Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
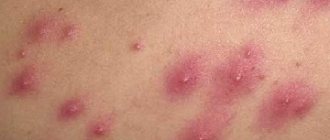
Folliculitis is an infectious process that develops in the middle and deep parts of human hair follicles. The pathology is accompanied by the formation of multiple pustules with purulent contents. The causative agent of the disease can be bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. As the infection progresses, the number of pustules on the patient's skin increases. When the primary lesion is opened, ulcers form, and when they heal, small scars form.
general information
The pathology is widespread among residents of countries with high humidity and air temperature. Such climatic conditions contribute to the spread of infectious lesions of the hair follicles. The risk group is represented by socially disadvantaged segments of the population: a person’s failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene leads to the active reproduction of pathogens on the skin.
Often the causes of folliculitis are superficial inflammation of the follicles - ostiofolliculitis. The spread of infection to the lower parts of the follicle leads to the formation of purulent pustules.
Folliculitis: causes of inflammation
The causative agents of the pathology are predominantly Staphylococcus.
They belong to the order of gram-positive bacteria.
Less common is folliculitis, the occurrence of which requires other infectious agents: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, treponema, gonococcus.
The reasons are:
- fungal infection of the skin: candidiasis, Malassezia, Microsporum
- viral infections: herpes, chickenpox
- parasitic pathogens: acariases, mites
The risk of infection increases with various injuries, burns, chronic venous ulcers and other skin disorders.
People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to the disease.
Reasons for the development of pathology
In 70% of cases, inflammation of the hair follicles develops under the influence of staphylococci and streptococci. Somewhat less frequently, the causes of the disease are pseudomonas, pathogens of syphilis and gonorrhea, or Candida fungi. Molluscum contagiosum and herpes zoster viruses are less common causes of folliculitis. About 10% of clinically recorded cases of inflammation of the hair follicles occur due to the activity of parasitic mites Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis.
Pathogens enter the follicles through damaged areas: scratches and abrasions. People suffering from itchy dermatitis and excessive sweating are susceptible to infection. The weakening of the patient's immunity leads to the penetration of infection into the hair follicles. For this reason, dermatologists recommend taking preventive measures for men and women with diagnosed diabetes and chronic infections. The disease often occurs in HIV-infected people and patients taking immunosuppressive drugs.
What causes inflammation?
The infectious agent penetrates into the cavity of the hair follicle through microscopic damage, provoking an inflammatory reaction.
The likelihood of a pathological process is several times greater in patients with skin disease.
Such as eczema, dermatosis, various types of dermatitis.
The weakening of the barrier function of the skin contributes to the development of the infectious process.
The presence of diabetes mellitus in the patient is identified as provoking factors.
Diabetes is accompanied by a violation of the protective function of the immune system.
Elevated blood sugar levels and its presence in the urine cause frequent bacterial infections.
This is due to the ability of some types of pathogenic microorganisms to draw energy from glucose (simply, to feed on it).
The second provoking factor is acute immunodeficiency conditions: HIV, AIDS.
Long-term use of corticosteroids weakens the immune response and causes general immunosuppression.
The main result of a compromised immune system is the body's inability to fight infections.
Types of pathology
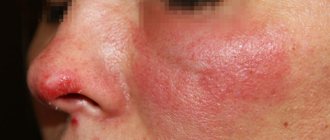
In the process of diagnosing folliculitis, dermatologists determine the form of the disease that the patient suffers from. Thus, the staphylococcal type of pathology is often localized on the face of men, affecting the chin and the skin around the lips. Infection occurs during the process of shaving stubble hair.
The pseudomonas form of the disease occurs as a result of the patient bathing in hot water with an insufficient level of chlorination. The heat helps open the pores into which infectious agents enter. Foci of inflammation form on the face and upper torso of a child or adult.
The syphilitic type of pathology develops against the background of secondary syphilis. Typical symptoms of this form of folliculitis are the formation of areas of bristly hair loss in men and multiple pustules on the temples in women.
The herpetic type of hair follicle infections affects the skin of the chin and nasolabial triangle of patients. Characterized by the formation of large vesicles in the follicular ostia.
The candidal form of pathology manifests itself when occlusive dressings are applied to the patient’s skin, preventing pathogenic microflora from entering the wound on the chest.
The gonorrheal type of disease becomes a complication of gonococcal infection. Pustules form in the perineum (in women) and on the foreskin (in men).
Folliculitis caused by mites can be localized on any part of the human skin. The activity of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis leads to the formation of clusters of small pustules.
Complications of Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis
Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is not life-threatening. The disease must be treated because it causes aesthetic discomfort and sometimes pain to the patient. If you neglect the disease and do not adhere to hygiene standards, folliculitis will spread to other parts of the skin with hair. Abscess folliculitis can lead to the following complications:
- Scarring of the affected skin.
