated him for several teeth with caries and periodontitis. The next day, the patient developed headache, swelling, and severe pain along the left side of the face, but more in the left forehead area. He was referred to an otolaryngologist, who prescribed antibiotics and NSAIDs, which turned out to be ineffective. Three days later, the patient developed periorbital swelling and pain in the area. Laboratory tests showed leukocytosis 14 × 109/L and CRP 30.7 mg/L. The otolaryngologist thought about the development of periorbital cellulitis, prescribed carbapenems and referred the patient for hospitalization.
On admission, the patient had ptosis, proptosis and chemosis of the left eye, but the body temperature was within normal limits. Upon examination of the face, pronounced swelling of the middle and upper thirds of the face on the left was observed. A neurological examination revealed paralysis of the left trochlear nerve and decreased sensitivity of the branches of the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves - branches of the left trigeminal nerve.
An examination of the oral cavity revealed multiple caries and periodontitis, but no abscesses. Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid showed the presence of leukocytes 1 cell/μl with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The protein level was elevated (0.94 g/l), the glucose concentration was 1.65 g/l (blood 3.6 g/l). Blood and CSF cultures were negative.
CT and MRI of the head with contrast agents showed unfilled left cavernous sinus with dilatation of the superior ophthalmic veins on both sides, similar to case 1, and poor enhancement of the inferior ophthalmic vein. All this indicated obstruction of the cavernous sinus.
Figure 4 | Axial (A) and coronal (B) images obtained with contrast-enhanced CT. Filling defect of the left cavernous sinus (arrows)
Figure 5 | Axial (A, B) and coronal (C) images obtained with 1T gadolinium MRI. Filling defect of the left cavernous sinus (arrows A, C) and dilatation of the superior ophthalmic veins on both sides and insufficient contrast enhancement of the left ophthalmic vein (arrows B)
Doctors assumed the development of periorbital cellulitis after the development of thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus caused by an odontogenic infection, and began treatment with meropenem, which had previously been prescribed by an otolaryngologist. Ptosis disappeared on day 2 of hospitalization. The headache decreased by day 4, and trochlear nerve palsy began to subside on day 9. Antibiotic therapy was continued for 2 weeks until body temperature and tests were completely normalized. Mild pain and slight tenderness around the left orbit continued after hospital discharge for 21 days.
Case 3
In this case, thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus is caused by a non-odontogenic infection. A 52-year-old man was admitted to the hospital with high-grade fever, chills, and right ophthalmoplegia.
Figure 6 | Damage in the “triangle of death” area and ptosis on the right
15 days before hospitalization, the patient developed a boil just above the tip of the nose, which subsequently began to enlarge, and swelling of the adjacent tissues and upper lip appeared. The man was prescribed antibiotics, after which the swelling and boil began to decrease. However, the temperature did not decrease, and the day before hospitalization the patient felt pain in the eye and forehead on the right, with ptosis and diplopia observed.
Figure 7 | (A) - paralysis of the right lateral rectus muscle of the eye; (B) - paralysis of the right medial rectus muscle of the eye
Examination by a neurologist revealed complete right ophthalmoplegia. A clinical blood test showed leukocytosis. The results of a biochemical blood test, a general urinalysis, and a chest x-ray were normal. Blood cultures were negative and HIV was not detected. MRI of the brain revealed heterogeneous soft tissue enhancement in the region of the right cavernous sinus extending posteriorly along the tentorium cerebellum.
A diagnosis of thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus was made due to retrograde spread of infection from the “triangle of death” area. The patient was prescribed intravenous infusions of ceftriaxone + vancomycin and low molecular weight heparin for 6 weeks. After therapy, pain and fever subsided, ptosis disappeared, and movements of the right eye were restored.
Figure 8 | Axial post-contrast image obtained using 1T MRI (note - heterogeneous soft tissue enhancement is detected in the region of the right cavernous sinus, extending posteriorly along the tentorium cerebellum)
The diagnosis of thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus is made on the basis of the clinical picture, characterized by fever, pain, proptosis, chemosis, periorbital edema, ophthalmoplegia and sensory disturbances in the area of innervation of the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves. The VI pair of cranial nerves is often affected, because the abducens nerve passes medially through the cavernous sinus and is often affected by the inflammatory process in thrombophlebitis. The third and fourth pairs of cranial nerves are affected less frequently because they pass in the lateral part of the sinus, which contains thick fibrous tissue. Visual impairment up to blindness occurs in 20% of patients. If the disease progresses, the patient falls into a coma.
Thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus, as already mentioned, is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate treatment, but there may always be a delay due to confusion in making a diagnosis, since the disease is rare and its manifestations are unique. Therefore, the diagnosis of cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis should be considered primarily in patients with cavernous sinus syndrome with fever, facial edema, and laboratory findings consistent with inflammation. To clarify the diagnosis, CT and MRI with contrast agents are used: stretching of the cavernous sinus, bulging of its lateral part, and asymmetric contrasting of the sinuses on the left and right are characteristic. A filling defect caused by thrombosis is easily detected. An indirect sign of cavernous sinus thrombosis is dilatation of the superior ophthalmic veins on both sides and/or exophthalmos.
Cerebral angiography has been reported to be of no use in making this diagnosis because, even normally, the cavernous sinus is poorly visualized. Moreover, there are studies reporting dissemination of infection and increased thrombosis with this study. In the first case, doctors performed angiography to rule out other diseases, such as a carotid-cavernous fistula. Some patients with cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis have been found to have changes in the internal carotid artery, such as stenosis, occlusion, or aneurysm. In the first case, doctors discovered a narrowing of this artery, which may indicate its spasm, thrombosis or inflammation.
The most common causes of thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus are sphenoid and ethmoid sinusitis. Odontogenic infection is less common and is the cause in 10% of cases or less. Infection of the oral cavity can enter the cavernous sinus from the orbit, pterygopalatine fossa, pterygoid plexus, or hematogenously through the facial vein.
Adequate antibiotic therapy is important. The most common pathogens are Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA. In patients in whom thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus is associated with odontogenic infection, beta-hemolytic streptococci, other types of streptococci, obligate anaerobes and mixed infections are found.
Recommended for the treatment of most etiologies are broad-spectrum penicillins, third-generation cephalosporins or carbapenems, which are prescribed for at least 2 weeks to prevent relapse. In the cases described above, cultures were negative because the patient was on antibiotics prior to admission and evaluation.
The prescription of anticoagulants is a controversial issue. Thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus is a fairly rare disease, so only retrospective studies are available. Review of 84 cases from 1940 to 1984. found that mortality was lower in the group of patients who took heparin than in the group who did not take it (14 vs. 36%). Therefore, it is quite justified to prescribe anticoagulant therapy, although there have been cases of bleeding as a complication of taking the drug.
Systemic administration of glucocorticosteroids is also controversial, but may help restore sensitivity to cranial nerves and reduce orbital swelling. True, this in turn can increase the degree of thrombosis and worsen the prognosis.
There are reports of recurrent thrombophlebitis of the cavernous sinus. Moreover, an intracavernous aneurysm developed secondarily, and such arterial changes appeared within 3 months after the onset of the first symptoms. Therefore, patients with cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis should be monitored for at least several months after antibiotic therapy.
Sources:
- Eckberg TJ The dangerous triangle (still dangerous) //JAMA. – 1969. – T. 209. – No. 4. – pp. 561-561.
- Okamoto H. et al. Cavernous Sinus Thrombophlebitis Related to Dental Infection //Neurologia medico-chirurgica. – 2012. – T. 52. – No. 10. – pp. 757-760.
- Pannu AK, Saroch A., Sharma N. Danger triangle of face and septic cavernous sinus thrombosis // Journal of Emergency Medicine. – 2022. – T. 53. – No. 1. – pp. 137-138.
Special triangle
The area of the nasolabial triangle requires sufficient attention and careful treatment, because:
- In this area on the face there are especially many blood vessels.
- The veins located in this area do not have valves; accordingly, infectious agents can even penetrate into the brain through them. That is why doctors strongly do not recommend squeezing out acne in such an area.
- By the color and condition of the nasolabial triangle, one can judge the presence of some disturbances in the functioning of the body. A change in the normal color of the skin in this area helps to detect in time quite serious diseases in a child and even in adults who are still asymptomatic.
