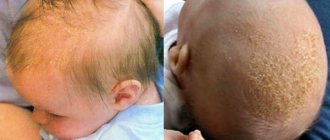
Redness of the scrotum may be a sign of some dangerous disease that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. In fact, there may be many reasons for the occurrence of this symptom, but self-medication is in any case unacceptable. You should contact a medical professional, regardless of your age and even if there are no other symptoms other than this.
The doctor will prescribe the necessary diagnostic examination to determine the exact cause of the redness. If you delay this, the disease will be advanced and, accordingly, it will be more difficult to treat. For example, sometimes redness is not at all associated with irritation, and sometimes it’s the other way around. The results of the examinations will help the doctor make an accurate determination, and based on this, the correct therapeutic course will be prescribed.
Why does the scrotum itch?
Physiological reasons
In the absence of provoking diseases, the cause of the symptom is:
- Neglect of hygiene.
The skin of the scrotum contains a large number of sebaceous and sweat glands. Irregular hygiene procedures lead to the accumulation of sebum, sweat residues, waste products of microbes and other components that provoke itching and irritation of the skin. - Poor hygiene.
Itching may be caused by the use of hygiene products that cause dryness and irritation of the skin. Sometimes the symptom occurs when washing with too hard water. - Shaving.
When removing hair using a razor, microtraumas occur, which are manifested by pain, itching and burning at the site of damage. Another cause of discomfort can be ingrown hairs caused by shaving. - Wrong choice of underwear.
Insufficient ventilation due to too tight or synthetic underwear causes increased sweating. The problem becomes especially relevant in the summer and when staying in southern countries.
Prickly heat
Potentiating factors are wearing tight synthetic underwear, exposure to high temperatures, heavy physical labor, and the inability or unwillingness to carry out hygiene procedures. The pathology is caused by blockage of the sweat glands. In the groin area, as a rule, prickly heat develops, which is accompanied by severe itching, the appearance of blisters with cloudy liquid and small red nodules. Similar manifestations can be observed in the armpits.
Dermatitis
Simple contact dermatitis is characterized by the absence of an allergic component, develops as a result of the direct action of an irritating substance, and can be acute or chronic. With the erythematous variant, slight itching, redness, swelling, and sometimes dryness and cracks of the skin are noted. Patients with the bullous form complain of pain, burning, heat and itching. Objectively, blisters with clear liquid are found on hyperemic skin.
Allergic contact dermatitis is provoked by components of detergents, fabric dyes, sexual lubricants, and latex. The acute form is characterized by intense itching. Skin changes are located in the area of contact with the allergen and have clear boundaries. Swelling and hyperemia are replaced by the appearance of papules, which turn into vesicles and open to form erosions. In a chronic course, the itching becomes constant, the boundaries of the lesions are blurred. Dryness and flaking of the skin are detected.
Atopic dermatitis develops in childhood and is chronic. In adults, it is more often detected on the face, in skin folds and the groin area. Sometimes there is spread to the scrotum. Pale pink lesions are detected in the affected area. The skin is dry, rough, flaky. The appearance of papules and cracks, secondary infection is possible. Exacerbations are caused by contact with mold, animal hair, house dust and other allergens.
Perhaps explicit images of genitals are hidden here
Are you over 18 years old?
Yes
No
Allergic dermatitis of the scrotum
Eczema
Most often, post-traumatic microbial eczema is detected in the scrotum area. The affected areas are localized around scratches and abrasions from shaving and scratching that occur against the background of other pathological conditions. In rare cases, itchy and weeping red lesions of sycosiform microbial eczema are visualized in the groin and scrotum.
In true eczema, involvement of the scrotum is also rare. The pathology is characterized by the formation of papules and vesicles, transforming into microerosions with copious serous discharge. The severity of itching varies significantly - some patients complain of minor or moderate discomfort, while in others the symptom is so painful that it causes insomnia and the development of neurotic disorders.
Other skin diseases
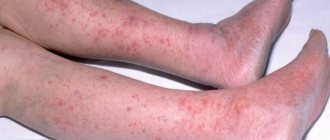
Inguinal epidermophytosis has a fungal etiology. Inguinal folds are typically affected, sometimes spreading to the intergluteal fold, thighs and base of the scrotum. The pathology is manifested by severe itching and discomfort when walking. Upon examination, round, flaky pink spots with a tendency to increase, vesicles and pustules along the periphery are determined.
Erythrasma is caused by corynobacteria. Large skin folds, including the inguinal folds, are affected. As in the previous case, when spreading, the changes can cover the base of the scrotum. The itching is minor, often asymptomatic. Brownish or brownish spots with rounded or scalloped edges are found on the skin, gradually merging with each other.
