Urticaria is a skin disease associated with the appearance of an allergic rash. In shape and size, it resembles the blisters that appear after being struck by nettles, hence the name. In the acute form, rashes appear literally in the first minutes after interaction with the provoking factor, they pass quickly - within a few hours. If the effect of the allergen is not eliminated, a recurrent form of the disease occurs. A single episode does not require treatment, but chronic urticaria will not go away without treatment. If you experience symptoms of hives, you should definitely consult a doctor.
At CELT you can get advice from a gastroenterologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
Mechanism of disease development
Urticaria differs from other dermatological and allergic diseases in the presence of a clear and understandable relationship between exposure to an allergen and the appearance of rashes. Most often, patients can independently name the provoking agent - symptoms appear within a few minutes after contact with the provoking agent. If the causes of urticaria are unknown, then first of all it is recommended to pay attention to contact with animals and diet.
An immediate allergic reaction develops as follows: an allergen enters the body, mast cells are immediately sent to it - they cause the release of immunoglobulin E. When a mast cell is in conditions of increased immunoglobulin content, it produces histamines - substances that increase vascular permeability and cause swelling . This is a protective mechanism that allows the body to block part of the allergen, and remove part as quickly as possible.
The provoking factor may not be a substance, but a physical effect - heat or cold, stress. Allergies can also be caused by the presence of a source of infection in the human body.
In clinical diagnosis, acute and chronic forms of urticaria differ in duration - if episodes of urticaria are present for 6 weeks and are interspersed with periods of remission, then a diagnosis of chronic urticaria is made.
Allergic urticaria: recommendations to avoid
If the allergy trigger for hives is known, patients should avoid exposure to it as much as possible.
If you know that you are susceptible to spontaneous allergy symptoms due to hives, follow these guidelines:
- abstain from alcohol or reduce its consumption;
- do not prescribe any medications for yourself;
- avoid stress as much as possible;
- use anti-allergenic soaps, skin creams and cleansers;
- Avoid foods that trigger the production of histamine (they are listed in the “Causes of urticaria” section).
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
Causes of development and forms of urticaria
The main cause of hives is contact with an allergen. There are many factors that can provoke a pathological response of the immune system (this is an allergy). Most often, urticaria is caused by contact with such groups of substances as:
- Medicines, especially antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
- Dust.
- Animal fur or feathers.
- Plant pollen, poplar fluff.
- Substances that get under the skin from insect bites.
- Compounds that parasites secrete are most often caused by Giardia.
- Some substances contained in food products.
For the development of acute urticaria, short-term contact with the allergen is sufficient. The chronic form is characterized by frequent relapses and is associated with prolonged proximity to the substance causing the pathological reaction. Therefore, at the first manifestations of an allergy, it makes sense to conduct special tests, find out what exactly caused the rash, and exclude any contact with this substance.
In the chronic form, the rash and inflammation are less pronounced. After an exacerbation, the symptoms disappear for a while. Recurrent urticaria may be associated with the presence of a source of infection in the body and requires consultation with a specialist.
When and which doctor to contact
Usually a doctor is consulted:
- if the rash spreads over a large area;
- when symptoms increase;
- when signs of general intoxication occur;
- if the urticaria does not go away on its own after eliminating the factor that caused it;
- if the disease becomes chronic or often recurs,
It is advisable not to delay your visit to the doctor and come when the first manifestations of the disease occur. Then it will be easier to establish the cause, and treatment will take less time. In addition, the doctor will recommend what to do to prevent hives.
A therapist or pediatrician, a dermatologist can provide assistance with urticaria, and an allergist is involved in targeted diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of urticaria
The disease has specific manifestations, so there are usually no problems with making a diagnosis.
Specific symptoms of allergic urticaria:
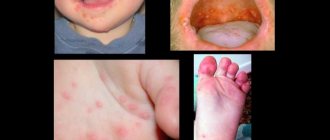
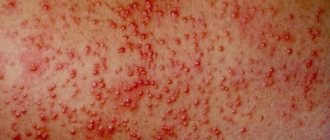
- Skin rashes resembling blisters from contact with nettles.
- When pressed, the blisters are white and lose color.
- Itching that leads to scratching.
- The skin at the site of the lesion is swollen and red.
