On the one hand, the sun's rays warm people with their warmth, helping to strengthen the immune system, and on the other hand, many people experience an allergic reaction as a result of exposure to the sun. Statistics show an increase in the number of cases of allergic reactions to the sun. According to statistics, 20% of people in the world suffer from this disease. However, such allergies do not always take a chronic form. Accordingly, if treatment is prescribed correctly, the allergy may go away forever.
Allergy to sunbathing is understood as photodermatitis or photodermatosis, since the allergic component itself is not present in the sun's rays. The sun's rays themselves are not allergens, but under their influence substances that cause allergies can accumulate in the human body.
Photodermatitis is caused by increased sensitization of the skin when exposed to sunlight. Exposure to ultraviolet rays causes a photochemical reaction that changes the structure of substances found in or on the skin. These altered compounds then increase skin sensitivity.
In accordance with the provoking factor, photodermatitis is divided into endogenous and exogenous:
— endogenous photodermatitis is caused by metabolic disorders (metabolism) and immune pathologies;
- exogenous photodermatitis is associated with substances that enter the skin and change under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
The following categories of people are most often at risk of developing photodermatitis:
- people with light and thin skin;
- children;
- pregnant women;
- people whose close relatives suffer from photodermatitis;
- patients suffering from atopic or other types of dermatitis;
- people who abuse solariums and tanning;
- people who take a number of medications;
- People who have recently undergone peeling or tattooing;
- People who actively use cosmetics or perfumes.
Main reasons
Despite the existence of the term “sun allergy,” sunlight itself is not an allergen. On the contrary, sunlight in safe quantities has a beneficial effect on the human body - it improves mood, promotes the absorption of vitamin D, and stimulates the immune system. Only when the ultraviolet component of sunlight interacts with any substance located on or in the skin do compounds with antigenic properties appear. It is these compounds, not the sun's rays, that cause sun allergy symptoms. Doctors call this disease “photodermatitis.”
Typically, photodermatitis can occur during periods when a person is exposed to significant sun exposure by spending a lot of time outdoors, that is, in the spring and summer. But this disease can also be provoked in winter: after all, some begin preparing for the beach season in advance by visiting a solarium, while others go to the south or to tropical countries for additional sun during the cold season. Therefore, sun allergy has become a year-round disease for many.
First aid for fainting
If a person with ultraviolet radiation intolerance spends a long time in the open sun, his blood pressure often drops and faints.
Usually this happens suddenly and unexpectedly for him, so only other people can help in this case.
In order to help a person come to his senses, you need to take the following actions:
- move it to the shade, or create an artificial shelter over it;
- raise your legs, thereby increasing blood flow to the head;
- sprinkle cool water on the face, neck, chest;
- It is advisable to bring a cotton swab soaked in ammonia to your nose.
Most often, after these events the patient comes to his senses. But if fainting lasts a long time, or it occurs in a child or pregnant woman, you should call an ambulance. There are situations when a person must stay in the hospital for a couple of hours.
Why do sun allergy symptoms occur?
The appearance of photodermatitis is promoted by internal and external causes.
Internal causes include chronic diseases of the liver and adrenal glands, some metabolic disorders, and malfunctions of the immune system. It should also be noted that people with fair skin and children are prone to photodermatitis.
External causes are the effects on the body of substances that can be divided into three large groups:
- Furocoumarins are special substances secreted by plants such as hogweed, parsnip, ash, parsley, dill, St. John's wort, and can cause allergies. Bergamot, lavender, musk, and sandalwood oils also have an allergenic effect.
- Components of cosmetics - eosin, para-aminobenzoic acid, retinoids, boric and salicylic acids, phenol, mercury compounds.
- Medicines - sulfonamides, barbiturates, aminazine, some antibiotics (doxycycline, tetracycline), some cardiovascular drugs (amiodarone, Trazicor), cytostatics, oral contraceptives, some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, ketoprofen, naproxen, meloxicam, diclofenac, lornoxicam) , both in the form of tablets and in the form of ointments, creams and gels.
Cosmetic peeling, permanent make-up or tattoos, even temporary ones, can also trigger photodermatitis.
Read also
- How to treat cystitis? Does it only affect women or men too? We tell you all the details
- How to distinguish ARVI from coronavirus?
- A sore back is a problem for office clerks and boxers and tennis players. Is everything that serious? Can it be fixed?
- How to boost immunity for an adult?
- How does immunity work? Is it possible to strengthen it?
- How to boost immunity at home
- What to do if you have acute back pain?
