Men and women of any age can face the problem of dry lips. To cope with this, you need to determine the cause of the abnormal condition of the delicate skin. Depending on them, methods of moisturizing lips are selected. Among the help options there are both natural remedies and artificial compounds that will help restore your natural smile. Professional doctors in the field of aesthetic medicine at the clinic “DOCTOR DENT. Cosmetology" provides advice on skin care and prevention.
Causes of cheilitis
- adverse weather conditions
- allergies
- lack of vitamins
- bad habits (licking and biting lips, habit of chewing pens)
- bad habits (licking and biting lips, habit of chewing pens)
- anomaly of the lip structure
- emotional and physical overload
- infections
Cheilitis often occurs against the background of diseases of the digestive, endocrine, nervous and immune systems. An important role is played by poor oral hygiene and multiple caries, since in this situation the number of microorganisms in the mouth increases.2 Cheilitis is often found in children with bronchial asthma and diabetes.3
Classification of cheilitis 4
Cheilitis is divided into:
Cheilitis (only the lips are affected)
- meteorological cheilitis
- contact cheilitis
- exfoliative cheilitis
- actinic cheilitis
- glandular cheilitis
- chronic cracked lip
Symptomatic cheilitis (lip damage is a symptom of another disease)
- atopic cheilitis
- eczematous cheilitis
- Rossolimo-Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome
- Misher cheilitis
- cheilitis due to hypovitaminosis
Infectious cheilitis is also isolated .
Cheilitis (only lips affected)
Meteorological cheilitis
Most of us have encountered it; it occurs due to weather conditions - wind, cold, high or low air humidity, and dustiness. Men are more likely to get sick because women usually protect their lips with lipstick or balm, and also because men usually work more outdoors.
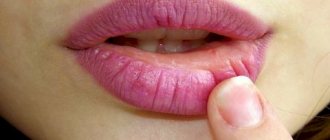
Manifestations : lips are bright red, dry, tight and covered with small scales, in simple terms “chapped”. Dry lips lead to constant licking, which aggravates the disease.
Contact cheilitis
It is a consequence of an allergy to cosmetics, toothpaste, ointments, material of crowns, braces, etc.
Women often encounter it when they are allergic to a new lipstick. Symptoms: dryness, itching, burning, redness and peeling appear at the site of contact with the allergen, blisters may appear that burst, leaving cracks and erosions (superficial defects of the skin and mucous membranes). When contact with the allergen is stopped, the disease goes away and spontaneous relapses do not occur.
Exfoliative cheilitis
It is a chronic (i.e. lasts many years) disease, which is accompanied by peeling.
Causes : disruption of the nervous and immune systems, genetic predisposition and psychosomatic disorders (depressive conditions), predominantly affecting young women. Exacerbations of the disease often occur in the fall, and in the summer the symptoms subside.
It occurs in two forms: dry and exudative (exudate is liquid released during inflammation).
In the dry form , the lips are dry, scales form on them, and sometimes there is itching and burning. After about 7 days, the scales are easily removed, leaving in their place a bright red surface without damage. People “bite off” the scales, but after a few days they form again.
Exudative form of cheilitis
The lips are swollen, painful and bright red, most often only the lower lip is affected.
Large yellow or brown crusts appear on the lips. After removing the crusts, a red surface of the lips with milky exudate is revealed, there are no erosions. With this form, the process never extends to the corners of the mouth and the skin around the lips. The dry form can turn into exudative and vice versa.
Actinic cheilitis
Occurs with increased sensitivity to sunlight.
Men from 20 to 60 years old are more often affected; exacerbations appear in summer and spring.5 The lower lip is affected more often than the upper lip, and can rarely be accompanied by facial eczema (a skin disease characterized by inflammation and itching). There are two forms:
Dry: with this form, the lips become dry and covered with white scales.
Exudative: in this case, the lips are swollen, bright red, bubbles appear, then they burst and crusts, cracks, and erosions form.
Important! This cheilitis can lead to complications. Requires urgent treatment and observation.
Glandular cheilitis
It occurs due to the movement of the salivary glands in the tissue of the lip, their enlargement and strengthening of their function; it can also be caused by a congenital structural anomaly. Those. Normally, there are no salivary glands on the red border of the lips, but with this disease they appear. The lower lip suffers twice as often as the upper lip; people aged 40-60 years are more often affected. There are simple glandular cheilitis and complicated by serous or purulent inflammation .
With a simple form of complaints, there may be no complaints or there may be roughness and tuberosity of the lips.
Serous inflammation is manifested by swelling and redness, as well as the release of drops of light liquid, this is called the “dew symptom”. Due to the constant wetting of the lips with saliva, they peel off, cracks and erosions form. The purulent form occurs due to infection in the salivary glands. The lips are covered with brown or yellow-green crusts, pain and enlargement of the lips appear. There are cracks and erosions around the salivary glands, and purulent exudate is released from them. May lead to the formation of an abscess (purulent inflammation of tissue).
