Fungal nail infections are quite easy to get. If you have a fungal infection on your foot, it may gradually spread to one or more of your nails. This happens quite often in both children and adults. You can get a fungal nail infection in a warm, humid place, such as a pool or gym locker room. If someone else in your circle has a yeast infection and has been walking on the floor barefoot, all you have to do to get the infection is walk barefoot in the same area.
Wetting your nails for a long time can also lead to nail fungus. Some people suffer from yeast infections because they wear the same pair of sweaty or wet shoes every day. Nails that become damaged due to work or hobbies are also susceptible to fungus. What you see externally on infected nails depends on the type of fungal infection.
Treatment can prevent nail infections from developing. If you have diabetes or a weakened immune system, comprehensive treatment is especially important. Once a fungal nail infection develops in people with diabetes, there is an increased risk of developing trophic ulcers that do not heal. At the first sign of problems with your nails, it is important to consult a dermatologist (or mycologist - a specialist in fungus). A dermatologist can tell you whether you have a nail infection or something else.
General rules
Therapeutic and hygienic measures must be carried out regularly; treatment cannot be interrupted until the fungus is completely eliminated. The duration of the recovery process depends on the degree of neglect of the disease and the affected area. Read also: Fungus on the fingers: treatment and symptoms with photos.
For a successful outcome of treatment and prevention of infection of others, it is recommended to follow the basic rules:
- For the entire period of treatment, you should avoid visiting swimming pools, saunas, beaches, and pedicure rooms.
- The patient must have individual means for hygienic treatment of feet: files, pumice stones, soap, towels, etc.
- Shoes must be thoroughly disinfected and dried. Insoles and the inner surface of shoes can be treated with special solutions or sprays.
- Feet must be dry at all times. Fungal pathogens actively reproduce in warm and humid environments. After water procedures, feet should be dried with a clean towel, and if the feet are sweating, use talcum powder, powders and powders.
- Particular attention is paid to hosiery. It is better to choose socks made of natural cotton. This material absorbs moisture well and ensures normal ventilation of the skin of the feet. Socks should be changed as often as possible, and used items should be boiled.
- Drug treatment is carried out strictly in accordance with the instructions of the attending physician after confirmation of the diagnosis by the results of laboratory tests of the infected material.
The keratinized skin of the fingers and soles must be constantly removed with a special foot brush or pumice stone. Otherwise, cracks may form through which the fungus penetrates into the deep layers of the epidermis and the bloodstream.
Preference should be given to comfortable shoes made from natural materials to prevent the accumulation of excess moisture.
Removing the nail plate
Surgery is a radical method of treating nail fungus in a complicated clinical picture, when the structure of the nail plate is affected by 70% or more. The doctor recommends a matrixectomy. The essence of the surgical method is to forcefully damage the nail matrix - the area where the nail body is formed. In this mechanical or chemical way, it is possible to give rise to the growth of a new, already healthy surface. This is an extreme measure of surgical treatment that doctors rarely use. The disadvantage is the long rehabilitation period.
Foot baths
Therapeutic baths are a must in the treatment of fungal diseases of the feet at any stage of development of the infectious process. Procedures for steaming the feet in hot water with the addition of various active ingredients are a preparatory stage before applying the main antifungal drugs.
Foot baths can be used twice a day or daily before bed. The duration of the procedure depends on the composition of the bath, but does not exceed a half-hour threshold.
Healing herbs
For antifungal foot baths, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used:
- plantain;
- wormwood;
- burdock;
- milkweed;
- yarrow;
- calendula flowers.
Herbs can be combined or steamed separately. For the best effect, the decoction should be strong enough. The required amount of plant material must be poured with boiling water. As soon as the temperature of the decoction becomes tolerable for the skin, you can put your feet in the bath and steam your feet for 15-20 minutes.
Celandine
Celandine preparations are often used in the fight against foot fungus. To prepare foot baths, it is recommended to use dried celandine herb. You can buy it at the pharmacy or prepare it yourself.
