Cheilitis is an isolated inflammatory process in the area of the mucous membrane, skin and red border of the lips. Outwardly it looks like swelling with redness and peeling of tissue. It can be an independent disease or a symptomatic manifestation of other pathologies. Sooner or later, almost every person encounters it, but at a young age the disease is noticeably milder, recurs less often and has no complications. In older people, due to a weakened immune system, periodic relapses of cheilitis can cause malignant tissue degeneration.
Causes of cheilitis
Cheilitis is a polymorphic and multifactorial disease that can be triggered by infections, physical and chemical environmental factors, as well as internal characteristics of the body. Among them:
- constant exposure to the open air - inflammation and peeling of the lips occurs when chapped by hot or cold air, excessive insolation;
- the presence of chronic diseases with skin manifestations of symptoms - various types of dermatitis, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, syphilis, etc.;
- allergic reactions of the body - mainly with food allergies;
- tissue irritation from regular exposure to chemicals, including medications (for example, nasal drops);
- various neurological disorders, severe stressful situations, depression, constant anxiety;
- endocrine abnormalities - primarily hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, diabetes mellitus.
The main reasons why lips burn
0
Source:
See all photos in the gallery
The following factors can cause a burning, itching and tingling sensation in this sensitive area:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Due to long exposure to the sun, which contains ultraviolet rays, lips dry out, begin to peel and look swollen;
- burn. A reaction may occur to some hot food or drink;
- weathering. In cold weather, as well as when the climate changes, the sensitive area may react with dryness, cracking, and soreness;
- avitaminosis. Lack of vitamins affects the condition of the skin and especially the lips;
- mechanical impact. Lips can be accidentally damaged, for example, by a false jaw, an incorrectly growing tooth, or simply by sharp biting or chewing;
- disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. Stress and various mental disorders lead to a deficiency of saliva, which affects the condition of the oral cavity and lips;
- excitement. In this state, all processes in the body accelerate, blood rushes to the skin, causing redness and a burning sensation;
- chemical exposure. Both decorative cosmetics and regular hygienic lipstick or toothpaste can lead to the feeling of burning lips;
- hormonal changes. More often they affect women during periods of sharp hormonal fluctuations: puberty, pregnancy, lactation, menopause.
The skin may also sting due to certain eating habits, in particular, a passion for citrus fruits, salted fish, and pineapple. If the reasons are not pathological, the discomfort will go away on its own after a few hours or at most a day.
Types of cheilitis
Manifestations of cheilitis may vary depending on the type and cause of the disease. There are:
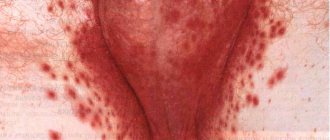
- Exfoliative cheilitis - manifested by peeling of the red border of the lips, with rare areas of burning and dryness of the lips themselves.
- Exudative cheilitis - symptoms of the disease are supplemented by swelling and severe pain. The skin in inflamed areas may become covered with baked crusts, which greatly complicate the patient’s life.
- The glandular form affects the minor salivary glands. Their congenital or acquired proliferation is observed, followed by infection with bacteria. In this case, the source of infection can be caries, periodontitis or banal plaque. Outwardly it manifests itself as the formation of cracks on the surface of the lips, which begin to become wet over time.
- The allergic form occurs under the influence of household, cosmetic or food irritants (often this is lipstick). There are characteristic manifestations of allergic cheilitis in musicians who play wind instruments and in those who like to chew pencils. This type of inflammation is characterized by severe swelling, often with the formation of blisters, as well as itching, severe redness and burning.
- Meteorological cheilitis develops under the influence of weather conditions (wind, sun) and is manifested by burning, itching with small weeping blisters, in place of which erosions and ulcers form over time.
- The atopic form manifests itself as a symptom of dermatitis or neurodermatitis. Manifests itself in the form of redness and ulcers in the corners of the lips.
- The hypovitaminosis type of the disease is formed in response to a severe lack of vitamins, mainly vitamins A, C, B2. A characteristic burning sensation affects the surface of the lips, mouth and tongue. The mucous tissues take on a swollen appearance, cracks on the lips peel and bleed.
- Macrocheilitis is a response to damage to adjacent nerves (facial nerve neuritis), while itching and swelling from the tongue can spread to other parts of the face.