- More about training, nutrition, sports medicine and sports as an activity - in the “Health” section
- Subscribe to the Sports.ru telegram channel about health
Photo: unsplash.com; en.wikipedia.org
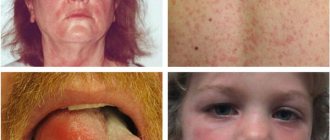
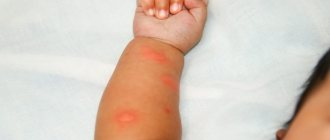
Symptoms of sun allergy: manifestation options
Within a day or a little later after exposure to the sun, soreness and itching of the skin begin to bother you. Then areas of redness and a rash appear on the skin in the form of spots, nodules, plates, blisters, sometimes merging into plaques. There is often a deterioration in the general condition. Most often, the rash occurs on the face, less often on the body and limbs. Rashes on the face may be accompanied by conjunctivitis, cracks in the corners of the mouth (cheilitis). After the acute symptoms subside, peeling of the skin is observed. With repeated sun exposure, the disease may worsen again.
It is important to distinguish photodermatitis from an ordinary sunburn. It is also accompanied by pain and redness of the skin, and in severe forms blisters may occur. But the rash and severe itching characteristic of photodermatitis do not bother you with a sunburn.
Doctor, is this forever?
Treatment of sun allergies involves eliminating exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In the case of solar urticaria, antihistamines help, and there are special medications that thicken the skin and reduce its sensitivity to sunlight. Treatment in this case consists of gradually accustoming the skin to the sun while taking medication.
To relieve exacerbation of photodermatitis, local treatment is prescribed in the form of ointments, sometimes hormonal, and internal treatment: vitamins B, E, C, nicotinic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antihistamines. Usually the course of treatment continues for several days or weeks. During this time, it is recommended to spend less time in the sun, wear a wide-brimmed hat, clothes with sleeves and sunglasses.
If sun allergy is left untreated, repeated episodes will lead to the development of photodermatosis. When you have managed to stop the allergy attack by carefully taking care of protecting your skin, eliminating provoking factors and strictly following the sunbathing regime, you have the opportunity to bask in the gentle rays. Sun allergies can be controlled and prevented, and children may even outgrow this disease.
medkrug.ru
Recommendations and treatment
At the first symptoms of a sun allergy, you should consult a doctor and strictly follow his instructions. The doctor’s very first recommendation for any allergy is to eliminate or reduce contact with the allergen.
- Avoid direct sunlight, stay in the shade, under an awning.
- Avoid visiting the solarium.
- Use UV protective products by applying them to your body 20 minutes before going outside.
- Don't forget about hats with brims or visors and clothing with long sleeves.
- After swimming in open water, blot your skin, but do not dry it. This will preserve the layer of sunscreen.
- Minimize the use of decorative cosmetics, creams, perfumes, etc.
- Carefully read the instructions for medications - medications should not contain substances that can cause photodermatitis. Talk to your healthcare provider ahead of time about options for changing medications for sun allergy symptoms.
- Avoid contact with plants containing furocoumarins.
- Increase your consumption of fresh vegetables, fruits and berries; they help restore damaged skin due to the presence of antioxidants and B vitamins.
How to eliminate sun allergy symptoms
To relieve allergy symptoms, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines (for example, Cetrin ® ). In the future, it is advisable to keep these medications on hand: unfortunately, an allergic reaction to the sun may recur.
To treat local skin manifestations, the doctor may recommend cold lotions, as well as external ointments or creams containing glucocorticosteroids.
If the cause of photodermatitis is internal, be sure to treat the disease that triggered the allergy to the sun.
Following these recommendations and following your doctor’s prescriptions will help you significantly reduce the appearance of sun allergy symptoms or completely get rid of the manifestations of photodermatitis.
Folk remedies
The remedies that we “got” from our grandmothers are also very effective in treating the described illness.
- But, before using them, in any case, you need to consult a specialist. As mentioned above, the cause of this type of allergy can be some medications, as well as cosmetics.
- An ordinary cabbage leaf “saves” very well from the negative manifestations of ultraviolet radiation. It needs to be applied to the inflamed area and after a while the problem will disappear. Instead of cabbage, you can use raw potatoes, cucumbers and other vegetables for the same purpose.
- To restore a sun-damaged area, you can use an infusion of geranium leaves. To do this, pour 2 tablespoons of geranium into 2 cups of boiling water and leave for 20 minutes. After that, lotions are made based on the resulting product.
- Also, lotions to eliminate the symptoms of photodermatitis can be made using horse chestnut pulp or grated carrots. These remedies treat itchy skin and urticaria.
- Another effective remedy for itching is a bath of string. To do this, pour a glass of boiling water over the dry string (2 tablespoons) and boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. Then the broth should be poured into a warm bath. Twenty minutes of such a bath daily will help cope with the problem and improve skin condition.
External remedies will be good only if there are no toxins left in the body.
