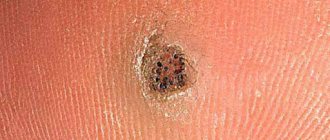
Any punctured, chopped, torn or cut wound can be complicated by the process of suppuration. Even if you cut your finger with a knife in the kitchen, you should not think that this is a trifle, because an insufficiently treated wound can fester. Everyone should know the first symptoms of wound suppuration for the reason that in most cases this problem has to be solved exclusively by surgery.
This problem is especially relevant for those who have undergone any surgery and were discharged home after rehabilitation. If postoperative sutures are not cared for at home as prescribed by the doctor, then if an infection occurs, suppuration may begin. Contrary to the generally accepted opinion of patients, suppuration after operations begins not because of the conditions during the operation, but precisely due to the fault of patients who irresponsibly approach the doctor’s prescriptions when they find themselves at home.
During surgery, it is essential to maintain absolute sterility, and this principle is never violated. Medical doctors recommend that you always fully follow the prescriptions they make to avoid such serious complications.
Causes of suppuration
If pathogenic bacteria penetrate into a stab, cut, chopped, lacerated wound or postoperative suture, the process of suppuration will begin. The process is accompanied by pain, swelling, the damaged tissue consists of dead cells, requires immediate medical treatment - otherwise gangrene may develop, and the affected limb will have to be amputated.
Reasons for the development of a purulent process:
- penetration of pyogenic microbes into the wound - staphylococci, streptococci, Proteus, E. coli;
- large affected area, deep wounds;
- the presence of dead tissue, a foreign body, or blood clots in the wound cavity;
- small but long hole for puncture wounds;
- a peculiar reaction of the body to medications that are used for dressings.
Staphylococcus pyogenic microbes
The likelihood of developing a purulent process increases in the presence of diabetes mellitus, vascular pathologies, obesity, sexually transmitted diseases, in elderly people, people with weakened immune systems, and in the hot season.
Any accidental wound in surgery is considered infected, so even minor scratches and abrasions should be treated immediately, especially in children.
How scabs form and their functions
Scabs form whenever there is damage to the skin. These could be scratches, abrasions or burns. They can also occur with certain types of skin diseases.
The scab immediately begins to cover the surface of the wound, forming from dead particles of the epidermis, blood, ichor, and pus. All these secretions are dried by the action of oxygen.
The main function of this crust is to protect the damaged area of skin from infection. Neither pathogenic bacteria nor dirt enter through it. But such a protective reaction of the body can also lead to unpleasant complications, so it is worth treating the wound immediately after receiving it.
The scab remains on the damaged area until the epithelium is completely restored, then it falls off. You should not tear it off yourself, as you can cause bleeding, then the recovery process will be interrupted. In addition, you can introduce an infection into the wound.
Types of purulent wounds
Purulent wounds can be open or closed, accompanied by a process of infiltration and necrosis. Most often, suppuration begins in random wounds and postoperative sutures and can develop as a gangrenous type, occurring in the form of phlegmon or abscess.
The main types of purulent dermatological lesions:
- boils - pus accumulates in the follicles and sebaceous glands, the problem most often develops in diabetics and overweight people;
- carbuncles - an infectious process develops simultaneously in several hair follicles, the disease is diagnosed in older people, with endocrine diseases;
- hidradenitis – inflammation of the sweat glands due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, careless shaving of the armpits;
- abscess - occurs in places of puncture wounds, after injections, is accompanied by necrotic pathologies, the inflamed area is limited to the capsule;
- phlegmon - a purulent-necrotic process occurs in the cellular space, the affected area does not have clear boundaries;
- paronychia - inflammation of the periungual fold on the hands;
- panaritium - pus accumulates in soft tissues, bones, joints of the legs, and fingers.
Collection of pus in the big toe
The color and consistency of pus allows us to identify the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process. White or light yellow discharge indicates a staphylococcal infection; when E. coli penetrates into the wound, the mass is liquid and has a brown-yellow color. Infection with staphylococcus is indicated by watery formations of a greenish-yellow color, brown mucus with a strong fetid odor - a sign of an anaerobic infection. A yellow exudate that turns brown when exposed to air appears when infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Diagnosis of felon
The diagnosis is made based on the patient’s complaints and clinical symptoms of the disease. To determine the shape of the panaritium and clarify the localization of the abscess, palpation is performed with a button probe.
To exclude bone and articular panaritium, radiography is performed. It should be taken into account that, unlike bone panaritium, in the articular form of the disease, changes are not immediately detected and may be mildly expressed. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, comparative radiographs of the healthy finger of the same name on the other hand should be prescribed.