Attention! With a long course, there is a high probability of inflammation degenerating into a malignant neoplasm. This is especially typical for the meteorological form, which, in the absence of proper treatment, is often complicated by precancerous diseases.
Causes of dry mouth
Both certain physiological factors and various pathological conditions lead to subjectively felt drying of the epithelium. Natural causes of dry mouth are the consumption of pickles, herring, and other foods containing a lot of salt. Drying of the mucous membranes occurs when there is insufficient humidity in the room. Dryness of the mouth of varying intensity, associated with sympathetic release, is possible during conflicts, quarrels, fear, and chronic stress.
Sialadenitis
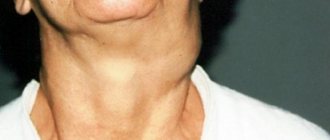
The most common cause of severe xerostomia is inflammation of the salivary glands. The pathological process is initially one-sided, but after a few days the inflammation spreads to the opposite side. Patients complain of swelling in the area of the salivary glands, increased body temperature, and painful opening of the mouth. Eating is difficult due to pain and dryness of the epithelium, which is caused by the cessation of secretion from the affected gland. Chronic sialadenitis is characterized by moderate pain and normal size of the salivary gland.
Other diseases of the salivary glands
Complaints of dry mouth are made by patients with mumps, a viral infection that primarily affects the parotid salivary glands in children, and less commonly, the submandibular and sublingual glands. The symptom is combined with general intoxication, pain and swelling of the glands on both sides, deforming the contours of the patient’s face. Severe xerostomia with high temperature, swelling, hyperemia in the area of inflammation are symptoms of a salivary gland abscess, complicating the course of sialadenitis and sialolithiasis.
Sjögren's disease
Dryness of the oral mucosa against the background of insufficient secretion of tear fluid, burning in the eyes, drying and peeling of the skin is typical for autoimmune damage to the glands in Sjögren's disease. The normal secretion of saliva is prevented by the infiltration of the ducts by lymphocytes and plasma cells, an autoimmune reaction with the formation of antibodies to the glandular epithelium. The parotid glands usually increase symmetrically in size; upon examination of the mouth, bright pink redness of the mucous membrane, contact bleeding, folded tongue, and multiple caries are revealed.
Diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx
The close location of all anatomical structures, general innervation and blood supply cause disruption of the salivary glands when various organs of the oropharynx and nasopharynx are affected. Dryness of the epithelium is observed during inflammatory processes, some rare pathological conditions - glossalgia, parotid fistula, galvanosis. Common causes of xerostomia are:
- Stomatitis
. With an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, dryness is combined with pain when eating, bad breath, and bleeding. The catarrhal form is characterized by redness and swelling; in the aphthous form, blisters and erosions form. With allergic stomatitis, hyperemia, ulcers, and erosions are determined. In older people, prosthetic stomatitis is possible. - Candidiasis
. When epithelial cells are damaged by fungi of the genus Candida, a white coating appears on the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks, a burning sensation and severe dry mouth are disturbing. Cracked lips are typical. The disease should be distinguished from hairy leukoplakia, which has a similar clinical picture, but affects patients with immunodeficiencies when exposed to a virus. - Hypertrophic rhinitis
. When the epithelial layer of the nasopharynx is thickened and the airways are partially blocked, patients breathe predominantly through the mouth, especially at night. This leads to severe dryness, which reaches its maximum intensity in the morning. A similar mechanism for the development of xerostomia is observed in nasopharyngeal cancer.
Infectious diseases
The appearance of dry mouth is characteristic of intestinal infections, especially those accompanied by watery diarrhea and leading to severe dehydration. Xerostomia is pathognomonic for cholera, a gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis. It is possible to identify a symptom during the febrile period of other infectious pathologies - brucellosis, psittacosis, Crimean fever. The oral mucosa dries out during the polyuric stage of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, which is caused by dehydration due to the release of up to 5 liters of urine per day.
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
Xerostomia with thirst and polyuria is a specific symptom. In patients with type 1 diabetes, microangiopathies and elevated blood glucose levels are predisposing factors to dry mouth. In elderly patients with insulin-dependent diabetes, the symptom is considered a manifestation of diabetic polyneuropathy. In addition to dry mouth, the patient is concerned about constant weakness, itchy skin, rashes, pustules, and fungal skin infections. Similar symptoms occur with steroid diabetes.
