Causes of roughness on the face and head
On the skin of children's faces, more often on the cheeks, rashes and roughness are caused by allergens of household origin, that is, food products. The reason for this manifestation is the products consumed by the nursing mother or those introduced into complementary foods. The baby’s digestive tract is not yet able to cope with the latter, for example:
- Whole cow's milk.
- Chicken eggs.
- Citrus fruits and nuts.
A rash appears in the form of red or pink spots that are flaky and very itchy. Redness behind the ears of newborns may appear due to the frequent flow of formula or breast milk into this area, the excess of which is not eliminated by parents in a timely manner.
A dry spot on the fontanelle or forehead is observed in almost all newborns. If parents do not take measures to combat this, after some time the dry scales will spread throughout the head and will not allow the hair follicle to develop. You can eliminate roughness on your head with the help of special baby oils and a soft brush; with their help, you need to remove dry scales every day and very carefully to prevent them from spreading.
The pediatrician will give a more detailed recommendation for eliminating rough skin on the face and head after examining the baby, and will also recommend a nutritious diet after allergies.
Rough and dry skin on a baby's belly most often occurs due to the following reasons.
Walks in the open air
If peeling appears on the skin, walks are not canceled. They must be daily. You should not keep a newborn with dry skin in direct sunlight for a long time.
Children with skin problems are protected from direct sunlight
If it's hot outside, use UV creams for protection. At any age, children benefit from regular air baths, as well as short light massages.
You should not keep a newborn with dry skin in direct sunlight for a long time.
Features of children's skin
A baby's skin is significantly different from the skin of its parents. She is more vulnerable, gentle. Sweat glands are not sufficiently developed in the first year of life, and therefore the baby has to transfer excess heat through pulmonary breathing. If at the same time the baby has to breathe too dry air, or he lives in a room where, thanks to the efforts of his mother and grandmother, it is hot all the time, then the load on the immature sweat glands increases and the skin deteriorates.
The stratum corneum (the uppermost layer) of children's skin is well supplied with blood, so any scratches on a baby heal faster than on an adult. However, the stratum corneum, which is thin and loosely connected to other skin layers, creates favorable conditions for irritation and injury.
Initially, dry skin in babies practically never occurs due to the saturation of lipids - an innate feature of all toddlers. But these fats perfectly dissolve most of the chemicals that are contained in washing powder, soap, and urine, and therefore inflammation of the skin in children is common. Dry skin can also become due to health problems.
The most common cause of dryness, in which the skin becomes somewhat rough to the touch, is contact dermatitis, says Evgeny Komarovsky.
Features and functions of baby skin
Newborns have very thin, easily vulnerable skin, which loses heat very quickly. It also has an insufficient pH level up to a certain point, which causes various microbial diseases.
In addition, infants have a very low concentration of melanin, a pigment that protects against ultraviolet rays.
The thickness of children's skin becomes close to adult parameters only by the age of 7 years.
The epidermis is the most important part of the human body and performs the following functions:
- Protective. In newborns, this quality is poorly expressed, so their skin is often inflamed and damaged.
- Respiratory. The skin absorbs oxygen and evacuates carbon dioxide. The intensity of skin respiration in infants is much stronger than in adults.
- Sensitive. Receptors that perceive irritation are localized in the skin. In infants, the most sensitive parts of the body are the hands, face and soles of the feet.
- Thermoregulatory. The epidermis gives off heat and evaporates sweat. In babies, thermoregulation is imperfect, so they quickly overheat and become hypothermic.
- Immune. The skin contains cells that carry out many immune responses.
The epidermis is the place of formation of biologically active substances, enzymes and vitamins. This is why it is so important to keep your skin healthy.
Dry skin in a newborn is a natural phenomenon caused by a change in microclimate.
Diathesis (exudative and allergic) in a child
In newborns and infants, flaky areas of skin on the face, tummy, butt, back, arms and legs often appear due to diathesis. Contrary to popular misconception, this phenomenon does not apply to diseases. This is nothing less than a constitutional anomaly. In pediatrics, this term refers to the hereditary predisposition of the body to the appearance of certain pathological reactions or diseases. The table shows the characteristics of the types of this phenomenon.
Bathing helps keep your baby clean and also promotes better blood circulation.