Symptoms of festering wounds
The main local signs of a purulent process are the presence of exudate of different colors in the wound, pain, local increase in temperature, redness and swelling around the wound. When infected, a large amount of toxins enters the body, which leads to the appearance of signs of intoxication at a later phase of the development of the disease.
Read also: Causes of elevated ALT and AST
Signs of a purulent process:
- increased sweating;
- loss of appetite, nausea;
- weakness, fever;
- migraine, fever;
- pain in the affected area is of a pressing or bursting nature;
- sometimes a rash appears on healthy areas of the skin that are located near the source of inflammation.
The presence of a purulent and inflammatory process helps to identify a clinical blood test - the ESR increases, the leukocyte formula shifts to the left.
Excessive sweating may indicate wound suppuration
Prevention
To prevent infection of the damaged skin surface, you must follow simple rules:
- if the skin on the legs is injured, carry out antiseptic treatment;
- do not manipulate with dirty hands;
- cover the wound surface with a plaster or bandage to prevent contact with pathogenic microbes.
If large abscesses appear, general condition deteriorates, or body temperature rises, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and qualified treatment.
Tags: abscess, hidradenitis, pus, abscess, diabetes, infection, infected wound, carbuncle, honey, open wound, panaritium, wound, phlegmon, boil About the author: Andrey Stepanovich
« Previous entry
Treatment of purulent wounds
To eliminate purulent-necrotic processes, complex therapy is used, which is aimed at suppressing the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, eliminating pain, and accelerating the regeneration process. Most often, local treatment is used; in severe forms, antibiotics in tablet form should also be taken.
Local therapy
The use of external medications with various therapeutic effects is the main method of treating purulent wounds. Before applying the ointment or solution, the damaged area should be cleaned with warm water and soap and blotted with a soft cloth. For dressings, you can only use sterile gauze and bandages; wipe all instruments with alcohol.
How to treat festering wounds:
- Enzyme-based drugs – Chymotrypsin, Streptokinase. With regular use, the affected area is gradually cleared of fibrin and dead tissue, the healing process is accelerated, these drugs increase the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics. The solution should be soaked into gauze, applied to the wound for an hour, and therapy should be carried out for 10 days.
- Levomekol is an ointment with a combined therapeutic effect, contains an antibiotic and an immunomodulator, helps to quickly remove pus. The product is used for compresses and applied directly to wounds. Duration of therapy is 4 days.
- Ichthyol ointment is a safe antiseptic and analgesic that is suitable for the treatment of pregnant women and children over 12 years of age. Because its active components do not penetrate the bloodstream. The drug is applied under a bandage, dressing should be done every 8 hours.
- Magnesia will help get rid of swelling - you need to soak a cotton pad with a medicinal solution and apply it to the inflamed area for 1.5–2 hours.
- Lincomycin, gentamicin ointment - contain antibacterial components. They can be applied 2-3 times a day, the duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
- Sodium chloride solution - reduces the synthesis of purulent exudate, used for dressings, which need to be changed every 5 hours.
- Dimexide is a solution for compresses with anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antihistamine effects.
- Powder Baneocin, Xeroform is a drying agent with an antibacterial effect, it stops bleeding well.
- To eliminate signs of intoxication, you need to drink more warm liquids with a diuretic and immunomodulating effect - rosehip decoction, mint tea, lemon balm, lingonberry and cranberry juice.
Baneocin powder antibacterial agent
Folk remedies for quick healing
Non-traditional treatment methods help speed up the healing process, help eliminate inflammatory processes and strengthen local immunity. Folk remedies can only be used in combination with drug therapy; all therapeutic measures should be agreed upon with the attending physician.
How to get rid of festering wounds using folk methods:
- Ointment for drawing out pus - grind 1 lower large leaf of aloe and a small carrot in a blender, add 20 ml of liquid honey and melted butter. Apply the mixture under the bandage, carry out the procedure 3-4 times a day.
- Healing ointment from Juna - mix raw chicken yolk with 5 ml of honey and 15 g of wheat flour. Apply the composition to the source of inflammation, cover with a paper napkin and a protective bandage. The compress should be changed every 3 hours; in case of severe pathologies, the mixture can be left overnight.
- Compress with an antiseptic effect - mix fresh onion puree and crushed grape leaves in equal proportions. Apply the paste to the inflamed area, secure with a bandage, change the bandages every 4 hours.
- Chamomile decoction is one of the best natural antiseptics. To prepare the infusion, you need to brew 20 g of crushed raw materials with 220 ml of boiling water, leave in a closed, wrapped container for 2 hours. Soak gauze with the solution and apply to the wound for 45 minutes.