If this form exists for a long time, it can turn into fibrous form , i.e. connective tissue grows, while the salivary glands become clogged, their contents cannot be released, and cavities with fluid - cysts - form inside the lip. With this form, the lips greatly increase in size, their surface is bright red and lumpy.
Chronic cracked lip
The causes of the disease are not fully known; it is believed that psycho-emotional factors, vascular pathology, bad habits, the structure of the lip with a longitudinal crease, and chronic injury occur.
Manifestations: a single, painful deep crack, usually on the lower lip, may affect the mucous membrane of the lip, but never extends to the skin. A peculiarity is the constant appearance of a crack in the same place. If it persists for a long time, the edges of the crack may become denser, and if treated incorrectly, complications may occur.
Why do lips dry out?
Before looking for a way to quickly moisturize your lips, you should find out the cause of the problem. Depending on what formed the basis for the lack of moisture, you can choose a suitable remedy for complete restoration.
Causes of dry lips:
- Harmful environment. Cold, heat, windy weather and poor air quality. Cold and heat provoke a decrease in moisture in tissues. The condition worsens during strong winds.
- Stress. Situations when a person is very nervous and involuntarily licks his lips (a standard human reaction). The saliva that covers the delicate skin dries quickly, drying out the problem area.
- Medicines that affect the salivary glands, for example, drugs aimed at reducing appetite.
- Oral care products with high fluoride content. The element is characterized by a dehydrating effect. Thin skin is not able to retain moisture for a long time, as the dermis does on other parts of the body.
- Cosmetics: long-lasting lipsticks, matte formulations, tints and products with a dry/powdery effect. Pigments for artistic makeup. Powdering for better durability of conventional products speeds up drying.
- Unhealthy lifestyle: poor nutrition worsens the situation with vitamin saturation of the whole body. Lack of water (maintaining water balance is the key to health), alcohol, and tobacco are harmful.
- Diseases that cause dry mouth. These include allergic reactions, lip burns, dental diseases, inflammatory pathologies, bacterial and hormonal diseases.
Excessive dryness can be caused by a cold with a profuse runny nose and nasal congestion. With frequent inhalation and exhalation through the mouth, the lips become chapped and dry. During such a period, it is especially important to know how to keep your lips moisturized.
Symptomatic cheilitis
This is a symptom of atopic dermatitis (atopy is a tendency to allergic reactions). It is more often observed in children and adolescents aged 7 to 18 years, equally often in girls and boys. People suffering from this disease are allergic to many foods and medications, and close relatives have similar symptoms. As a rule, this disease has a genetic predisposition. In most children, symptoms disappear over time; in others, the disease recurs throughout their lives.
The red border is affected, especially the corners of the mouth; the skin around the lips and the mucous membrane of the lips are never affected. Itching appears, the lips become red, slightly painful and slightly swollen, there is also redness, peeling and small cracks in the corners of the mouth, and at the same time a small area of skin around the lips becomes inflamed. When the inflammation subsides, peeling and dryness appear. It may also be accompanied by skin lesions on the elbows, behind the knees and on the cheeks.
Eczematous cheilitis
It has a neuro-allergic nature, often accompanied by facial eczema. The disease can have an acute and chronic course. In acute cases , itching, swelling of the lips, redness first occurs, it becomes difficult to open the mouth, small blisters filled with liquid appear, which merge with each other, burst and become wet, then straw-yellow crusts appear in their place.
The entire red border and a significant area of the skin of the lips are affected. If the action of the allergen continues, the process becomes chronic. In the chronic course , the swelling is less pronounced, the lips are slightly reddish, peeling, cracks and blood crusts are observed.
Rossolimo-Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome
This is a chronic disease, its causes are unknown, and women are affected somewhat more often. It manifests itself with three symptoms:
- paresis (decreased muscle strength and limited mobility) and paralysis (complete lack of movement) of facial muscles
- swollen tongue - macroglossia
- · persistent swelling of the lips – macrocheilia 6
Cheilitis with this syndrome is manifested by swelling, redness of the lips (sometimes with a blue tint), the lips are dry, flaky, and cracks appear. Lip augmentation is asymmetrical. In rare severe cases, a shapeless swollen lip is observed that lags behind the teeth, a distortion of the face and drooping of the corner of the mouth appear.
Miescher granulomatous cheilitis
The disease is manifested by severe inflammatory swelling of the lips, usually of the lower lip; the swelling never disappears completely. Subsequently, the lips steadily increase in size, and the disease can spread to the cheek.
Cheilitis due to hypovitaminosis
With a lack of vitamin A , lips become dry and cracks appear.
With a lack of vitamin B2, cracks appear in the corners of the mouth, so-called “jams”, burning and dry lips, then blisters and crusts appear. Rarely, the lip may swell, it becomes shiny with small scales, painful cracks appear and glossitis (inflammatory disease of the tongue) develops.
With a deficiency of B6, cracks appear in the corners of the mouth, and redness appears on the red border.
With a lack of vitamin PP, the lips become swollen, dry, and cracks form that become covered with blood crusts. The tongue is also affected; it is crimson in color, shiny and smooth.
Infectious cheilitis
More often they appear in the form of angular lesions - jammed.