The decoction is prepared at the rate of 8 tablespoons of herb per 2 liters of boiling water, then cooled to a temperature of 50˚C and placed in a convenient container. Feet should be kept in the bath until it cools down. The course of treatment is 20 days.
Vinegar
An acidic environment has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microflora that causes mycoses. Baths with vinegar essence are used as an effective treatment for foot fungus at home using folk remedies.
Vinegar is taken at the rate of 100 ml of essence per 2 liters of warm water. The estimated duration of the procedure is a third of an hour. Such a home remedy for fungus can significantly speed up the treatment carried out with modern pharmaceuticals.
Soda and salt
Salt and soda solutions for soaking the feet allow you to fight foot fungus in the initial stage. There are a lot of options for preparing foot baths with salt and soda at home. The simplest and most effective recipes:
- Dissolve 2 tablespoons of table salt and baking soda in two liters of warm water and soak your feet for up to 20 minutes.
- To two liters of boiling water add a similar amount of strong oak bark decoction, a few drops of peppermint oil and tea tree essential oil, 2 tablespoons of soda, 2 tablespoons of sea salt. The duration of steaming is half an hour. The treatment period takes 14 days.
- Mix 1 heaped tablespoon of soda and coarse salt in warm water, add a couple of tablespoons of liquid soap with an antibacterial effect (you can use tar). Steam your feet in the prepared solution for up to half an hour; at the end of the procedure, let your feet dry without wiping or rinsing with clean water.
Salt helps strengthen nails and regenerate epidermal tissue, and soda softens the skin, cleansing and disinfecting the surface of the feet. Salt solutions containing iodine have a pronounced fungicidal effect.
Foot steaming with vodka, ammonia, propolis, strong coffee, birch tar, hydrogen peroxide and garlic juice helps perfectly.
Symptoms of pathology
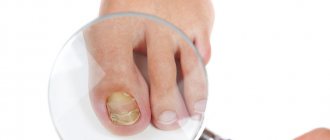
Toenail fungus is medically called onychomycosis . A characteristic feature of the pathology is slow progression and the inability to make a diagnosis at the initial stage. The nail of the thumb is usually affected. Symptoms of the pathological condition directly depend on the stage of its development, of which there are several:
- Initial stage. Characterized by changes in the skin between the toes. Bubbles and cracks appear, the epidermis peels off, itching and hyperemia (redness) occur. Symptoms may not cause discomfort if they are mild. Diagnosis is extremely difficult.
- Middle stage. It begins when the infection penetrates the nail plate. There are signs of destruction of the nail plate, its color changes, black, yellow or white spots of different sizes and shapes appear. The shine of the plate is not lost, the structure is gradually deformed, and the nail becomes thinner. Sometimes the nail takes on a green or bright yellow tint.
- Advanced stage. It is characterized by an extremely severe course with complete destruction of the affected plate. It gradually crumbles, the subungual space is constantly injured and bleeds. At this stage, there is a high risk of infection entering the blood.
In children, symptoms appear more intensely, especially in children under 3 years of age. The child is restless, constantly tries to scratch the affected area, he is worried about pain, and sudden movements provoke injury.
If you do not contact a specialist in time to prescribe adequate therapy, gradual decomposition of the subungual space and deep layers of skin begins. Pathology at an advanced stage is dangerous due to the spread of infection to healthy tissues, a high risk of developing sepsis and fungal infections of internal organs. This is especially true for children, since their disease progresses much faster, and the chance of complications increases several times.
If symptoms of a fungal infection of the toenails appear in an adult or child, you should immediately contact a mycologist who specializes in such pathologies. In his absence in a medical institution, such diseases are usually dealt with by a dermatologist.
Compresses, rubbing, lotions
You can remove foot fungus using compresses and various rubs according to alternative medicine recipes. The procedure is carried out after thorough treatment and steaming of the legs.
The healing mass is applied to the affected area, fixed with a gauze bandage and insulated on top with clean socks. Provided there are no aggressive substances in the compress, the bandage is left overnight.