- To quickly cleanse the wound of pus, you can use a saline solution - dissolve 30–40 g of salt in 1 liter of warm water, wash the infected areas 4–5 times a day.
Read also: Pimples in the ears - what to do?
Chamomile decoction is a natural antimicrobial agent
Important! Purulent processes cannot be treated with essential oils - they can provoke an exacerbation of the pathology. During therapy, you should stop eating peanuts, other allergenic foods, and alcoholic beverages.
Urine therapy in the treatment of purulent wounds
Urine has long been used as a wound-healing agent for the rapid elimination of purulent processes - an absolutely sterile liquid contains hormones, microelements, and well softens the crusts that appear during the healing process, but modern non-traditional treatment is also carried out using urinotherapy. Fresh urine meets all therapeutic requirements.
How to remove purulent processes using urine:
- Soak a sterile bandage generously in urine and wrap tightly around the affected area.
- Wet the bandage with urine without removing it as it dries.
- The compress needs to be changed every 3-5 days, depending on the severity of the pathology.
Urine has healing properties
Treatment with urine is an effective way to eliminate purulent processes, but it is better to use it in extreme cases, when there are no medications or other means of therapy at hand.
When a scab is a problem
What is a scab? This is a natural function of the body. The main purpose of the skin is protection. Therefore, the scab, which protects the body from the entry of pathogenic bacteria from the outside, is important for ensuring this function. And in most cases there is no need to interfere with the natural wound healing process.
But there are exceptions to the rule. For example, the wound may not crust over, but remain wet or inflammation may begin underneath it. If the affected area is large, the scab can cause serious inconvenience. Then you will need the help of a specialist who will cut it. Sometimes this procedure is performed as an emergency measure when a scab interferes with adequate blood supply.
Features of treatment of purulent wounds in diabetes
In the event of traumatic injuries, the immune system of a healthy person begins to suppress foreign bodies, which reduces the risk of developing infectious pathologies; in diabetics, the body performs these functions worse. In diabetes, the process of glucose breakdown slows down, which reduces the rate of regeneration, promotes the active growth of pathogenic microorganisms - all this leads to long-term non-healing wounds, trophic ulcers, nerve endings lose sensitivity, and without proper treatment, amputation will be required. All the consequences of untimely treatment of wounds in diabetes can be seen in the photo.
Purulent wound on the leg with diabetes
How to heal wounds with diabetes quickly:
- Solcoseryl - normalizes metabolic processes in tissues, accelerates the regeneration process;
- Delaxin is a tannin-based ointment with a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect;
- Fusicutan is an antibacterial drug for external use;
- Zinc ointment – dries damaged areas, prevents suppuration;
- Levomekol, Dioxyzol - significantly accelerate the healing process;
- Baneocin - ointment and powder, the product is a strong antibiotic;
- Ichthyol ointment is an anesthetic and disinfectant for lotions and compresses;
- Vishnevsky ointment, streptocidal ointment - destroy pathogenic microbes, draw out pus.
Read also: What is FGDS (fibrogastroduodenoscopy)
Vishnevsky ointment destroys microbes well
All medications should be applied at least twice a day. Damaged areas should first be washed, dried, and treated with hydrogen peroxide.
Ointments for the treatment of purulent wounds in diabetes should not contain alcohol, salicylic acid, synthetic dyes and preservatives, or glycerin.
What to do if inflammation begins under the crust
If pus or pain suddenly appears in the wound, then you will have to answer differently what a scab is. This is a crust that prevents the skin from regenerating and therefore requires medical intervention. It is recommended that you consult a surgeon to carefully open the wound and clean it.
If this is not possible, you can disinfect it yourself. To do this, you need to make the surface of the wound accessible for manipulation. The scab should not be torn off, as after healing it may leave an unsightly scar. It is better to use a compress that will help soak the crust. An infusion of calendula and chamomile is best suited for this.
A warm compress should be applied to the crust and left for 15 minutes. Then, when it gets wet, you can use a cotton pad to treat the wound and apply an ointment containing an antibiotic, and apply a bandage over it. This treatment needs to be done several times a day.
How to cure purulent sores in the mouth
Ulcers in the oral cavity can appear due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, against the background of infectious or fungal pathology, long-term use of medications, diabetes, and frequent stress. The best medications for treatment are Benzocaine ointment, Solcoseryl. If the wounds occur due to an exacerbation of herpes, Acyclovir, Famciclovir will help.
Effective home therapies:
- Rinse - dissolve 5 Furacilin tablets in 400 ml of water, add 5 g of salt and soda. The procedure should be carried out 3-4 times a day.