- The rash can appear on any part of the body in its acute form; sometimes urticaria even affects the mucous membranes.
- In chronic pathology, the rash often appears on the bends of the arms and legs.
With direct contact with the allergen, rashes appear quickly, within a few minutes, and disappear without a trace in a maximum of 2 days. The rash subsides within 3-6 hours.
If complications develop, skin symptoms may be accompanied by swelling of the larynx, fever, weakness, headache, nausea, and difficulty breathing.
If life-threatening complications occur, you must take any antihistamine and call a doctor. If allergy symptoms only include hives, then emergency care is not required. In this case, it is worth making an appointment with an allergist to establish a diagnosis and avoid chronicity of the disease.
2.What are the types of urticaria and Quincke's edema?
There are several different types of urticaria and angioedema:
- Acute urticaria and acute angioedema
. This is hives or swelling that lasts less than six weeks. The most common causes of this reaction in the body are food, drugs, latex or infections. Insect bites or some kind of internal disease are another cause of acute urticaria. When it comes to foods, the most common causes of hives are nuts, chocolate, fish, tomatoes, eggs, fresh berries, soy, wheat and milk. Especially if they are all consumed in their raw form. Medicines that may cause hives or angioedema include aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen), high blood pressure medications, or pain relievers (codeine). - Chronic urticaria or Quincke's edema
. In this case, the hives or swelling last for more than six weeks. Usually the causes of this type of urticaria are more difficult to determine than in the case of the acute form of the disease. In fact, the cause of chronic urticaria may be the same, but perhaps it is all due to an autoimmune disease, chronic infections, hormonal disorders or malignant neoplasms. - Physical urticaria
. This is a rash caused by direct physical impact on the skin. For example, from cold, heat, sunlight, vibration, pressure, sweating or exercise. In this case, hives usually appear in the area where the skin was directly exposed and rarely occur elsewhere. In most cases, physical hives go away within an hour of stopping exposure. Cold allergy is one of the most common forms of physical urticaria. - Dermatographism
is hives that appear when the skin is rubbed or scratched too hard. Such urticaria can begin simultaneously with other forms of this disease. - Hereditary angioedema
. This is a painful swelling of the tissue. The disease is inherited.
Visit our Allergology page
Diagnosis of urticaria
Diagnosis begins with an examination by a medical specialist and most often ends at the stage of collecting an anamnesis. Typical urticaria is associated with the presence of a specific allergen. Most patients had atopic reactions in childhood. Visual assessment of the skin helps to make a final diagnosis - urticaria can be easily distinguished from other skin diseases.
If there are symptoms, but the patient finds it difficult to name the reason for the development of the pathological reaction, a number of specific tests are performed. Laboratory tests include determination of general and specific immunoglobulin E, as well as a general blood test. Special provocative tests allow you to identify a fairly specific allergy provocateur. If the cause is not established, further diagnosis involves testing for parasitic infestations.
General information
The name of the disease is due to the fact that outwardly it looks like a nettle burn - the skin turns pink and swells, while small blisters can merge into large local spots (angioedema) of irregular shape.
Papules cause itching and discomfort; when scratched, the wound surface can become infected, and then dermatitis and other complications join the underlying disease. The disease is very common; every third person on the planet has suffered from urticaria in one form or another.
Our doctors
Shundeva Oksana Veniaminovna
Allergist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Orlova Tatyana Vladimirovna
Doctor - allergist-immunologist, pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
First aid for urticaria in a child
The primary task is to identify and eliminate the provoking factor. The main problem during this period is not rashes, but itchy skin. When providing first aid, it is important to eliminate it if possible - gently trim the nails, put on protective gloves for infants, apply an available non-hormonal anti-allergic cream (for sunburn, mosquito bites, etc.) to the site of the rash. If there is no cream, you can use a cool compress.
All this is done before medical assistance, which should be provided immediately. In case of development of edema and severe symptoms, it is necessary to call an emergency team.
Treatment of the disease
If the allergen is known, then the main recommendation is to avoid, if possible, contact with the substance that provokes hives. That is why accurate diagnosis is important - it is necessary to understand which group of chemical compounds can lead to the development of urticaria. It often happens that the same substance is found in different foods or in different pharmaceuticals. And an allergy to pets can affect only one breed or spread to almost all pets, from cats to hamsters.