Diuretics are indicated for this. For example, celery juice, string tea and decoctions of St. John's wort and aspen buds.
List of photosensitizers
Photosensitizers are substances of various origins that cause increased sensitivity of the skin to solar radiation. Often they are the ones who provoke negative conditions in the dermis.
Therefore, if you belong to a risk group or are planning a vacation in the midst of summer days, then you should exclude the list of the following products and medications from use:
- alcoholic drinks, especially red wine;
- tomatoes, carrots, sour apples, citrus fruits, figs, pomegranate, parsley, celery;
- freshly squeezed juices from these products;
- cosmetics containing oils of musk, bergamot, lime;
- aspirin;
- cardio medications (Cardiomagnyl, Magnicor, etc.);
- retinol cream;
- vitamins B6 and B2;
- diuretics (Furasemide, Pamid, Indap);
- antifungal agents (Griseofulvin, Lamisil, Tsidokan, etc.);
- fluoroquinolones (Ofloxocin, Ciprofloxocin, etc.);
- cream or medications containing St. John's wort;
- antibiotics of the tetracycline group (Doxal, Doxycillin, Unidox, Tetracycline, Rondomycin, etc.);
- corticosteroid hormonal drugs (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone, Sinaflan, Dermovate, etc.);
- drugs that slow down cell division (Flutamide, Methotrexate, Azotriopine, etc.);
- means for lowering blood sugar (Diabeton, Siofor, Novonorm, etc.);
- antidepressants, antipsychotics (Bifol, Azafen, Aminosyl, Truxal, etc.);
- oral contraceptives with a high content of estrogen (Tri-regol, Ovidon, etc.).
In order to protect yourself and your loved ones, carefully study the instructions for medications and follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Dosage form, composition
The active component of the drug is fluocinolone acetonide. Sinaflan is available in several forms for external use:
- liniment: yellowish viscous substance containing 0.25 mg of active substance per 1 g;
- gel: transparent yellow mass with similar content of fluocinolone acetonide;
- cream: a homogeneous oily substance.
Among the form-building compounds and stabilizers of the product: glycerin, paraffin, liquid paraffin, lanolin, ceresin, propylene glycol, purified water and other components.
All dosage forms of the drug are packaged in 10 or 15 ml tubes and cardboard boxes, equipped with instructions for its use.
Prevention
Prevention helps prevent skin problems and promotes joyful sun exposure. Preventive measures include:
- Do not use perfumes and cosmetics containing essential oils, alcohol, fragrances, or acids;
- Start strengthening your immune system at the end of winter: drink vitamins, walk more in the fresh air;
- Eat berries and fruits containing antioxidants, vitamins A, E, B. For example, blueberries, apples, pomegranates, bananas;
- If possible, avoid spicy foods and exotic fruits;
- Staying on the beach when solar activity is low (morning and evening);
- Using sunscreen and after-sun lotion;
- Vary the time spent in the sun and shade;
- Wear a summer hat and glasses;
- Dry your skin after bathing and reapply the cream;
- Avoid dehydration, drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water per day;
- Conduct a preventive examination of the whole body to detect health problems in a timely manner.
Proper sun protection and self-care will help make the summer time carefree and joyful.
Sunburn How to treat a mosquito bite in a child at home Urticaria Cetirizine Polysorb MP Application of ASD fraction 2: benefits and harm to humans
Diagnostics
Preliminary diagnosis includes interviewing the patient and external examination. To determine the type of allergen, the doctor prescribes application tests to the patient. To detect the endogenous causes of sun allergies, the doctor will prescribe the following studies to the patient:
- Zimnitsky samples;
- biochemical analysis of urine and blood;
- CT and ultrasound of the kidneys;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- hormone analysis;
- excretory urography.
When studying sun allergies, a distinction is made between diseases such as:
- lichen;
- sunburn;
- erysipelas;
- atopic, allergic, contact, radiation dermatitis;
- superficial form of SLE.
Healthy foods
To prevent the occurrence of unwanted allergic reactions, you need to adjust your diet:
- eat a large amount of foods containing vitamins C, B and E. It is especially useful to eat fresh berries and fruits - blueberries, pomegranates, currants;
- drink a lot of clean water. Thanks to this, it will be possible to cleanse the body of toxic substances. At the same time, it is recommended to completely exclude carbonated drinks, alcohol and juices.
- When on vacation, be careful about exotic dishes. If you are highly sensitive to sunlight, such experiments should be avoided.
Clinical researches
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children and adults with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
Based on the results of joint research, the following information is placed on product packaging: “Recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.”
Sources:
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, GEOTAR-Media, 2022.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, Notabene, 2017.
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Illustrated clinical dermatology. Brief alphabetical reference book, Lux Print publishing house, 2010.
Photos of dermatitis
Photo album on the disease