Neurological dysfunction
The prerequisites for dryness of central origin are considered to be incoordination of the nervous system, disruption of connections between higher cortical structures and the vegetative nuclei of the medulla oblongata. The symptom is observed in patients with neuroses, panic attacks, and organic anxiety disorder. Drying of the oral mucosa is characteristic of peripheral autonomic failure and polyneuropathy of pregnancy. Xerostomia develops in Lambert-Eaton syndrome, an autoimmune disease that affects the presynaptic membranes of neurons.
Gastroenterological diseases
Dry mouth is a common sign of damage to the pancreas. In case of fibrosis of the organ, it is caused by secondary diabetes; in case of pancreatitis and a split pancreas, it is caused by digestive disorders. The symptom is detected in chronic gastritis and is combined with epigastric pain, stool instability, nausea and vomiting. Dryness, which is accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, often becomes a sign of hepatitis.
Urological pathology
In diseases of the urinary system, dry mouth is usually caused by two mechanisms: dehydration due to polyuria and the accumulation of toxic protein compounds in the bloodstream. With renal colic caused by obstruction of the ureter or pyelocaliceal system, the situation is aggravated by pain with a pronounced sympathoadrenal reaction. In this condition, in addition to dry mouth, unbearable pain in the lower back, nausea and vomiting, and painful tenesmus are disturbing.
Often, xerostomia is provoked by nephrosclerosis, polycystic disease, and other severe kidney diseases with increasing chronic renal failure. The combination of dryness with swelling and lower back pain is characteristic of nephritic syndrome of various etiologies. Drug-induced nephropathy is often accompanied by drug-induced xerostomia. The feeling of dry mouth is typical of paraneoplastic nephropathy, which occurs with severe metabolic and immunological disorders.
Intoxication
Xerostomia in case of exogenous poisoning and endotoxemia is provoked by disruption of all body systems, discoordination of the nervous and humoral regulation of salivary secretion processes. In case of foundry fever and other poisonings involving inhalation of aggressive substances, the situation is aggravated by the direct damaging effect of vapors on the oral mucosa. The prerequisites for dry mucous layer are:
- Bad habits.
Xerostomia is observed during hangover syndrome, which is caused by severe intoxication of the body. The symptom is also typical of nicotine addiction, in which it is caused by constant irritation of the epithelium with cigarette tar. Dry mouth in combination with convulsions and hyperthermia can be a sign of poisoning with alcohol surrogates. - Cathinone abuse
. Abuse of norepinephrine provokes an increase in the activity of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, which is manifested by dilated pupils, dry mucous membranes, and psychomotor agitation. Over time, the euphoric effects of taking the drug decrease, and encephalopathy increases.
In cancer cachexia, xerostomia occurs as a result of gross disturbances in the functioning of the body caused by endogenous intoxication by tumor metabolic products and decaying cancer cells. The condition is accompanied by dyspeptic disorders, exhaustion, severe anemia, changes in emotional and mental status, and insomnia. Dry mouth worries patients with massive intoxication of the body by tissue decay products during gangrene.
Metabolic and endocrine disorders
The secretion of saliva has not only nervous but also humoral regulation. Various deviations from normal levels of hormones and biologically active substances cause disturbances in the functioning of all organs, including the salivary glands. The appearance of dry mouth mucosa is associated with secondary fluid losses that develop due to disturbances in water-salt metabolism and homeostasis. Xerostomia is potentiated by endocrine disorders such as:
- Algodismenorrhea
. Painful menstruation can occur at different ages, but most often dysmenorrhea is diagnosed in adolescents during the period of formation of sexual function. Complaints of dry mouth are due to the increased influence of prostaglandins on the level of salivation. With algodismenorrhea, pain is accompanied by dyspeptic disorders and asthenia. - Hypercalcemic crisis
. Xerostomia in this disorder is associated with dehydration accompanied by polyuria, repeated vomiting and diarrhea. An increase in calcium levels is manifested by abdominal cramps, muscle weakness, and severe thirst. Similar symptoms occur in Burnett syndrome, a dysmetabolic pathology with hypercalcemia and metabolic alkalosis. - Hypovitaminosis
. The combination of angular cheilitis and dry lips and oral cavity is typical for pyridoxine (vitamin B6) deficiency. For hypovitaminosis, a change in the appearance of the tongue is specific - it becomes bright red with a shiny “varnish” surface due to atrophic processes in the epithelial layer. - Pheochromocytoma
. With a tumor of the adrenal medulla, dry mouth is caused by increased endocrine function with a significant increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the blood. These substances enhance the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which inhibits the secretion of the salivary, gastric and intestinal glands.