Therapy is needed if the disease has become a recurrent form - this happens if it is impossible to stop contact with the provocateur. In a situation where test results show the presence of an infectious focus, it is necessary to determine the infectious disease. It is likely that the urticaria will go away after healing.
If a patient is diagnosed with an allergy to dust, food or plants, then lifestyle changes are required: frequent wet cleaning, following a proper diet and avoiding walking during the flowering period of plants. Concomitant treatment is designed to alleviate symptoms when they reappear.
Causes
In children, the main cause of the disease is allergies; in adults, the disease often occurs for other reasons.
The appearance of a rash is both a reaction to specific allergens and a consequence of a disease. So, the reasons could be:
- taking certain medications;
- consumption of allergen-containing products;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- exposure to environmental factors;
- some infectious diseases;
- gastritis;
- colitis;
- hepatitis;
- diabetes;
- leukemia, lymphoma.
In more than half of the cases in adults, symptoms of a disease that is difficult to confuse with something else appear due to malfunctions of the immune system. This is the so-called idiopathic urticaria. It is difficult to treat and symptoms persist for a long time. The disease in adults can be a consequence of taking certain medications, or, less commonly, food. If allergic urticaria is the result of taking any medication, it should be completely eliminated, as further use can provoke Quincke's edema and lead to serious consequences, including death.
If a rash appears on the skin after being in the sun, the disease is a consequence of exposure to ultraviolet rays. This is possible with high sensitivity of the skin. These people develop symptoms after being in water.
Additional research:
- skin test when using autologous serum;
- rheumatological tests;
- nasal swab for the presence of eosinophils;
- TSH, T3, T4, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin;
- culture of throat flora, throat culture for sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriophages;
- stool analysis for sensitivity to bacteriophages and dysbacteriosis;
- antibodies to helminths, as well as roundworms and lamblia;
- coprogram;
- HBsAg, AT to hepatitis C, RW, AT to HIV;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- consultation with a gastroenterologist to identify H. pylori, endoscopy, consultation with a neurologist, ENT specialist (VSD);
- ECG;
- if urticarial vasculitis is suspected, a dermatovenerologist performs a skin biopsy.
Diet
Diet is very important to prevent the occurrence of both acute and chronic allergic urticaria and its treatment. To determine what exactly triggered the allergic reaction, either the method of introducing a single product or allergy tests are used.
If it is not possible to identify a specific product, general recommendations should be followed:
- exclude products with a high and moderate degree of allergenic activity: chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, nuts, fish, red fruits and berries, poultry, mushrooms, spices, vinegar, honey;
- exclude tonic drinks – tea, coffee, alcohol;
- exclude products with dyes and preservatives from the menu.
It is recommended to include water porridge (oatmeal, rice, buckwheat), vegetable soups, baked goods made from soft dough, and fermented milk products into the diet. Food processing helps reduce the allergenicity of food: peeling, heat treatment, freezing.
To speed up the removal of the allergen from the body, you need to drink a sufficient amount of water - up to 2-2.5 liters per day.
For what indications is specialist consultation necessary?
Consultation with an allergist is necessary in case of exacerbation of chronic recurrent urticaria, as well as in intermittent acute form of the disease. The causes of diseases associated with urticaria can be determined by an allergist. It is also necessary to consult a dermatologist, rheumatologist, parasitologist, endocrinologist and, possibly, an oncologist.
Brief description of some clinical forms of urticaria
Allergic urticaria
- Most often acute or episodic
- The most common allergens are food, medications, insect poison, latex
- Patients also have other manifestations of allergy pathology, allergic heredity
- Positive results of allergological examination
- Elimination measures are effective
Autoimmune urticaria
- Current type of chronic idiopathic urticaria
- Frequent presence of autoimmune thyroiditis and thyroid diseases in the family
- Severe general symptoms (weakness, malaise, gastrointestinal dysfunction)
- Presence of histamine-releasing anti-Fcε-RI antibodies and anti-IgE antibodies
- Positive test with autoserum
Cold urticaria
- It can be acquired (idiopathic and arising against the background of an underlying disease, for example, viral hepatitis, lymphoproliferative disease, etc.) and congenital.
