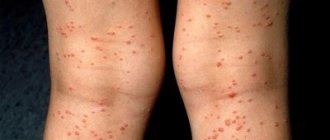
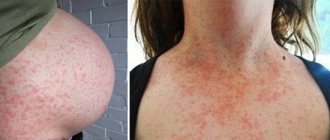
Human papillomavirus infection today is the most common disease with predominant sexual transmission.
The causative agent of the infection is human papillomavirus, abbreviated as HPV.
Young women aged 20-35 years have the greatest risk of contracting HPV.
Although in most cases the infection is asymptomatic and tends to heal on its own, sometimes papillomaviruses cause serious conditions.
Such as anogenital warts and cervical cancer (93% of all episodes of the latter disease are associated with HPV, of which 70% are provoked by HPV types 16 and 18).
Of particular interest to women of reproductive age is the answer to the question: does HPV affect pregnancy?
The fact is that during pregnancy, changes in the hormonal background and immune system of the body contribute to the “retention” of HPV, increasing the risk of a woman becoming infected and transmitting the virus to her partner.
In addition, any infection in the mother's body can affect the health of the unborn child.
What is HPV infection?
A specific feature of HPV is its tendency to infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes.
Several dozen known types of human papillomaviruses are grouped into three groups according to their ability to provoke cancer.
In this case, they distinguish:
- non-oncogenic, examples of which are types 1,2,28, 41, etc., responsible for the appearance of skin warts (plantar, vulgar, etc.);
- with a low risk of developing oncopathology, such as types 6,11, 15, 25, 43, etc., infection with which can manifest itself in the form of anogenital warts (otherwise genital warts) and be accompanied by the development of malignant transformations only in extremely rare cases;
- with high risk, including types 16, 18, 33, 52, etc., infection with which is associated with precancerous/cancerous changes in the cervix, as well as a disease such as bowenoid papulosis.
When is it necessary to remove papilloma?
Benign skin tumors cannot always be removed; sometimes observation and regular examinations are sufficient. The most common indications for removal are the following:
- papillomas located on visible parts of the body and causing psychological discomfort;
- papillomas that are constantly injured by clothing, jewelry, and a comb;
- neoplasms that increase in size, tend to spread, change size, shape and color;
- papillomas located in the intimate area or soles;
- if the tumor begins to hurt, itch or bleed.
How does HPV infection occur?
Papillomaviruses can only be transmitted from person to person.
Since some types can persist for a certain time in exfoliating skin cells, they may pose a risk of household contact infection.
This option is typical for the non-oncogenic group; for example, infection with the formation of plantar warts is likely in the presence of microdamages to the skin of the feet.
Low- and high-oncogenic viruses are transmitted sexually, including various types of sexual contact.
Infection of newborn children by sick mothers occurs occasionally.
Interestingly, women with diabetes, when their glucose levels are well controlled, do not have an increased risk of HPV infection.
The incubation period is quite long and can vary from three months to several years.
How does the infection manifest?
Symptoms of infection are determined by the type of virus and the type of illness it causes.
HPV can be located either outside the cell chromosomes, the so-called. benign form of the disease, and integrated into DNA, the malignant form.
The following development options are typical for human papillomavirus infection:
- latent course - without cell changes, without symptoms;
- the formation of warts, condylomas, papillomas, when the virus affects cells, provoking their growth;
- neoplastic changes (dysplasia) – changes in cellular structure under the influence of a virus;
- carcinoma formation - the appearance of numerous atypical cells characteristic of a cancerous tumor.
An important feature of HPV infection is its ability to self-heal.
In 90% of all episodes of infection, the virus is destroyed by the body within two years.
Clinical manifestations of infection are quite characteristic.
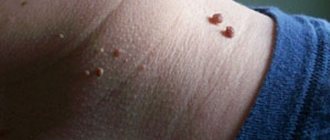
Thus, vulgar warts look like grayish-brown warty nodules, which are usually located on the fingers and the back of the hands.
Flat warts affect the face and hands and usually appear during adolescence.
Plantar warts appear in areas where the skin rubs against shoes and are characteristic thickenings that are painful when pressed.
Genital warts are shaped like a rooster's comb or a cauliflower stalk, have a thin stalk and a wider head.
In women, such formations are usually located at the entrance to the vagina, in the area of the labia and anus. Multiple flat papules, as a manifestation of infection caused by HPV of low oncogenic risk, are called epidermodysplasia verruciformis.
With laryngeal papillomatosis, typical growths are detected in the larynx.
Dome-shaped and flat, smooth, velvety papules on the genitals are a characteristic manifestation of bowenoid papulosis.