Scabies
A typical localization is the peri-umbilical zone; in men, the process may spread to the scrotum and penis. Patients are bothered by unbearable itching, which intensifies in the evening and at night. During examination, itch tracts are revealed on the skin of the scrotum in the form of short straight or curved lines with a small vesicle and a bloody crust at the end. When allergization occurs, nodular scabies forms with a rash in the form of brownish nodules over the scabies tracts.
Pediculosis
Persistent itching of the scrotum and perineum occurs due to pubic lice bites. The symptom intensifies at night and is accompanied by scratching and the appearance of bluish-bluish spots at the bite sites. Low-grade fever and regional lymphadenitis are possible. Itching can also be provoked by body lice, but in this case the unpleasant sensations occur not only in the groin, but also in other parts of the body; the bite sites are erythematous papules.
Other reasons
Sometimes itching of the scrotum develops against the background of systemic metabolic disorders. Unpleasant sensations are not limited to the groin, but spread throughout the body; other signs are revealed that indicate the presence of one or another pathology. Possible reasons are:
- Endocrine disorders:
diabetes mellitus. - Damage to the liver and biliary tract:
cholelithiasis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver. - Kidney disease:
severe renal failure.
In some men, the symptom appears against the background of strong experiences or accompanies mental disorders of a neurotic level. It can be detected in obsessive-compulsive disorder, hysteria, and some other pathological conditions.
Consultation with a dermatologist
Structural features
As mentioned above, the scrotum creates and maintains the optimal temperature for spermatogenesis (34.5ºC). Stable maintenance of this temperature is achieved due to the sequential arrangement of several layers of the scrotal wall:
- Dermis (inner layer of skin). Its structure is no different from the skin of other parts of the body. It may have more pronounced pigmentation than the rest of the skin and is slightly more elastic.
- Fleshy shell. A connective tissue structure located just under the skin of the scrotum. Unlike most parts of the body, there are practically no fat cells in the musculature, it consists mainly of muscle fibers.
- Outer leaf of the spermatic fascia. This is a connective tissue formation that continues the superficial fascia of the abdomen.
- The levator testis muscle and its fascia. This is a rudiment of a formation found in some animals. The contraction of this muscle causes the testicle to be removed from the scrotum into the abdominal cavity. Thus, it is protected from injury. In humans, this muscle does not perform its function and is a rudiment.
- The inner layer of the spermatic fascia is a continuation of the fascia of the abdominal wall. It is fused with the surface layer of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle.
- The tunica vaginalis of the testicle is an analogue of the peritoneum and in embryogenesis is formed from its protrusion. It consists of two layers - the superficial (parietal), which fuses with the internal spermatic fascia, and the internal (visceral), directly adjacent to the testicle. Between them is a cavity filled with water.
Such a complex structure is not just a repetition and modification of the abdominal wall, it provides optimal conditions, gives the testicle a certain mobility, and protects it from injury. In addition, the scrotal tissue is rich in blood vessels and nerves, making it one of the most sensitive places on a man’s body.
Based on the anatomical structure, there are several general patterns of pathological processes in the scrotum. In particular, purulent inflammations are well contained by numerous fasciae; they usually take on a localized character.
Diagnostics
Most pathologies manifested by itching of the scrotum are under the jurisdiction of a dermatologist. According to indications, patients are referred for consultation to an allergist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and other specialists. The examination includes the following diagnostic procedures:
- Inspection.
The doctor identifies changes (swelling, hyperemia, rashes) that suggest the nature of the disease and determine a list of other studies. To identify scabies, it may be necessary to apply aniline dyes. - Luminescent diagnostics.
In the zone of fungal infections, a greenish glow is visible under a Wood's lamp. With erythrasma, the shade of the changed areas becomes reddish-brick. The fluorescence of nits in head lice is also visualized in the rays of the lamp. - Lab tests.
If an allergy is suspected, allergy tests are performed, immunoglobulin determinations, and a blood test for eosinophilia are prescribed. Scabies is confirmed by the results of a scraping examination. If mycoses and bacterial lesions are suspected, in doubtful cases, culture is performed on nutrient media.
The presence of pubic lice indicates promiscuity when choosing sexual partners and is an indication for testing for STIs. The examination plan for systemic diseases is drawn up taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, and may include laboratory tests, ultrasound, and MRI. If a mental disorder is suspected, consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist is required.
Symptoms of pathological processes
The course of pathological processes in the scrotum has a number of features determined by its anatomical structure. Therefore, when identifying symptoms of a particular disease in a patient, the doctor will pay attention to some manifestations of scrotal diseases:
- The pain can vary in nature. Its intensity, as a rule, depends on the individual characteristics of the patient - pain threshold, characteristics of perception, psychological factors. It accompanies almost any pathological process in the scrotum - inflammatory processes, varicocele (varicose veins of the scrotum), trauma and testicular torsion.