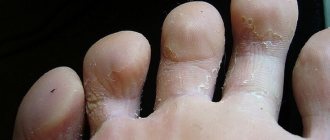
Dry skin on feet
As already mentioned, roughness and dry skin can appear in various parts of the body. Very often such lesions occur on the skin of the legs. Most often, rough skin on a child’s legs is observed in the summer, when high temperatures and wind dry the legs, it cracks and hurts due to loss of moisture. During this period, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes that allow your feet to have maximum air access.
- For better security, it is advisable for the child to wear socks - this will protect the feet and prevent dirt and dust from getting on them, especially if there are already cracks and wounds.
- Before putting your child to bed, it is imperative that you carefully care for his feet. Use baby soap for washing. After this procedure is completed, the feet should be wiped dry, and then a special fortified cream should be applied to soften the skin. It should be rubbed in, carefully massaging the area to be rubbed. This will eliminate roughness of the skin of the legs and reduce its sensitivity, as well as avoid complications.
- With all the well-known prickly heat, the appearance of diaper rash, as well as diaper dermatitis, parents also need to show care and concern. After all, they tend to spread quickly and even in some cases lead to the formation of a pustular rash. There may be no consequences if the child is shown to a doctor in a timely manner and treatment is started.
During this period, it is recommended to wear sandals or other shoes that allow your feet to have maximum air access.
Prevention of dry and flaky skin in children
Everyone is familiar with the well-known truth that it is always easier to prevent a disease than to undergo long and expensive treatment later.
Dry skin and the appearance of flaky spots are no exception, and you need to think about preventive measures in advance.
Use only high-quality mixtures from well-known manufacturers.
Prevention measures
To avoid dry skin, offer your child something to drink often. Make sure there are enough vitamins in his diet. Moisturize your baby's skin after bathing. In your care, use only hypoallergenic products tested by dermatologists.
The creams should include moisturizing and soothing components: panthenol, niacinamide, oils (shea, olive, wheat germ), zinc oxide, vitamins A, B, E, F, plant extracts (chamomile, calendula, string).
Exposure to cold and dry indoor air contributes to excessive dryness of the skin.
Worm infestation
The appearance of dry patches on parts of a child’s body sometimes indicates the presence of parasites in the child’s body. This reason is detected extremely rarely; experts generally associate changes in the condition of the skin with the above factors. Doctors consider dry skin as a reaction to toxins. With this diagnosis, the child will be prescribed antiparasitic treatment.
Treatment of dry skin in children.
Causes of dry and rough skin
The skin of a baby is distinguished by tenderness, thinness and increased sensitivity. Pediatricians identify the following causes of skin problems in children under three years of age:
- Incorrect, unbalanced diet. A lack of vitamins and microelements in a child’s body affects the condition of his skin, making it pale, dry, rough and flaky.
- Violation of the drinking regime. If a baby drinks less than 1.5 liters of water during the day, this leads to dehydration and dry skin.
- Unsuitable cosmetics (baby cream, soap and other hygiene products). It is important to select high-quality cosmetics that include only natural ingredients and are appropriate for the child’s age.
- Allergic reactions.
- Hormonal disorders.
In some situations, dry skin becomes due to frequent bathing, dry indoor air and other external factors.
However, sometimes a similar phenomenon in children can act as one of the symptoms of diseases that require competent and timely treatment:
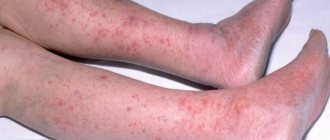
- Atopic dermatitis is a hereditary allergic disease. With this pathology, the child’s skin (not only on the legs, but also on the face and other parts of the body) becomes dense, rough, and covered with crusts.
- Eczema - accompanied by dryness, itching and burning sensation in the affected areas.
- Dermatitis - with this disease, individual dry spots appear on the child’s skin, having a predominantly round shape.
- Renal pathologies - manifested by disturbances in the process of urination, painful sensations localized in the lumbar region, permanent lack of appetite, and general weakness. The skin becomes not only dry, but also acquires a painful yellowish tint.
- Ichthyosis - with this disease, the skin becomes covered with blisters and specific scales.
- Hypothyroidism is a disease caused by disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, accompanied by swelling, dry hair and skin, brittle nail plates, general weakness and increased fatigue.
If a child has such symptoms, especially if they persist for a long time, despite proper care for the baby, it is important to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible.
Dry skin in a newborn
The problem is often associated with the physiological characteristics of the structure of the outer covering of infants. The fact is that the baby has difficulties with heat transfer, which is associated with insufficient development of the sweat glands.