Acute and emergency conditions
Xerostomia in critical conditions is caused by several mechanisms: severe dehydration, disturbances of neurohumoral regulation, reflex reactions due to excessive irritation of pain receptors. These pathologies are typically characterized by a severe and extremely serious condition of the patient, dysregulation of basic vital functions. The patient requires emergency medical care. Dry mouth is caused by:
- Bleeding
. Dryness of the oral mucosa during blood loss is promoted by significant dehydration of the body. The leading signs are pale skin, tachycardia, and a drop in blood pressure. The symptom develops both with internal bleeding and as a result of external blood loss. Ruptures of aneurysms of the renal and other arteries, leading to collapse, are life-threatening. - Acute abdomen syndrome
. Xerostomia is considered one of the manifestations of catarrhal appendicitis and other surgical conditions - obstetric peritonitis, biliary peritonitis, mesadenitis. The sign is pathognomonic for the initial phase of paralytic intestinal obstruction. Dry mouth is combined with severe abdominal pain and symptoms of peritoneal irritation. - Cardiovascular pathology
. The appearance of xerostomia is associated with autonomic reactions to severe pain in the heart or severe hemodynamic disturbances. Dry mouth is observed during hypertensive crisis and angina pectoris. The symptom is accompanied by headaches, blurred vision, and disturbances of consciousness. - Traumatic shock
. Symptoms of massive soft tissue injuries and bone fractures are explained by gross changes in autonomic reactions and a collapsing state due to severe pain. Pronounced pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, xerostomia, cold sweat. Impaired consciousness and lethargy are possible. - Fainting
. The post-syncope period of syncope is characterized by dry mouth and hyperhidrosis caused by dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. A similar mechanism for the occurrence of symptoms is observed after sunstroke. In this case, in addition to dry mouth, intense headaches, flashing “spots” before the eyes, and increased breathing are observed.
Diagnosis of cheilitis
There are no specific laboratory tests to detect cheilitis.
All diagnosis of the disease is carried out by visual examination. To determine the causes of inflammation, diagnostics of the gastrointestinal tract may be prescribed for the presence of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Additionally, allergy tests are performed to exclude food allergies. General laboratory tests allow you to check the condition of the body and determine the possible causes of cheilitis:
- low levels of vitamins due to hypovitaminosis can provoke exfoliative cheilitis;
- bacterial cultures of smears and biopsies are performed in patients with immune system disorders in the absence of results from the treatment;
- testing for markers of HIV infection, herpes, the presence of fungal or bacterial microflora, respectively, allows us to identify the viral, bacterial or fungal causative agent of cheilitis;
- a blood test for anemia, ESR are required to assess general health;
- examination of the function of the thyroid and pancreas for endocrine pathologies.
On a note! Cheilitis tends to be chronic with periodic relapses. Self-healing without medical supervision is almost impossible, so try to pay attention to such a “minor” problem and consult a specialist. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by a general practitioner or attending dentist. In some cases, consultation with an allergist, infectious diseases specialist, dermatovenerologist or gastroenterologist may be required.
How to treat lips with cheilitis
The most important thing in treating cheilitis is to identify its cause, which is difficult to do without professional help. You'll have to contact a specialist. First, it is better to go to a therapist, and he will then refer you to a specialist doctor.
Typically, treatment for diseases of the lips and skin around the mouth is based on eliminating not the symptoms, but the root cause. It includes lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, and medication.
If the cause of inflammation is an infectious or fungal infection, local drugs are included in the therapy. Typically, patients are prescribed various medicinal ointments for external use, which must be applied to damaged skin several times a day:
- anti-inflammatory – Tetracycline, Erythromycin;
- antifungal – Clotrimazole;
- hormonal – Prednisolone.
To cure lips, you need to influence them not only from the outside, but also from the inside. The skin around the mouth often suffers from a lack of B vitamins, so they are often prescribed in the treatment of lips.