- Compaction in the scrotum - part of the organ is palpated as a harder formation than other tissues. Palpation of the compaction can be painless (atheroma) or cause sharp pain (hematoma or varicocele). The cause of compaction may be a skin abnormality (atheroma, wart), hematoma due to injury, tumor, vascular disorders, or inflammatory process.
- Itching. This is one of the most intolerable types of itching because, unlike most other areas, it is not always possible to scratch the scrotum. The cause of itching can be allergic skin reactions, some sexually transmitted infections, prickly heat, irritation caused by uncomfortable underwear and clothing, poor hygiene, skin irritation from shaving or other procedures.
- Edema. It can be uniform or uneven, which indirectly indicates the localization of the lesions. The swollen scrotum increases in size, its sensitivity changes, and itching may appear. The cause of swelling may be injury, varicocele, or allergic reactions.
- Redness (hyperemia) of the scrotum. It appears most often during inflammatory processes, less often - during disorders in the circulatory system. Most often combined with other signs of the disease, indicating its nature. With an inflammatory process in the scrotum, a characteristic combination of symptoms is hyperemia, compaction, pain, swelling, and increased local temperature.
Treatment
Patients with dermatitis, prickly heat, and eczema are advised to eliminate the provoking factor. For all diseases, it is advised to follow the rules of hygiene, use soft cosmetics, and wear loose natural underwear.
Local treatment is widely used. For prickly heat and inguinal epidermophytosis, baths with string, celandine, chamomile, and potassium permanganate are useful. For pathologies accompanied by weeping, use mash and powder, and treat with antiseptics and oak bark infusion. Antifungal, antibacterial, hormonal and keratolytic ointments are applied according to indications.
Antihistamines are recommended to reduce itching. If there is irritability or sleep disturbances caused by unpleasant sensations in the affected area, mild sedatives with herbal components are added to the treatment regimen. For large foci of erythrasma, systemic medications with antibacterial action are prescribed. For some conditions, UV therapy is effective.
To treat the skin for scabies, special emulsions and aerosols are used; to prevent re-infection, the body, underwear and bed linen are treated according to a special scheme. For lice, pyrethroids, organophosphorus compounds, polydimethylsiloxanes and essential oils are used. Carry out appropriate epidemiological measures.
Prevention
Measures to prevent scrotal peeling:
- Maintain intimate hygiene: wash your genitals twice a day with baby or intimate soap, if necessary, lubricate with moisturizers, use anti-sweat powders.
- Protected sex. A condom will not save you from fungus, so after questionable contact you need to wash your pubis and scrotum with soap.
- Comfortable underwear made from natural materials. Synthetic briefs and tight trousers are a direct path to dermatitis of the scrotal skin.
- Compliance with hygiene rules in the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool. You cannot use other people's towels, washcloths, sheets, or soap. Do not allow the scrotum to come into contact with surfaces.
If you are prone to allergies, you should not overuse citrus fruits, cocoa, and chocolate.
Stages of the disease
Stage 0 (hidden): lymphatic vessels are damaged, but this is not yet apparent. The transport capacity of the lymphatic system is still sufficient to remove lymph. No lymphedema.
Stage 1 (spontaneously reversible): When pressed with fingertips, a dimple appears on the skin, but it quickly returns to normal. Typically, when you wake up in the morning, the affected area is normal or nearly normal size.
Stage 2 (spontaneously irreversible): The scrotal tissue now has a spongy consistency and no dimple is left when pressing with your fingertips on the affected area. Fibrosis develops (overgrowth of connective tissue and scar formation). This marks the beginning of hardening of the skin and an increase in the size of the scrotum.
Stage 3 (elephantiasis or elephantiasis): At this stage, the swelling is irreversible and the affected area is usually very large. The skin is hard (fibrotic), warty.
Dermatitis on the penis
Dermatitis refers to fungal infections of the upper layer of the epidermis. The disease is usually typical for children and adolescents, as well as people who are overweight. Rarely, pathology occurs for no apparent reason in men and women and, despite its widespread prevalence, requires a thorough approach to prevention and treatment. Recently, dermatitis in the groin area in men and women has become a sensitive topic on medical forums.
Photos depicting pathology clearly demonstrate the picture of the disease and visual features of skin rashes. The most unpleasant sensations are associated with rashes on the head of the penis. To establish an accurate diagnosis and exclude, for example, candidiasis or syphilis, you should definitely visit a dermatovenerologist.