- The appearance of itching, burning, hyperemia, urticarial rash, angioedema in areas of the skin exposed to low temperatures
- Symptoms persist for 20-30 minutes and disappear without a trace after the patient warms up
- exposed
Delayed pressure urticaria
- Characterized by the appearance of swelling and blisters in pressure areas 4-6 hours after exposure.
- Characterized by resistance to treatment
Heat urticaria
- Occurs from exposure to heat.
- Hereditary local thermal urticaria has been described, characterized by a delayed (4-6 hours) appearance of elements after local thermal exposure.
- May be accompanied by systemic circulatory disorders and convulsions
Solar urticaria
- Occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation
- Blisters appear on exposed areas of the body after exposure to the sun; there may be fixed light urticaria
- The disease can be primary (idiopathic photic urticaria) and
- Secondary light urticaria may be associated with the action of drugs (tetracyclines, sulfonamides, quinolones) or associated with an underlying disease (SLE, thyroiditis, gastrointestinal dysfunction).
Dermographic urticaria
- The appearance of blisters due to mechanical irritation of the skin
- Itching precedes the appearance of rashes
- The phenomenon of dermographism is reproduced by intense line irritation of the skin with a blunt object (spatula)
Vibration urticaria/angioedema
- There are hereditary (autosmal dominant type) and acquired forms
- Characterized by the appearance of a rash and swelling in areas exposed to vibration
- Rash and swelling appear 4-6 hours after exposure to vibration and persist for up to 24 hours.
- The disease is caused by nonspecific degranulation of mast cells
Aquagenic urticaria
- The rash occurs only after contact with water of any temperature
- A rash with severe itching occurs immediately after contact with water
- Characterized by the appearance of small blisters surrounded by erythematous spots
Cholinergic urticaria
- Occurs more often in young people
- Characterized by the appearance of pale pink blisters with a diameter of 1-5 mm, often surrounded by erythema, the rash is generalized
- Provocative factors include exercise, stress, sweating, and hot showers.
- May be accompanied by systemic manifestations (hot flashes, weakness, rapid heartbeat, headache, abdominal pain, shortness of breath
- Can be reproduced by subcutaneous administration of acetylcholine
Adrenergic urticaria
- Rarely seen
- Characterized by the appearance of small papules with a white halo
- Triggered by stress
- Can be reproduced by intradermal injection of epinephrine
Anaphylaxis/urticaria caused by physical exertion
- Characterized by the appearance of skin itching, rashes, angioedema during or immediately after physical activity
- May be accompanied by systemic manifestations, including bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, vascular collapse
- A provoking factor may be the consumption of certain foods (alcohol, apples, shrimp, tomatoes, nuts, celery) before physical activity.
Treatment of urticaria in children
The choice of treatment tactics for urticaria in children depends on its cause, main symptoms, the age of the child, as well as the stage at which the disease is caught.
Only a doctor can prescribe complete therapy after an accurate diagnosis. The main goals include eliminating precipitating factors, prescribing medications to eliminate symptoms, and treating associated pathologies. The doctor makes the choice of antihistamines and other drugs based on the individual clinical picture. Modern medicine offers new generation drugs that minimize the risk of side effects, have a high level of safety and are easy to use for young children. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
Is it possible to bathe a child with hives?
If the disease is not aquagenic in nature, you can and should bathe your child, but it is important to follow the recommendations:
- do not heat the water above +37C;
- do not use washcloths and hygiene products with dyes and fragrances;
- maximum bathing time - 10 minutes;
- the use of herbal decoctions and potassium permanganate should be agreed with a doctor;
- Do not rub the inflamed skin with a towel.
Possible complications and their consequences
Urticaria, despite its apparent harmlessness, can lead to serious consequences, primarily to Quincke's edema. Its characteristic initial symptoms, in addition to the swelling itself, are difficulty breathing and paroxysmal cough with whistling (bronchospasms). Swelling of the internal mucous membranes is dangerous due to disruption of the housing and communal services, the first signs of which are a gag reflex and stool disturbance. From the nervous system, severe cases of urticaria are dangerous due to damage to the meninges, which can be fatal in the absence of medical assistance.