- Cauterization. Rinse your mouth with a soda solution, apply hydrogen peroxide or Chlorhexidine to a sterile piece of cotton wool, and apply to the wound for 5 minutes. Carry out the procedure throughout the day at intervals of 5–6 hours.
- Anesthesia and disinfection. Combine the juice of half a lemon with 3 g of soda, add 5 ml of cold water and liquid honey. Apply the composition to purulent wounds in the morning before breakfast and before bed.
Lemon juice and honey will help get rid of purulent sores in the mouth
If wounds in the mouth are accompanied by severe pain, a piece of ice can be used as first aid and pressed against the sore - this procedure will help prevent the development of inflammatory processes and quickly eliminate discomfort in the oral cavity.
Signs of wound infection
After the bacteria find themselves in favorable conditions, within 12 hours they already make themselves felt. Inflammation begins in the damaged area of the skin, manifested by the formation of pus and painful sensations of a pulsating nature, as well as tissue swelling and redness.
Wound infection can also have more severe manifestations. The severity is influenced by several factors: the area affected, the type of microbes, the state of the body’s immunity.
Thus, the patient may develop a fever, increased sweating, or, conversely, chills. Sometimes a rapid pulse and tachycardia are observed, and problems with sleep appear. The presence of infection can also be determined by analyzing urine (protein is detected in it) and blood (the level of leukocytes will rise).
Infectious infection can have dangerous consequences. In the most severe cases, blood poisoning can occur.
Wound treatment after surgery
After any surgical intervention, sutures remain on the body, which should be properly cared for in order to avoid suppuration and speed up the healing process. Wound care includes the mandatory use of antiseptics and agents that accelerate the resorption of scars; medications should be used at least twice a day.
How to treat postoperative sutures:
- antibacterial and disinfectant solutions - iodine, alcohol, brilliant green, Fukortsin;
- Vishnevsky ointment - draws pus from the wound, promotes rapid healing of wounds;
- Levosin is an ointment with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects;
- Actovegin - accelerates the healing of sutures, eliminates inflammatory processes, normalizes blood circulation in tissues;
- Naftaderm is a good pain reliever;
- Levomekol ointment – accelerates healing, prevents skin drying;
- D-panthenol – ointment for tightening scars;
- Contractubex ointment, Mederma - can be used 2-3 months after surgery to eliminate scars.
If the wound has healed, you can additionally use sea buckthorn and milk thistle vegetable oil to soften the skin and tighten scars smoothly. The use of special plasters that secure the incision sites and prevent the growth of the scar is also effective.
You should not remove sutures and postoperative staples yourself - this is fraught with infection of the wound and the development of a purulent process.
Purulent wounds are a severe and complex pathology that requires long-term complex treatment. Only a doctor can determine which drug is better, the principle and treatment regimen, based on examination and the results of clinical studies. Self-medication can lead to the development of complications, including amputation of a limb.
Classification of postoperative sutures
How quickly the sutures heal after surgery largely depends on the nature of their application and the materials used. In this regard, post-surgical procedures are usually classified as follows.
- Bloodless (the edges of the wound are glued together with a special plaster) and bloody (a classic suture that is applied manually with a medical instrument). In turn, the latter are divided into:
- simple knots (applied at a distance of 1–2 cm from each other, after which the knot is tightened until the edges of the incision touch);
- intradermal continuous (considered the most effective, since after their healing there are no traces left);
- mattress (applied after abdominal surgery);
- purse string (used in plastic surgery, as well as in operations to reduce the volume of the stomach);
- entwining (circular sutures that are used to sew together blood vessels and hollow organs).
- Manual (applied with a needle, thread and other special tools) and mechanical (performed with a medical stapler).
- Submersible (applied during operations on internal organs with threads that are absorbable or implanted into living tissue) and removable (they are used to stitch the skin, and after the edges of the wound have fused, the threads are removed).
Absorbable sutures are made in cases where long-term fixation of the edges of the incision is required, for example, when cutting the uterus during a cesarean section. As a rule, they are performed with threads from purified connective tissue, which is subsequently rejected into the organ cavity. To apply removable sutures, threads and other fasteners made of cotton, silk, metal and other non-absorbable materials are used (more than 30 varieties in total).
Hand stitching tools
Methods for softening the crust
You can soften the scab on the wound for subsequent removal in the following ways:
- If a crust has formed on your leg, you can steam it in water with the addition of soda and laundry soap. Then treat the damage with ointment.
- Softening crusts from wounds on the face after acne removal with Chlorohexidine. A sterile bandage is generously moistened in the solution and applied to soften the scab, then removed.
- You can soften the scab with healing ointments, the doctor will tell you the name, when using them you need to follow the instructions.