The cause of which is predominantly HPV-16 (a representative of the high oncogenic risk group).
Malignancy of such formations is observed in approximately 3% of episodes.
Dysplasia (neoplasia) of the cervix is a process of atypical changes in epithelial cells in the zone of transition of squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium.
This condition is considered precancerous.
Depending on the severity of cell changes, different degrees of dysplasia and cancer itself (squamous cell carcinoma) are distinguished.
Promote the development of dysplasia:
- multiple pregnancies and births before the age of 20;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- promiscuity;
- chronic inflammation of the uterine cervix;
- damage by genital warts;
- smoking, etc.
Reasons for the development of skin tumors
- prolonged exposure to direct ultraviolet rays;
- global disruptions in the immune system (granuloma annulare);
- decreased protective functions of the body (plantar and palmar warts);
- bad habits;
- frequent stress;
- disturbance of metabolic processes in the body (keratomas, fibromas, nevi, xanthomas);
The main danger to human health is due to the fact that many benign tumors are prone to malignancy (malignancy).
Only complete removal of the tumor can prevent its malignancy. Patients of the multidisciplinary medical center have access to a full range of services in the field of detection and treatment of dermatological tumors. Surgical treatment of tumors in our clinic is carried out by highly qualified plastic surgeons and dermatosurgeons; advanced equipment is used during the procedures. During surgical treatment of tumors, our patients are provided with the maximum therapeutic and aesthetic effect.
What are the consequences of HPV during pregnancy?
To date, there is no reliable evidence of a pronounced negative impact of infection on the course of pregnancy.
Pregnancy pathologies such as miscarriage, premature birth, etc., which are characteristic of other sexually transmitted infections, have not found unconditional confirmation of the connection with HPV.
However, if a woman’s primary infection occurs during pregnancy, there is a risk of developing various complications.
Anogenital warts in the mother caused by HPV types 6 and 11, localized in the area of the labia minora and the vestibule of the vagina, have some consequences for the fetus during pregnancy.
Such genital warts carry a small risk of infection of the fetus during childbirth, leading to the development of respiratory papillomatosis in the latter.
Respiratory, or otherwise laryngeal, papillomatosis (also called laryngeal papillomatosis) most often develops in children 2 to 3 years old.
As a result of infection from a sick mother during the latter’s pregnancy or immediately at birth.
The route of transmission during pregnancy through the placenta, during childbirth or immediately after it is not yet entirely clear.
The main symptoms of the disease are hoarseness, up to the complete disappearance of the voice, and difficulty swallowing.
As the disease progresses, shortness of breath and cough appear.
In severe situations, blockage of the upper respiratory tract and asphyxia are possible, especially in the case of formations with a long thin stalk.
During examination using a laryngoscope (sometimes a bronchoscope is also used), typical growths - condylomas - are found on the laryngeal mucosa.
This pathology has a rather aggressive course: after removal of the formations, relapses often occur, requiring repeated surgical interventions.
If pregnancy occurs due to infection with highly oncogenic papillomaviruses (especially HPV 16, 18), the woman must inform her obstetrician-gynecologist about the presence of infection.
The fact is that changes in a pregnant woman’s body can provoke more intense cell transformation.
Actually, such viruses do not affect the course of pregnancy itself or the child, but they pose a certain threat to the woman’s health.
In a situation where no infection was detected in the past, a cytological Papanicolaou smear (Pap test) is taken, among others, when registering.
If the analysis shows abnormalities, the doctor prescribes additional tests (for example, colposcopy).
Also, situations when pregnancy occurs in women with erosion require special attention.
PCR diagnostics are required to exclude infection with high-oncogenic risk HPV.
As a rule, in the routine practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist, such a combination as HPV and pregnancy is not specifically examined.
Tests for the virus are recommended only if pathological abnormalities are detected.
At the same time, there are research studies demonstrating the effect of the virus on pregnancy.
Thus, it has been shown that infection of women with HPV slightly reduces the likelihood of embryo implantation, and in men it reduces sperm motility.
And since in a married couple, as a rule, both partners are infected, the onset of pregnancy is associated with some difficulties.
As a result, when planning a pregnancy against the background of an infection caused by HPV, planning an IVF procedure, this factor should also be taken into account.
Post-procedure care
For a quick and complete recovery and to avoid possible complications, the following measures are recommended:
- avoid contact with water in the first 2-3 days;
- Do not remove the crust that has formed (it will fall off on its own);
- Treat the wound with an antiseptic 2 times a day;
- protect the manipulation site from injury;
- wounds and new skin formed must be protected from ultraviolet radiation;
- refrain from shaving and epilation if the papilloma was in this area until complete healing.