The most popular recipes for homemade antifungal compresses for the treatment of mycoses of the feet:
- Apply finely chopped fresh rowan leaves to the infected skin, cover with a burdock leaf on top and wrap in cellophane.
- Apply 35% salicylic ointment evenly to the fungal lesions and cover with cling film. Change the bandage once a day.
- Pass a few cloves of garlic through a press and mix with an equal amount of butter until smooth. Apply the resulting mass to the sore spot, cover with film, and leave overnight. Garlic will sting, but it is a good way to quickly cure foot fungus.
- Onion pulp is used for compresses in its pure form; you just need to change the dressings as often as possible. If the itching becomes unbearable, you can dilute the onion with Vaseline in a 1:1 ratio.
- Night vinegar compresses show good results. It is more convenient to use a cotton pad soaked in a weak solution of vinegar essence.
- Alcohol wraps help against foot fungus. A small piece of linen fabric soaked in an aqueous solution of ammonia is wrapped around the sore leg and insulated with polyethylene. The course lasts 7-10 days.
- Mashed potato sprouts are infused with vodka for 24 hours. The prepared pulp is used for foot compresses before bed.
- If the fungus is localized in the interdigital folds, you can apply a paste of peppermint herb and salt to the affected skin. This product perfectly combats itching, removes unpleasant odor and other symptoms.
The method of rubbing the affected skin with birch tar, an alcohol solution of iodine, garlic juice, tea tree and celandine oils helps to quickly get rid of foot fungus at home.
Many pharmaceutical local antifungal drugs are recommended for use in the form of compresses if mycosis has reached an advanced stage.
Forms of nail damage
There are three main types of nail fungus:
- normotrophic - stripes and spots appear, color changes, but the thickness of the nail remains unchanged;
- hypertrophic - the color of the nail changes, it loses its shine, becomes thicker, and becomes deformed. Partial destruction of the nail along the edges is often observed;
- onycholytic (atrophic) - the affected part of the nail atrophies and is torn away from the nail bed.
Based on location (localization), the following forms of nail fungus are distinguished:
- total (damage to the entire nail);
- distal (damage to the nail at the free edge);
- proximal (damage to the posterior cushion);
- lateral (damage to the lateral sides).
Antimycotic drugs
The fastest way to cure a mycosis infection is the right combination of folk remedies and antifungal drugs. Medicines for fungal diseases are divided into two main groups: for local and systemic use.
Oral antimycotics are prescribed for drug therapy of fungus in an advanced form in the absence of contraindications. Taking tablet medications is associated with a risk to the liver; they should be taken only in the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Systemic antifungal drugs include:
- Ketoconazole;
- Intraconazole;
- Candithral;
- Terbinafine;
- Griseofulvin and numerous of their analogues.
The choice of local medicines depends on the species of the causative agent of the disease and the financial capabilities of the patient. It may take several months to remove the fungus, and not everyone can buy expensive drugs.
Preparations for external use are available in the form of creams, gels, ointments, sprays, varnishes and solutions. Well-known pharmaceutical companies produce entire series of products for the complex treatment of fungus.
Regardless of the form, brand and price category, the main difference is the type of active ingredient of the drug. It is this criterion that determines the effectiveness of the drug against a specific type of infectious agent.
Antifungal drugs contain fungistatic substances: sertoconazole, bifonazole, ketoconazole, oxyconazole, terbinafine, ciclopiroxalamine, amorolfine.
It is easier to defeat foot fungus with the help of local medications in the early stages of the disease when the first signs of infection appear, if treatment is carried out continuously in accordance with the attached instructions.
Laser therapy
This gentle and at the same time progressive method is used in advanced clinical situations and is implemented with the participation of a local antiseptic. The essence of the technique is as follows: first, the doctor applies a pigment gel, then uses a laser beam to treat the problem area (removes the mycelium), thereby destroying the pathogens of the disease. Positive dynamics are achieved in 3–4 procedures with a break of 1 month. Advantages: painless session, effectiveness. The disadvantage is the high price.
