July 5, 2020
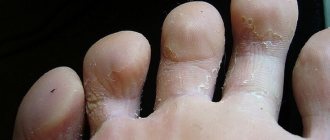
Dry patches on the skin are a common dermatological symptom that can indicate either a temporary failure and disruption of the barrier functions of the epidermis, or a skin disease. It all depends on the size of the spots, the clarity of their boundaries, as well as the duration of their presence on the skin.
The causes of dryness can be divided into two large groups:
- nonspecific - allergic reactions to household chemicals, laundry soap, cosmetic products, dehydration due to cold and wind;
- specific - then the spots become a manifestation of dermatological diseases.
Sometimes a person himself may notice that dry spots appear on his skin after a certain event occurs, for example, after washing clothes by hand. Then the reason is obvious and easy to eliminate. But if dry spots on the skin do not go away, they itch, or flake, you should consult a doctor.
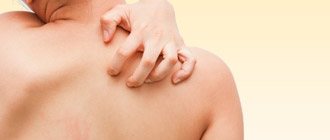
What is itchy skin like?
Itching of the skin can be of various types:
- Physiological and pathological itching. In the first case, the skin may itch due to some mechanical or chemical irritants, as well as insect bites. Pathological itching is a sign of a skin disease or other pathological condition, for example, neurological disorders or hormonal imbalance;
- Localized and generalized itching. Itching can be localized in a specific place, for example, under the hair on the head, in the genital area or anus, etc. As a rule, the symptom is paroxysmal in nature, often combined with other pathological manifestations of a particular disease. We are talking about generalized itching when literally the whole body itches. Often the symptom is associated with an allergic reaction or dry skin caused by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- Constant and paroxysmal itching. With constant itching, the symptom persists throughout the day, its intensity may increase at a specific time of day, often in the evening. Paroxysmal itching appears independently or under the influence of certain irritating factors.
Atopic dermatitis and its differences from psoriasis
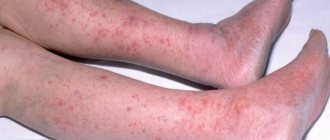
Atopic dermatitis may also cause dry patches to appear on the body. And as with psoriasis, they cause itching. Due to the increased sensitivity of the skin to environmental factors, the mechanisms of its self-regulation are disrupted, including the barrier function. That is, the trigger for atopic dermatitis is an allergy, but the tendency to such a skin reaction is genetically determined.
Most often, atopic dermatitis occurs in children. The disease has a chronic course, when exacerbations are replaced by periods of remission. Here are the typical signs of atopic dermatitis:
- dry skin;
- peeling and redness of the eyelids;
- dry flesh-colored plaques on the trunk and extensor areas of the body;
- cracks.
It is difficult for a person without medical education to distinguish psoriasis from atopic dermatitis, but a doctor can easily make a differential diagnosis. There are several differences that may speak in favor of one or another pathology. Atopic dermatitis most often affects children, psoriasis can debut in adulthood. Psoriatic plaques are raised above the skin, and scales can be seen. Dry spots in atopic dermatitis are flat. It is also important to consider the typical location.
Useful links: State Center of Urology in Moscow - Clinic of Urology named after R. M. Fronshtein of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov
When to see a doctor
You should consult a dermatovenerologist if skin itching and peeling do not go away for a long time (more than two weeks), contribute to sleep disturbances and decreased performance during the day, spread throughout the body, and are combined with other pathological symptoms. These symptoms in combination with an inflammatory or infectious process require urgent contact with a specialist.
Itchy skin, as well as flaking of the skin, can indicate a serious illness, the absence of treatment of which will lead to serious complications. Experienced doctors at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribe adequate therapy for the identified pathology in order to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and their cause.
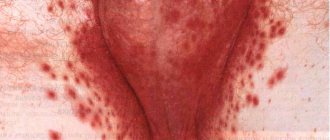
Dry patches with scales
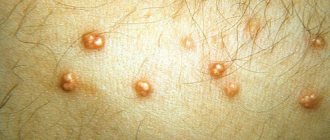
Pink, raised, dry patches on the body and head may indicate psoriasis. With this dermatological pathology, raised plaques appear on the skin of a person - psoriatic papules. They protrude above the surface of the skin, cause intense itching and flake, and tend to spread and coalesce.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease in which rashes are most often localized on the elbows, head, knees and groin. Dry pink spots covered with white scales are foci of chronic inflammation. Under the influence of internal autoimmune processes, epidermal cells divide several times faster than necessary. As a result, small flakes of dying skin cells are constantly separated.
What diseases cause itching and flaking of the skin?
There are quite a few diseases accompanied by itching and peeling of the skin of varying degrees of intensity and prevalence:
- allergies to food, medications;
- contact dermatitis;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- eczema;
- fungal skin diseases;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- infectious diseases;
- diabetes;
- hormonal disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- blood diseases;
- parasitic diseases (scabies, demodicosis, etc.).
Dry eczema
Sometimes white, dry, flaky patches on the skin of the legs can indicate dry eczema. With this disease, dryness and tightness of the skin first occurs, then peeling and unbearable itching occur, and cracks may occur. In addition to the legs, the hands, the space between the fingers, and even the face are often affected.
The causes of dry eczema can be bacterial and fungal infections, allergens, synthetic clothing, poor hygiene and other factors.
As you can see, the appearance of dry patches on the skin can be due to a variety of reasons.