How is HPV diagnosed in pregnant women?
First of all, the diagnosis of infection begins with a clinical examination.
Genital warts, like other types of formations, are easily identified by their appearance.
If condylomas are present, examination of the cervix is also required.
In most cases, HPV infection is diagnosed on the basis of a Pap test, which is the primary screening for precancerous changes and cervical cancer caused by the virus.
Papanicolaou cytological examination is a variant of microscopic examination using various groups of dyes.
There are characteristic signs of cell changes detected in this study that support infection with the papilloma virus.
These signs include:
- koilocytosis - a change in the shape and color of the nucleus, an increase in the number of nuclei, the appearance of vacuoles in the cell;
- the appearance of dyskeracites - small cells with colored nuclei and altered cytoplasm.
Another test for HPV during pregnancy is papillomavirus typing using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
However, due to its high sensitivity, such a study often leads to overdiagnosis of diseases, since in most cases the infection is short-term.
This method is important when HPV is detected against the background of a characteristic clinical picture.
As a result, global medical guidelines do not recommend the use of PCR as a prognostic test in women under 30 years of age.
At an older age, such a study, especially in the case of determining the group affiliation of the virus, is more significant.
If necessary, additionally resort to instrumental diagnostic methods, such as colposcopy and urethroscopy.
Colposcopy and biopsy with histological examination are performed for all women with neoplasia detected during the Pap test.
During colposcopy, a test with acetic acid and Lugol's solution is also performed.
A colposcopic sign of HPV infection is uneven staining with iodine solution, blanching of areas after treatment with acid.
How is HPV infection treated during pregnancy?
When infected with HPV, pregnancy and childbirth have some specifics.
Thus, in some women with HPV infection, during pregnancy, the manifestations of the disease may increase, such as changes in cervical cells and genital warts.
However, doctors are usually in no hurry to prescribe treatment.
Since the latter can provoke premature birth, in addition, after childbirth, the manifestations of infection may noticeably decrease on their own.
Therefore, it is recommended, if possible, to adhere to expectant management and dynamic monitoring of the pregnant woman.
However, there are situations when genital warts grow noticeably and their number increases.
They merge into giant formations.
Women may experience pain when walking, difficulty defecating and urinating.
During childbirth - traumatization of formations, bleeding, problems with the passage of the fetus through the birth canal, ruptures of the vaginal walls.
In such cases, it is necessary to remove condylomas before delivery.
If the removal of the formations could not be carried out on time, the doctor may decide to deliver the patient by cesarean section.
In routine practice, this measure is not used to prevent fetal infection.
Since there is no reliable data confirming that cesarean section prevents the development of respiratory papillomatosis in children of sick mothers.
If abnormal cell changes were detected during pregnancy, a Pap smear test should be repeated a few weeks after birth.
Often, after childbirth, both genital warts and cellular changes disappear on their own.
Accordingly, treatment of such conditions is not required.
In other situations, certain therapeutic procedures are carried out.
In pregnant women, removal of condylomas can be carried out through cryotherapy, using a carbon dioxide laser, electrocoagulation, or surgitron.
For large, easily traumatic formations, it is recommended to remove them surgically after the first trimester until the 36th week of pregnancy.
The use of drugs such as podophyllin, 5-fluorouracil, as well as the use of intralesional interferon is not allowed during pregnancy.
Accurate diagnosis and quality treatment versus quick and cheap removal of papillomas
Although some types of HPV cause cancer, many people ignore them.
“Well, just think, several skin tumors. I’ll go to a beauty salon and quickly remove them,” that’s what they think.
Not everyone wants to go to a medical center to get rid of papillomas. This is why such people often have problems with incomplete removal of tumors or even complications due to improper treatment of papillomas.
You will avoid these troubles if you remove the papilloma in the clinic.
If you absolutely need to get rid of a tumor, contact experienced dermatologists.
Removing a papilloma on the vocal cord, mouth or lip is very difficult. You definitely don't want to go through this procedure twice. But if the operation is unsuccessful, then you will have to pay for the removal of the tumor again
Therefore, we recommend making an appointment with a medical doctor.
Our doctors will carefully review your medical history and ask additional questions. Then they will examine the papillomas that are bothering you. Dermatologists will check all suspicious tumors with an electronic dermatoscope Delta 20 T. This device helps to detect the degeneration of tumors in the early stages.
Our doctors remove papillomas on the face, neck, chest, mouth and other parts of the body. Make an appointment with dermatologists at the Lasersvit clinic and they will get rid of tumors in 1 session.
Do you want to know how much this procedure costs?
Now we will try to answer this question.