Treatment of cheilitis
Different forms of cheilitis differ in their approach to treatment. Collectively, the impact may include:
- correction of the psycho-emotional sphere - a neurologist prescribes sedatives, tranquilizers, a psychologist or psychotherapist conducts appropriate psychotherapy;
- physiotherapy - treatment with laser, ultrasound, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis is prescribed locally; they relieve irritation and accelerate tissue regeneration;
- drug symptomatic therapy - non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed; in case of severe inflammation - hormonal drugs;
- immunotherapy – strengthen the immune system by taking immunomodulators and immunostimulants;
- vitamin therapy - taking vitamins A, C, group B (mainly vitamin B2) is of great importance;
- surgical treatment – typical for glandular cheilitis with enlargement of the salivary glands; Both laser ablation with a surgical laser and direct removal of areas of the gland are used;
- antiallergic therapy with antihistamines.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe diet therapy with the exclusion of foods that provoke allergies or chemical irritation of tissues (spicy foods, saltiness and marinades). When staying outdoors for a long time, it is imperative to use special protective equipment.
My lips are dry, what should I do?
It is advisable to deal with the problem at the earliest stages, and not to bring the matter to the point of deep neglect.
Your body makes the task easier by signaling in every possible way that something is wrong with it. So, symptoms of dry lips include: redness in the corners of the lips, white saliva and difficulty swallowing. If you notice these symptoms, immediately take measures to treat your lips.
First you need to eliminate the very cause of dryness. Throw out your lipstick and change your toothpaste, and to keep your lips hydrated, use honey, cocoa butter or Vaseline.
Stop licking your lips, and certainly don’t even think about peeling off the skin from them, because such actions will only complicate the situation: cracks and painful wounds will appear on your lips, and in addition, this will cause an infection.
Understand your diet. It should contain a lot of greens, fresh vegetables and fruits. The consumption of harmful foods must be limited in your diet. Proper and nutritious nutrition will have a beneficial effect not only on the skin of the lips, but also on the body as a whole. Various lip masks will help get rid of itching, dryness and other unpleasant sensations on the skin.
Prevention of cheilitis
The main prevention of cheilitis is maintaining a healthy lifestyle and timely treatment of any infectious and allergic diseases. Basic list of measures:
- Eat right - a balanced menu should contain an abundance of fruits, vegetables, herbs, nuts, fish, and high-quality dairy products.
- Reduce the use of cosmetics - try to choose hypoallergenic formulations and constantly monitor the skin's reaction.
- Dose your exposure to open wind or direct sunlight.
- Protect your lip skin from physical and chemical damage.
- Take vitamin and mineral complexes periodically in courses (after consultation with your doctor).
- Give up bad habits.
- Seek medical advice promptly if you have characteristic symptoms.
Remember: your health is the greatest value, and constant monitoring of its condition is very important to maintain the body’s performance, especially in old age.
Diseases in which the lips hurt and a burning sensation is felt
0
Source:
The condition called burning lips syndrome is not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of certain ailments. Most often observed in the following cases:
- Diabetes. With uncontrolled diabetes, neuropathy is often observed - inflammation of nerve endings, which can be expressed in pain in various parts of the face.
- Allergic reaction. Lips can become swollen and sore as a result of drinking certain drinks and foods to which a person is allergic. This reaction is often observed to alcohol and certain medications.
- Candidiasis. A fungal infection causes inflammation, manifested by the formation of a whitish coating on the oral mucosa. When affected, the lips also suffer, and small, painful cracks often appear in the corners of the mouth.
- Stroke. Burning of the face and hands, turning into numbness, is a serious symptom that may indicate a stroke. A sharp headache, blurred vision, problems with speech – these are signals indicating the need to immediately call an ambulance.
×
How to get rid of dry lips at home
Sour cream mask
Mix a teaspoon of lemon juice and sour cream, and also add a little vegetable oil to the mixture. Regularly apply the product to the lips and surrounding area for 20 minutes, then rinse with warm water.
Honey lip massage
Rub a small amount of honey into your lips with light massaging movements or apply it to the corners of your lips if necessary. You can use this mask as often as you want.
Baby cream to help you
Apply a high-quality baby cream to your lips in a thick layer. After 15 minutes, simply blot off any remaining product with a clean napkin.
Vegetable oils for lips
You can also use sea buckthorn, almond, and wheat oils. Such oils are applied to the lips twice a day, and a couple of drops of vitamins A or E are often added to them to enhance the effect.