Of course, a change in the condition of the skin on the face cannot be considered as a 100% symptom of one or another health disorder. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, focusing on other signs of the disease and data from studies performed.
How to treat acne on the nose?
For acne on the nose, the causes can be relatively harmless. Sometimes just changing your cosmetic product or stopping certain medications is an important step in controlling your rash. Is it worth the risk of popping pimples yourself?
The treatment of acne, boils, and other inflammatory elements should be handled by a specialist. A dermatologist conducts an examination, makes a diagnosis and prescribes therapy based on the severity of acne or other disease.
For acne, your doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics18. These drugs include Clindovit® gel. The main active ingredient in its composition is the antibiotic lincosamide clindamycin6. It helps reduce the colonization of propionibacteria by exhibiting antibacterial activity against a wide range of propionibacterial strains6. The drug helps reduce free fatty acids on the skin6. Clindovit® gel is recommended to be combined with azelaic acid (for example, Azelik® gel) or benzoyl peroxide; this combination helps reduce the risk of developing antibiotic resistance28.
White nasolabial triangle
Quite often the skin on the face looks different in color. And if the area of the nasolabial triangle noticeably stands out on the face, becoming pale or blue, this is a serious reason to take a closer look at your health. So, such a pathology may indicate:
- For various disturbances in the activity of the heart. In particular, in many children, pallor or blueness of the nasolabial triangle becomes the first manifestation of congenital heart disease (of course, we are not talking about serious illnesses that can be easily diagnosed soon after birth). A white nasolabial triangle in an adult may be a sign of heart failure.
- For insufficiently good functioning of blood vessels, for example, for the presence of spasms, atherosclerosis, disorders of elasticity, strength, etc.
- On the active development of certain diseases associated with the functioning of the respiratory system. Doctors note that the nasolabial triangle often turns pale or blue with bronchitis, pneumonia, severe inflammation of the adenoids, bronchial asthma and respiratory failure.
- The development of anemia, in which the volume of hemoglobin in the body decreases and the cells receive less oxygen.
Sometimes the appearance of a white circle or triangle around the mouth is associated with a local disturbance of blood flow in small subcutaneous vessels. This situation can be completely normal if a person goes outside into the cold or is very worried.
Red nasolabial triangle
Sometimes the color of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle changes to the red side, which can also be a rather serious symptom and indicate:
- Development of various allergic reactions. Unexpected symptoms of individual intolerance may appear when the skin is directly affected by allergens (cosmetics, drugs, herbs, etc.), as well as with systemic allergies (to wool, food, medications, etc.). Hyperemia in this case is often accompanied by unpleasant itching and flaking; reddish skin may become covered with rashes. It is also possible to experience an allergic runny nose, watery eyes, sneezing, etc.
- Perioral dermatitis. In principle, this condition is a type of allergic reaction, but it is typically precisely located in the area of the nasolabial triangle (and near the mouth, in particular). With the development of perioral dermatitis, the skin first turns red, irritation occurs on it, and then it is covered with a small and frequent pustular rash. Most often, this problem occurs in adults - young girls and mature women. Some doctors suggest that the occurrence of perioral dermatitis may be associated with certain components of cosmetic products. A new toothpaste can also contribute to its appearance.
- Demodecosis. This disease occurs due to the aggression of a microscopic parasite – the Demodex mite. It can live quietly on the skin for many years, but under the influence of provoking factors (decreased immunity, hormonal fluctuations, etc.) it begins to actively multiply and provokes inflammation, acne and other problems. Most often, demodicosis begins with redness of the nose and nasolabial triangle, after which it progresses and spreads to the cheeks.
- Other dermatological diseases. In particular, the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle may turn red and become covered with rashes due to streptoderma (in this case, a weeping rash or crater spots are visible to the naked eye), fungal diseases, etc.
As a rule, the nasolabial triangle in children turns red in response to various allergic reactions. Subsequently, the redness may be accompanied by a rash and peeling.
Numbness of the nasolabial triangle
The unpleasant feeling of numbness is not just uncomfortable. Its occurrence in the area of the lips and nose can warn of:
- Cervical osteochondrosis. This pathology can also manifest itself as frequent headaches, excessive fatigue, and pain when moving the neck.