The epidermis of an infant contains an increased amount of lipids, which, on the one hand, protect his skin from external influences, but on the other, can lead to dryness and irritation.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of dry and rough skin in a newborn:
- general overheating of the body;
- prolonged exposure to the sun;
- the use of air conditioners and heaters that dry out the air in the room;
- violation of hygiene standards.
To avoid troubles such as dry skin, you need to properly care for your child and humidify the air during the heating season, using special devices for this purpose or placing containers of water around the apartment.
Symptoms of diathesis
Inflammation of the skin during diathesis is the body's reaction to contact with an allergen. The main way an allergen enters a child’s body is food, but a reaction to contact with the skin of the allergen is also possible (the allergen, for example, can be components of washing powder that get on clothes during washing, plant pollen, dust, animal hair, etc.).
Diathesis in children under 3 months of age
The first manifestations of diathesis most often appear at the age of 2-3 months. This:
- diaper rash that does not disappear even with careful care;
- profuse prickly heat with mild overheating;
- sebaceous crusts of gray-yellow color on the head in the hairline area (seborrhea).
Diathesis in children aged 3 months and older
In older children, a typical manifestation of diathesis is red spots on the cheeks. As the condition worsens, the skin becomes crusty. The crusts become wet, the child experiences discomfort, itches, becomes excitable, sleep and appetite may be disturbed, and loose stools may appear.
Which doctor should I contact?
If your child has dry and rough skin on his legs, and even more so if there are other alarming symptoms, you should see a pediatrician.
The doctor will conduct an examination, study the clinical picture, analyze the collected medical history, and write out directions for tests. If necessary, the local pediatrician will refer you to such highly specialized specialists as a pediatric dermatologist, allergist, and endocrinologist.
Prevention of allergies in a child after birth
Only breastfeeding a baby until at least 5-6 months will reduce the risk of developing allergies.
Complementary foods are introduced during the “tolerance window” period (4-8 months), when the child reacts to new foods with minimal allergic manifestations.
It is better to prepare complementary foods yourself. This way, parents can choose a heat treatment option that will reduce the likelihood of developing allergies. Long-term cooking (at least 20 minutes) followed by removal of the water in which the product was cooked is preferable.
It has been proven that if a child lives in the same room with pets for up to a year, then in the future he may develop immunity to allergens from cats and dogs.
It is important to maintain a hypoallergenic lifestyle - a minimum of carpeting, rugs, and heavy curtains.
All these things are dust collectors. Wet cleaning is carried out at least 2 times a week.
Treatment
Therapy for dry skin of the feet in a child is prescribed individually, depending on the root causes that provoked this phenomenon and the age category of the little patient.
If dry skin is a symptom of a certain diagnosed pathology, then first of all it is necessary to treat the underlying disease. The course of health measures is developed by the doctor depending on the diagnosis, the age of the child, the stage and degree of the pathological process, and other features of a particular clinical case.
If the problem is caused by allergic reactions, poor nutrition or skin care for the baby, then it is enough to adjust your lifestyle to achieve positive results.
Medicines
Medications are prescribed for diseases such as dermatitis, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, renal and endocrine pathologies. Systemic medications are selected by a doctor according to an individual scheme. If dry, rough spots appear on the baby’s skin, the use of external medications (Fenistil ointment, etc.) may be recommended.
In the case of atopic dermatitis or severe allergic manifestations, the child is prescribed ointments and creams that contain hormones - glucocorticosteroids. Such drugs provide a good therapeutic effect, but they should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, strictly observing the dosage.
Hormonal drugs are discontinued gradually, reducing the amount of the drug over several days. In particularly complex, advanced cases, the use of antihistamines, calcium, and glucocorticosteroids may be recommended.
Diet
Diet therapy is the main method of treating and preventing dry skin in children. If the baby is breastfed, then the mother should exclude from the menu all foods that cause allergies.
If the problem arose after the introduction of complementary foods, it is recommended to restore the child’s usual diet for two weeks, and then reintroduce complementary foods.
Any product is included in the menu in a minimum quantity for three weeks. Such a scheme helps doctors identify the presence of a certain food allergen in a child that negatively affects the skin.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis and emollient therapy
The basis of treatment is to constantly moisturize dry, damaged skin and prevent provoking factors.