- Carbuncles.
- Boils.
- Abscesses.
In advanced and severe cases, the patient’s life is at risk, since with reduced immunity, pneumonia, meningitis and other disorders develop.
- Read - how to treat oil folliculitis
Share this article:
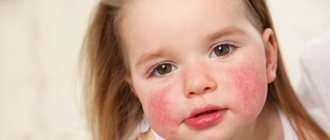
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of folliculitis in men and women are the same in most forms of the disease - dermatologists prescribe similar treatment for patients of both sexes. The most pronounced sign of an infectious lesion of the hair follicle is a single pustule filled with purulent contents, the center of which is penetrated by hair. After several days, the formation opens on its own, releasing a small amount of pus. In place of the pustule, an ulcer with a dense bloody-purulent crust forms. Healing of the resulting wound leads to the formation of a focus of hyperpigmentation or scar.
In 80% of clinically diagnosed cases of the disease, multiple pustules form on the skin of patients. Common places for their localization are the face, scalp, armpits, pubis, and inner thighs. Severe pain and itching appear after the formation of a large cluster of pustules. In the absence of medical care and refusal to observe personal hygiene rules, the patient may encounter complications: abscesses, cellulitis and hidradenitis.
Deep and superficial folliculitis
Ostiofolliculitis or superficial folliculitis is an exudative element of the rash (pustules) measuring 1-2 mm.
It is characterized by a rapid course and the absence of serious complications.
After a few days, the pustule dries out and a crust forms in its place, which falls off on its own, leaving no scars.
Deep (purulent) is accompanied by the formation of a nodule 2-3 mm in size, dark red in color, in the middle of which there is a purulent accumulation.
After 3-4 days, the formation resolves, and an ulcerative lesion appears in its place, leaving scars after healing.
If we are talking about an infectious lesion of the facial area, then acute sycosis is diagnosed.
In addition to the two main ones, a chronic bacterial process is distinguished.
The disease is accompanied by healing and the constant appearance of new elements.
Upon detailed examination, you can see rashes and purulent formations at various stages of development.
The facial area is most often affected by the chronic course of the disease in men who prefer to wear a beard.
Even minor damage to the epidermis, for example, during shaving, can provoke sycosis.
The risks of infection increase in the presence of predisposing factors: immunodeficiency, chronic foci of infection (sore throat, caries, sinusitis).
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist. The doctor examines the patient, during which he performs dermatoscopy. Studying damaged hair follicles using an optical device allows us to determine the depth of penetration of pathogens into the structures of the dermis. Samples from pustules obtained during the examination are subjected to laboratory testing. The study of biomaterials in the laboratory is carried out to identify the causative agent of infection. If signs of gonorrhea or syphilis are detected, the doctor will refer the patient for PCR testing.
Differential diagnosis allows doctors to exclude drug-induced toxicoderma, pityriasis rosea, streptococcal impetigo, furunculosis and ostiofolliculitis from the patient’s history.
Characteristic symptoms
The symptomatic picture for this disease is as follows:
- Infiltration and redness at the site of the hair follicle;
- Formation of pustules with purulent exudate, accompanied by itching and pain;
- After some time, a scar or spot with increased pigmentation forms in this place.
If you notice such symptoms, you should consult a dermatologist.
Treatment
The treatment tactics for folliculitis are determined by the doctor, taking into account the type of disease identified in the patient. For bacterial types of pathogens, antibiotic ointments are recommended for adults and children. The fight against fungal pathogens is carried out using antifungal agents. Antiviral drugs are used to combat the herpetic form of the disease.
Local therapy for the treatment of folliculitis localized on the face is effective at the initial stage of the disease. If multiple pustules appear, the patient will need to treat the rash with alcohol solutions of brilliant green or fucarcin. The spread of infection can be stopped by regularly treating the skin with salicylic or boric alcohol. Ultraviolet irradiation of the body and limbs of a child or adult becomes an auxiliary therapeutic measure.
The complicated course of the pathology requires complex therapy aimed at treating the disease that is the root cause of folliculitis - gonorrhea or syphilis.
How to diagnose
To make a diagnosis, the specialist prescribes:
- Microscopy with bacteriological examination of discharge;
- Dermatoscopy;
- PCR diagnostics;
- Testing for Treponema pallidum and mycotic infections.
Treatment
Therapy includes:
- Antifungal drugs;
- Local antibiotics;
- Solutions of aniline dyes that need to be used to treat lesions;
- UV therapy.
Prognosis and prevention
If you treat the disease consistently, strictly following the doctor's instructions, the prognosis is quite favorable. The risk of relapse remains because the trigger for the development of this disease is not infection, but physiological features. And it’s difficult to influence them.