In the case of infection caused by staphylococci and streptococci, erosions appear, covered with yellow crusts, and the skin around the mouth is often also affected. Opening the mouth is painful, making it difficult to speak and eat. It is also not uncommon for the lymph nodes to become enlarged and painful.
Viral cheilitis
Most often caused by the herpes simplex virus. The disease begins with redness and itching, then a group of blisters appears on the lip, they burst and form erosions, which then become covered with a crust. At the same time, stomatitis and enlarged lymph nodes may appear. Herpes is a chronic infection, so this cheilitis appears again and again. Usually, it reoccurs with decreased immunity (ARVI, influenza, etc.) and stress. The frequency of relapses varies from person to person and depends on the strength of the immune system.
Candidal cheilitis
This is a fungal disease caused by the Candida fungus. The presence of white plaque in the oral cavity and bright red mucous underneath is characteristic. The lips become red, swollen, dry, and covered with gray scales. A combination with damage to the oral mucosa (stomatitis) and tongue (glossitis) is possible. It can also appear in the form of candidiasis - deep cracks in the corners of the mouth, covered with white plaque and scales, more common in older people.6
Important! If wounds on the lips do not heal for a long time or if there are constant relapses of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor!
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms at home
It is not worth treating at home without seeing a doctor. However, there are ways that you can resort to to reduce discomfort:
- If your lips become inflamed due to the sun or cold, it is advisable that they are always covered with a protective layer of balm.
- For severe itching and burning, which occur in almost all forms of cheilitis, cold compresses will help. Before applying them, the skin is covered with a layer of balm so that the lips are treated simultaneously with the reduction of pain.
- If your lips are red and covered with cracks, sores or any other open wounds, you need to make sure that bacteria do not get into them. The surrounding skin and teeth should be treated with a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide or Miramistin. Special antiseptic ointments will have the best effect.
- If pain and itching are unbearable, painkillers can be used. Ointments with a cooling effect will have the same effect.
All methods of folk treatment for cheilitis will be useless if you resort to them thoughtlessly - without consulting a doctor. In most cases, inflammation, redness and itching of the lips are harmless. Such symptoms can go away even without therapy, but sometimes they indicate dangerous diseases, so medical help should not be neglected.
Treatment of cheilitis
Treatment is always complex and depends on the form of cheilitis.
General treatment:
- Normalization of nutrition, adherence to a diet that does not contain allergens, exclusion of spicy, irritating foods
- Taking vitamins, especially group B and PP (nicotinic acid)
- Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral drugs - for infectious cheilitis Important! These drugs are taken only as prescribed by a doctor!
- Antiallergic drugs
- Sedatives Prescribed strictly by the attending physician!
Local treatment:
- Painkillers (if necessary)
- Antiseptics
- Proteolytic enzymes for cleaning erosions
- After inflammation and pain have subsided - healing ointments
- Corticosteroid ointments Important! They are rarely prescribed and only by a doctor, as they have many side effects.
- Physiotherapy
- Surgery
Also, with actinic cheilitis, it is necessary to reduce exposure to the sun, and the mandatory use of cream and lipstick with SPF.
Treatment of cheilitis is often carried out by a dentist together with a therapist and neurologist.
Prevention of cheilitis
Consists of the following items:
- strengthening immunity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- use of creams and lipsticks with SPF
- use of hygienic lipsticks
- balanced diet
- regular visits to the dentist
- proper teeth cleaning at home, as well as professional removal of dental plaque in the dentist’s chair
- avoiding contact with allergens
- undergoing an annual medical examination to identify common diseases
- treatment of systemic diseases
- Antibacterial drugs should be taken exclusively as prescribed by a doctor and in conjunction with a course of probiotics
Is cheilitis treated surgically?
Yes, some forms require surgical treatment (Mischer cheilitis, glandular cheilitis, chronic fissure), but most cheilitis is treated conservatively.
How do you know if you are deficient in B vitamins?
Signs of a lack of B vitamins are fatigue, insomnia, muscle pain, dry mouth, seizures, peeling facial skin, brittle nails, fainting, and memory problems. The surest way is to take a comprehensive vitamin test.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diseases and pathological conditions accompanied by swelling of the lips is carried out by a dentist. According to indications, patients are referred for consultation to an allergist or oncologist. Objective examination methods are of key importance. The diagnostic program includes the following procedures:
- Survey
. The doctor finds out the time and circumstances of the onset of the symptom, determines other manifestations, and examines the dynamics of the course of the disease. - Physical examination
. The specialist evaluates the localization, severity, and extent of swelling, detects other changes (discoloration, cracks, crusts, ulcers), examines the mucous membranes and skin of other areas, and conducts a dental examination. - Lab tests
. If an endogenous cause of edema is suspected, a biochemical blood test is prescribed. To determine the type and level of differentiation of neoplasms and distinguish cheilitis from other pathologies, a biopsy is performed followed by histological examination. - Allergy tests.
Indicated for allergic reactions, prescribed to clarify the allergen. Skin tests, provocative tests, and other studies are performed. Allergy testing is carried out in a specialized office.
Allergy tests