Before bathing, the child’s skin must be cleaned of crusts with aqueous solutions and syndets (soap substitutes, cleansers without adding alkali), because Antiseptics are effective for a short time. In the last 2 minutes of bathing, add softening oil to the water. Doctors recommend adding sodium hypochlorite to reduce itching and inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Products with emollients are well absorbed by the skin - these are fatty components of cosmetics. Emollients are prescribed in a dose of at least 150-200 grams per week in young children and up to 500 g in adults. Cream with emollients is applied immediately after the bath, for 2-3 minutes. In winter, emollients with a large amount of lipids are prescribed. Glycerin in the base of emollients is better tolerated than urea.
It is necessary to constantly, often and in large quantities use moisturizers and emollients (at least 3-4 times a day) both independently and after water procedures using the “wet and spread” principle.
After water procedures, the skin must be wiped with blotting movements, avoiding friction.
Corneoprotectors (products that protect the stratum corneum) should be used on unaffected skin.
Consequences
If timely measures are not taken, dry skin on a child’s feet can lead to the following complications:
- the appearance of painful cracks;
- ulcerative, erosive lesions of the skin;
- eczema;
- chronic form of atopic dermatitis.
If the cause of dry and rough skin lies in the last of the listed points, then the development of chronic allergic reactions, bronchial asthma, and neuropsychiatric disorders is possible.
Types of allergies in children
What symptoms in a child can be considered allergic? As a rule, true (IgE-mediated) allergies in children have severe symptoms.
The most common manifestations of the disease:
- hives, in which pale pink itchy lesions appear on the skin;
- swelling of facial tissues and redness of the upper half of the body is a serious condition that requires urgent medical attention. Associated symptoms are swelling of the tissues of the face and upper body, difficulty breathing;
- allergic bronchial asthma;
- symptoms of intoxication - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
- eczema, in which areas of redness, blisters with liquid, and itching appear on the skin;
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- allergic rhinitis.
In addition, in children, allergies can manifest themselves in the form of enterocolitis (inflammation of the large and small intestines). Most often, enterocolitis is observed in children due to an incorrectly selected mixture. Such children need a therapeutic mixture based on protein hydrolyzate or amino acids.
In children diagnosed with eczema, allergies are not always the only provoking factor of the disease. Most often this is a polyetiological disease that develops for many reasons. One of the culprits is an inherited defect in the filaggrin gene (a structural protein of the skin).
For eczema, consultation with an allergist-immunologist and observation by a dermatologist is necessary. A diet limiting confectionery products and foods high in histamine is definitely recommended.
The intensity of allergy manifestations may vary. The interval between the onset of symptoms ranges from a few minutes to 2-4 hours.
Attentive parents will definitely notice warning signs and contact a specialist in time.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent any problem than to treat it. To avoid dry and rough skin on a child’s feet, doctors advise parents to pay attention to the following preventive recommendations:
- Take care of the child’s proper, balanced nutrition, provide his body with the necessary amount of vitamins A, B and E.
- Give your child as much fluid as possible, especially during hot periods, giving preference to clean water, milk, natural juices, and fruit drinks.
- Use natural children's cosmetics and avoid regular soap.
- Choose high-quality shoes made of genuine leather for your child that match his size.
- Avoid using socks, tights, and rompers made from synthetic materials.
Dry skin on a child’s feet is not the most serious problem, but this symptom causes the baby some discomfort and may also indicate the development of serious allergic diseases. Therefore, you should not ignore such a manifestation. Provide your baby with proper care, and if this does not help, first consult a pediatrician.
Infant skin care rules for the prevention of dermatitis
- Bath at least 2-3 times a week (ideal temperature - 37 °C, duration 15 minutes);
- Apply moisturizer after swimming;
- Carefully examine the area behind the ears and folds of skin (elbows, knees, groins): there may be redness or peeling;
- At each diaper change (every 2-3 hours), protect the skin with cream;
- Use cosmetics approved for use in children.
Atopic dermatitis is a multifactorial inflammatory skin disease characterized by itching, a chronic relapsing course and age-related characteristics of the localization and morphology of lesions.
During an attack, dermatologists advise using creams or ointments with dermocorticoids; they help eliminate the symptoms of the disease. Once symptoms subside, emollient creams restore moisture to very dry skin. It also helps prevent new attacks. Creams for allergy-prone skin should be applied to the entire body once or twice a day.
Attention: topical corticosteroids should not be applied under the diaper of newborns and infants in order to prevent primary diaper dermatitis - infantile gluteal granuloma.
To reduce the number of attacks, doctors recommend:
- take a shower instead of a bath
- Use gentle, fragrance-free, soap-free cleansers
- wear cotton clothes rather than wool and synthetic ones.
- maintain low room temperature.