The characteristics of the immune system and the tendency to allergic reactions play an important role. But in any case, when dry spots appear, it is important to consult a dermatologist and determine the cause of this skin condition. July 5, 2020
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
Causes of the disease
The reasons for the development of the disease are not completely clear. Seborrheic dermatitis is not a disease of the sebaceous glands, although it develops in areas saturated with them.
A significant role in the development of the disease is played by yeast-like fungi of the genus Malassezia (they exist on the skin of most healthy people, but in some they can cause rashes and skin irritation), the composition of lipids on the surface of the skin, as well as the characteristics of the immune response to Malazessia fungi and their metabolic products.
In adults, severe disease is associated with the following conditions:
- oily skin (seborrhea);
- lack of sleep and stress;
- history of seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis in relatives;
- states of immunosuppression (organ transplantation, HIV, lymphoma);
- neurological or psychiatric disease.
The main cause of seborrheic dermatitis in children is increased activity of the sebaceous glands (rapid growth and secretion of sebum), which occurs due to the circulation of maternal hormones in the child’s blood in the first weeks of life. Malacesia is not a leading factor in children, unlike in adults.
Forms and complications of seborrheic dermatitis
There are pediatric and adult forms of seborrheic dermatitis.
Sometimes the disease is associated with psoriasis (seborrheic psoriasis).
The severity of the disease varies from mild dandruff to severe erythroderma. Dandruff affects the scalp in the hair growth area. In 70% of children, seborrheic dermatitis usually appears by 3 months of age and resolves spontaneously by 6-12 months.
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis begins in adolescence. Predominant in young and elderly people. More often affects men.
Symptoms
Seborrheic dermatitis is manifested by redness, peeling with “oily” scales with a certain localization of foci.
In children - isolated on the scalp (in the frontal area it is called the “baby cap” or “milk crust”), behind the ears and in the external auditory canal, on the face (in the area of the eyebrows, wings of the nose), on the back of the neck (along the edge of hair growth), in areas of skin friction (in folds), under diapers.
Sometimes seborrheic dermatitis in children is widespread. These are rashes in the form of spots with greasy crusts, merging into larger areas. In some cases it is accompanied by itching.
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis is presented in the scalp area, on the face: in the area of the eyebrows, behind the ears, inside the ears, on the wings of the nose and in the areas of the cheeks adjacent to the nose.
It can manifest itself as separate spots with peeling, total damage to the scalp, damage to the eyelids in the form of blepharitis, damage to the chest wall in the form of individual nodules and spots with crusts on the surface, inflammation of the hair follicles on the skin of the upper half of the body (ostiofolliculitis).
What can you do at home?
At home, to eliminate negative skin reactions - rashes, redness, peeling, you can use decoctions of medicinal plants - chamomile, string. Washing with decoctions of these plants helps eliminate inflammatory skin processes and improves the condition of the skin. Perfectly eliminates skin itching - a decoction of flaxseed. Skin diseases of a fungal nature have long been treated with birch tar.
The skin is the largest human organ, which is connected to all vital systems of the body. Therefore, any skin rash cannot be ignored. Beautiful skin is healthy skin. Take care of your health and your skin will have a radiant, fresh look. Be beautiful!
Solving the problem yourself
Temporary, or transient, redness of the facial skin is not considered a pathology. It disappears on its own and does not cause much discomfort other than psychological. To remove occasional cases of hyperemia on your own, you should follow simple steps:
- Remove the irritating factor
. Change the environment, wash off the allergen or toxic substance from the surface of the skin, try to calm down. - Restore natural skin color
. Folk remedies and herbal remedies help with this. You must first make sure that you are not allergic to the components. - Take care to strengthen the protective barrier
. To do this, it is advisable to carry out a set of measures aimed at improving the health of the body as a whole and maintaining the functional properties of the skin.
The following recommendations can also help get rid of a red face, but will require a long time and lifestyle adjustments.
Gentle cleansing and care.
You should wash your face with warm water, without contrasting temperatures, and dry with a soft towel with light blotting movements.
Prevention of infections.
An important rule is to never touch your face with your hands unnecessarily. The habit of removing pimples yourself can lead to infection not only local, but also general. Even with minor damage and scratches, it is worth immediately treating the area of microtrauma with an aseptic substance.
Lifestyle.
The diet must contain foods rich in fiber and vitamins.
It is worth avoiding the consumption of salty foods, smoked meats, spicy seasonings and alcohol. Good sleep and a calm microclimate also help remove redness on the face. Caring cosmetics.
The beauty industry provides a wide range of cleansing, lipid-restoring and healing products. It can be difficult to understand them on your own, however, dermatologists recommend not to get carried away with cosmetics based on alcohol solutions and to carefully choose them. Individual consultation
Carrying out therapeutic therapy
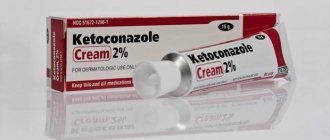
When it is confirmed that a red spot with a white center is of fungal origin, antifungal drugs are used. This may be Lamisil, Clotrimazole (effective in the early stages of the formation of the disease). In case of a complicated course of the pathological process, it is allowed to prescribe systemic treatment - a combination of local and general drugs. Fluconazole and Clotrimazole may be prescribed, which have minimal negative effects on the liver.
If the red spot is of infectious origin, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
If elements of the rash appear due to allergies, then taking antihistamines is justified.