Rules of personal hygiene as prevention against foot fungus
Prevention of foot fungus is, first of all, personal hygiene measures aimed at preventing infection and creating an environment hostile to microorganisms.
It is important to remember that mycotic lesions of the feet can last for a long time, almost without manifesting themselves; they are characterized by a chronic relapsing course.
Pathogenic microorganisms that affect the foot are unusually tenacious; they love dampness, damp, unventilated interdigital folds of the feet, the lower and lateral surfaces of the sole.
Below is a short list of personal hygiene rules (well known, however, not always followed) to avoid catching this obsessive infection:
- Keep your feet dry and cool;
- Do a pedicure in a timely manner using tools that have undergone proper disinfection, using modern auxiliary and care products;
- Wash your feet with warm soapy water daily, use antibacterial soap if necessary, wash your feet several times a day;
- Wipe your toes dry from the base to the very tip, the skin between the toes, and the entire foot;
- Fight sweaty feet;
- Use antifungal foot powders, and, if necessary, antifungal cosmetic and medicinal creams, gels, nail polishes;
- Go barefoot, at least at home, in the country;
- Keep your toes slightly apart;
- In locker rooms, showers, gyms, fitness clubs and other public places, do not walk barefoot - wear flip-flops (rubber slippers, waterproof flip-flops);
- Do not use someone else’s sponge, washcloth, towel, slippers (even within the family);
- If infected, provide a separate towel for the affected area or use disposable paper towels;
- Wear comfortable shoes that fit properly, made of leather and other natural materials;
- Avoid rubber and plastic shoes - a favorable environment for the growth of dermatomycetes;
- Keep your shoes clean and dry, ventilate them, treat the inside of your shoes with antifungal powder or aerosol;
- In summer, wear light, well-ventilated shoes;
- Change your sneakers in a timely manner; if they can be washed, wash them at least once a month;
- Change socks (socks, stockings, tights) more often, especially with hyperhidrosis, more often if necessary;
- Wear socks made of hygroscopic materials (natural fibers or special synthetics);
- To kill fungal spores, wash socks twice in very hot water; rinse your socks thoroughly after washing to remove the washing powder so as not to worsen the condition of the skin;
- For proper sanitary and hygienic condition of sinks, showers, bathtubs, basins, wash them regularly, use special products;
- Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor in the early stages of a fungal disease; do not expose others to the risk of infection;
- Be especially careful if you have fungal diseases in your household;
- Help elderly family members comply with dermatological orders and the necessary sanitary and hygienic requirements aimed at treating this disease.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of the disease in children and adults is damage to the nail plate and subungual space by a fungal infection that penetrates from the outside. The predisposing factors are:
- regular visits to public swimming pools, saunas, gyms;
- poor production conditions, humidity in workshops;
- chronic pathologies of the stomach - gastritis, peptic ulcer;
- type 1 diabetes mellitus;
- wounds, abrasions, cracks in the area of the big toe;
- the period after oncology treatment with chemotherapy;
- regular violation of personal hygiene rules;
- wearing uncomfortable, tight shoes made of artificial materials;
- chronic dermatological diseases affecting the feet - psoriasis, eczema, dermatitis.
The most likely cause of nail fungus is considered to be a weakened immune system due to colds, viral diseases, and the recovery period after severe and long-term illnesses.
In children, toenail pathologies result from contact with infected family members or people in preschools, schools, or other public places.
Giving up bad habits is a significant contribution to the prevention of foot fungus
Bad habits (excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, drug addiction), improper wakefulness-sleep, work-rest patterns, inappropriate behavior in stressful situations usually lead to a serious decrease in immunity and poor circulation.
Unreasonable unbalanced nutrition, excessive consumption of light carbohydrates, physical inactivity lead to obesity. Against the background of weakened immunity, poor circulation and obesity, a favorable climate is formed for infection and the development of infection into a generalized dangerous disease.
This indicates an urgent need to give up bad habits.