To the dissatisfaction of patients, when deep foci of perifolliculitis heal, scars and baldness remain. The situation can only be corrected by skin plastic surgery. Conservative methods, including folk ones, will not solve the problem.
The disease is prevented with the help of vitamins required to maintain the normal condition of the skin (A and E), suppression of the growth of staphylococcus (propolis has shown itself well) and with the help of personal hygiene rules.
Don't let your hair get greasy, and the risk of relapse will be minimal. [carousel-horizontal-posts-content-slider]
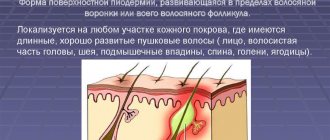
Hair follicles - definition
What are hair follicles? These are the channels from which hair grows. Hair and fat glands protect the skin from damage (lipid coating) and ensure its gas and heat exchange.
When the follicle is damaged, for example, by aggressive cosmetics or during depilation, microbes enter the base of the follicle and multiply there. The body begins to defend itself against bacteria, and this is how inflammation occurs. Those. folliculitis is an inflammatory reaction to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria or substances dangerous to the body.
Folliculitis
Risk factors
Folliculitis is a purulent disease that affects the hair follicles. The disease has a racial basis and can be inherited, as a result of which it occurs more often in African Americans.
The risk group also includes people who:
- have increased oily skin and, as a result, frequent blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- do not observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- often injure the skin by scratching after insect bites, scratches, abrasions;
- work in difficult working conditions;
- have complications after poor-quality cosmetic procedures.
The disease affects men and adolescents aged 15 to 35 years.
Signs of perifolliculitis
Mostly men suffer; the first signs of the disease are diagnosed at a young age (25-30 years), which is especially unpleasant for men. Since this is the age of maximum sexual activity, and external defects lead to psychological complexes and a decrease in the level of communication with the opposite sex.
The onset of the pathological process is characterized by:
- itching;
- burning;
- During examination, the doctor detects areas of redness on the skin.
Figure No. 1. Undermining folliculitis, hair loss
The first lesions are located in the crown and on the back of the head. The lesions are multiple, but fortunately, they rarely cover most of the head. If this happens, healthy tissue appears as thin stripes between the bumps (knots) of inflamed tissue with areas of hair loss.
At the stage of disease development:
- nodules transform into pathological openings (medical term “fistulas”) with a diameter of up to 2 cm;
- from the fistula, when you press on the skin around it, pus flows out;
- nodules may become covered with ulcers;
- the skin around the inflamed area becomes thinner;
- hair also falls out in a healthy area in a strip up to 2 cm wide around the red bumpy area.
Figure No. 2. Undermining folliculitis, scalp abscesses, hair loss
Unfortunately, the lost hair is not replaced by new ones, and nodes, lumps and abscesses continue to form around the diseased area. The disease takes a long (up to several years) course with stages of relapse and remission.
Figure No. 4. Hoffmann’s perifolliculitis: alopecia, nodes, tubercles
If the disease is caused by toxigenic staphylococcus (its waste products cause acute intoxication), the patient will experience symptoms of general intoxication.
Figure No. 5. Hoffmann's perifolliculitis: nodes, bumps, scars
Application of traditional medicine
Treatment with unconventional methods has long established itself among the people. These are truly effective remedies against many diseases, including folliculitis.
But you need to be careful when using traditional recipes - they can cause allergic reactions. Before use, it is better to consult a doctor. Let's look at some of them:
- Tea tree oil is one of the most popular and effective remedies against this disease. Has an antiseptic and healing effect. Apply 3-4 times a day, smearing onto affected areas.
- Calendula decoction has an anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial effect and accelerates healing. To prepare such a decoction, you will need to pour 5 grams of calendula into 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 20-30 minutes, then strain. Apply 3-4 times a day, moistening the affected areas.
- Chamomile decoction can be prepared by pouring 20 grams of dry chamomile with a glass of boiling water, letting it brew for about half an hour and straining. Moisten the inflammation every 3-4 hours a day.
- Thistle , which contains many useful active substances, copes well with wound healing. For folliculitis, crushed fresh thistle is applied to the inflamed areas and covered with a sterile gauze bandage.
- A multi-component product made from viburnum berries (200g), rose hips (200g), dried nettles (10g) and crushed walnut shells (10g). You will need 3 tbsp. Pour 300 ml of boiling water over the resulting dry mixture and cook over low heat for about 10 minutes. Then pour into a container, close the lid and leave for 24 hours, then strain. Mix 50 grams of the resulting infusion with 1 tbsp. honey and 50 grams of cottage cheese. Apply the mixture to the ulcers, leaving for 20 minutes. This remedy is used only for superficial folliculitis.