- Lack of B vitamins. Also, such a disorder often leads to excessive fatigue, memory impairment, lack of concentration, sleep problems, etc.
- Bell's palsy or facial neuritis. This pathology is difficult to ignore, as it causes pain behind the ears, prevents the eyelids from closing fully and causes visually noticeable asymmetry of the face.
- Neurosis, depression or vegetative-vascular dystonia.
One-time numbness is not a reason to immediately run to the doctor. But if such a symptom bothers you from time to time, and even more so is complemented by other health problems, it is better to play it safe and undergo a full examination.
Blue, pale nasolabial triangle
Lips turn blue after sleep
Post by Ja_Lisa » Thu Sep 29, 2005 18:53
Post by Tettigona » Thu Sep 29, 2005 19:19
Post by Natalya Borisovna » Fri Sep 30, 2005 23:21
Post by Ja_Lisa » Sat Oct 01, 2005 08:45
Post by Mother Julia » Sat Oct 01, 2005 10:11
Post by Nusya » Sat Oct 01, 2005 10:23
Post by Ja_Lisa » Sun Oct 02, 2005 07:58
Posted by Helen » Sun Oct 02, 2005 10:41 am
Post by Nusya » Sun Oct 02, 2005 10:54
I would be cold in pajamas, but WITHOUT a blanket. For fidgety babies you can use a sleeping bag, you can make one yourself from a blanket
Post by Ja_Lisa » Sun Oct 02, 2005 12:46
Helen , the further we discuss all this, the more I am inclined to believe that Natalya Borisovna is right, as always!
Nusya , sleeping bag Nooooo, it’s better to wear warmer pajamas.
We'll go for a cardiogram on Tuesday - it won't hurt.
Post by Nusya » Sun Oct 02, 2005 18:02
Ja_Lisa , what made you laugh so much about the sleeping bag? This is not the same bag as people take on hikes to sleep in tents.
special ones are sold for children - they look like regular baby blankets, only they have special fasteners that are fastened to the mattress, and the baby does not open up. It’s also easy to make such a design yourself
Post by Ja_Lisa » Mon Oct 03, 2005 07:36
Nusya , don’t be offended, it wasn’t your proposal that made me laugh, but I just imagined how my daughter was struggling with the bag! You probably just can’t imagine how many kilometers up and down my madam can wrap around the bed. Now, however, he’s already sleeping in his little one, but he still turns over 200 times during the night and his legs can end up in the most unexpected places
(By the way, we have such a bag (a transformable blanket with buttons), we have never used it. There is a new one, waiting to become a gift for someone)
Post by Nusya » Mon Oct 03, 2005 09:15
I can really imagine, I’ve had the same “twirler” at home for 11 years now, and everything is spinning and spinning, constantly opening up, getting tangled in the blanket and in his own pajamas
How to improve your appearance after coding
If you apply it to the bottle frequently, you can forget about its impeccable appearance. The problem is aggravated by the fact that cosmetics are not able to cope with appearance defects. A thick layer of foundation only further accentuates imperfections. Excessive consumption of strong alcoholic drinks is the enemy of beauty.
The so-called “alcoholic face” in many cases haunts a person who has recovered from addiction for many years, sometimes remaining with him forever. Much depends on what stage of development the disease was at, the duration of its course, genetic characteristics, and the age of the person. It's not that easy to get back into shape. Some manage to get rid of their drunken face within six months after recovery, while others have to struggle with the external manifestations of the disease all their lives.
Coding is the first step towards getting rid of the disease. However, even after overcoming addiction, a person will have to face the consequences in the form of deterioration in appearance. The recommendations of doctors and cosmetologists on how to correct the face of an alcoholic are as follows:
- lymphatic drainage procedures and massage will help remove excess fluid from the intercellular space and get rid of swelling;
- therapy using biomicrocurrents will improve muscle tone;
- Laser therapy reduces spider veins.
Noticeable improvements in appearance appear only 2-3 years after treatment for alcoholism. However, medical procedures will help speed up recovery.
It is quite difficult to restore the original appearance to a person who has been abusing alcohol for more than 3 years. Strictly following the recommendations of doctors and cosmetologists will improve your appearance.
However, the first and main step is a complete abstinence from alcohol! And we can help with this.