Research methods:
- microscopic examination. It is performed quite quickly, but the sensitivity of the method is not very high and requires a lot of experience from the laboratory assistant. As a rule, microscopic examination alone cannot determine the type of fungus.
- cultural examination (seeding). A highly accurate diagnostic method that allows you to determine the type of fungus. It involves growing a fungus from taken biomaterial on special media, which takes 1-2 weeks.
- PCR diagnostics (practically not used);
Due to the fact that a huge number of species of fungus live in the external environment and normally on human skin, it is necessary to collect the material from a qualified specialist, and the study itself - in a specialized mycological laboratory with extensive experience. Poor quality of research leads to false negative results, the need for multiple repeat tests and wasted time.
Folk and pharmacy remedies for the prevention of foot fungus
When choosing folk remedies for the prevention of foot fungus, you should remember that fungi do not like an acidic environment; to stop the growth of fungi, a slightly acidic environment (pH 5.5) is sufficient. For preventive purposes, it is advisable to periodically:
- Treat your feet with diluted lemon juice or fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, etc.)
- Make baths with salt water (2 tablespoons of salt in 0.5 liters of water) or light vinegar water (1 glass of table vinegar in 3 - 4 liters of water) or soda water (1 tablespoon of sodium bicarbonate in 1 liter of water).
Sources
- Tiwari D., Das CR., Sultana R., Kashyap N., Islam M., Bose PD., Saikia AK., Bose S. Increased homocysteine mediated oxidative stress as a key determinant of hepatitis E virus (HEV) infected pregnancy complication and outcome: A study from Northeast India. // Infect Genet Evol - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.104882; PMID:33905889
- Salmanian B., Belfort MA., Shamshirsaz A.A. The risk of placenta accreta spectrum in women with in vitro fertilization in different populations. // Am J Obstet Gynecol - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33905744
- Olmos-Ortiz A., Olivares-Huerta A., García-Quiroz J., Zariñán T., Chavira R., Zaga-Clavellina V., Avila E., Halhali A., Durand M., Larrea F., Díaz L. Placentas associated with female neonates from pregnancies complicated by urinary-tract infections have higher cAMP content and cytokines expression than males. // Am J Reprod Immunol - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.e13434; PMID:33905581
- Tandl V., Hoch D., Bandres-Meriz J., Nikodijevic S., Desoye G., Majali-Martinez A. Different regulation of IRE1α and eIF2α pathways by oxygen and insulin in ACH-3P trophoblast model. // Reproduction - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904834
- Ji S., Gumina D., McPeak K., Moldovan R., Post MD., Su EJ. Human placental villous stromal extracellular matrix regulates fetoplacental angiogenesis in severe fetal growth restriction. // Clin Sci (Lond) - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33904582
- Shmeleva EV., Colucci F. Maternal natural killer cells at the intersection between reproduction and mucosal immunity. // Mucosal Immunol - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33903735
- Moreno-Sepulveda J., Espinós JJ., Checa MA. Lower risk of adverse perinatal outcomes in natural versus artificial frozen-thawed embryo transfer cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis. // Reprod Biomed Online - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.; PMID:33903031
- Owen MD., Cassidy AL., Weeks AD. Why are women still dying from obstetric hemorrhage? A narrative review of perspectives from high and low resource settings. // Int J Obstet Anesth - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.102982; PMID:33903002
- Liu CN., Yu FB., Xu YZ., Li JS., Guan ZH., Sun MN., Liu CA., He F., Chen DJ. Prevalence and risk factors of severe postpartum hemorrhage: a retrospective cohort study. // BMC Pregnancy Childbirth - 2022 - Vol21 - N1 - p.332; PMID:33902475
- Munoz JL., Kimura AM., Xenakis E., Jenkins DH., Braverman MA., Ramsey PS., Ireland KE. Whole blood transfusion reduces overall component transfusion in cases of placenta accreta spectrum: a pilot program. // J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med - 2022 - Vol - NNULL - p.1-6; PMID:33902384